Automatic Screwdrivers

An automatic screwdriver is a piece of equipment that automatically inserts screws into a product during assembly and production. Since every production operation is unique and requires a...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article takes an in-depth look at industrial robots.
Read further to learn more about topics such as:
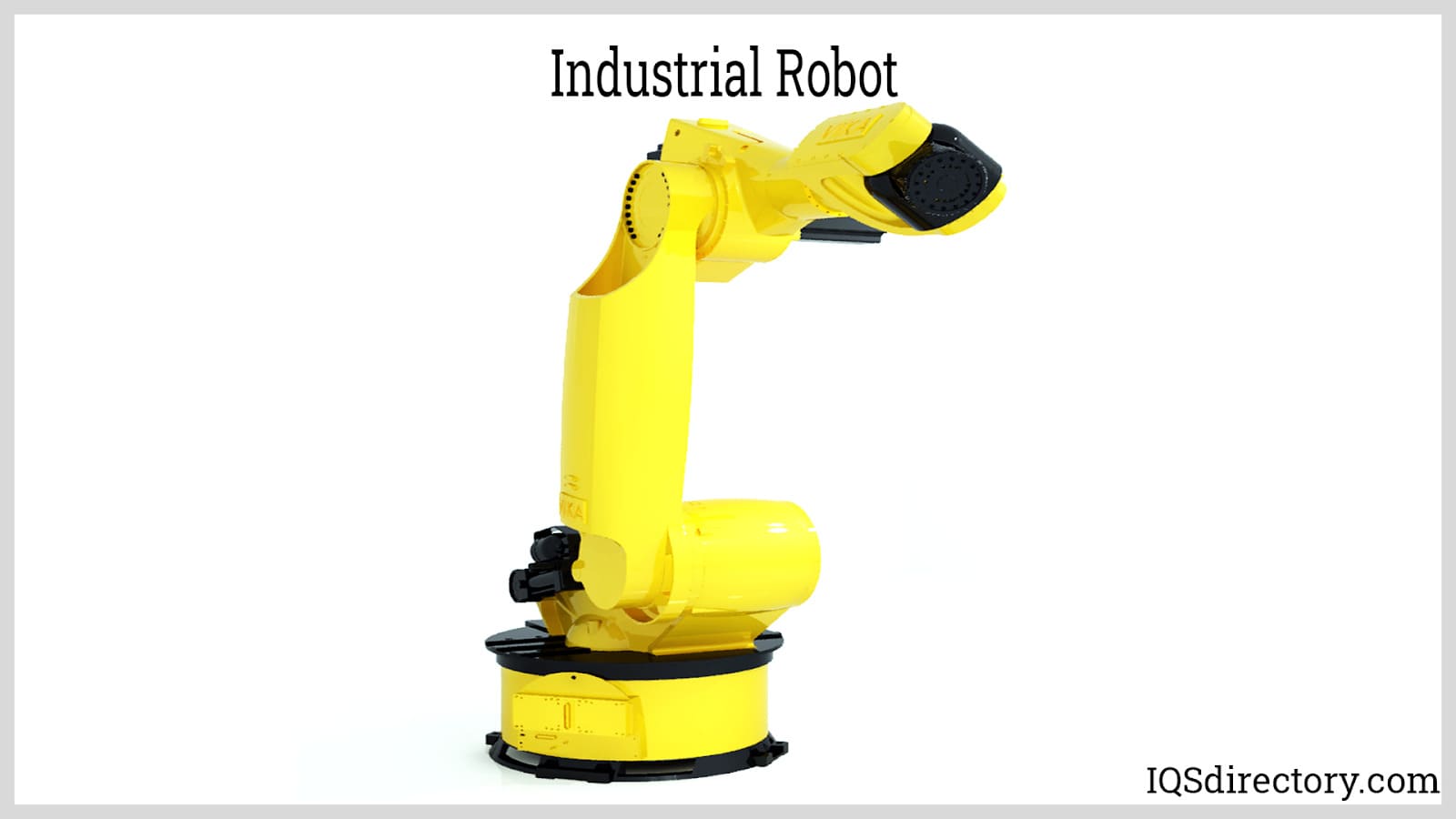

An industrial robot is an automated system equipped with sensors, controllers, and actuators, mounted on an articulated frame. These robots execute specific tasks and operations within manufacturing or processing settings. They operate continuously, performing repetitive movements according to a programmed instruction set. By minimizing or even removing the need for human intervention, industrial robots significantly boost processing speed, capacity, and output quality.
Traditional industrial robots should not be confused with the new-age robotic technology known as collaborative robots. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work side by side with human operators. Cobots are safe for human interaction due to their enforced speed limits and restricted force generation. This capability, combined with sophisticated motor current sensing, ensures they halt upon encountering an object or person.

The fundamental structure of an industrial robot is its arm, comprising links and joints. Links are rigid sections that span the robot's range of action, while joints connect these links, facilitating either transitional (prismatic) or rotational (revolute) movements. The setup and arrangement of these elements dictate the classification of different industrial robots.
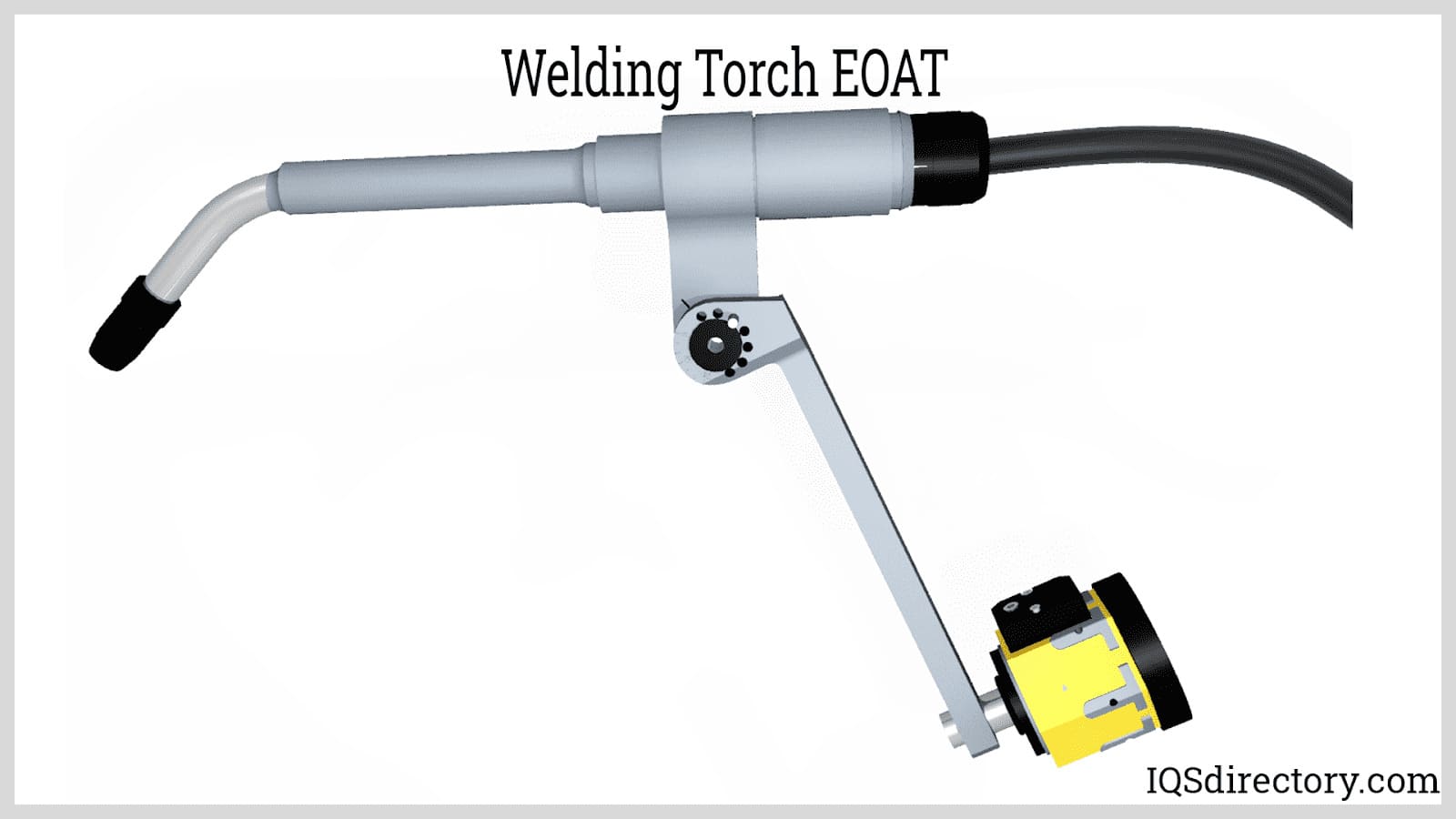
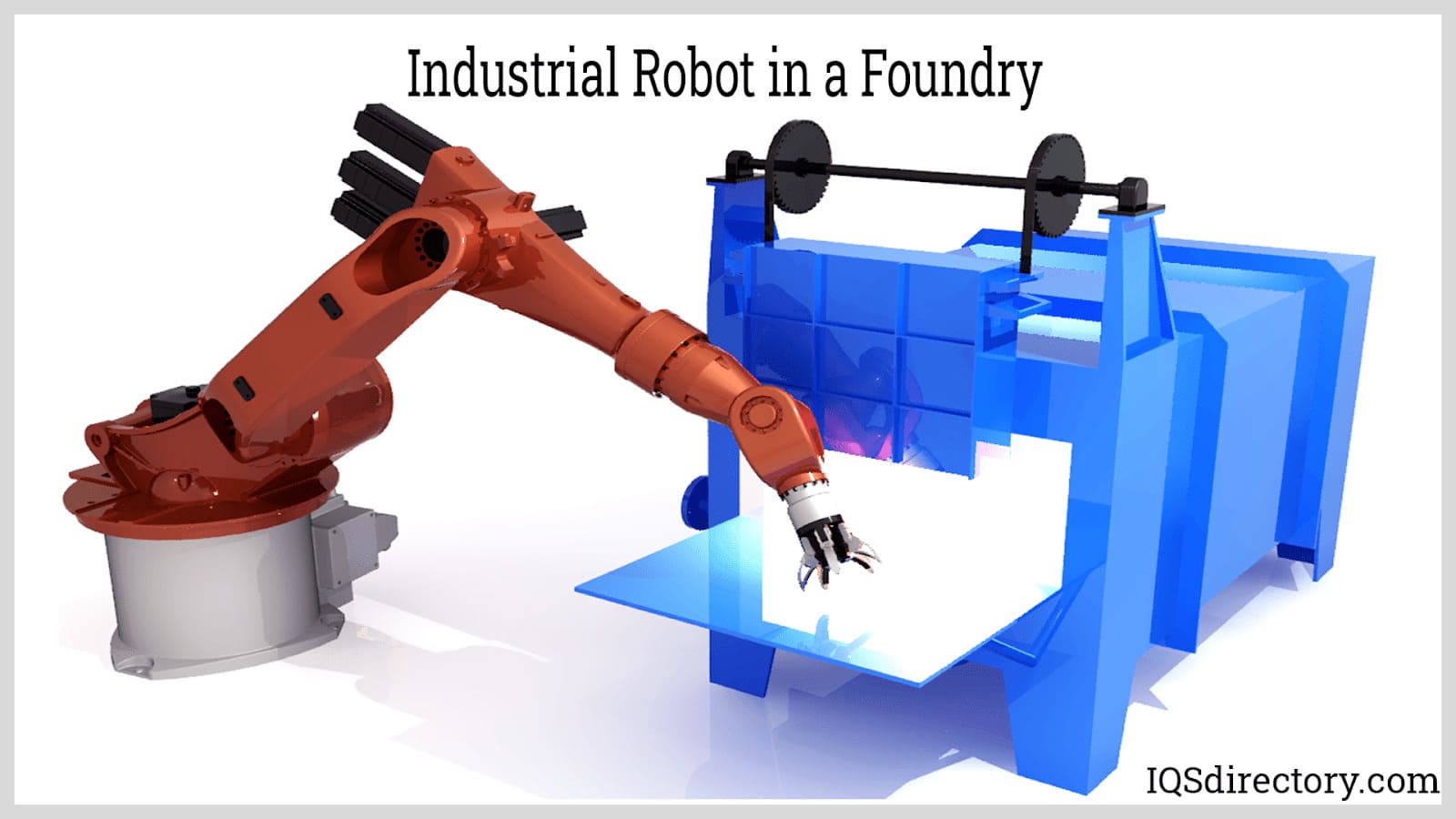
Central to the robot's capabilities is the end-of-arm-tool (EOAT), or end effector. This component of the robot interacts directly with products or processes, performing tasks such as handling and manipulating. It is integral for carrying out specialized functions like welding, measuring, marking, drilling, cutting, painting, and cleaning.
Incorporating an industrial robotic solution involves choosing between working with a manufacturer or an integrator. An industrial robotics manufacturer is a company that internally produces robots, often identified as original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). They are responsible for the design and fabrication of the robots, providing valuable expertise regarding the installation, operation, and maintenance of their machines.
An industrial robot integrator delivers robotic systems made by an OEM. A robot integrator, or “system” integrator, can supply a full “turn-key” robotic work cell, complete with parts feeders, end effectors, and protective guarding to create a comprehensive work cell. Robotic integrators offer a broader spectrum of solutions, as they have the flexibility to provide products from multiple companies under each robot category.
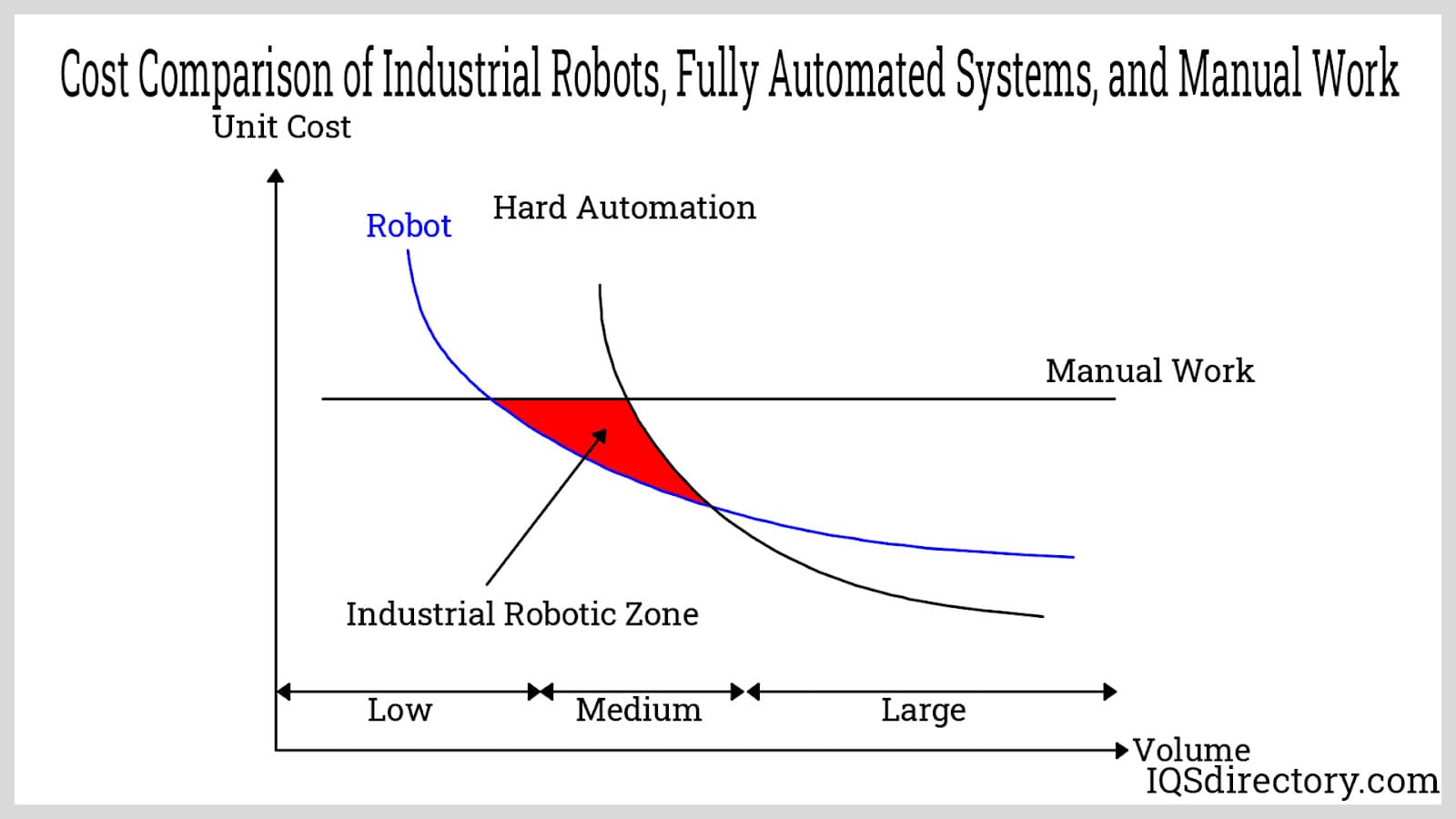
This chapter explores the multifaceted benefits of integrating industrial robots into modern manufacturing systems. In today’s competitive market, the adoption of industrial automation and advanced robotic technologies has become essential for manufacturers seeking reliable, scalable, and efficient production solutions. While the upfront investment and capital costs for industrial robots, automation equipment, and robotics integration services can be significant, the long-term advantages often outweigh initial expenditures. Industrial robot systems deliver numerous economic and intangible benefits, including higher process efficiency, improved product quality, and streamlined workflows. Their efficient performance and ability to automate repetitive or hazardous tasks frequently result in a rapid return on investment (ROI), often within 2 to 5 years, making them an essential component of smart factories and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
Faster Rate of Production: Achieving a higher production rate is consistently recognized as the primary driver for implementing an industrial robot system. Robots deployed in manufacturing environments, such as robotic assembly lines, automated welding cells, or robotic pick-and-place applications, can operate around the clock without experiencing fatigue or slowdowns. By reducing cycle times and optimizing throughput, they accelerate manufacturing processes and minimize downtime in production lines. Their programmable automation and ability to adapt to complex, multi-axis tasks ensure that all movements are completed accurately and rapidly, regardless of complexity. This speed, combined with relentless precision, enables companies to meet tighter deadlines and scale up operations efficiently.
Higher Load Capacity: Industrial robots utilize powerful actuators and advanced drive systems that far surpass the strength capabilities of human operators. The typical "muscle" in a modern industrial robot is a servo motor, engineered for precise positioning and torque control. Combined with high-precision planetary, harmonic, or cycloidal gearboxes, these components enable robots to handle exceptionally heavy payloads and support material handling, palletizing, and heavy-duty machining operations across a variety of industries. Enhanced load handling not only improves workplace ergonomics and safety by mitigating injury risks from heavy lifting, but also supports high-mix, low-volume production runs where flexibility and adaptability are essential.

