Alloys
Alloys are formed by combining two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal, resulting in a material with distinct and improved properties compared to the individual components. The process of creating alloys dates back to the Bronze Age when early humans discovered that mixing copper with metals like tin, lead, or zinc created a stronger and more durable material.
Creating Alloys
There are various methods for creating alloys, such as melting, powder metallurgy, and solid-state reactions. The most common method is melting, where two or more metals are heated to high temperatures and combined to form a uniform mixture. Powder metallurgy involves mixing metal powders, compacting them under high pressure, and then heating them to create a solid alloy. Solid-state reactions occur when metals are heated in a vacuum or inert gas, promoting diffusion and bonding between the atoms.
The purity of the constituent metals is vital in the alloy-making process. Impurities can significantly alter the alloy's properties, including its strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. To ensure high-quality alloys, manufacturers employ advanced techniques to maintain the purity of the metals involved.
Popular Alloys
There are numerous alloys used across various industries, with some of the most common ones being:
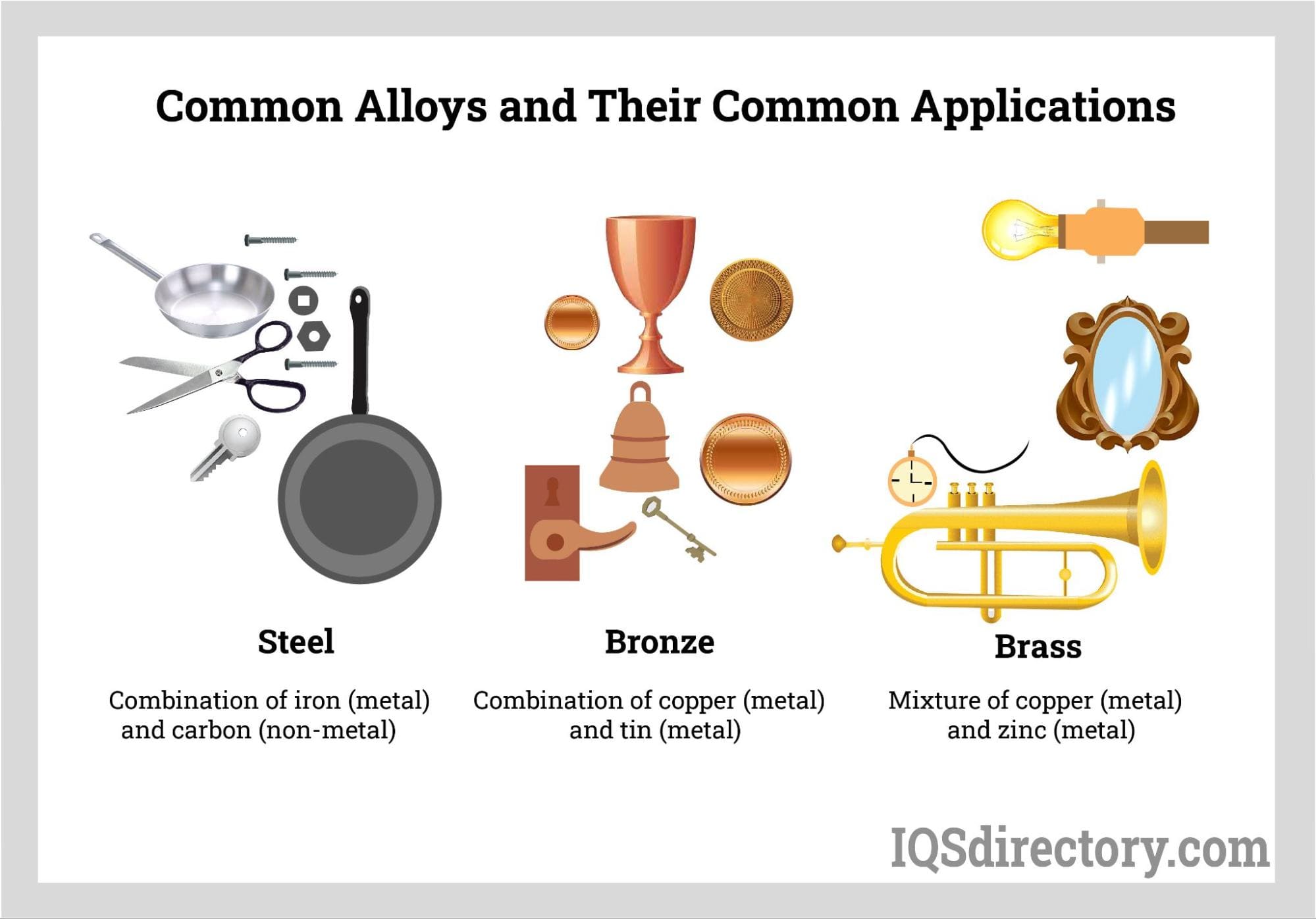
Steel
Made from iron and carbon, with small amounts of other elements like manganese, silicon, and chromium, steel is known for its high strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Brass
A mixture of copper and zinc, brass is malleable, ductile, and corrosion-resistant. It's commonly found in plumbing fixtures, musical instruments, and decorative items.
