Plastic Bags
Plastic bags are highly versatile containers or carriers made from thin, flexible polymeric films. These bags are used in a variety of industrial, commercial, and residential applications to store, transport, ship, and package goods. Known for their practicality, plastic bags are often waterproof, offering some protection against the elements. Commonly referred to as poly bags, they are made from processed polymer resins.
The History of Plastic Bags
Multiple American and European patent applications for various plastic bags can be traced back to the 1950s, though most of them did not include handles. Handles had to be added in a separate process, which complicated production and increased costs.
In the early 1960s, Sten Gustaf Thulin, an engineer at the Swedish company Celloplast, developed the modern plastic shopping bag. Thulin created a method to fold, weld, and die-cut a plastic tube to form a one-piece bag with integrated handles.
In 1965, Celloplast patented this innovation for a strong, lightweight, and flexible bag. The bag gained widespread popularity, and in 1977, Celloplast’s U.S. patent was overturned, opening the U.S. market. This led to the rise of numerous plastic bag manufacturers across the country.
The Dixie Bag Company was one of the many companies that refined the manufacturing and distribution of these bags. Cincinnati-based Kroger supermarket was among the first to replace paper bags with plastic shopping bags.
From there, plastic shopping bags quickly became ubiquitous. Over the seven decades since their creation, plastic bags have evolved, but the core principle remains the same: strong, flexible, convenient, and easy to manufacture.
Advantages of Plastic Bags
Before the development of shopping bag manufacturing processes, paper bags were the standard. While paper bags were suitable for carrying groceries, they lacked the strength and flexibility of plastic. Plastic bags are more durable, resist tearing more easily, and are less prone to having their bottoms give way when overloaded. Additionally, plastic bags are cheaper to produce and easier to ship.
In recent years, environmental concerns have driven a resurgence in the use of paper bags. However, contrary to popular belief, paper bags also have a negative environmental impact. They are less reusable and contribute to paper waste.
Reusable bags, often made from thick plastic or canvas, are generally considered a more eco-friendly option. Moreover, compostable plastic bags represent a significant advancement in environmentally-conscious packaging. These bags break down along with their contents, returning to the earth over time. Compared to paper bags, compostable plastic bags are made with fewer resources, biodegrade faster, and are easier to reuse. In contrast, paper bags are more expensive to produce, take longer to break down, and are more likely to tear, making them harder to reuse. Plastic bags, on the other hand, typically last much longer than paper bags.
How Plastic Bags Are Made
Plastic bags are deceivingly simple and inexpensive to manufacture. The process remains largely the same since their invention. Most retailers use polyethylene bags. Polyethylene is a strong plastic made from a film of resin. These bags are made in a two-step process.
The first step is to use a specialized piece of equipment, called an extruder, to heat polyethylene plastic to approximately 500 degrees Fahrenheit. The melted plastic is pushed into a die that determines how thick the bag will be. This plastic film is cooled by the outside air and cut into the desired size and placed on a spindle.
The spindle is sent to a conversion area where the film roll is unraveled and cut with a heated knife. The heated knife seals the sides of the bag together. After it is cut the manufacturer will add letters, graphics, or designs (if it is an order for printed poly bags). The final step is the cutting of handles into the bag. The process is highly-efficient and can yield thousands of bags per minute, which helps to keep the price down. These bags remain flat which allows for easy, stack-able, bundles.
Uses for Plastic Bags
Specific materials for plastic bags abound, but polyethylene bags, polypropylene bags and vinyl bags are among the most popular and find great use as anything from medical plastic bags to plastic shopping bags. Beyond the basic material construction, plastic bags as a grouping may have little else in common due to the extreme variety in not only material choice, but also size, color, shape, closure and style which exhibit extreme variation. The selection often depends on the intended use of the bag. Clear plastic bags, for example, are a popular choice for plastic merchandise bags as they allow consumers to preview items before purchase. Resealable plastic bags and ziploc bags are also purpose driven as they provide users with a reliable closing and the option to reuse and reseal bags for extended use. While many of these factors are determined in manufacturing, post-production options such as custom printed plastic bags ensure the perfect fit, both functionally and aesthetically, for any application for all industrial, home or commercial locations.