Improved Safety: Automated robots are transforming workplace safety by taking on dangerous, dirty, and physically demanding tasks that frequently pose risks to human workers. In manufacturing settings where operations expose workers to extreme temperatures, hazardous chemicals, high pressures, heavy machinery, fast movements, or repetitive strain, industrial robots provide reliable risk reduction and enhanced compliance with occupational safety standards. By performing material handling, welding, painting, or even hazardous assembly tasks, robots help eliminate the potential for accidents, injuries, or fatalities on the factory floor. Additionally, the integration of collaborative robots (cobots) and comprehensive safety features ensures safe, productive human-robot interaction without sacrificing operational efficiency.
Lower Operating Cost: Industrial automation systems, powered by robotics, lead to lower operating costs through reduced material waste, increased production efficiency, and fewer human resource expenses. Robots contribute to manufacturing cost savings by lowering scrap and rework rates, optimizing resource usage, and improving yield with every production cycle. Over time, operational expenses are minimized due to reduced dependency on manual labor, elimination of overtime costs, and fewer workplace injuries (which lower insurance premiums and compensation claims). Furthermore, the automation of monotonous or repetitive tasks allows human employees to focus on higher-value, strategic responsibilities such as system supervision, quality control, and process improvement.
Better Repeatability and Precision: Consistency is a hallmark of robotic automation. A robotic system’s repeatable performance remains exact, even after running hundreds of thousands of cycles. Industrial robots are equipped with high-resolution sensors, advanced control software, and closed-loop feedback systems that ensure precise, repeatable operation with minimal variability. This reliability is essential for mass production, precision assembly, quality inspection, and other applications where even slight deviations can lead to product defects or process inefficiencies. In sectors such as automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing, repeatability and accuracy are critical in meeting strict regulatory and quality assurance requirements.
High Accuracy: Robotic systems consistently achieve higher operating accuracy compared to human labor, thanks to integrated sensor systems, precision rotary encoders, and sophisticated motion controls. This high accuracy is indispensable for automated manufacturing processes that demand tight tolerances and minimal error margins, such as CNC machining, electronics assembly, or aerospace component fabrication. Robotics-driven solutions provide real-time monitoring and feedback, making them ideal for sectors where component interchangeability, product traceability, and strict conformance to engineering specifications are essential.
Excellent Product Quality: Today, industrial robots are at the core of many quality-driven manufacturing operations. Their unparalleled repeatability and accuracy produce reliable, high-quality products, minimizing human error or subjective judgment in the process. Robotic systems can be customized with specialized end effectors, force sensors, and vision systems to handle fragile, delicate, or intricate parts with care, delivering consistent results for assembly, packaging, inspection, or even advanced surgical procedures. As a result, businesses can confidently meet customer expectations, regulatory demands, and evolving market standards for quality assurance.
Industrial robots are also essential in precision manufacturing environments such as semiconductor fabrication, food and beverage production, and pharmaceutical processing, where product integrity and contaminant-free handling are critical for compliance and market success.

More Compact Production Area: Robotics automation paves the way for more compact manufacturing layouts by consolidating a wide range of automated functions within a smaller footprint. High-speed, high-payload robots with integrated end effectors—such as grippers, welders, or cutting tools—allow manufacturers to optimize their production areas and reduce facility overhead costs. Unlike traditional manual labor, which requires additional workspace for multiple operators and support equipment, an automated robotic cell can often perform several tasks within the same area, maximizing efficiency and making more productive use of valuable floor space. Space savings are especially advantageous for manufacturers in urban locations or those seeking to expand output without major physical expansion.
As manufacturing evolves, the integration of robotics and automation continues to create new opportunities for growth, efficiency, and innovation. Industrial robotics solutions are essential for businesses seeking to improve scalability, support flexible manufacturing, and maintain a competitive edge in global markets. Robots enable rapid adaptation to changes in customer demand or product design without lengthy retraining, supporting agile manufacturing and mass customization. Modern industrial robots also utilize artificial intelligence (AI), machine vision, and IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity, unlocking predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and real-time data analytics that further optimize performance and productivity. Companies investing in robotics not only address immediate labor shortages but also future-proof their operations as digital transformation accelerates across the industrial sector. When evaluating leading industrial robot manufacturers and suppliers, consider solutions tailored to your industry, application, and integration requirements to ensure long-term success and sustainable ROI.
Industrial robots play a pivotal role in today’s manufacturing, assembly, and production sectors. While industrial robots are frequently deployed for basic pick-and-place automation, advancements in control software, powerful servo actuators, and next-generation sensors have significantly expanded their application. Modern manufacturing environments leverage industrial robots for both routine automation tasks and complex, high-precision industrial processes. Below are some of the most prevalent and impactful applications for industrial robots in the manufacturing and production industries:
Product Assembly: Industrial robots are widely used as assembly machines in the automotive, electronics, consumer goods, and medical device industries. They excel at performing highly repetitive, precise assembly tasks—such as screwdriving, part placement, soldering, and press fitting—that are tedious and error-prone for manual labor. Typically, their end-of-arm tooling (EOAT) is equipped with mechanical or pneumatic grippers for rapid pick-and-place automation and accurate part orientation. Increasingly, robots in assembly lines now utilize advanced sensors and force feedback to recalibrate for micro-positioning, ensuring critical assembly tolerances are met.
State-of-the-art end effectors integrate smart sensors and machine vision systems to verify component presence and orientation, enabling adaptive assembly even when parts have variable positioning. By using vision-guided robotics and artificial intelligence, manufacturers reduce downtime and increase yield through real-time error correction.