Bronze
An alloy of copper and tin, bronze is hard, strong, and resistant to corrosion. It's often used in statues, coins, and other ornamental items.
Stainless Steel
Composed of iron, chromium, and nickel, stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and staining. It's used in kitchen appliances, medical equipment, and other applications requiring high hygiene standards.
Aluminum Alloys
Combinations of aluminum with metals like copper, magnesium, and zinc, aluminum alloys are lightweight, strong, and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in aerospace and automotive industries.
Limitations of Alloys
While alloys provide many advantages, they also come with some limitations and drawbacks. For example, alloy production can be costly and energy-consuming, contributing to a significant carbon footprint. Additionally, certain alloys may lack ductility, making them brittle and susceptible to cracking when subjected to stress.
Benefits of Alloys
Despite their drawbacks, alloys offer considerable advantages across a variety of applications. For example, alloys can be tailored to exhibit specific properties, such as enhanced strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance, based on their intended purpose. This customization makes alloys ideal for a broad spectrum of uses, ranging from construction to healthcare. Furthermore, alloys are known for their exceptional resistance to wear and corrosion, ensuring they remain durable and reliable even in demanding environments.
Applications of Alloys
Alloys can be tailored to meet specific needs by adjusting the composition of their constituent metals, making them highly versatile materials across various industries. Some examples of industries that rely on alloys include:
Aerospace Industry
Alloys are essential in the aerospace industry because of their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Titanium alloys, nickel alloys, and aluminum alloys are commonly used in the production of aircraft and spacecraft.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, alloys are used to manufacture parts that are strong, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion. Common alloys in this sector include aluminum alloys, steel alloys, and magnesium alloys.
Construction Industry
The construction industry utilizes alloys to create building materials that offer strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Steel alloys, aluminum alloys, and copper alloys are often used for these applications.
Electronics Industry
In electronics, alloys are employed to produce components with desirable electrical properties. For example, copper-nickel alloys are used in resistance wires for heating elements, while aluminum alloys serve as electrical conductors.