Rigid, flexible, durable or tear away, plastic bags are a major part of the daily operations of many industrial and commercial outfits. Bags are practical and efficient for storage of parts, components and materials as they provide a safe and consistent barrier against moisture and other environmental contaminants. While some plastics are more susceptible to exposure to the elements, such as heat or UV light, others will last for extended periods of time with little to no change allowing their use in sterile and hermetic packaging of food and medical supplies as well as chemicals and biological materials. Pharmaceutical, retail, storage, sanitation, automotive, construction, electronics and chemical industries likewise take advantage of the many benefits afforded by plastic bags at a relatively low cost as compared to metal containment options. Big industry is not exclusive in its use of plastic bags which are also common household and office space goods. While the context and size may vary, plastic bags serve the same general purpose of storage, convenience and protection. No two plastic bags are alike. There are strong, well made, and environmentally friendly bags as well as flimsy, clumsy, wasteful, plastic bags.
Although the specifics are not always listed, plastic bags employ a large number of different materials to accommodate the growing needs of the aforementioned applications. The word ‘plastic' simply refers to the use of materials derived from polymer resins. These are long chains of molecules that consist of several smaller monomers held together by covalent bonds formed during calculated chemical reactions. This general description encompasses a diverse field of precise plastic compositions that may be synthetic, natural or organic. Polyethylene and polypropylene are two specific polymers that are commonly used in the production of plastic bags. Both thermoplastics, they provide the durable yet lightweight high-quality bag used in a number of industries. Vinyl bags are another popular option made of the polymer known as polyvinyl chloride. More rugged than polyethylene and polypropylene, this particular type of bag is well suited to harsher applications such as parts storage. Such use also requires a reliable seal, the design of which is most often a secondary step in the manufacturing of plastic bags. Before seams are heat-sealed, stitched or