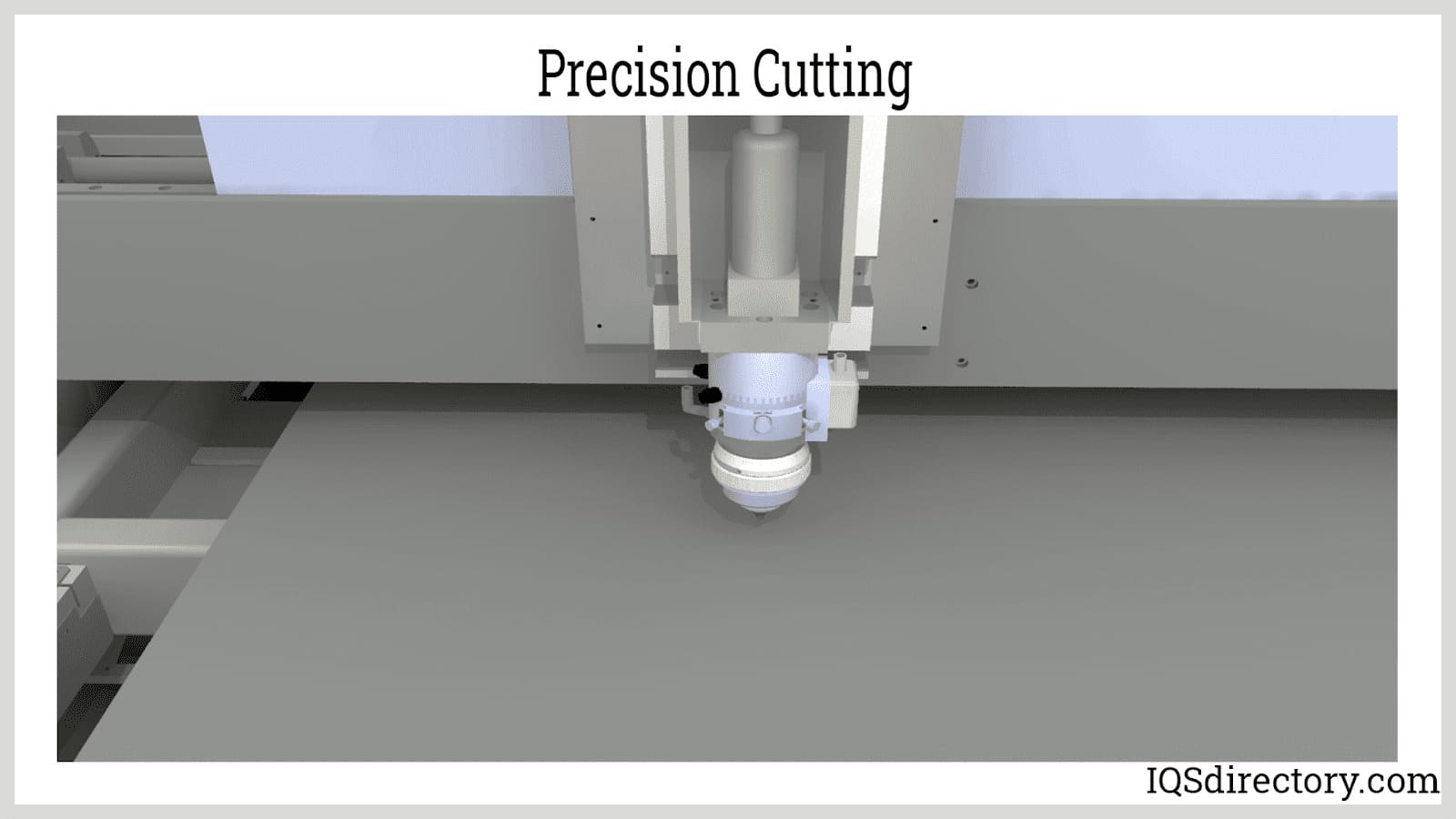
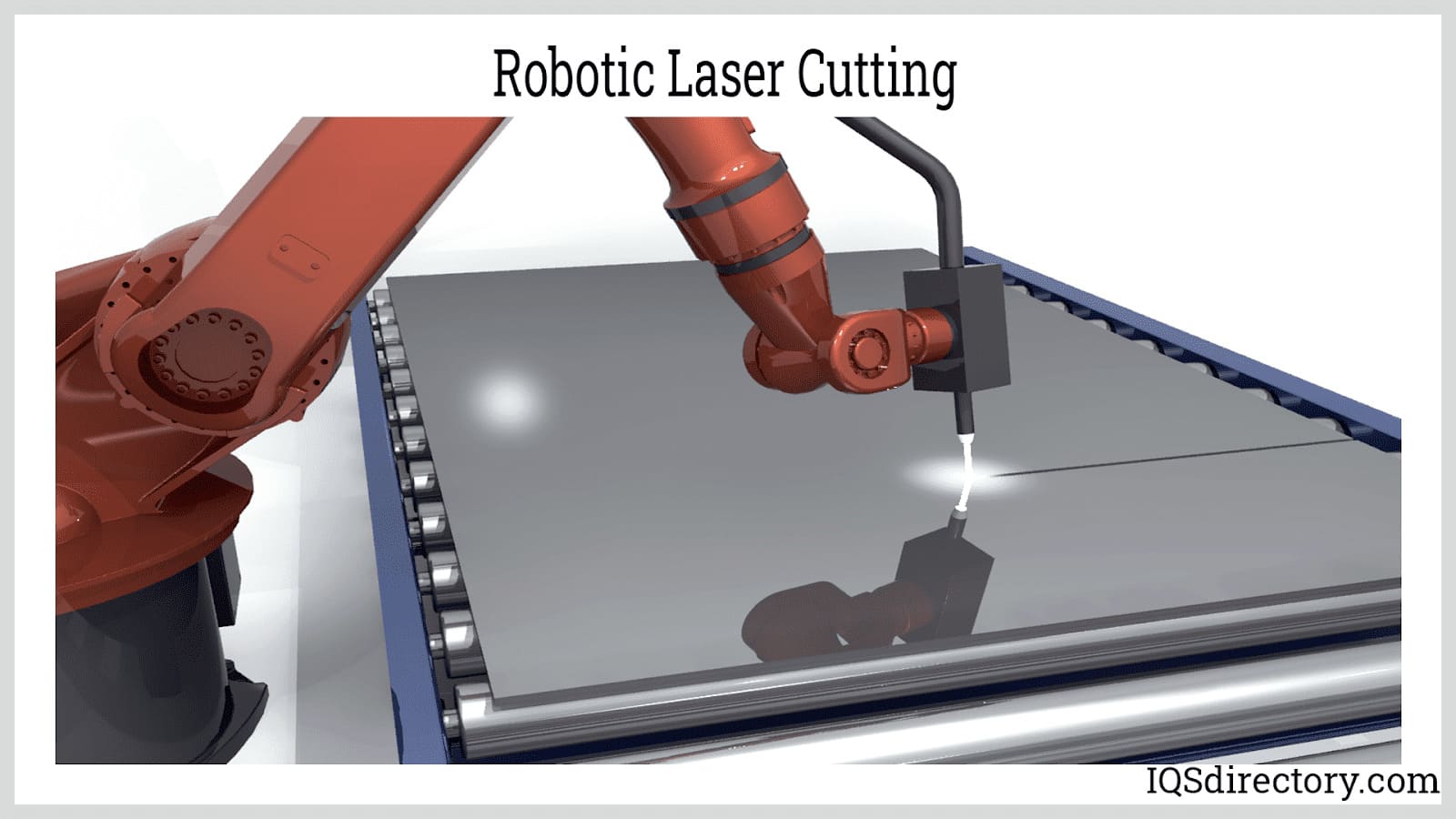
Non-Conventional Machining: Modern non-conventional machining methods—such as waterjet cutting, robotic laser cutting, abrasive jet machining, electric discharge machining (EDM), and plasma cutting—enable manufacturers to shape, engrave, and process materials with extreme accuracy and minimal manual intervention. These non-contact automation processes use highly concentrated streams of water, laser beams, electrical currents, or plasma to erode, melt, or vaporize workpiece material without physical contact.
High-precision robotic arms are programmed to manage complex cutting paths, maintaining the optimal cutting speed, stream stability, and critical cutting parameters (including power, pressure, and flow rate) through computerized control systems. By automating these machining operations, manufacturers achieve consistent product quality, reduce material waste, and increase throughput in high-mix, low-volume production runs.
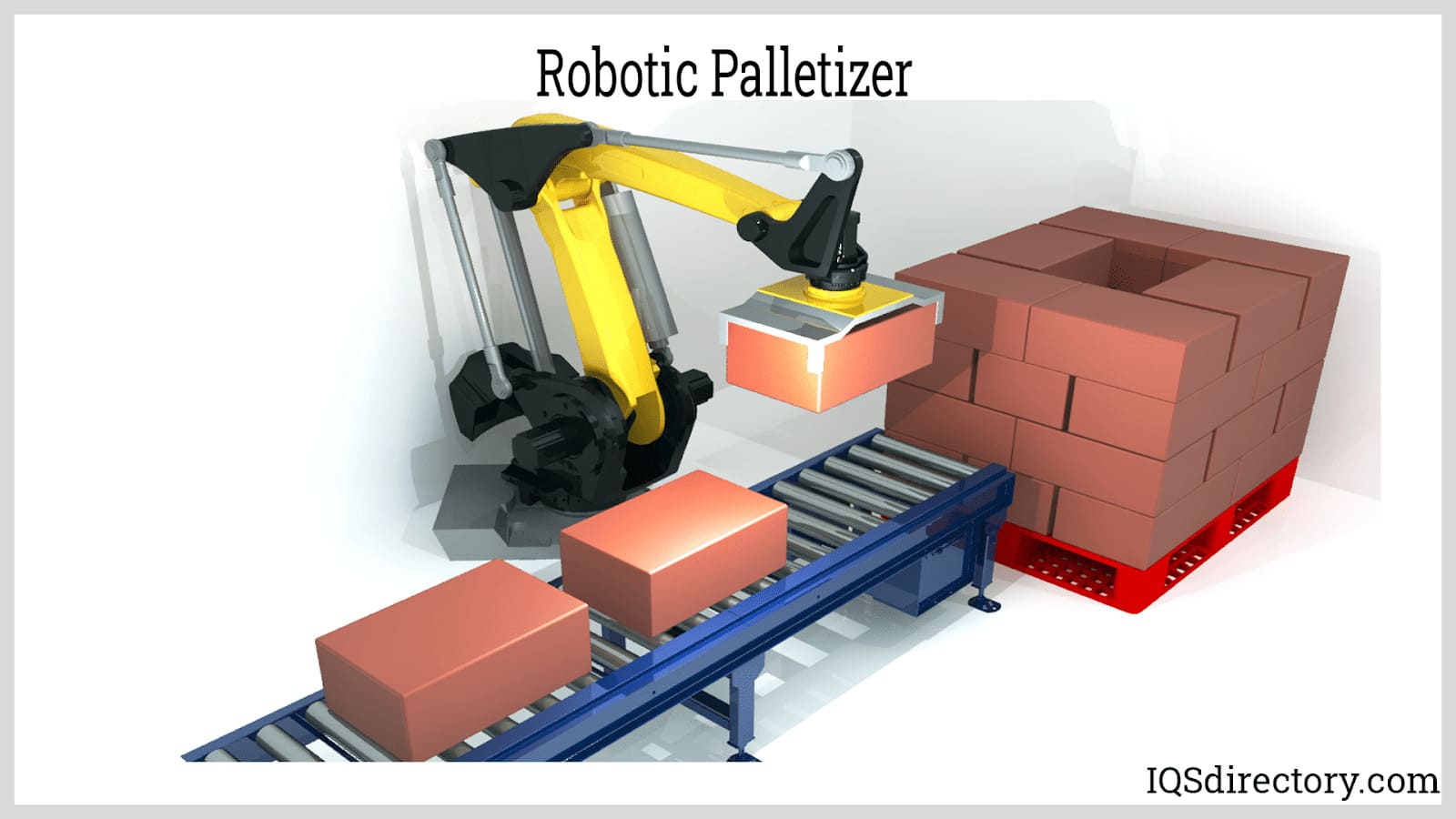
Palletizing and Depalletizing: Robotic palletizing and depalletizing significantly streamline logistics, warehousing, and material handling processes. Palletizing combines multiple packaged products or boxes into a single secure load for efficient handling, storage, and distribution, while depalletizing involves disassembling palletized units. Both processes are repetitive, labor-intensive, and susceptible to ergonomic risks without automation.
Robotic palletizers increase throughput, reduce labor costs, and minimize product damage by leveraging advanced industrial automation and intuitive programming interfaces. These systems use a range of EOAT, including mechanical, pneumatic, and vacuum grippers, to manipulate packages of varying shapes and weights. Modern palletizing robots support multi-line integration, real-time load pattern optimization, and traceability features vital for supply chain automation.
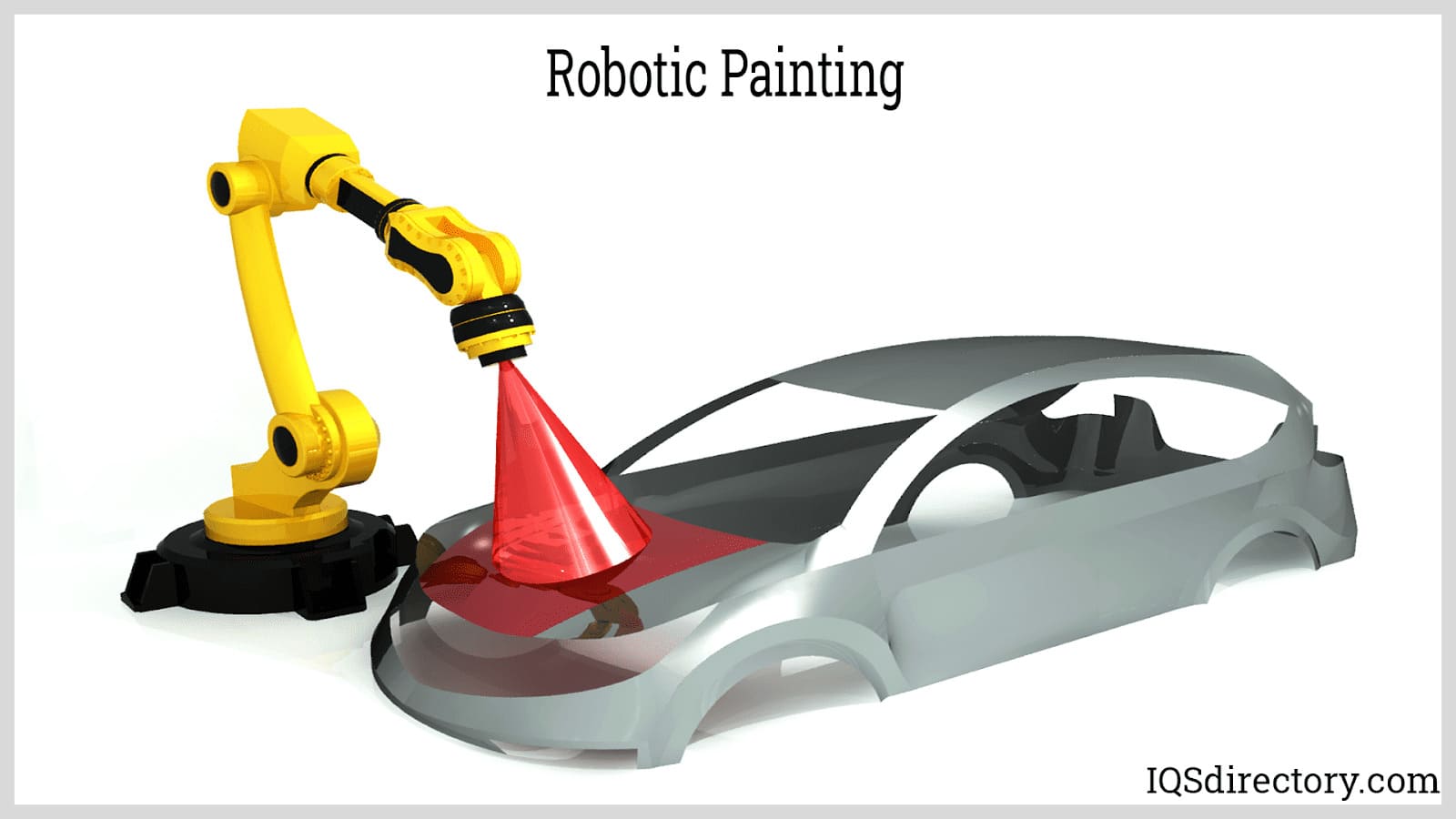
Painting and Coating: Precision robotic painting and automated coating are indispensable in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer appliance manufacturing. Robots achieve uniform paint application and consistent coating thickness, reducing waste and producing a superior surface finish. Since industrial-grade paints, pigments, and solvents can be hazardous or flammable, automated paint robots ensure a safer working environment, lower VOC emissions, and improved compliance with regulatory standards.
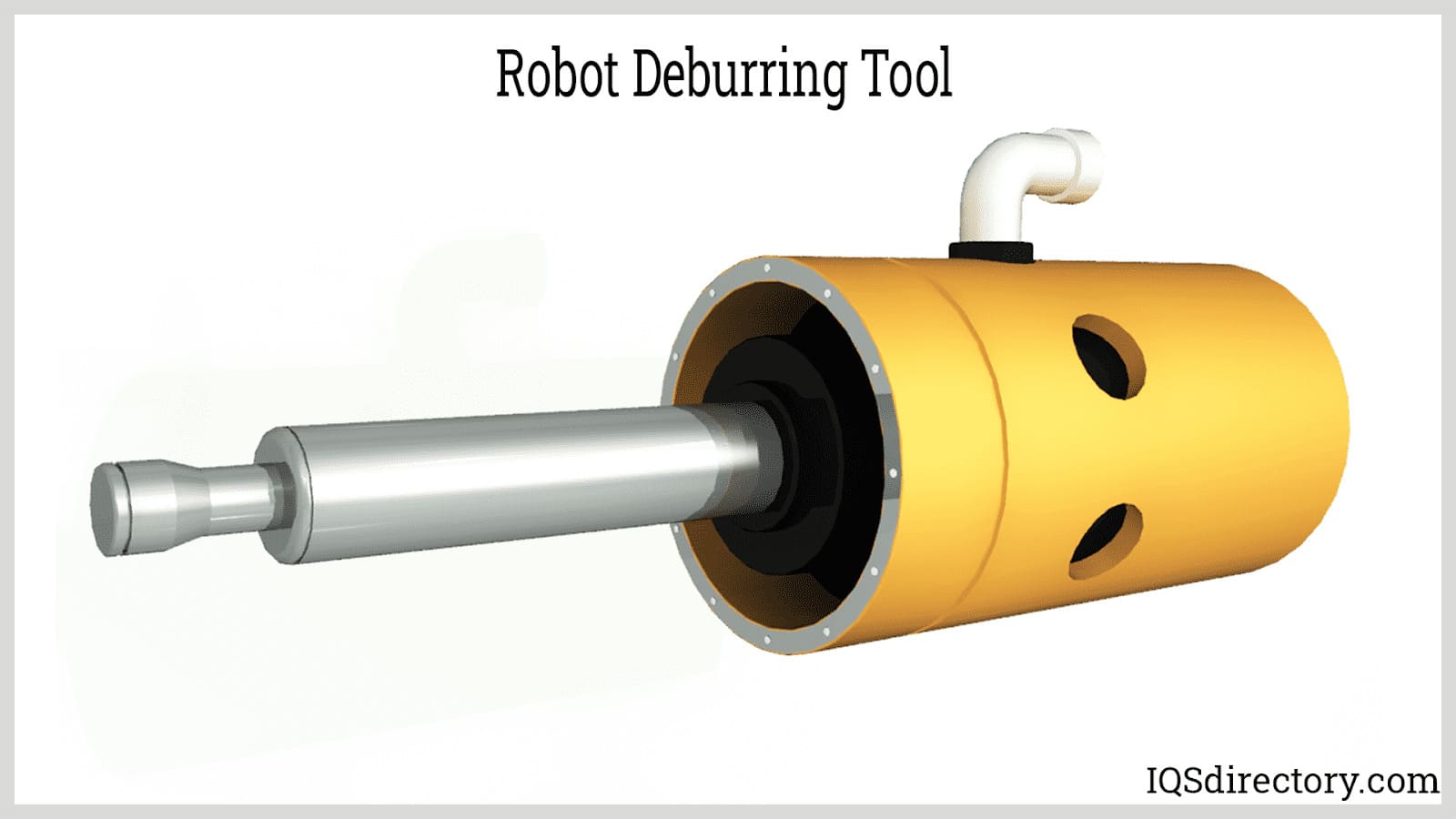
Deburring: Robotic deburring plays a critical role in finishing cast, molded, or machined components in automotive, aerospace, and die casting applications. Using programmable paths and specialized rotary tools—such as sanding drums, wire wheels, or carbide deburr tools—robots remove sharp edges, flash, and residual burrs to enhance part quality and assembly compatibility. Automated deburring not only safeguards operator health by containing dust and debris but also ensures higher consistency and repeatability in finishing processes.
Inspection: Robotic inspection systems are at the forefront of automated quality control. They utilize advanced measuring tools such as laser scanners, optical sensors, proximity detectors, force transducers, ultrasonic probes, and sophisticated machine vision systems to examine and verify dimensional accuracy, surface defects, and part integrity. Automated inspection enables real-time, 100% part inspection in high-volume production lines and supports non-destructive testing (NDT) for weld quality, material integrity, and finished assembly evaluation.

