Automatic Screwdrivers

An automatic screwdriver is a piece of equipment that automatically inserts screws into a product during assembly and production. Since every production operation is unique and requires a...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on Robotic System Integrator .
This article contains everything you need to know about robotic system integration and its use.
You will learn
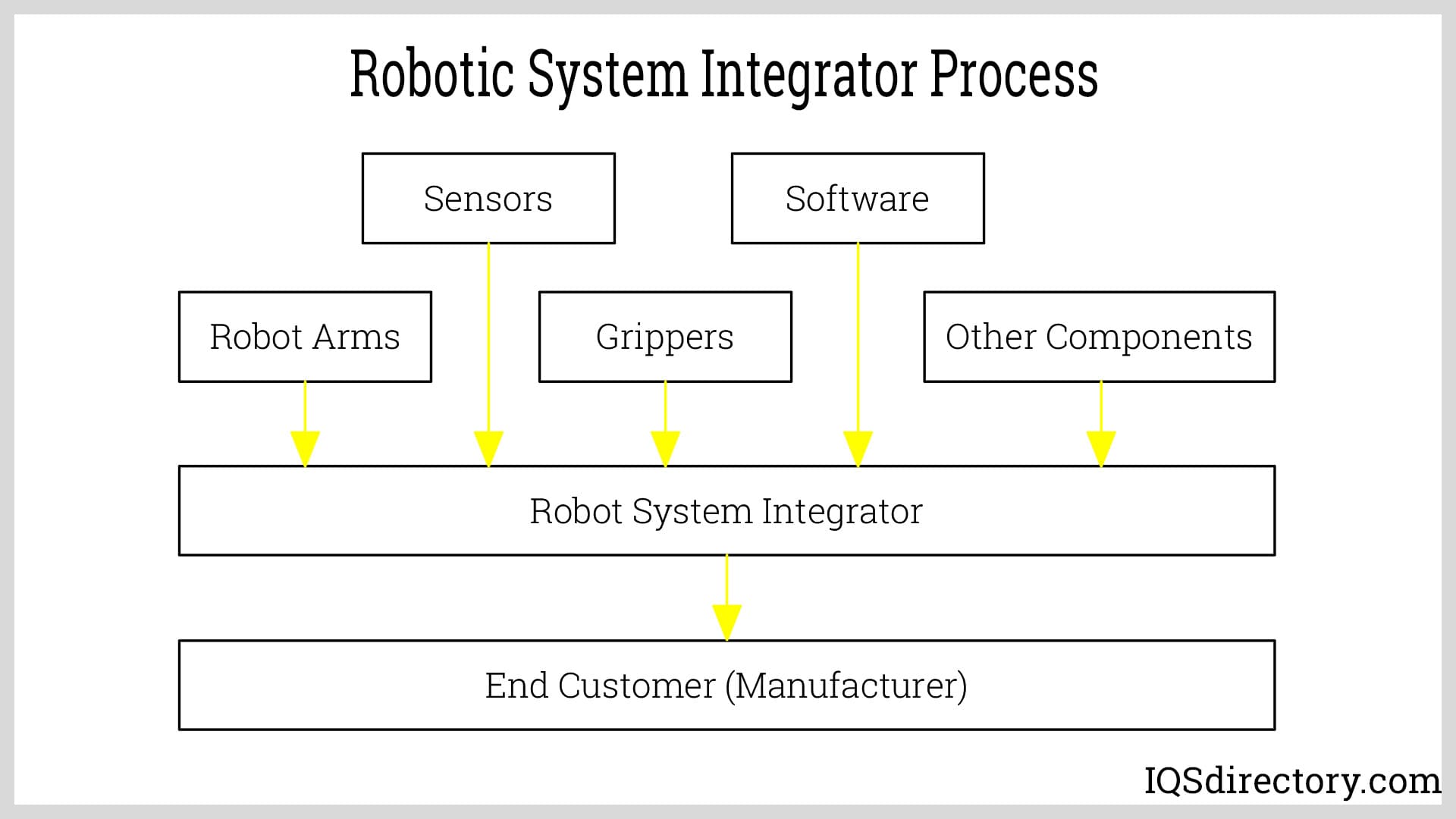
Robotic system integrators are experts dedicated to helping businesses automate a variety of functions. They craft robotic solutions customized to fit the unique requirements of an operation, providing comprehensive strategies for incorporating robotics into industrial workflows. Although robot manufacturers create a vast array of robotic technologies for many purposes, these are typically intended for generalized utilization.