glued in place, the film encasement of the bag is formed through casting, winding, sheet extrusion or blown film extrusion with the latter being the most common. In this process polymer resins are melted into a viscous fluid which is then extruded through a die, producing a tube of plastic. Cool air is forced through the center of the die at uniform pressure to create a bubble of even thickness. Additional treatments may be applied after the material is cooled.
While material and necessary treatments are among the most important concerns to consider before selecting an application specific plastic bag, there are several other factors that come into play. The size of the bag must be suited to its potential use as bags can range from a capacity of several cubic inches to several hundred. The area of the bag is determined by length multiplied by height multiplied by diameter or width. It is important to look at specific dimensions and not just the total volume especially when dealing with irregularly shaped items. The style and closure type should also be considered as well as the overall cost. With increasing concerns for the environment, the recyclability of a plastic should also be considered. In the United States alone, four out of five grocery bags used are plastic, but less than 0.5% of such consumer plastic is recycled. Reusable plastic bags made of thicker and recyclable plastics are gaining popularity as is the development of biodegradable polymer films in many applications. The variability of plastic bags gives consumers much to consider prior to use and purchasing, but also ensures that the proper container or carrier will be available no matter the task at hand.
Plastic Bag Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts

A plastic bag is an unwoven piece poly fabricated for packaging or storage.

The material that is liquified to make plastic bags.
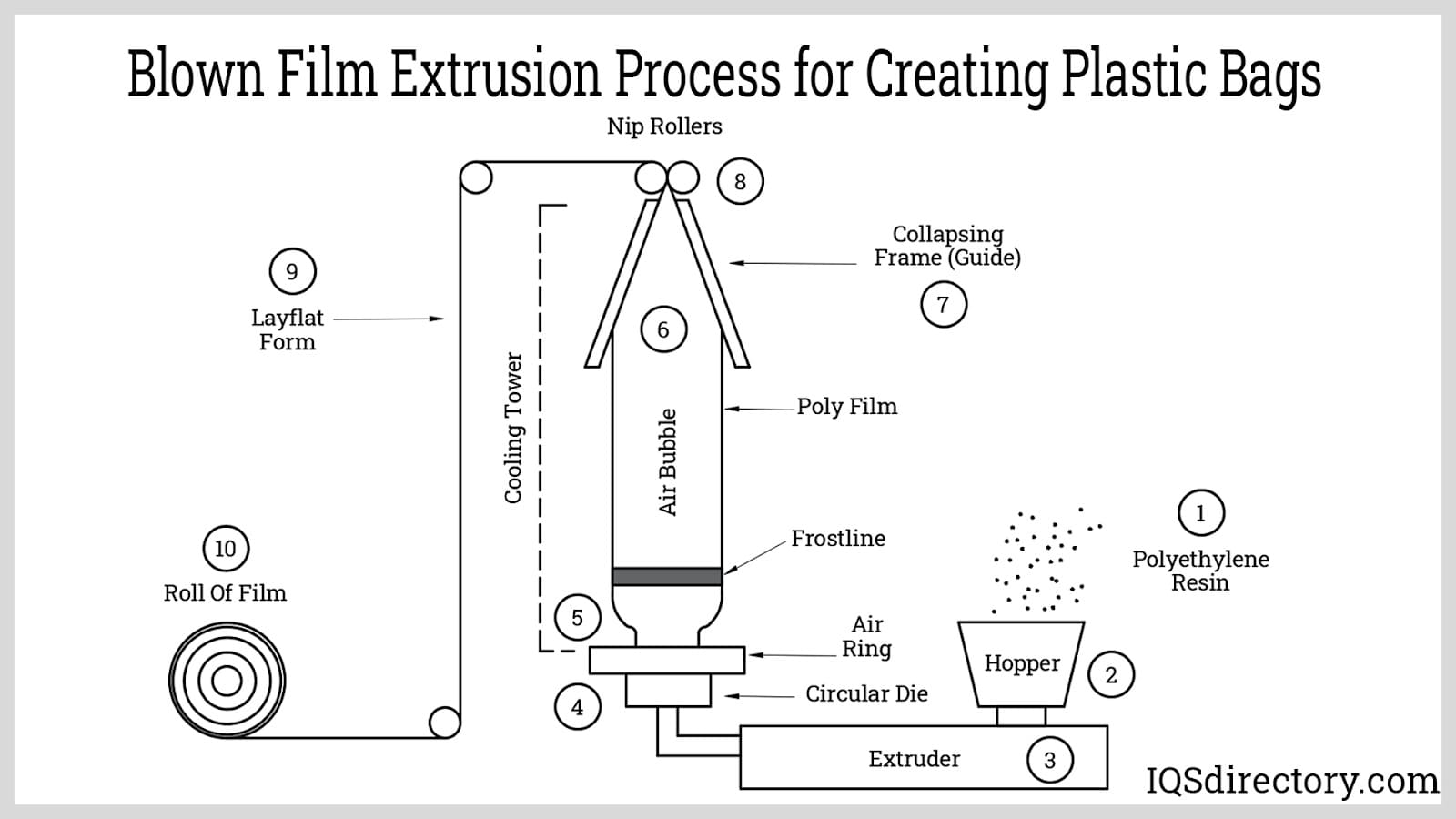
The process that turns the resin into a roll of material to produce plastic bags.
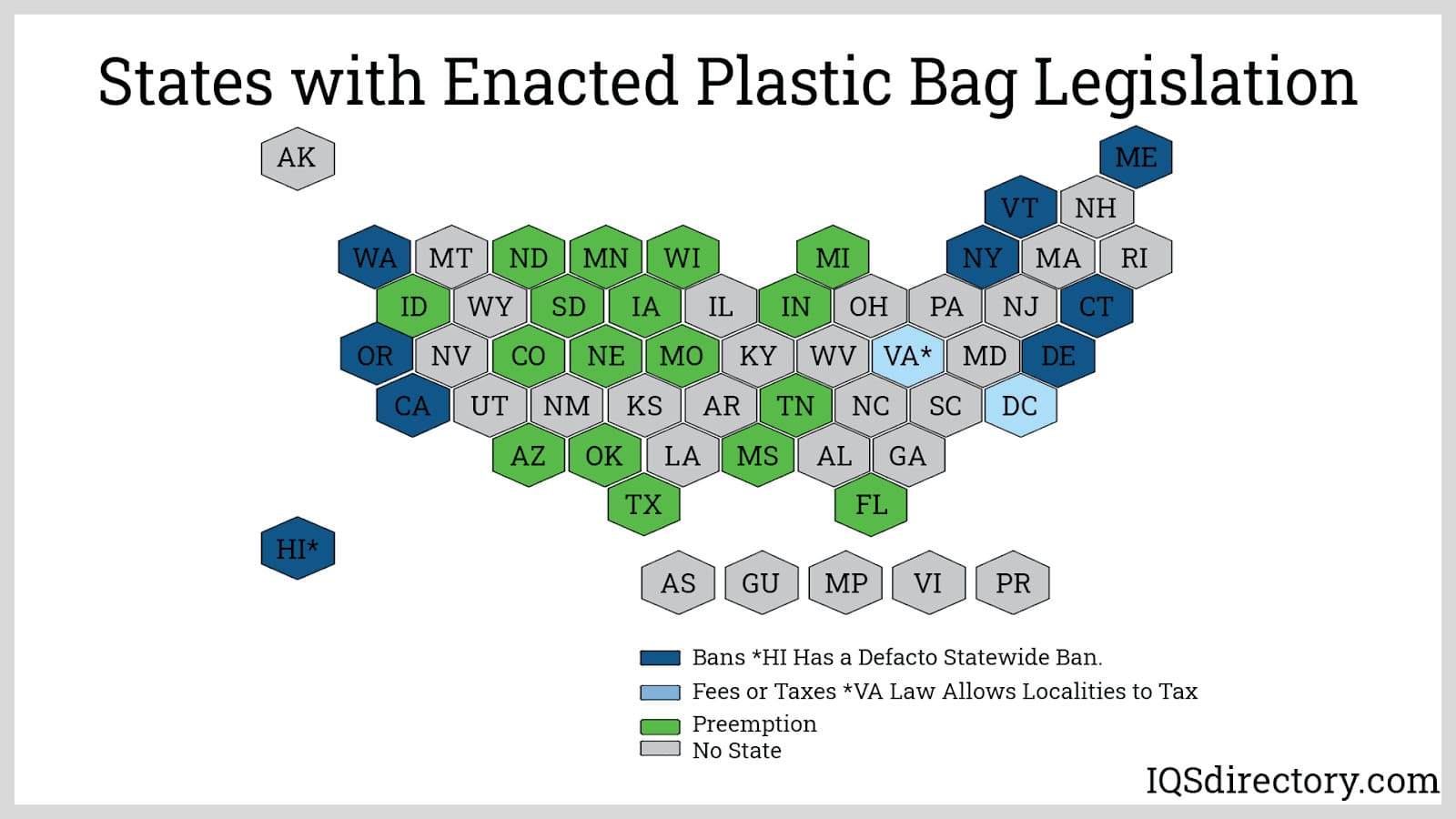
States that have passed plastic bag legislation to limit the usage of plastic bags.
Plastic Bag Types
Anti-Static Bags
These bags contain an anti-static additive that disperses static electrical charges. They are ideal for short-term storage of sensitive electronic equipment.
Baggies