Beyond these core functions, industrial robots are also essential in advanced manufacturing strategies such as flexible manufacturing systems, just-in-time production, and Industry 4.0 smart factories. Their ability to integrate with enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, cloud-based monitoring, and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices provides real-time production data and predictive maintenance capabilities. Integrating robotics with other automation technologies—such as collaborative robots (cobots), autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), and artificial intelligence for predictive analytics—continues to transform supply chain operations, improve plant safety, and accelerate return on investment for manufacturers seeking to enhance productivity, quality, and competitiveness in global markets.
When evaluating industrial robots for your application, consider essential criteria like payload capacity, reach, degrees of freedom, integration with existing automation systems, ease of programming, safety features, and cost of ownership. Proactively aligning your automation strategy with production goals ensures not only operational efficiency but also long-term scalability and market adaptability in an increasingly automated world.
Industrial robots are categorized based on their arm configuration, which consists of links and joints. By altering the number and type of these components, robots can be configured in various ways. Below are the six main types of industrial robots.
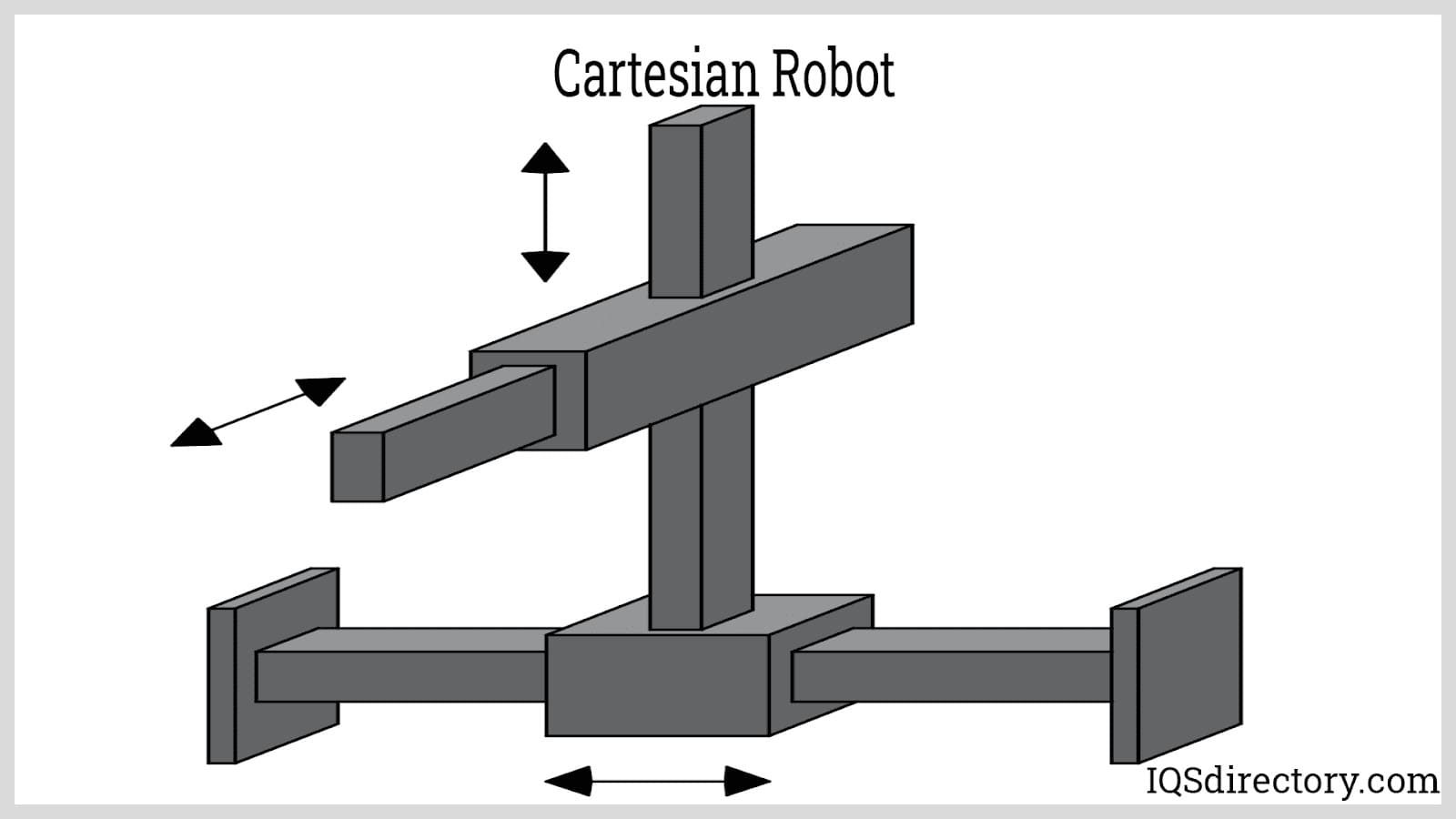
Cartesian Robot: A Cartesian robot is composed of three prismatic joints. Thus, the tool is limited to linear motion at each axis but can still generate circular moves through kinematic models that allow circular interpolation.
The name Cartesian is derived from the three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, which consists of X, Y, and Z axes. Cartesian robots are the simplest robotic system since their operation may only involve translational movements. They are suitable for applications that only require movement at right angles without the need for angular translations.
Since one or two of a cartesian robot’s prismatic joints can be supported at both ends, they can be built to handle heavier loads than other robot types. An example of a Cartesian robot is a gantry machine. Gantry machines, also known as gantry cranes, are used to pick and place large, palletized loads.
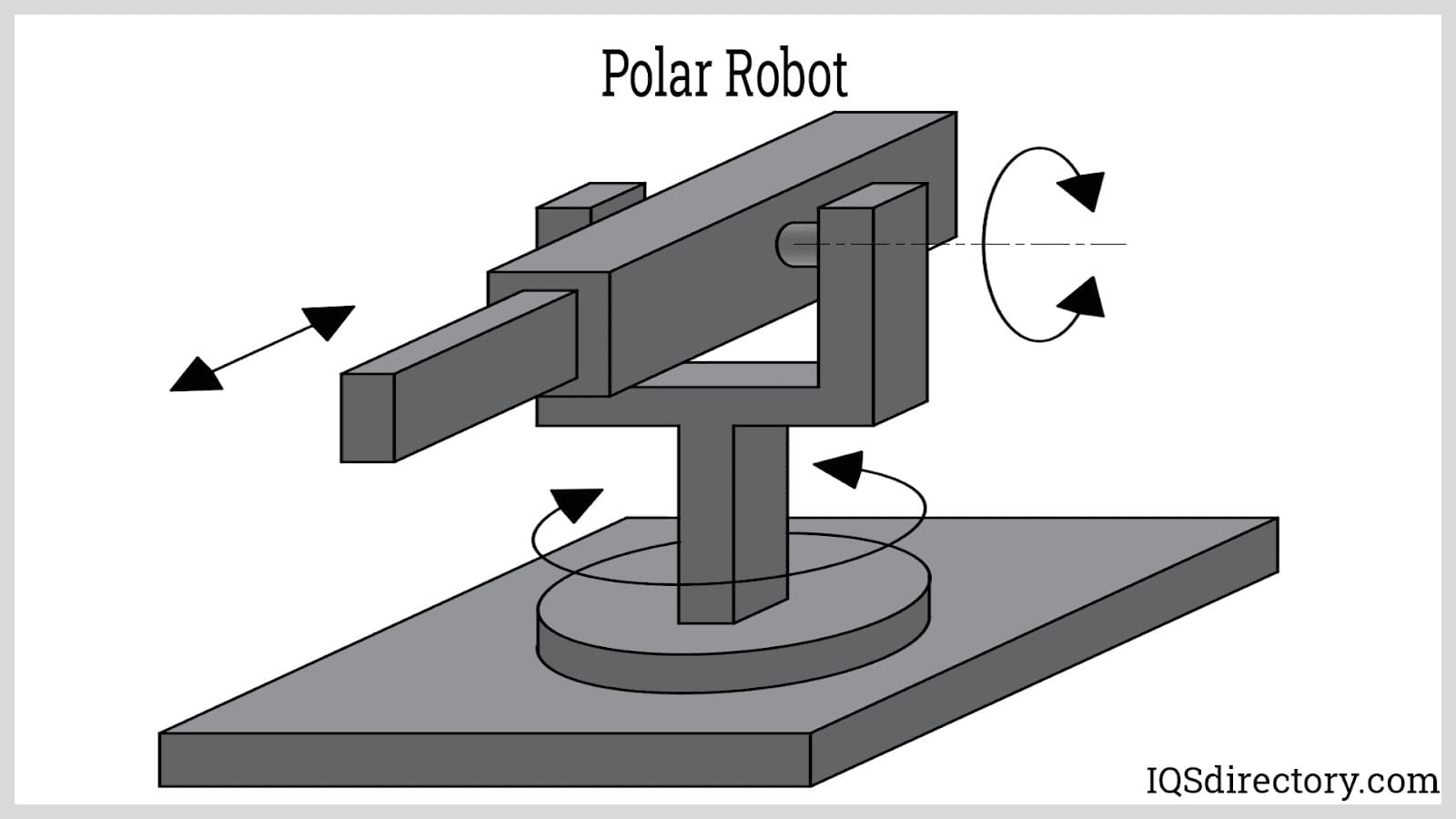
Polar Robot: Polar robots, also known as spherical robots, use the three-dimensional polar coordinate system r, θ, and φ coordinate. Instead of having a work envelope in the shape of a rectangular prism, polar robots have a spherical range. Their range of motion has a radius equal to the length of the link connecting the EOAT and the nearest revolute joint. This configuration allows polar robots to have the farthest reach for a given arm length compared to other robot types. The range of a polar robot can be further extended using a second link connected by a prismatic joint. Because of their wide reach, polar robots are commonly used in machine loading applications.
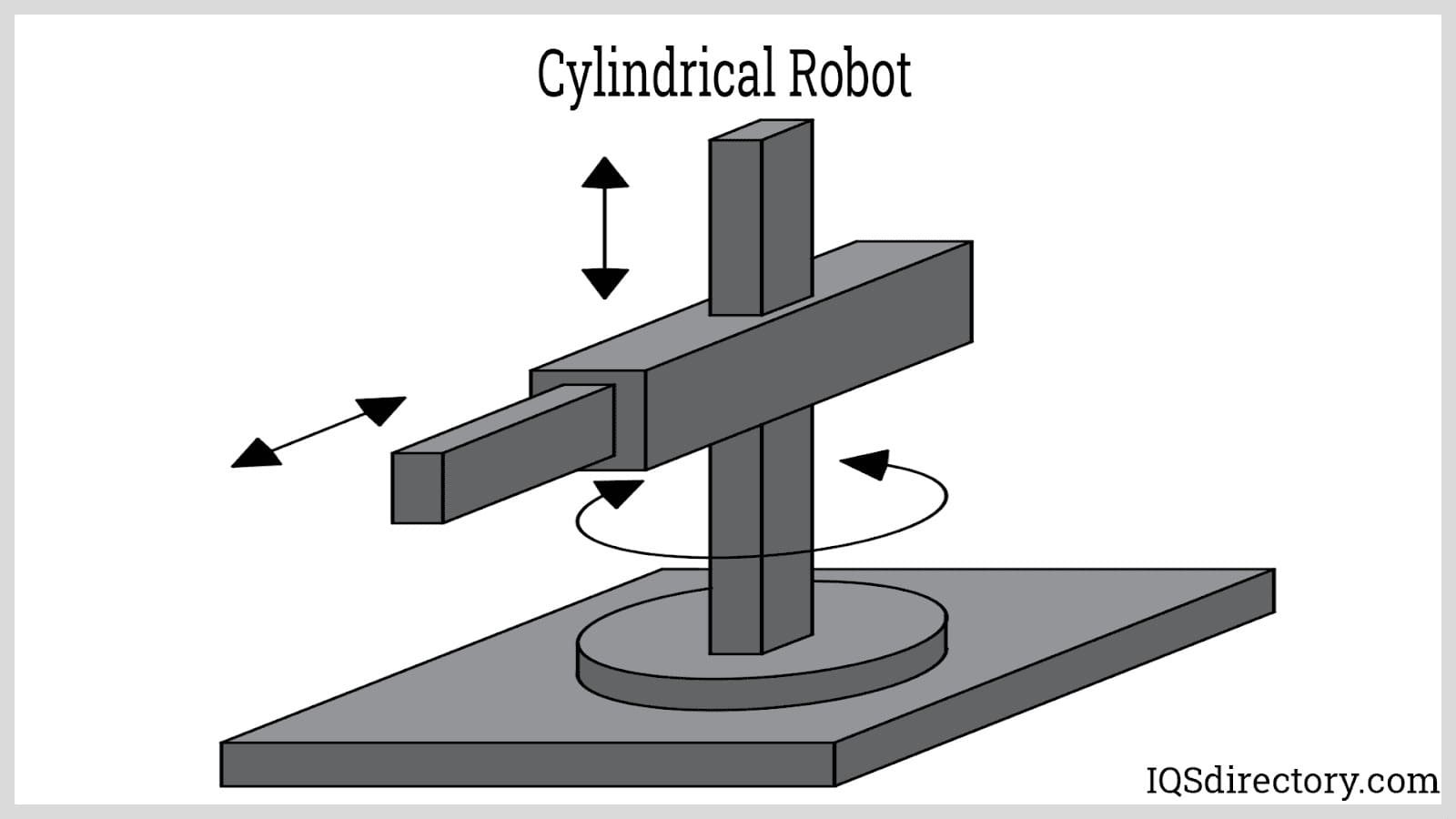
Cylindrical Robot: As the name suggests, a cylindrical robot has a cylindrical range of motion. This type consists of one revolute joint and two prismatic joints. The revolute joint is located at the arm's base, allowing the rotation of the links about the robot's axis. The two prismatic joints are used for adjusting the radius and height of the robot’s cylindrical work envelope. In compact designs, the prismatic joint used for adjusting the arm’s radius is eliminated. This one revolute, one prismatic joint configuration is useful in simple pick and place operations where the product feed is located only in one place.
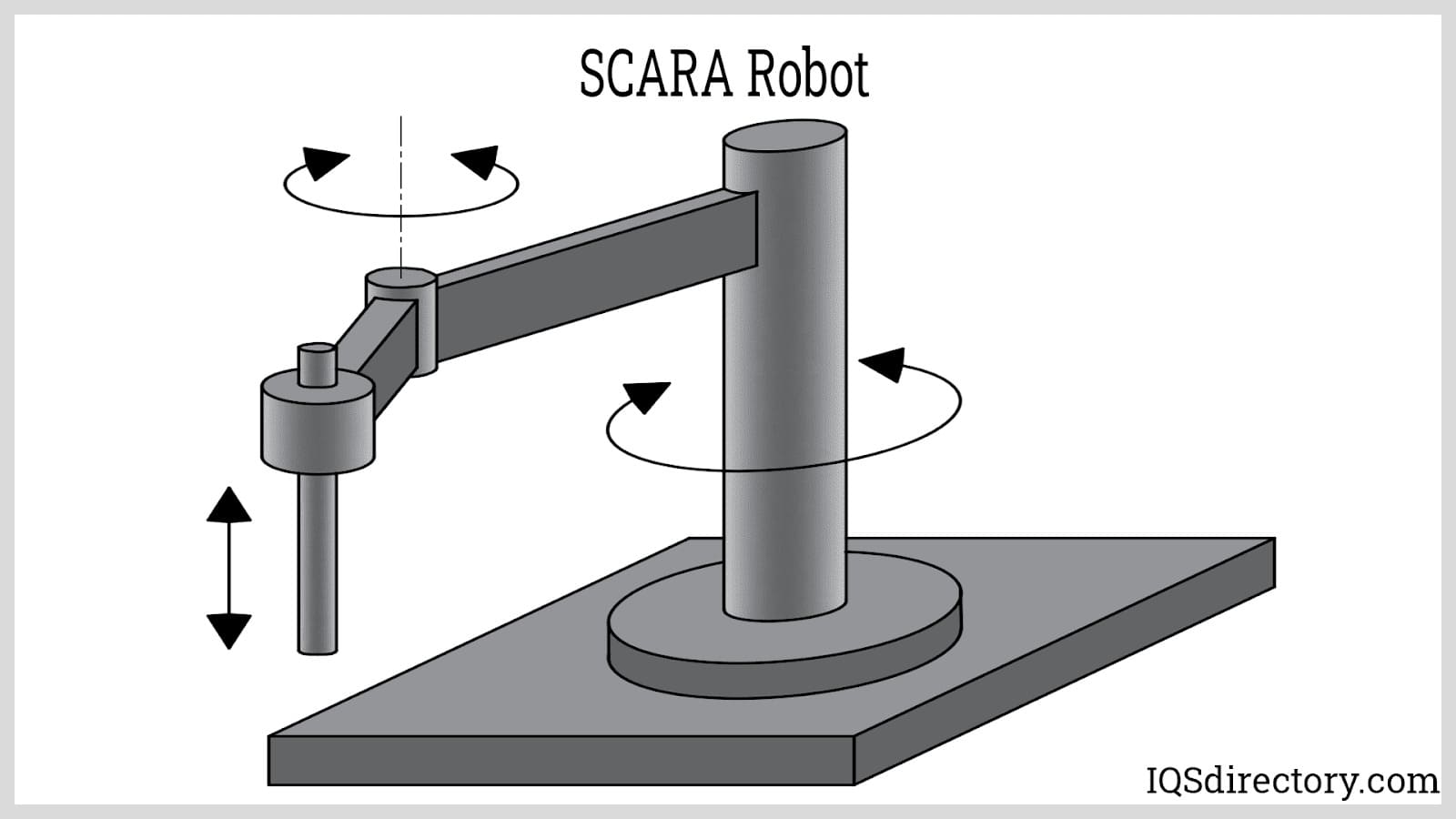
Selective Compliant Articulated Robot Arm (SCARA): A SCARA is a type of robot with an arm that is compliant or flexible in the horizontal or XY-plane but rigid in the vertical direction or Z-axis. Its translational movement on a single plane describes its “Selective Compliant” characteristic. A SCARA has two links, two revolute joints, and a single prismatic joint. The links and the base are connected by the revolute joints oriented at the same axis. The prismatic joint is only for raising or lowering the EOAT. The resulting work envelope of a SCARA is a torus. Its application is similar to that of a cylindrical robot.
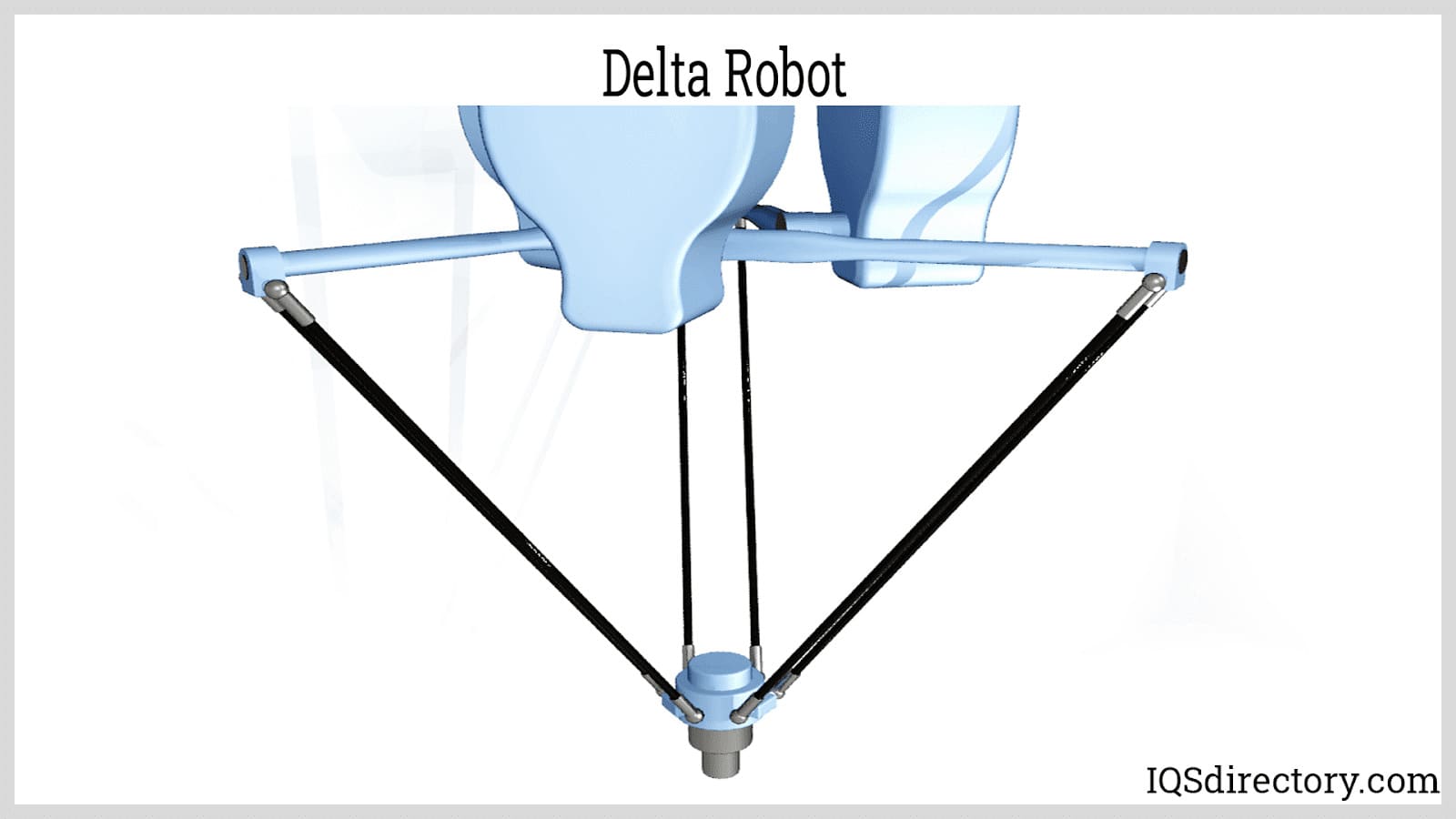