Manufacturers of robots rely on robotic system integrators for their proficiency in assisting end users with selecting the optimal robotic solution tailored to specific environments. These integrators play an essential role in deploying, distributing, and innovating automated robotic systems.
Not every robot integrator can offer a solution to every challenge, as each focuses on a different subset of solutions. The right integrator is chosen based on the process that requires integration and the alignment of their expertise with the specific application. Their success history in handling similar applications is also a key factor in their selection.
Robotic system integrators focus on different sectors such as material handling, warehouse automation, supply chain, and manufacturing, as well as production and assembly tasks. Customers choose an integrator according to the integrator’s area of expertise.
A robotic system integrator acts as a partner, collaborating with clients to develop optimal solutions for their production challenges. The key distinguishing characteristic of a robotic system integrator is their extensive knowledge and understanding of robotic solutions. After thoroughly examining and evaluating a client's processes, a trained integrator will outline various approaches to implementing robotic solutions.
Among the many factors in selecting a robotic system integrator, experience is the most vital. This experience goes beyond knowledge of robotic systems and their operation; it also includes familiarity with the specific industries they have served. For instance, a robotic system integrator specializing in material handling would be unqualified to develop a solution for an assembly operation, just as an expert in welding robotics would be unsuitable for inventory applications.
In the initial steps of searching for a robotic system integrator, clients must recognize the various types of specialists and choose one with expertise in their specific industry and processes.
A robotic system integrator with experience in a specific industrial or supply chain function must be knowledgeable about the best available solutions. Often, clients are unaware of the intricacies and complexities of robotic capabilities. They rely on their integrator to deliver the highest quality solutions that perfectly match their operations.
One of the challenges of being a robotic system integrator is developing a customized plan for each client, as no single solution fits all applications. Robot manufacturers produce thousands of different systems designed for various industrial operations, each of the highest quality and performance. The integrator's role is to understand the myriad of available solutions and select the right combination to meet the client's specific needs.
Once the selection process is completed, the robotic system integrator outlines a plan of how to implement and deploy the robots in the client’s environment. Each step of the plan clearly details the various robots and how they will interact without interfering with each other’s functions.
The plan is a crucial key to the success of a robotic implementation. The client must clearly understand how each element works together to improve efficiency, maximize uptime, enhance productivity, and reduce costs compared to their current operation.
A major component of the plan involves addressing the financial, technical, regulatory, and safety factors, which are the client's responsibilities, with the financial aspects clearly outlined. Clients will compare these cost factors to their current operations. The robotic system integrator may need to highlight that, although the initial cost may appear high, significant savings will be realized when amortized over several years.