These are small sacks or pouches made from thin, flexible polymer materials, commonly referred to as plastic bags.
Clear Plastic Bags
Transparent bags made from polymers such as low-density polyethylene and polypropylene, commonly used for packaging goods in retail settings.
Cellophane Bags
Known as "cello bags," these are thin, transparent bags made from cellulose. They are often used for gift packaging and occasionally for industrial and commercial purposes.
Custom Zip Top Plastic Bags
Primarily made from polyethylene, these bags are versatile and easily customizable with zip-top seals that help protect contents from external elements and prevent leaks.
Die-Cut Bags
Flat bags with a cut-out handle at the top for easy carrying. These bags are often seen in retail settings and at trade shows.
Drawstring Bags
Bags that feature either plastic or cotton drawstrings, allowing for easy closure and providing handles for carrying.
Electrically Conductive Bags
Made from carbon-impregnated polyethylene, these bags protect against static charges and are used for sensitive electronic components.
Flap Lock Bags
Often called "sandwich bags," these bags feature a lip that folds over and seals with side seams, providing a simple, effective closure.
Flat Bags
These bags offer versatile plastic packaging and are commonly heat-sealed at the sides or bottom. They are ideal for items of varying shapes and sizes, with bottom-sealed versions offering extra support for heavier items.
Food Storage Bags
Made from polyethylene, these bags are used to keep food fresh and are often sealed with zippers or slider grips. They include bags for sandwiches, freezers, and produce.
Gusseted Bags
These bags feature pleats, or gussets, that allow the bag to expand, accommodating larger or bulkier items. They come in various designs, including bottom-sealed, side-gusseted, and side-sealed, bottom-gusseted styles.
Header Bags
These bags have a continuous top seal and a hang hole for easy display, often used for retail purposes.
Medical Plastic Bags
Commonly used in healthcare facilities, these bags store medical supplies, specimens, and sometimes hazardous waste, providing protection and convenience.
Mulch Bags
Used for landscaping, these bags are designed for the storage and transport of soil, mulch, and other gardening materials.
Patch Handle Bags
These are flat bags with a die-cut handle reinforced by a heat-sealed patch for added strength.