Delta Robot: A delta robot consists of at least three links connected to an EOAT and a common base. The EOAT is connected to the links by three undriven universal joints. On the other hand, the base is connected by either three prismatic or revolute-driven joints. The driven joints work together to allow the EOAT to have four degrees of freedom. For designs using prismatic joints, a fourth link or shaft is usually connected to the EOAT to enable rotation. The EOAT of a delta robot can move along all Cartesian axes and rotate around the vertical axis, resulting in a dome-shaped work envelope. The simultaneous action of the three driven joints makes delta robots suitable for high-speed pick and place applications.
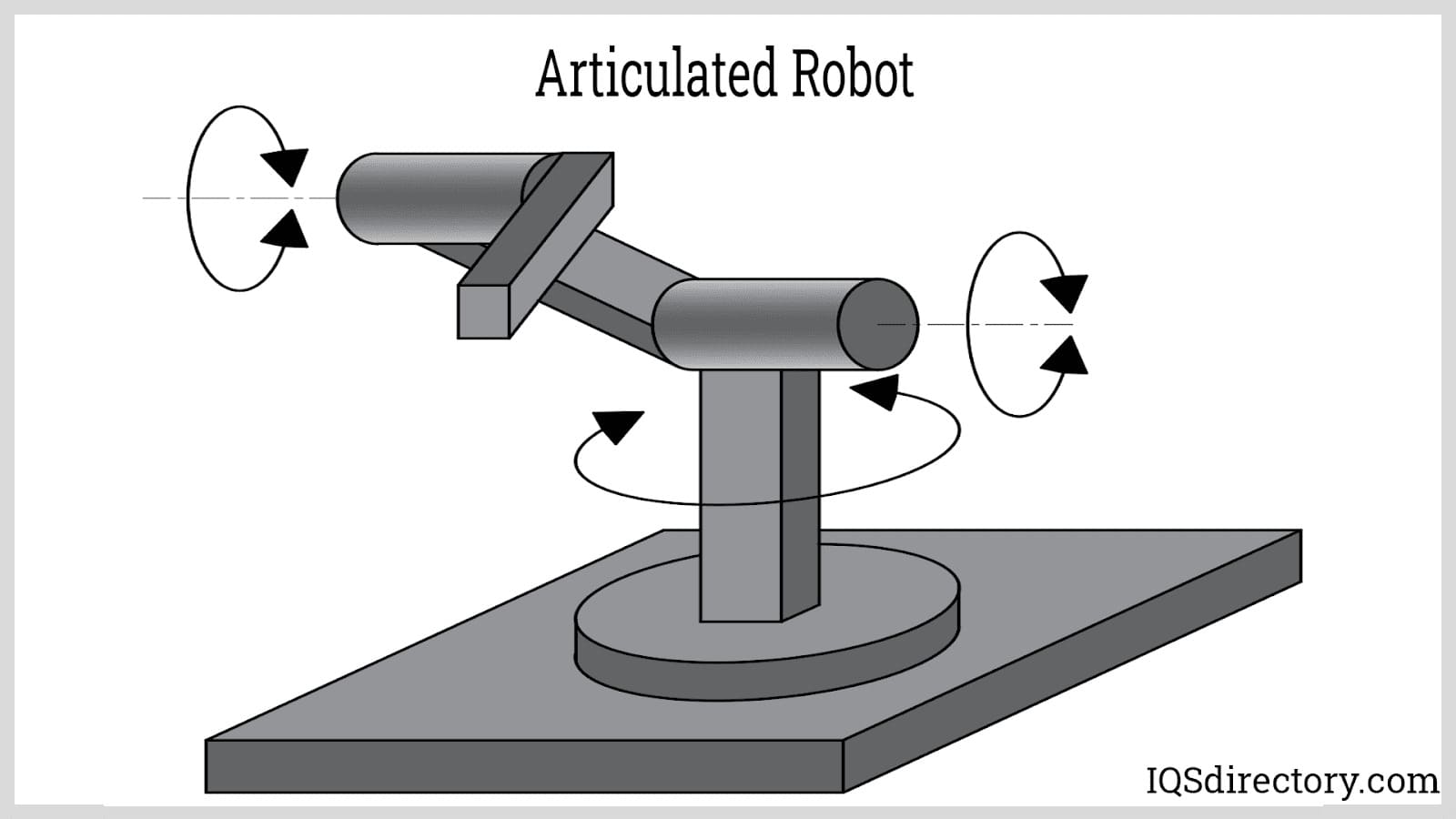
Articulated Robot or Anthropomorphic Robot: Articulated robots are the most common robots used in manufacturing processes. They perform more complex operations such as welding, product assembly, and machining. EOATs mounted on articulated robots are designed to have a full six degrees of freedom. The robot arm consists of at least three revolute joints. A fourth revolute joint can be added to the wrist of the arm for rotating the EOAT. Its work envelope is also spherical, similar to that of the polar robot type.
When selecting a specific robot, various design factors must be considered. Different applications demand specific performance parameters that must be weighed against the required investment. While higher specifications generally offer better performance, the associated costs increase almost exponentially.
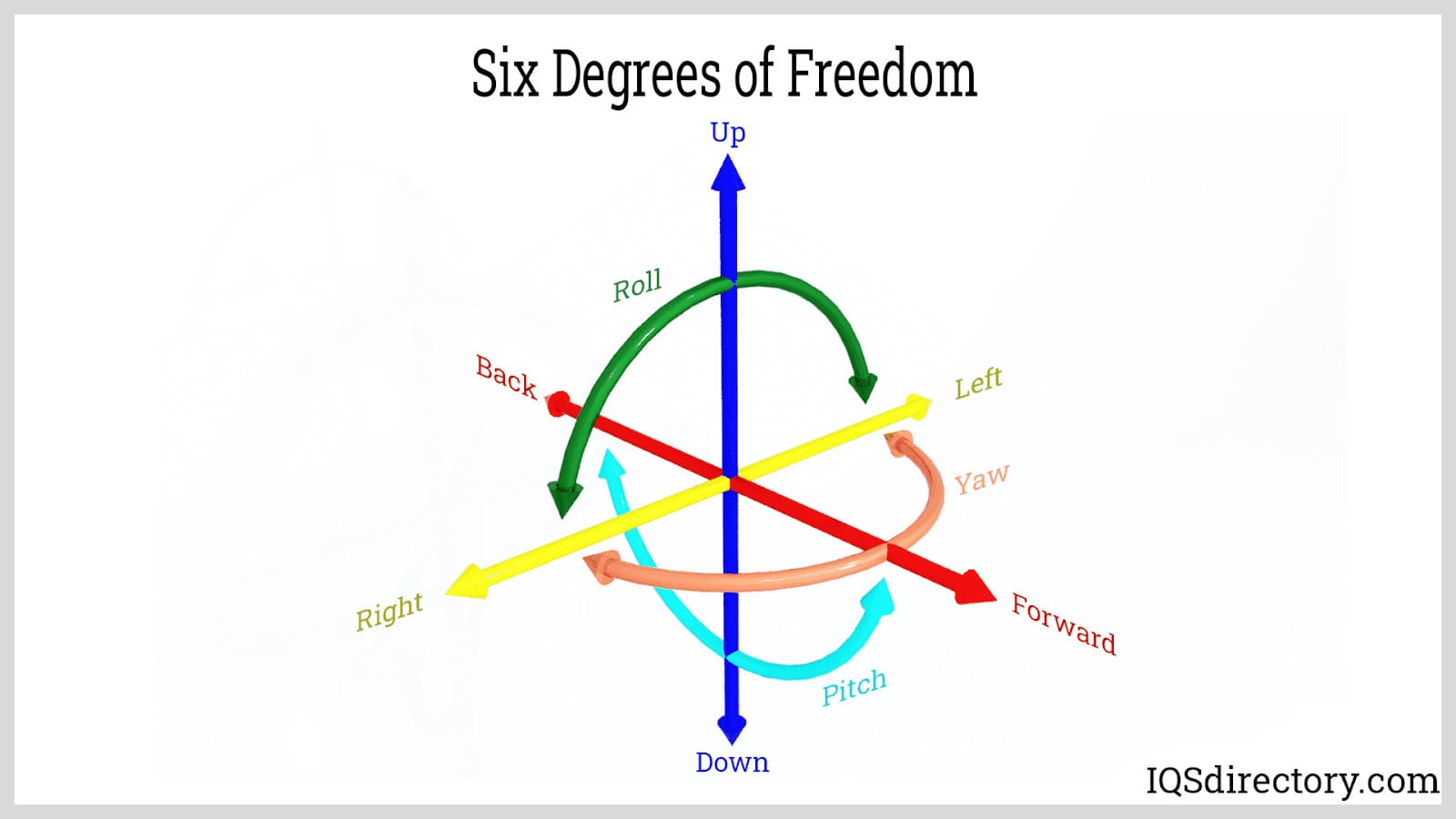
Number of Axes or Degrees of Freedom: The number of axes and degrees of freedom define the ability of a robot to move and orient the EOAT across a three-dimensional space. The definition of the degrees of freedom is in regard to the direction of a motion and the types of motion. The six degrees of freedom are forward or backward, up or down, left or right, yaw, pitch, and roll. Depending on a robot’s design, it can have all six axes, with a higher number giving it greater flexibility for its robotic arm.
Typical industrial robots used in simple pick and place applications have three to five axes, while robots used for more versatile applications have a full six degrees of freedom or more. For example, an assembly robot may have four degrees of freedom, while a robot performing complex operations such as welding may have over six degrees of freedom to be able to perform highly complex procedures.
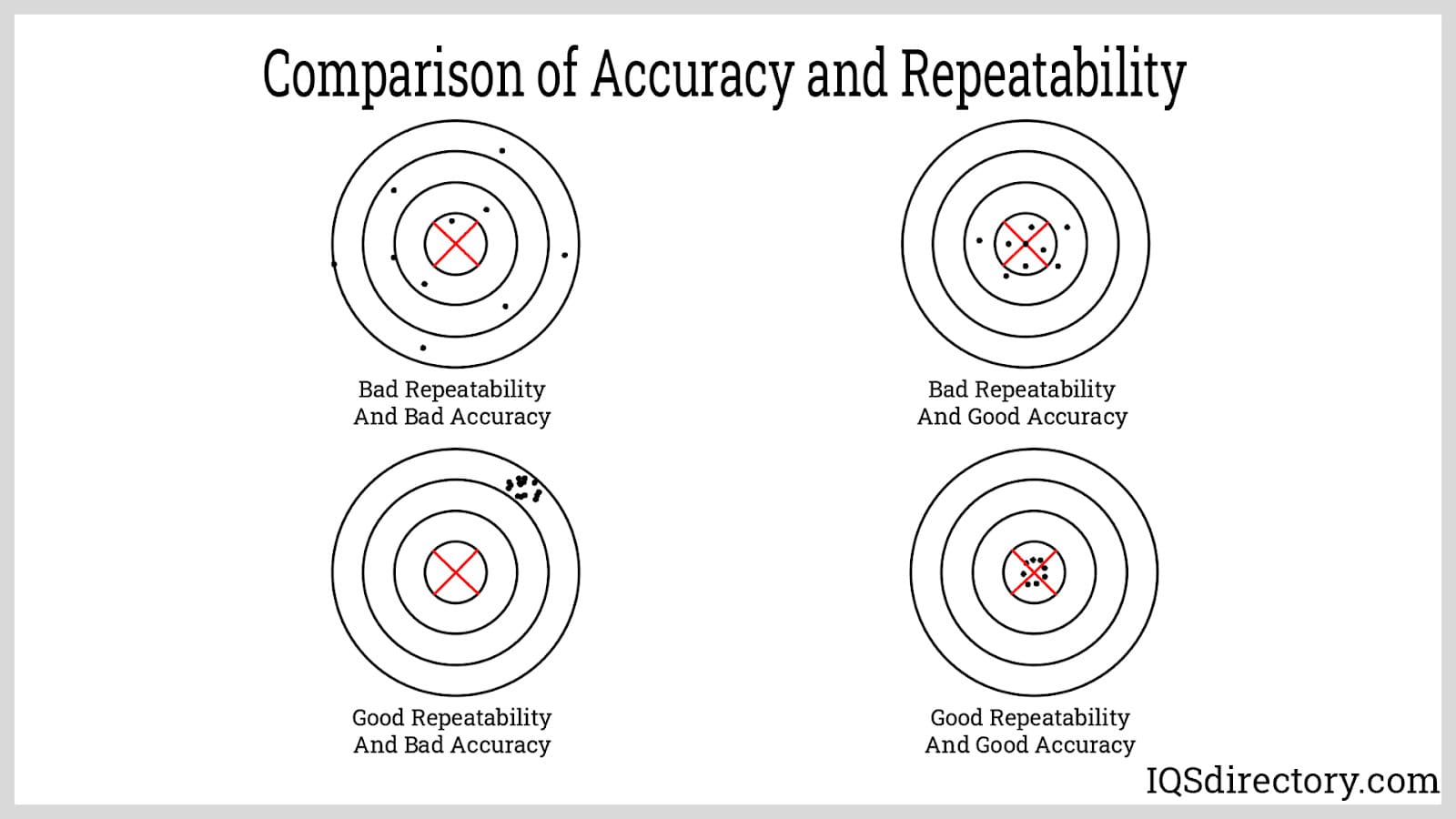
Accuracy and Repeatability: These are the two main characteristics determining the effectiveness of a robot in performing its tasks. Accuracy refers to the ability of a robot to position itself or its load at a specific point, which is measured by determining how close its final state is to a set state defined by the user.
Repeatability is the measure of how the robot maintains its final position across several operating cycles. This is measured by getting the average of the distances between the final positions of the EOAT or a point on the robot after each cycle. Repeatability is the primary concern when selecting a robot, as a pre-programmed position can always be “touched up” to get the robot where it needs to be, but the repeatability of a robot defines the consistency of an operation.
These usual definitions of accuracy and repeatability are known as the static case, which pertains to the ability of the robot to bring itself to a certain displacement. They are used to evaluate the path, position, and orientation of a robot and are necessary factors that must be achieved every time a robot and end effector is set in motion.
These usual definitions of accuracy and repeatability are known as the static case, which only pertains to the ability of the robot to bring itself to a certain displacement. Accuracy and repeatability can also be applied to the speed and acceleration of the robot.
Work Envelope: The work envelope is the spatial specification of a robot, which is defined by its swept area, reach, and stroke. The work envelope's essential part is the space the robot's EOAT can access. The size of the work envelope depends on the type of robotic arm (Cartesian, polar, SCARA, etc.) and the length of its linkages. The parameters of the work envelope are important for machine loading and unloading applications. A larger robot requires a bigger work envelope that necessitates greater space, which must be determined prior to installation.
The function of the work envelope is to control and define the area a robotic arm may reach, which is important for creating safe zones for workers in the area of the robot. Understanding the work envelope is essential since everything a robot does is associated with its work envelope.