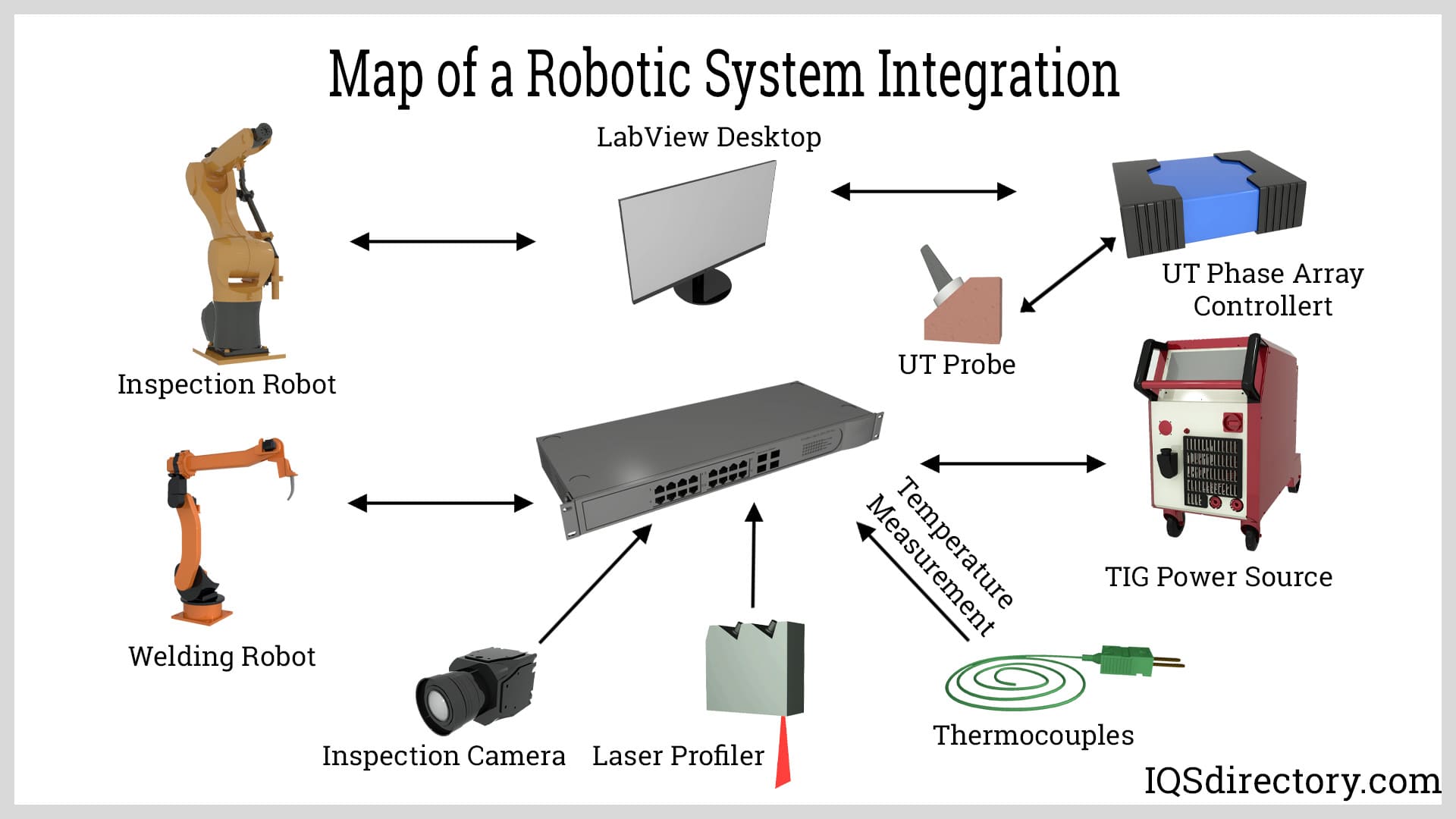
While all plans may appear perfect on paper, they often require adjustments during implementation. An experienced robotic system integrator is well aware of the challenges and issues that can arise and is prepared to address them. Each element of the integration must be tested, refined, and adjusted to ensure that the various components work together seamlessly to achieve a positive and productive outcome. During this phase, integrators must pay close attention to even the smallest details to optimize performance and ensure success.
Robotic system integration demands constant and ongoing support, which can be a crucial factor for clients, especially those unfamiliar with the technical aspects of robotics. It's highly unlikely to find a robotic system integrator that does not offer continuous support. Providing this support not only exemplifies excellent customer service but also allows the integrator to showcase their skills and expertise to potential clients.
In 2012, the Robotics Industries Association (RIA) established a certification process for robot integrator programs, setting a benchmark for assessing the technical expertise and business practices of robotic system integrators. An RIA certification signifies that a robotic system integrator has attained the highest levels of proficiency, experience, and success in their field.
The certification process goes beyond merely applying for a certificate. It includes on-site audits, evaluations of system integrator personnel, assessments of safety training, and a range of other criteria, all of which must meet the highest standards. Companies that achieve certification have demonstrated the capabilities, skills, and expertise needed to provide the highest quality service.
