Adhesive Tapes
Adhesive tapes are the materials you use when you need two or more objects to conjoin or bond with each other. Adhesive tapes come into play when other mechanical options like screws, nails, welding, etc are inapplicable.
There are many improvements in adhesive tapes. For example, these respond very well to pressures and can be activated by heat generation instead of losing its adhesive quality. Sometimes, these may use damp environments to activate.
Quick links to Adhesive Tapes Information
Benefits of Using Adhesive Tapes
There are many benefits of using adhesive tapes instead of other industrial replacements. Unlike mechanical fasteners or welding, adhesive tapes can ease the production process by regulating the heat coefficient. These are best for lower temperature applications. Other benefits of adhesive tapes include:
- No damage to surface area by drilling etc.
- Replacing liquid adhesive agents
- Best for automated production because it requires less work
Composition of Adhesive Tapes
There are two main components of adhesive tapes as shown in Figure 1. A backing or carrier is usually made up of paper, foil, PET, foam, or cloth, etc, and an adhesive solution. Sometimes there is also a release liner, but it usually depends on the application of these tapes.
The adhesive coating is applied all over the backing, and then it is rolled up into a giant tape roll. Then the roll is sliced and cut down as per the width required. The width of the bands and the size of the roll vary between industries and its applications.
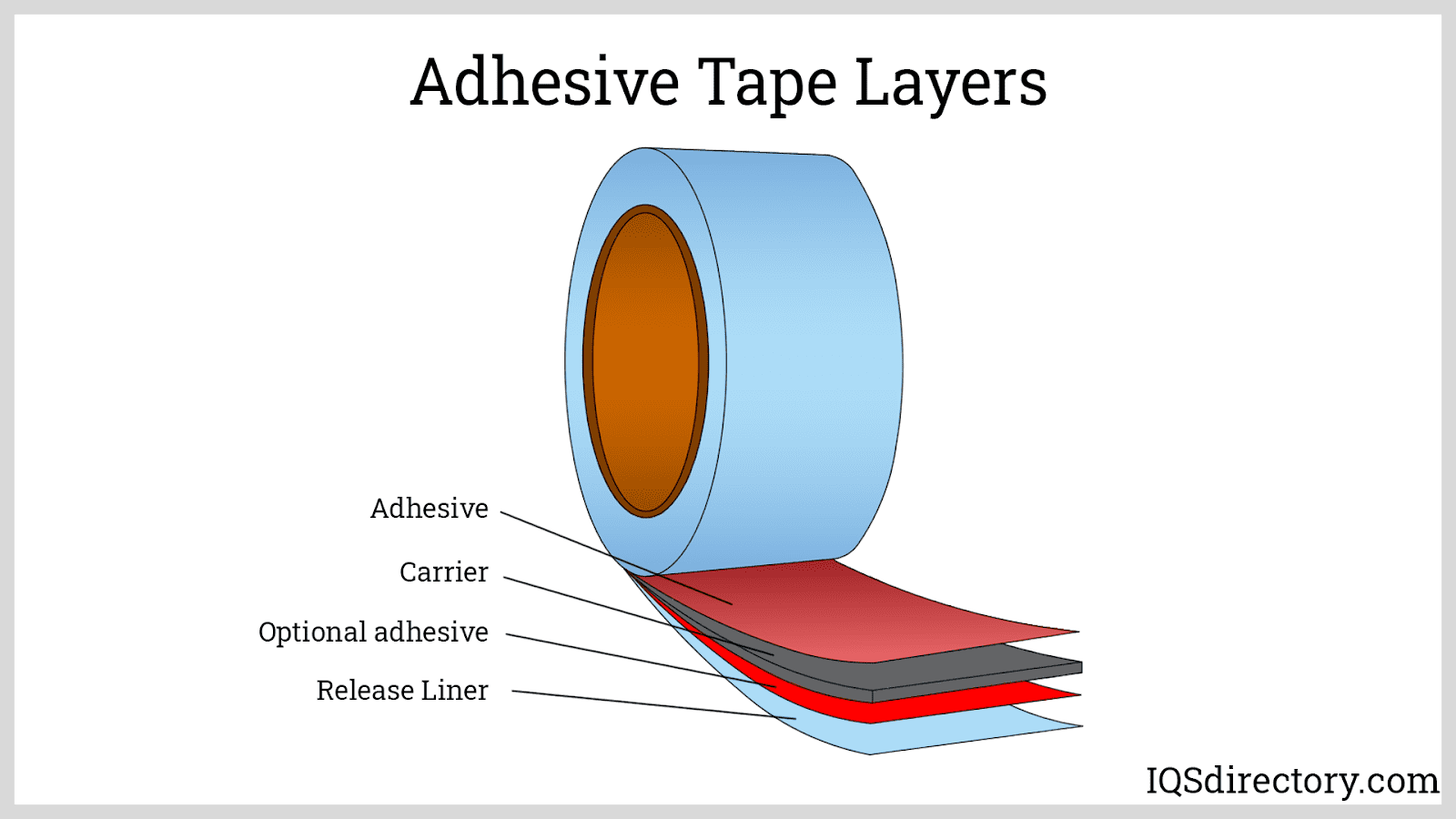
Figure 1
How to Select Adhesives
While selecting the right type of adhesive tape, one must be well versed about the characteristics of adhesives being used. Following are some adhesives used in adhesive tapes along with their application:
Acrylic Adhesives
The quickest setting adhesives of all. These are also resistant to environmental threats.
Epoxy Resins
Highly impenetrable by chemicals or other environmental factors. These are known to be very strong adhesives.