An automatic screwdriver is a piece of equipment that automatically inserts screws into a product during assembly and production. Since every production operation is unique and requires a...
An automation system is an integration of sensors, controls, and actuators designed to perform a function with minimal or no human intervention. The field concerned in this subject is called Mechatronics which is an...

Collaborative robots, also abbreviated as Cobots, are the newest technology in robotics. They have changed the automation world significantly. These robots can work safely together with workers, hence are...
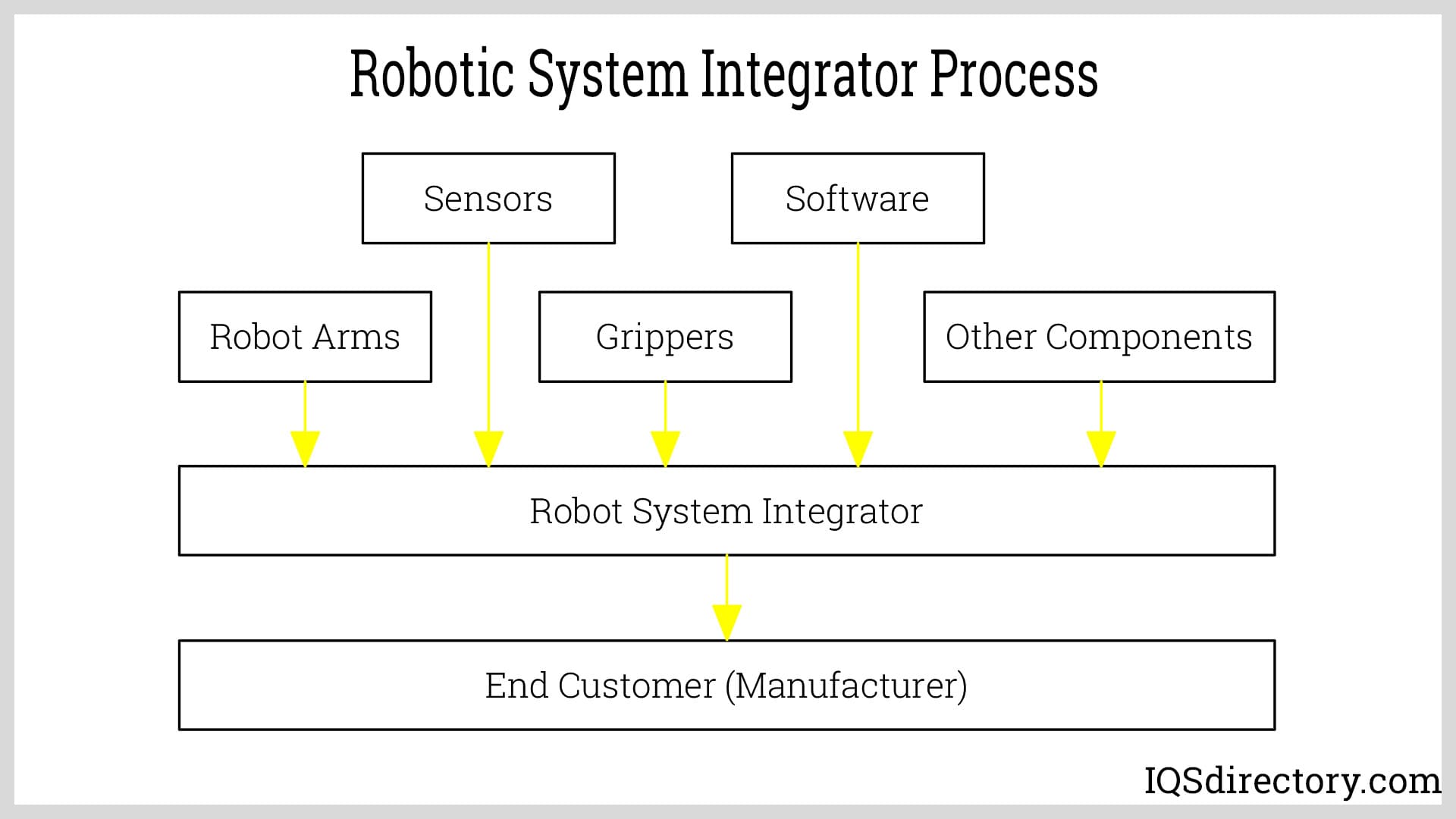
Robotic system integrators are companies that provide assistance in automating a wide range of applications. They help design robotic technologies that best suit the needs of an operation for a company and solutions as...

Warehouse automation is the process of replacing repetitive tasks with systems that are automated. The main goal is to remove labor-intensive duties that consume time. As a result, the workers can focus more on...
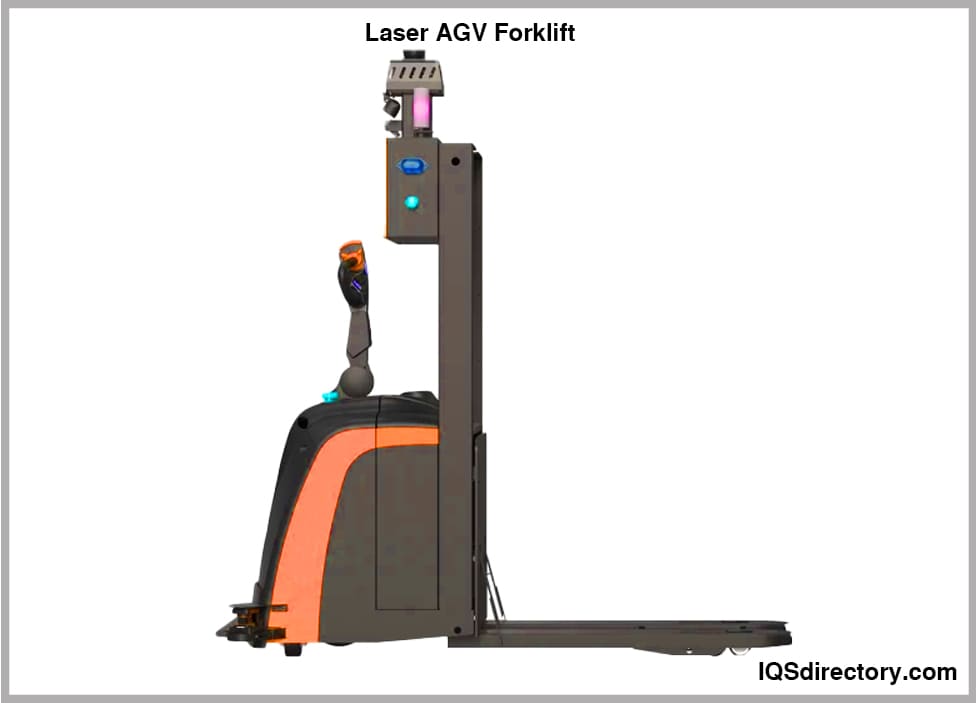

An AGV forklift is a driverless self-operating robotic device that has the ability to carry, lift, retrieve, and place loads for easy transfer from one location to another. An automatic guided vehicle (AGV) forklift is a computer controlled mechanism that...
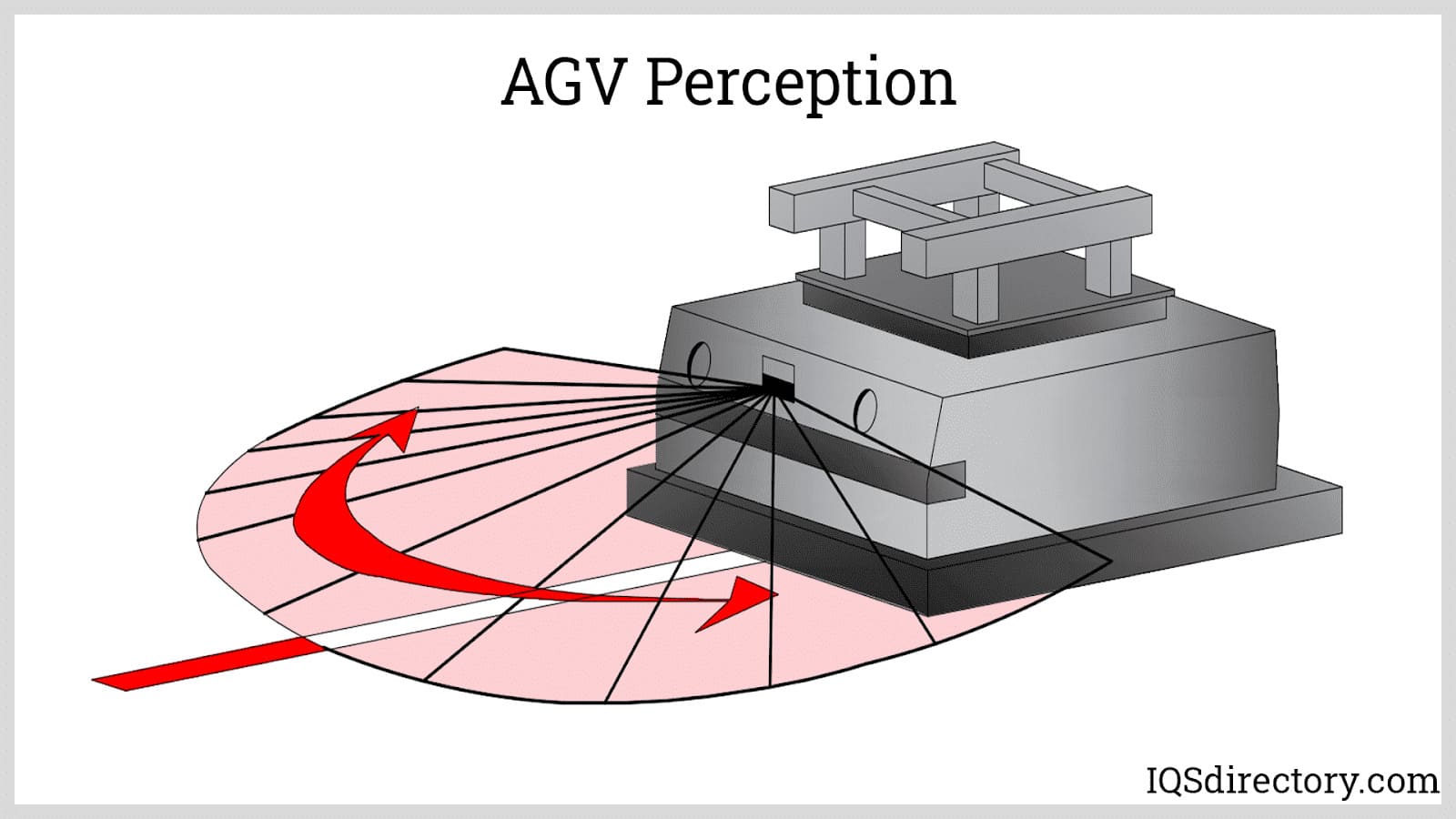
Automated guided vehicles (AGV) or mobile robots are types of guided robotic systems that are not bounded by a fixed range of motion. Rather, it is self-contained and can move along a line, surface, or space...