The types of robotic system integrators are as diverse as industrial operations themselves. They encompass a wide range of functions, applications, processes, and operations, with each specializing in a specific form of robotics. Whether installing, implementing, or updating robotic systems, a robotic system integrator is essential for ensuring a successful integration process.
As technology demands continue to grow and evolve, robotic systems are increasingly becoming a necessity. With rapid advancements in technology, it is crucial to hire an expert who is knowledgeable in the field and can deliver the most effective solutions
Warehousing has long utilized a variety of robotic solutions to streamline sorting, storing, picking, and packing orders. The surge in robotic solutions has been driven by the rise of e-commerce and online retailing, which demands timely and efficient deliveries.
One of the basic concerns in manufacturing is keeping workers on task and at their workstations. Collaborative robots work with employees to finish processes and assist in redundant or repetitive tasks such that workers can concentrate on more complex and mental work.
Over the last thirty or forty years, assembly operations have been slowly integrating robotics into the process to avoid human errors, reduce assembly times, and provide detailed inspection of final products.
There is a vast array of robots available for integration into production, manufacturing, material handling, hospitals, and other industries. Clients need only to inquire, and a robotic system integrator will provide a suitable robotic solution. With a robot for nearly every type of operation and process, an experienced robotic system integrator knows exactly where to find the right one for the job.

Although robotic functions and automated functions are two separate entities, they are processes that integrate for the improvement of production and efficiency. The focus of robotics is the design, construct, and programming of robots to complete different types of activities. They can be mobile or static and are capable of being adjusted and reprogrammed to meet the needs of an application.
While robots are oriented toward performing a single task or a set of tasks, automation operates on a grander scale and involves a wide range of technologies that include computer systems, software, building control systems, and is involved in the overall functions of a production system. Robots can be integrated into the automation process and may become a critical aspect.
Robots are tools that are designed to perform certain tasks. They are very much like the other pieces of machinery that stamp, bend, wire, and form various aspects of a product. In essence, they are highly developed and technologically advanced pieces of equipment that save on labor costs, work very efficiently, and are able to operate continuously.
By comparison, automation integration oversees every part of a production facility and coordinates the different activities to ensure the efficient completion of applications, processes, and product movement. In an organization that has several robots performing various tasks, automation integration ensures that all of the robots perform their functions without interfering with other processes and applications.
The processes of robotics and automation have become essential parts of advancing the modernization of industry. Their use in combination increases the precision, safety, and efficiency of manufacturing. Their interaction has led to innovations and improvements in industrial applications. The integration of AI with robotics and automation systems is rapidly improving the intelligence and adaptability of equipment to further increase and improve production.
Automation integration involves programming the tasks of robots into the control system of a manufacturer. It is a method that allows for control of all equipment in a facility from one location. The input actions are downloaded to the robot controller. This aspect of the process can be used for programming the actions of a single robot or a group of robots. The use of automation integration makes it possible to change the activities of robots and repurpose them.
Many years ago, when a factory was going through a changeover, operations would shut down for weeks or months depending on how much change was necessary. This practice was common in the auto industry, which went through model changes every year. Automation integration has eliminated the need for such stoppages and made it possible to easily alter and adjust production parameters.