Plastic Envelopes
Flat pouches or bags typically used for securing documents, often with an adhesive edge for closure.
Plastic Ice Bags
Manufactured in various shapes, sizes, and designs, these bags are used for storing and transporting ice.
Plastic Merchandise Bags
These bags are used in retail and commercial settings for storing and carrying goods.
Plastic Shopping Bags
Designed for transporting purchased goods, these bags are a staple in retail environments.
Poly Bags
A general term for various sacks, pouches, and flexible containment systems made from polymers, used across numerous industries.
Polyethylene Bags
These waterproof, translucent bags are commonly used in industrial, commercial, and domestic applications for storing and transporting goods.
Polypropylene Bags
Made from a strong, rigid material, these bags offer a good vapor and moisture barrier and are completely transparent.
Printed Plastic Bags
These can be mass-produced or custom-made, with permanent labels and designs added for branding or functional purposes.
Reclosable Bags
These bags are reusable and can be sealed multiple times, often used in the food service industry to preserve and reduce food waste.
Retail Bags
Used to store and carry merchandise, these bags are common in various retail environments.
Side Weld Bags
These bags are sealed on the sides and do not have a bottom seal.
Vinyl Bags
Made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), these bags are more rugged than polyethylene and polypropylene, suitable for harsher applications such as parts storage.
Waste Removal Bags
These include trash liners and bags for hazardous waste disposal, typically made from high-density polyethylene or linear low-density resin for strength and flexibility.
Wicket Bags
Designed for high-speed industrial applications, these bags are placed on a metal ring and used for fast packaging in automated manufacturing settings.
Zip Lock Bags
These bags feature an interlocking or slide lock closure mechanism, providing an airtight seal for contents.
Plastic Bag Materials
There are several types of plastic bags, but two common variations are frequently seen in most retail settings.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE bags are typically the thin, lightweight bags used at supermarkets. Made with high-density plastic film, they offer strength and stability despite their thin construction. These bags are easy to transport and store, and they are often used for trash drum liners and specific types of plastic wraps.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE bags are thicker and found in department stores. Their unique molecular structure gives them added thickness and strength. Both HDPE and LDPE bags are commonly referred to as "clear poly bags" LDPE is commonly used for high-strength black plastic bags, which are designed to hold a large volume of various materials due to their sturdier construction.
Biodegradable LDPE
In response to growing environmental concerns, some countries have enacted bans on traditional plastic bags, recognizing that discarded plastic contributes significantly to pollution. Biodegradable LDPE bags are made from materials that decompose over time, providing a more environmentally friendly option. These bags help reduce long-term waste accumulation, as they eventually break down and return to the earth. While this innovation helps mitigate waste, the environmental impact of these bags remains a concern. The production of biodegradable LDPE still relies on petroleum, a fossil fuel, which can harm the environment during manufacturing.
Standards and Specifications for Plastic Bags
Misinformation about the environmental impact of plastic bags has led to various legislative actions regarding their use. Many states and municipalities have introduced regulations and offered alternative packaging options.
Some states have launched effective recycling programs to extend the lifespan of plastic bags, promoting their reuse and repurposing. Meanwhile, other states have implemented complete plastic bag bans. For example, California passed a law in 2014 prohibiting large retailers from offering plastic shopping bags.
While the manufacturing process for plastic bags has remained largely unchanged for over 60 years, plastic bag technology continues to evolve. Efforts are consistently made to find new uses for old plastic bags and to reduce their environmental footprint.
Plastic bags may not always be top of mind, but they are a product we use almost every day.
The strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of plastic bags stem from the polyethylene plastic used in their production. The atomic structure of polyethylene gives it unique properties that benefit various industries.
Choosing the right plastic bag provider is an important decision that requires thorough research and due diligence. As with any product, there are high-quality plastic bags and poorly made, cheap alternatives. For some businesses, investing in high-quality bags is worthwhile, but for others, cost considerations may outweigh the need for premium products.
Even among reputable manufacturers, there are several factors to consider. Customization options and available sizes are key considerations when selecting a supplier. Finding the right manufacturer means ensuring they meet all your needs, not necessarily opting for the most well-known name. For a convenient list of plastic bag manufacturers, you can refer to the directory above.
The product must be durable enough to withstand its intended use. Many retailers seek to customize their plastic bags, and while most manufacturers offer custom orders, the level of customization varies. Some manufacturers provide highly detailed, vibrant graphics, while others may only offer basic lettering.