Rubber-Based Adhesives
Form flexible bonds. These are usually composed of butadiene-styrene, butyl, polyisobutylene, or nitrile compounds.
Silicone Adhesives
Very pliable and elastic in nature. These are heat resistant and are an appropriate choice for high temperature environments.
Polyurethane and Isocyanate Adhesives
Offer impact and permanence. These are strong adhesives as compared to others.
Types of Adhesive Tapes
Following are some of the most popular types of adhesive tapes used nowadays.
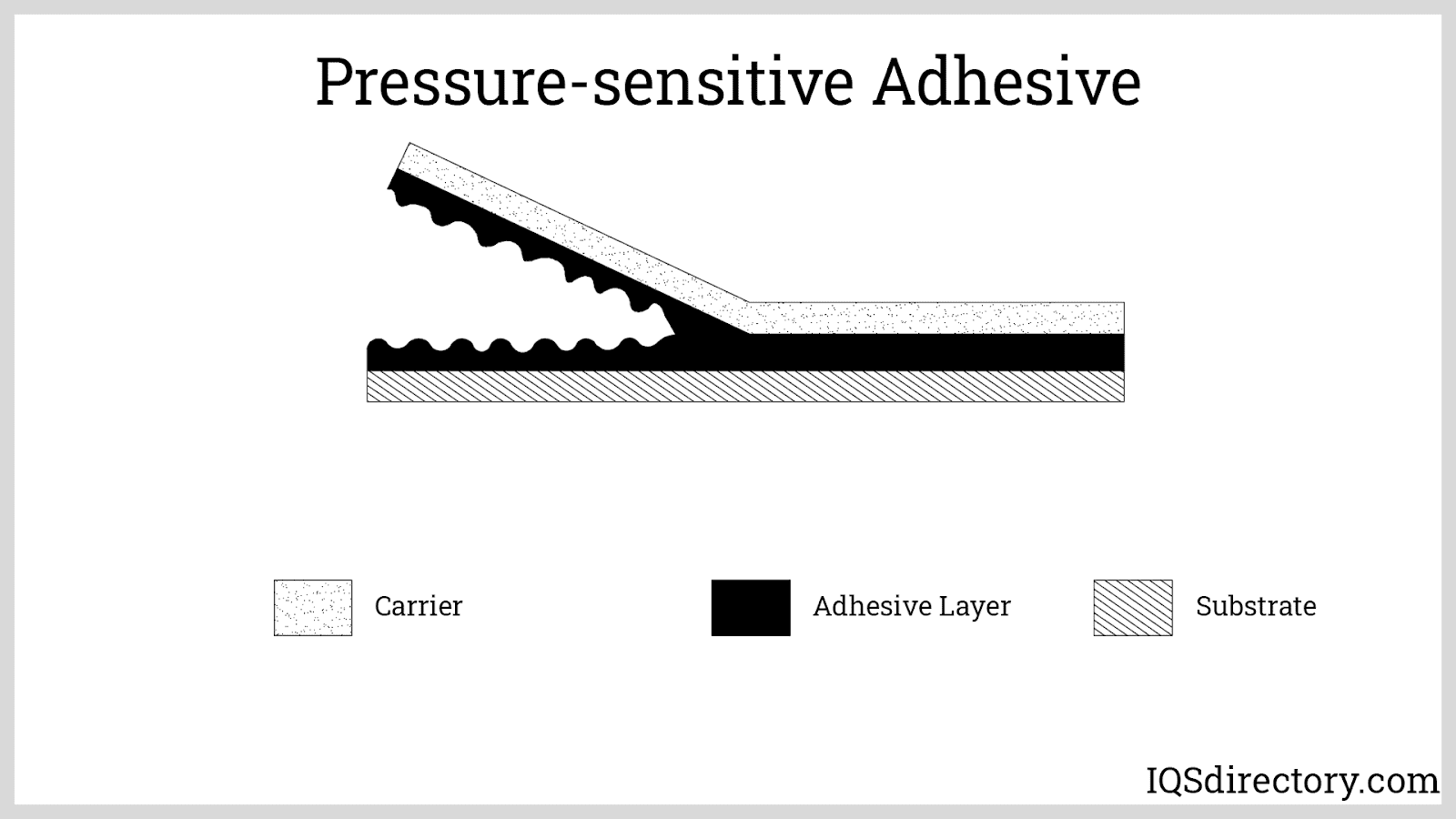
Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs)
Easy to apply by using small pressures, even by finger. These have great adherence qualities. These do not require moisture, water, or solvents to activate stickiness. The only thing to lookout for is the temperature because too much temperature will make these stretchy and too little temperature can generate moisture. Both these factors can affect the bonding characteristic and final application.
Heat-Activated Tape
Need higher temperatures up to 180°F and in some cases even more. Before heat activation, it usually is non sticky. These are ideal to use for difficult to bond with surfaces like rubber, PVC, etc. Multiple different backings can be used depending upon the surface to work better.
Water-Activated Tape
Also known as gummed paper tapes or gummed tapes. The names are inspired from the adhesive used in these. It consists of a Kraft paper carrier with an applied plant or animal based glue. It is activated by adding moisture to it. It is very easy to find and cheaper. It is usually used where very strong adhesions are not required, like closing boxes.
Non-Adhesive Tapes, Films, or Laminates
These films are self adhering and do not require any added adhesive materials like PTFE sealing tape.

Industrial Applications of Adhesive Tapes
Adhesive tapes have applications across multiple industries. The top five industries that use adhesive tapes excessively include:
- Automobile Industry
- Construction Industry
- Medical Equipment
- Electronics
- Household Industry
The main functions of these tapes are bonding, tying, securing, wrapping, splitting, cushioning, meshing, etc.