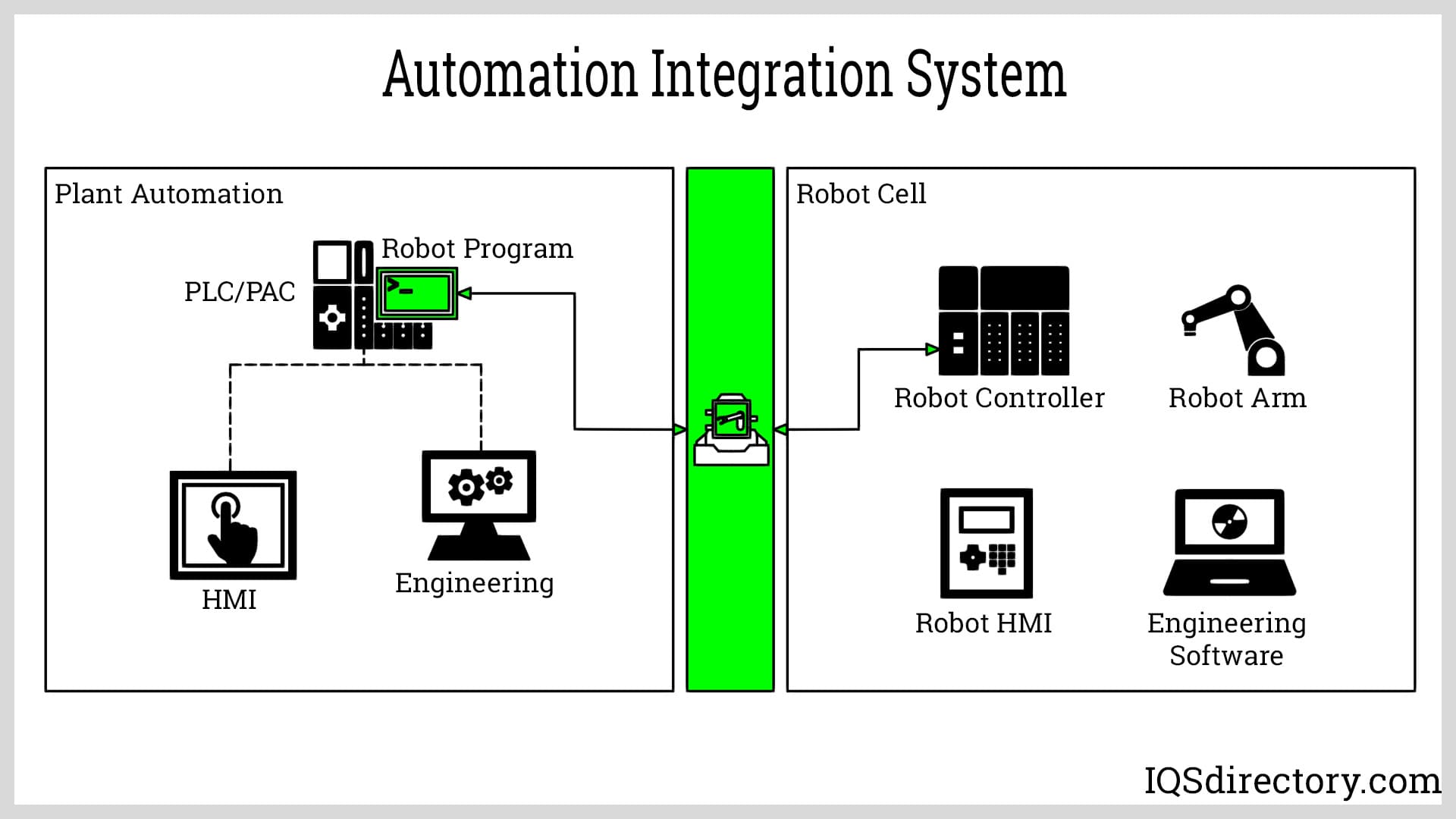
Although automation integration has become an excellent solution, in its initial stages, there were problems due to the inability to uniformly control all types of robots
since each robot manufacturer had their own unique software and programming. When robot manufacturers realized the division between control systems and programming made it difficult to use automation integration, the primary robot manufacturers, ABB, Comau, Epson, Fanuc, Jaka, Kawasaki, Kuka, Nachi, Panasonic, Stäubli, TM Robot, Yamaha, and Yaskawa, worked together to develop a shared solution to make the use of an automation integration system a reality.
The joint work led to the development of a uniform data interface between the PLC and the robot controllers to make robot programming more efficient. Robot programs are written using a PLC with the necessary functions and reporting data. Once the commands are received by a robot, they are converted into the proprietary language of an organization.
Automation integration is a major step in the progress of modern manufacturing. Its use has radically improved efficiency and productivity. The next steps in the process involve the use of AI to enhance the thinking and capabilities of the automation integration process to increase the abilities of robots to function more independently.