Since its creation, plastic has been used for nearly every application, from carrying goods to its life-saving role in medical equipment. Its versatility makes it an invaluable resource across industries.
Plastic Bag Terms
Additive
A substance incorporated into a polymer to enhance its performance without increasing its strength. Examples include flame retardants, anti-static agents, pigments, and lubricants.
Alloy
A combination of two chemically distinct polymers fused together to form a new material. Each polymeric unit in an alloy represents only one monomer.
Blow Extrusion
A process used to create plastic bags by using compressed air to fill an extruded plastic tube, causing the resin to expand and thin out.
Copolymer
A polymer made from two different monomers, where each repeating unit in the polymer chain contains units from both monomers.
Crazing
The formation of very fine cracks in a polymeric material, typically caused by exposure to chemicals or agents such as ultraviolet light.
Degree of Polymerization
The length of the molecular or monomeric chains in a polymer, which determines the polymer's physical properties.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
A copolymer produced by reacting ethylene with vinyl acetate. It’s commonly added to plastic resins to enhance their strength at low temperatures.
Gauge
A measurement referring to the thickness of a material. The smaller the gauge number, the thinner the material.
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
The temperature at which a substance changes from a rigid, glassy state to a flexible, rubber-like consistency. Below this temperature, polymers become brittle.
Grade
Polymers from the same chemical family and produced by the same manufacturer but differing in weight, additives, reinforcements, and processing methods.
Heat Sealing
The process of fusing two or more thermoplastic films, like low-density polyethylene, by applying heat and pressure.
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
A strong plastic with a density between .941 and .965 g/cm³. While more expensive to process, HDPE is stronger, stiffer, and more resistant than LDPE or LLDPE.
Light-Weighting
The process of reducing the weight of plastic by using less resin while maintaining the strength and functionality of the material.
Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
A polymer produced under lower temperatures and pressures than LDPE, resulting in a more crystalline structure that increases stiffness and melting point. LLDPE is more difficult to process but offers superior tensile strength and stress-crack resistance.
Lip
The extended edge of a bag, making it easier to open.
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
The most common and least expensive plastic used for bags, with a density between .910 and .925 g/cm³. LDPE is known for its durability, flexibility, water resistance, and clarity at low temperatures.
Melting Point
The temperature at which a substance transitions from a solid to a liquid state.
Metallocene
A puncture-resistant material that is thinner and stronger than LDPE.
Monomer
The basic building block of polymers, typically a liquid or gas composed of molecules from the same organic substance. When linked together, monomers form solid polymers.
Plasticizer
A chemical added to plastic resins to enhance flexibility.
Polyethylene (PE)
A common, lightweight, chemically resistant thermoplastic widely used in packaging and insulation, including varieties like LDPE, LLDPE, and HDPE.
Polymer
A material made by chemically bonding two or more monomers, forming a chain of repeating monomers.
Polypropylene (PP)
A light, durable thermoplastic with a high melting point, frequently used in packaging. PP is composed of propylene polymers, a colorless, flammable gas found in petroleum.
Reinforcement
Substances added to a polymer to increase its strength. Examples include clay, mica, and glass fibers.
Resin
A category of plastics, chemically distinct from natural resin, that includes materials like polyethylene, polyurethane, and acrylics.
Slip
An additive used to prevent bags from sticking together and reduce slippage when stacked.
Star Seal
A bottom seal design for liners that combines four sections into a star shape. Star seals are the strongest and maximize carrying capacity.
Stress Cracking
Cracking caused by mechanical stress, typically involving pre-existing tiny cracks that are exacerbated by exposure to chemicals or ultraviolet radiation.
Terpolymer
A polymer made from three different monomers, with each repeating unit in the chain containing all three monomers.
Thermoforming
The process of applying heat, pressure, or suction to form plastic sheets into specified sizes and shapes.
Thermoplastic
A type of plastic that softens and can be reshaped when heated and hardens again upon cooling without changing its chemical structure.
Thermoset
Plastics that cannot be reshaped or reformed once they have hardened. These materials remain permanently hard.
Ultraviolet Inhibitor (UVI)
An additive that helps plastic resist the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, such as fading or strength degradation.
Vapor Corrosive Inhibitor
A thermoplastic coating or film that protects sensitive items from harsh environmental conditions by releasing a vapor that forms a protective layer on the surface of the thermoplastic.
More Plastic Bags Information