An autonomous mobile robot (AMR) is a self-propelled self-powered mechanism designed to perform repetitive tasks or organizational functions using an internal guidance system. They are able to navigate their...

A belt conveyor is a system designed to transport or move physical items like materials, goods, even people from one point to another. Unlike other conveying means that employ chains, spirals, hydraulics, etc...
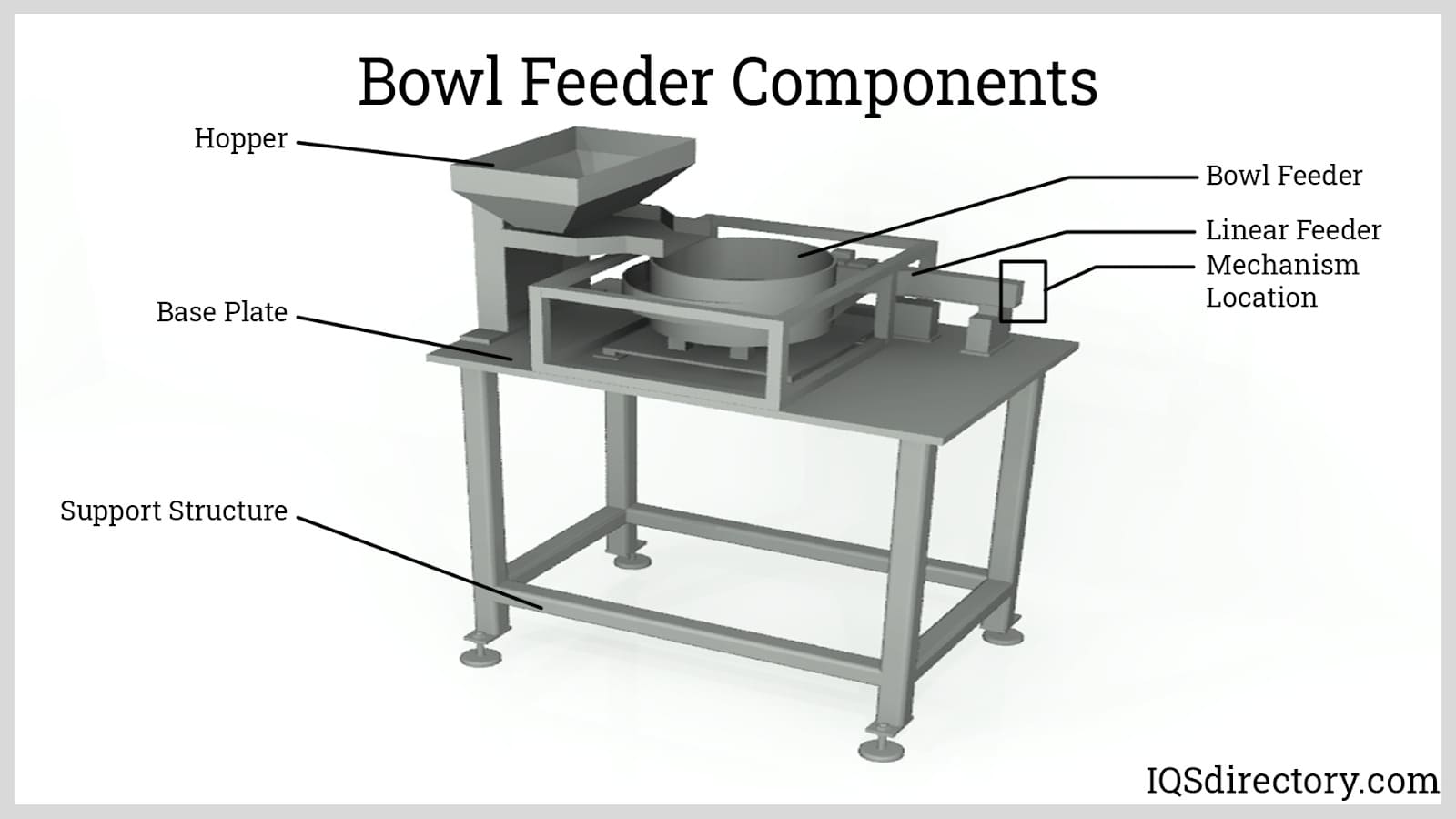