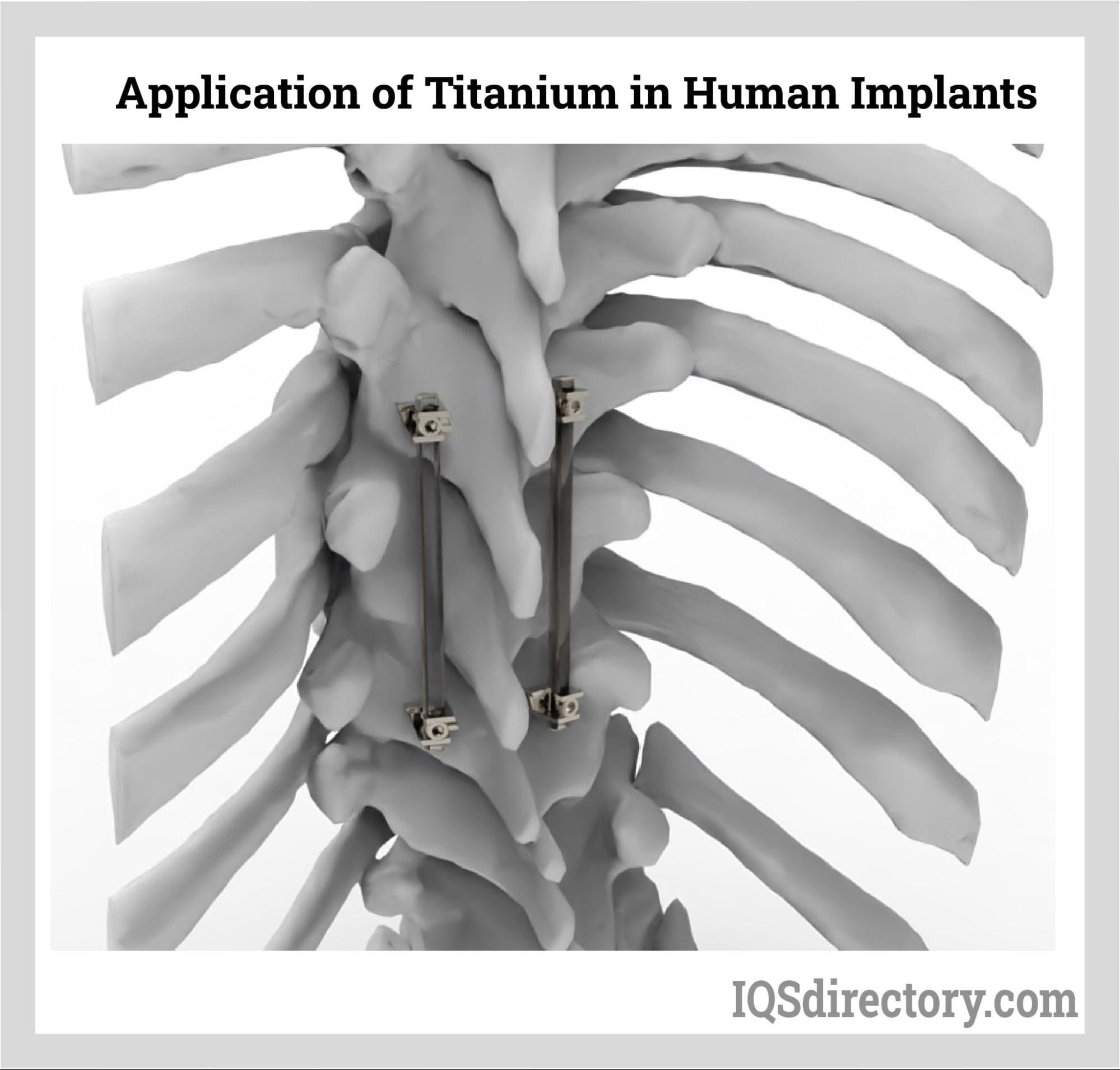
Medical Industry
Alloys are crucial in the medical industry for manufacturing surgical instruments, implants, and other medical devices. Titanium alloys, stainless steel alloys, and cobalt-chromium alloys are preferred due to their biocompatibility, strength, and resistance to corrosion.
Jewelry Industry
In the jewelry industry, alloys are frequently used to make precious metals more durable and affordable. For instance, 14-karat gold is an alloy that combines pure gold with metals like copper, silver, or nickel.
Food Industry
Alloys are also used in the food industry to create cooking equipment that is resistant to corrosion and oxidation. Stainless steel alloys are commonly found in pots, pans, and other kitchen utensils.
Choosing the Right Alloy Manufacturer
To achieve the best results when purchasing alloys from an alloy manufacturer, it is crucial to compare multiple companies using our directory of alloy manufacturers. Each manufacturer has a detailed business profile page showcasing their areas of expertise and capabilities, along with a contact form for easy communication to request more information or a quote. Use our proprietary website previewer to quickly explore each company’s specializations. Once you've reviewed the profiles, you can contact multiple alloy manufacturers at once by filling out our simple RFQ form.