A bowl feeder is a mechanism for supplying small parts and components to a production line or for sorting bulk items for rapid use. A self contained bowl feeder system has a bowl that sets on a spring loaded base that moves vertically...
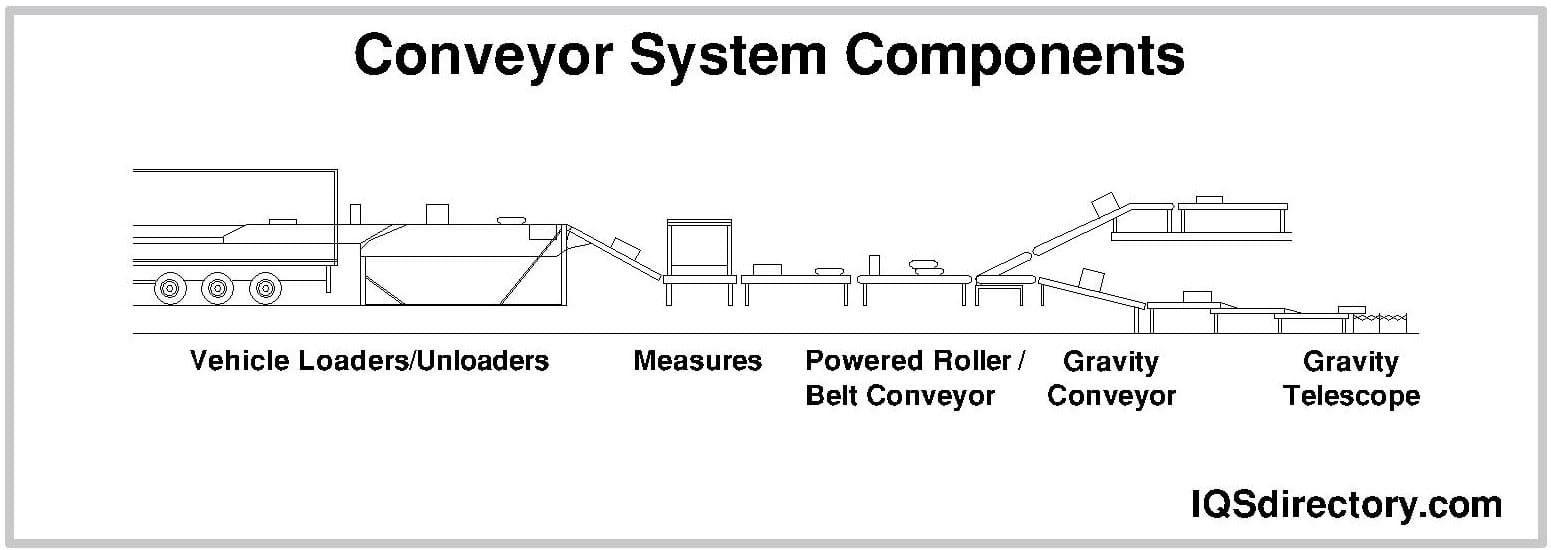
A conveyor system is a method for moving packages, products, supplies, parts, and equipment for production, shipping, or relocation. The different types of conveying systems include pneumatic, screw, belt, and roller. The construction of individual systems depends on the materials...
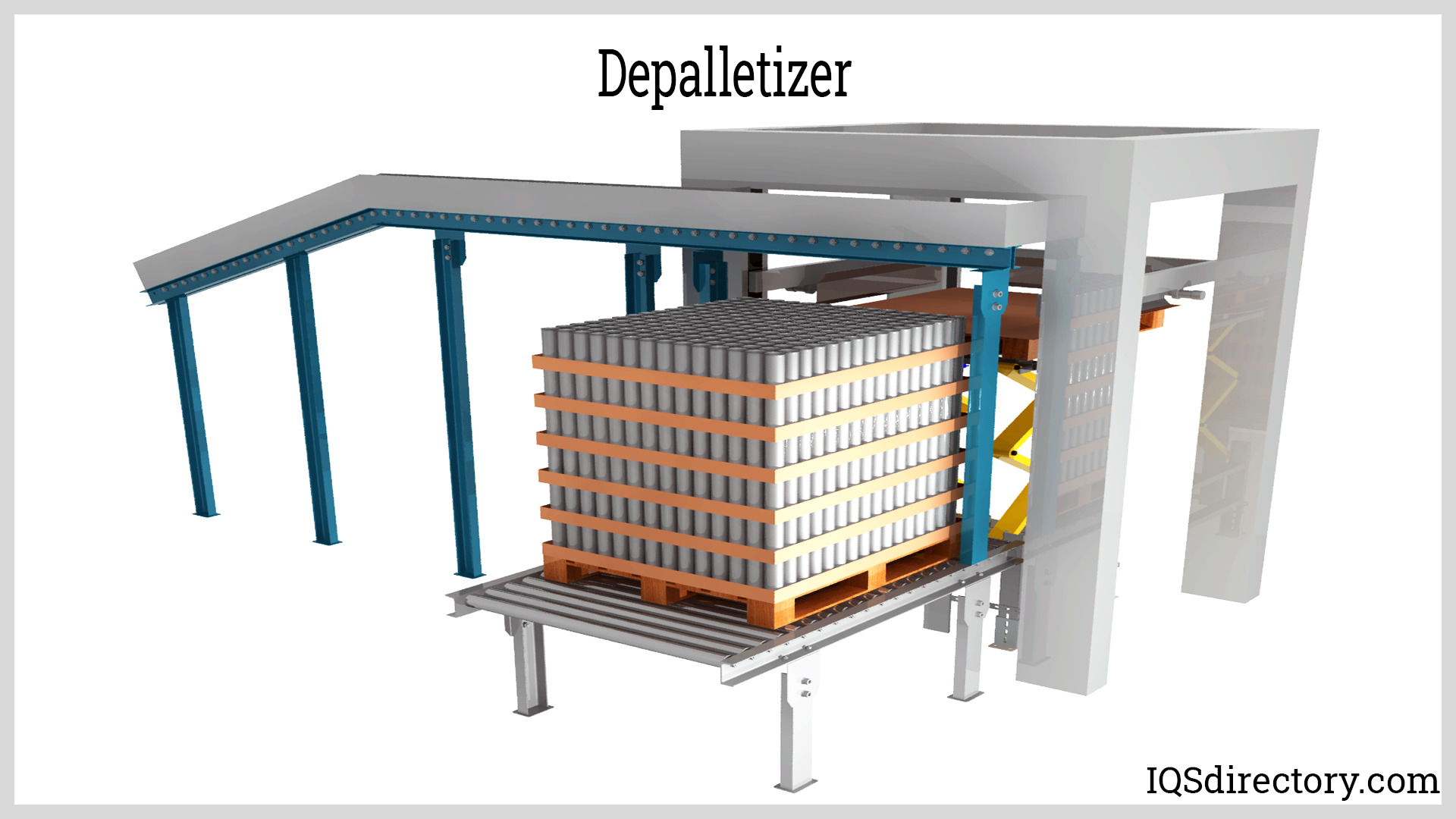
Palletizing is the process of putting items on a pallet. The process of emptying the loaded objects in the reverse pattern is known as depalletizing. A pallet is a flat, square-shaped platform used to transport and...
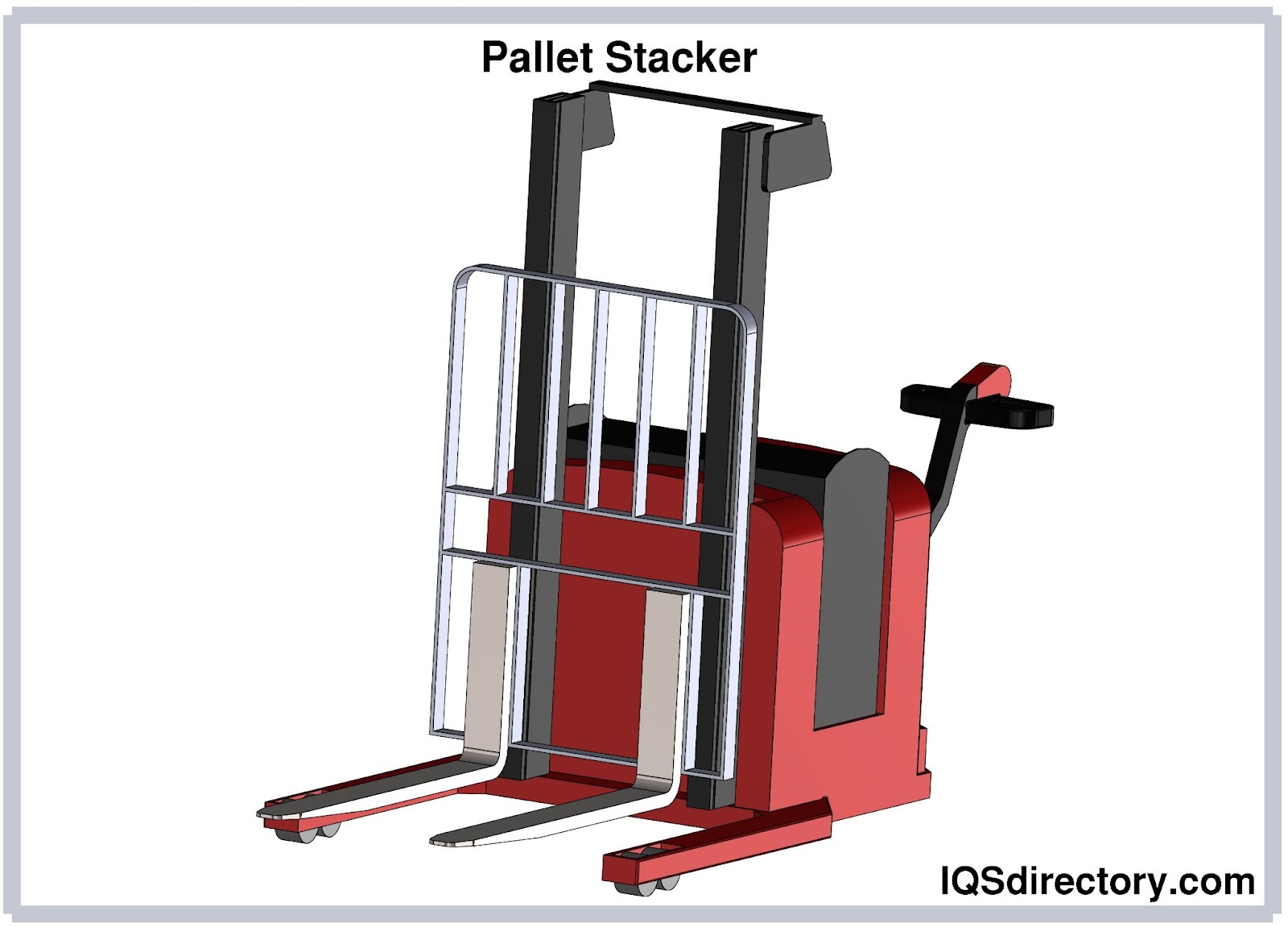
A pallet stacker is a machine designed to assist the user in lifting, moving and handling palletized materials with ease. A pallet itself is a flat and horizontal structure used to support goods in a sturdy fashion...
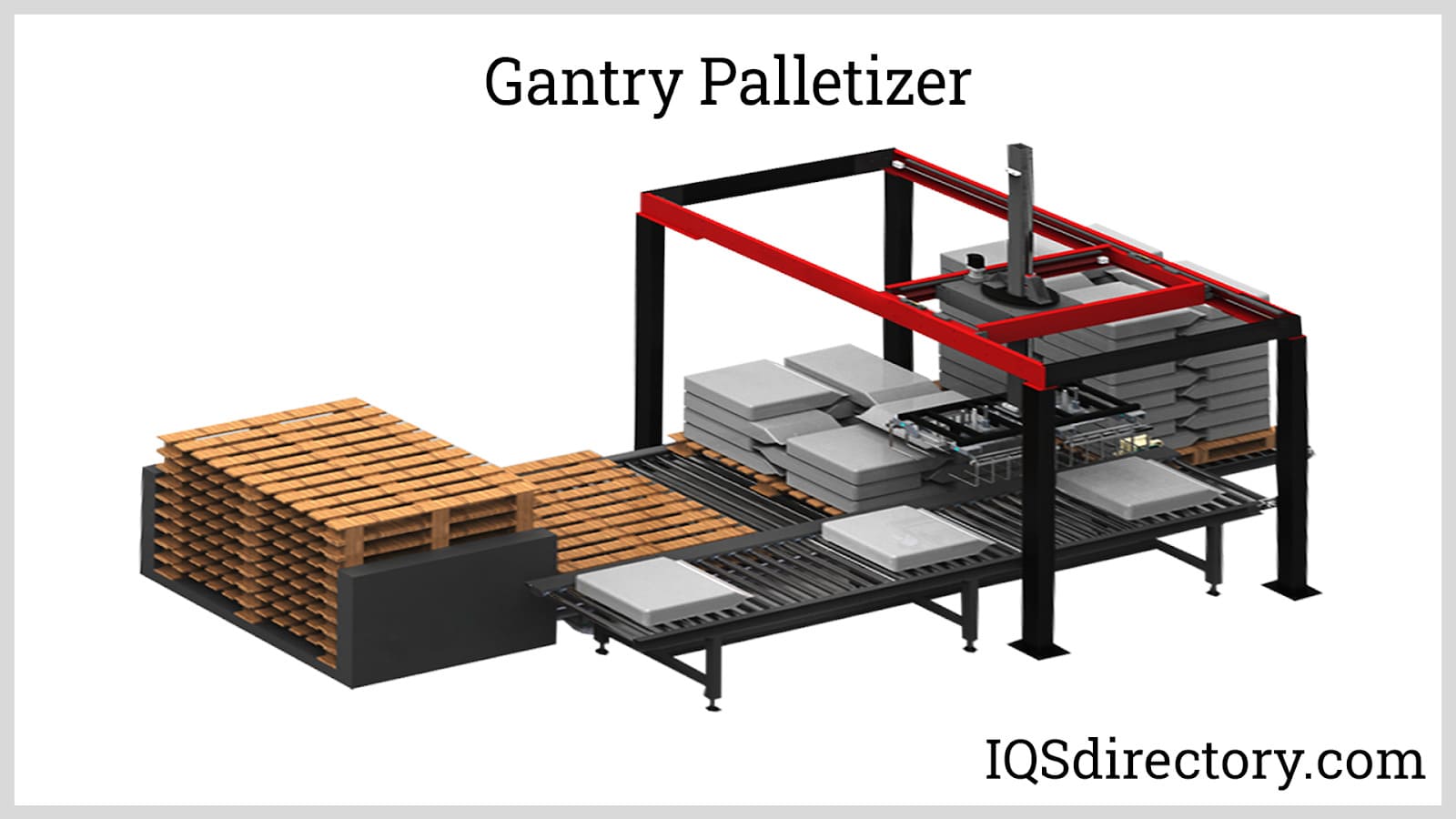
A palletizer is an automated material handling machine used to stack and orient several individual products into a single load for a more convenient and economical method of handling, storage, and shipment. Palletizers are usually part of a bigger packaging process...
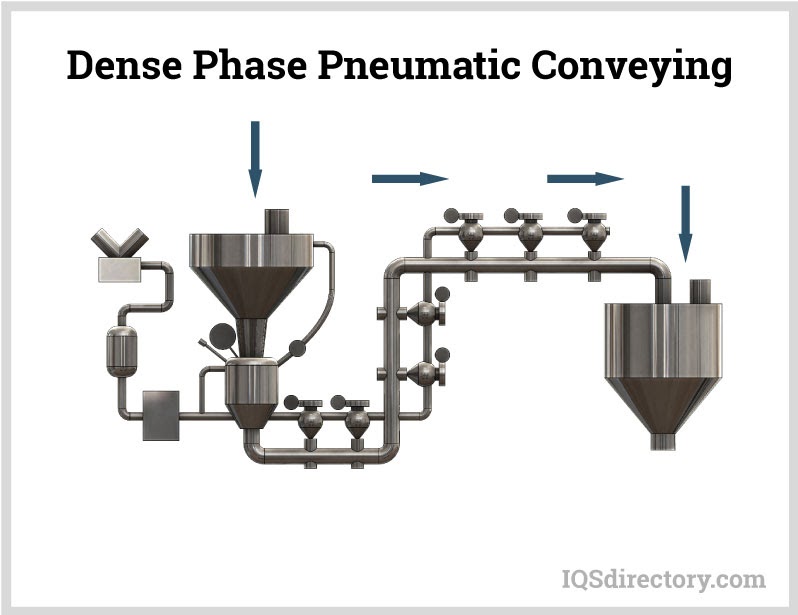
Pneumatic conveying is a method for transferring bulk materials, like powders and granules, using compressed gas or air, from one processing center to another. Material is moved through an enclosed conveying line or tube using a combination of pressure differential and airflow from a blower or fan...
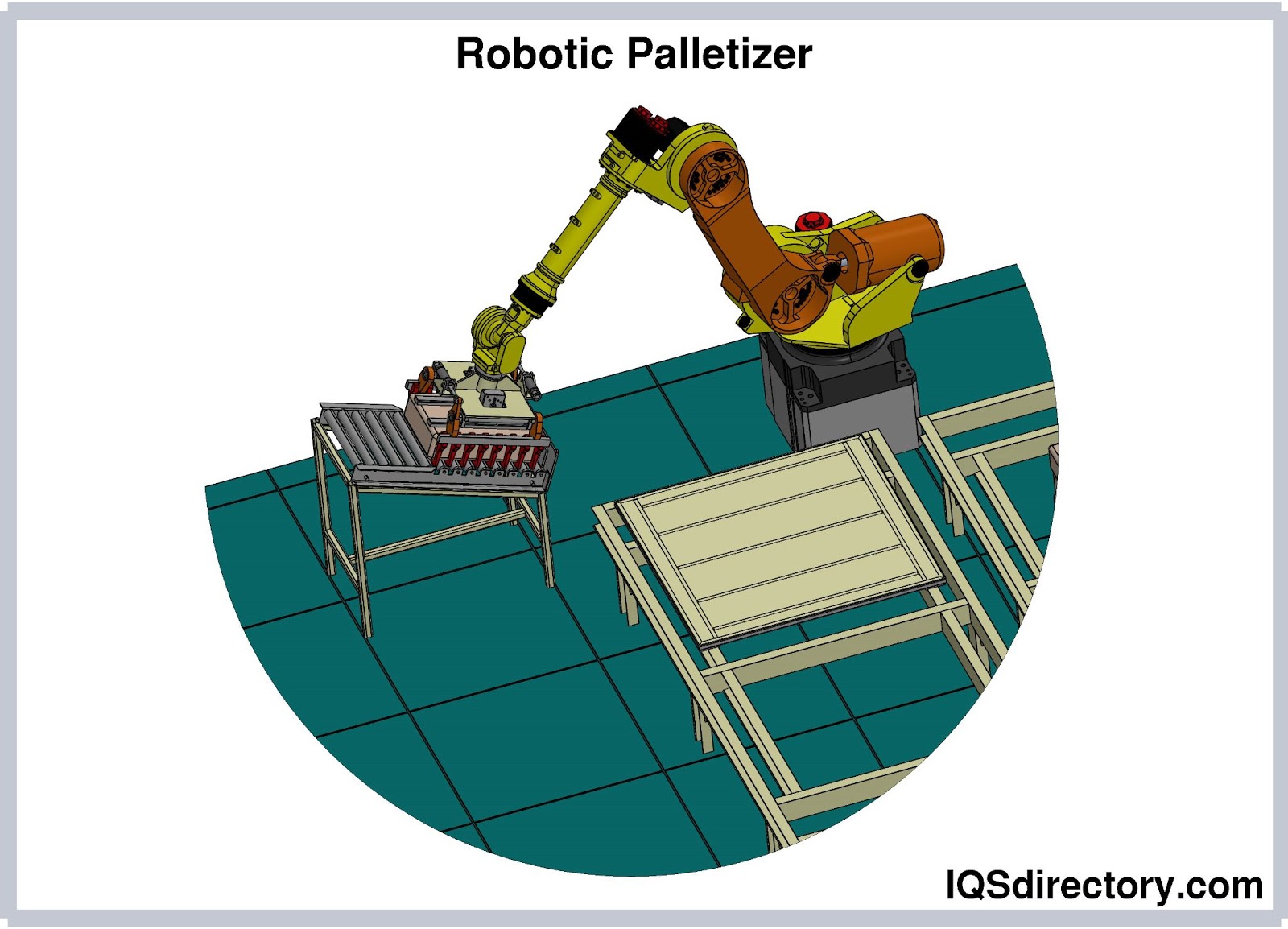
A robotic palletizer is a type of palletizer that employs a robotic arm to pick, orient, and place individual products and arrange them into a single stack of load. They are the next generation of palletizers, and they will supersede conventional palletizers...

Roller conveyors are a type of conveyor belt that allows objects to skate on its surface by using rollers, which are equally spaced revolving cylinders. They transport stuff from one location to another...

Screw conveyors, or auger conveyors, are industrial equipment used in transporting bulk quantities of granular solids (e.g., powder, grains, granules), semi-solids, liquids, and even non-flowing materials from one point to another...
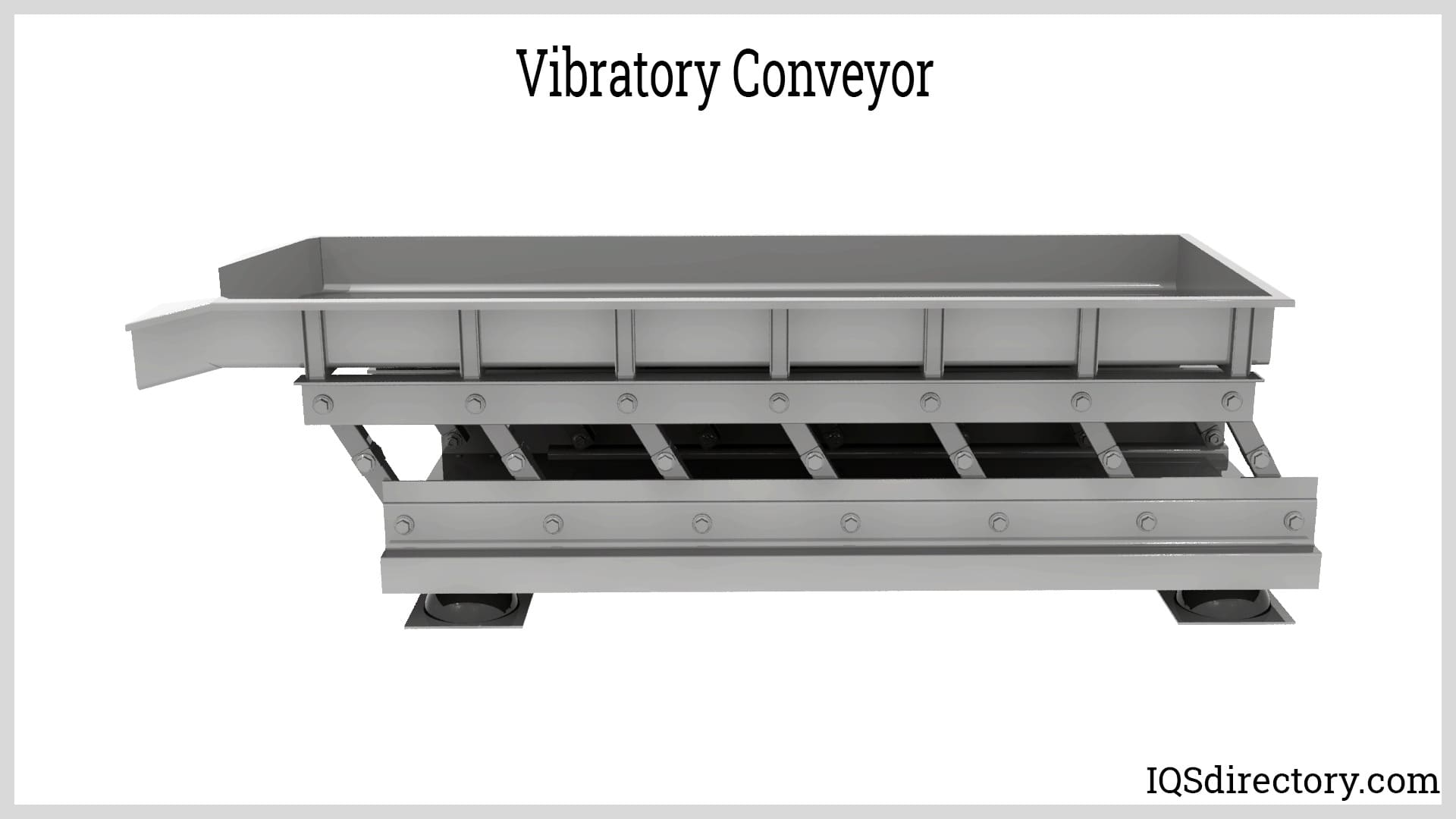

Vibratory conveyors are material-handling equipment used to transport fine to coarse-grained bulk materials. These vibratory conveyors are strong conveying equipment utilized for bulk commodities with fine to coarse graininess...
A vertical conveyor is an engineered mechanical method for moving goods, products, supplies, parts, and components from a lower level to a higher level or from a higher level to a lower level. They are...
Vibratory feeders are short conveyors used to transport bulk materials utilizing a controlled vibratory force system and gravity. The vibrations impart a combination of horizontal and vertical acceleration through tossing, hopping, or sliding-type of action to the materials being handled...
In 1954, when Arthur "Mac" Barrett, of Barrett Electronics Corporation, unveiled the first AGV, he named it Guide-o-Matic and described it as a driverless vehicle...