An automatic screwdriver is a piece of equipment that automatically inserts screws into a product during assembly and production. Since every production operation is unique and requires a...
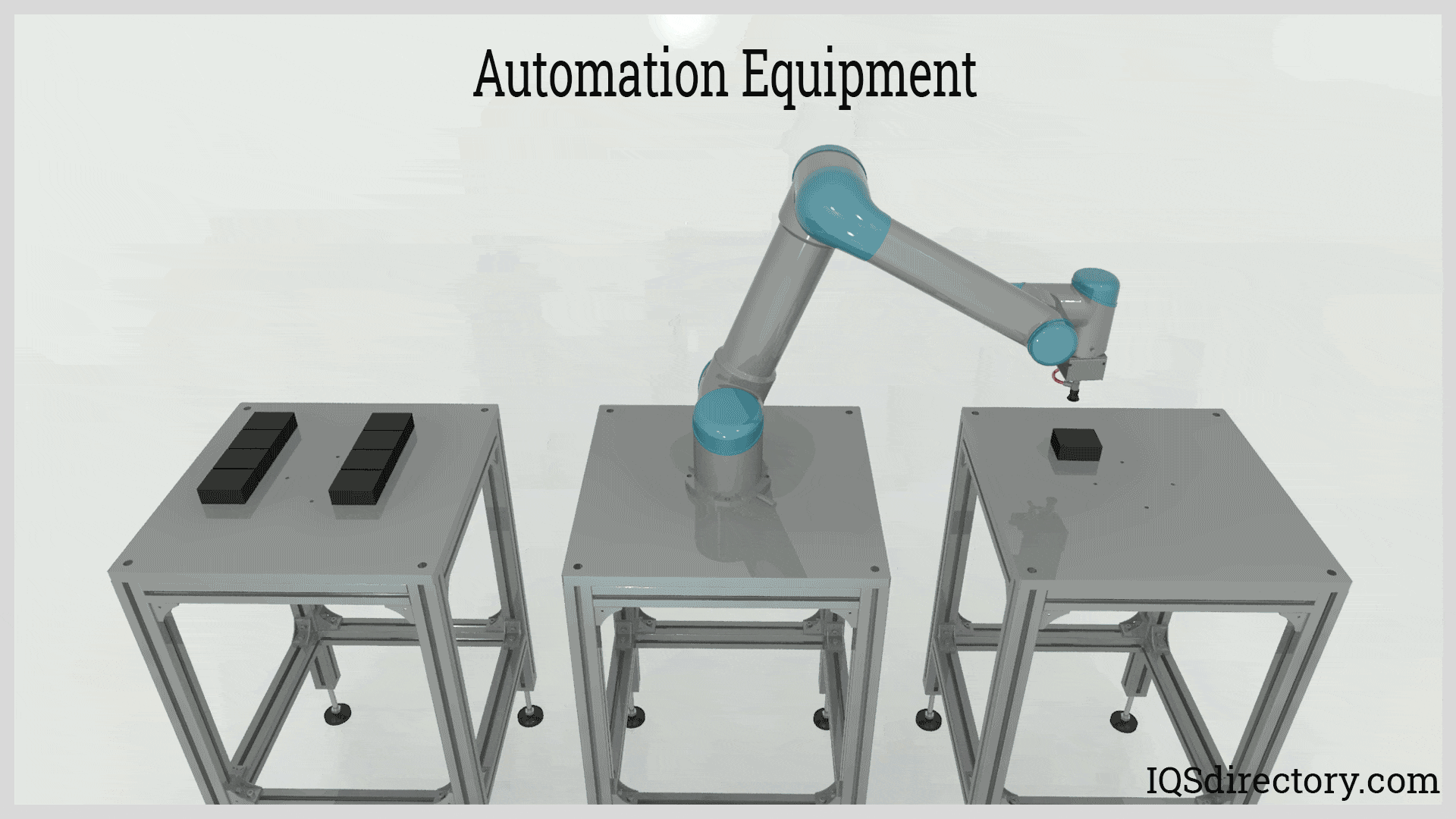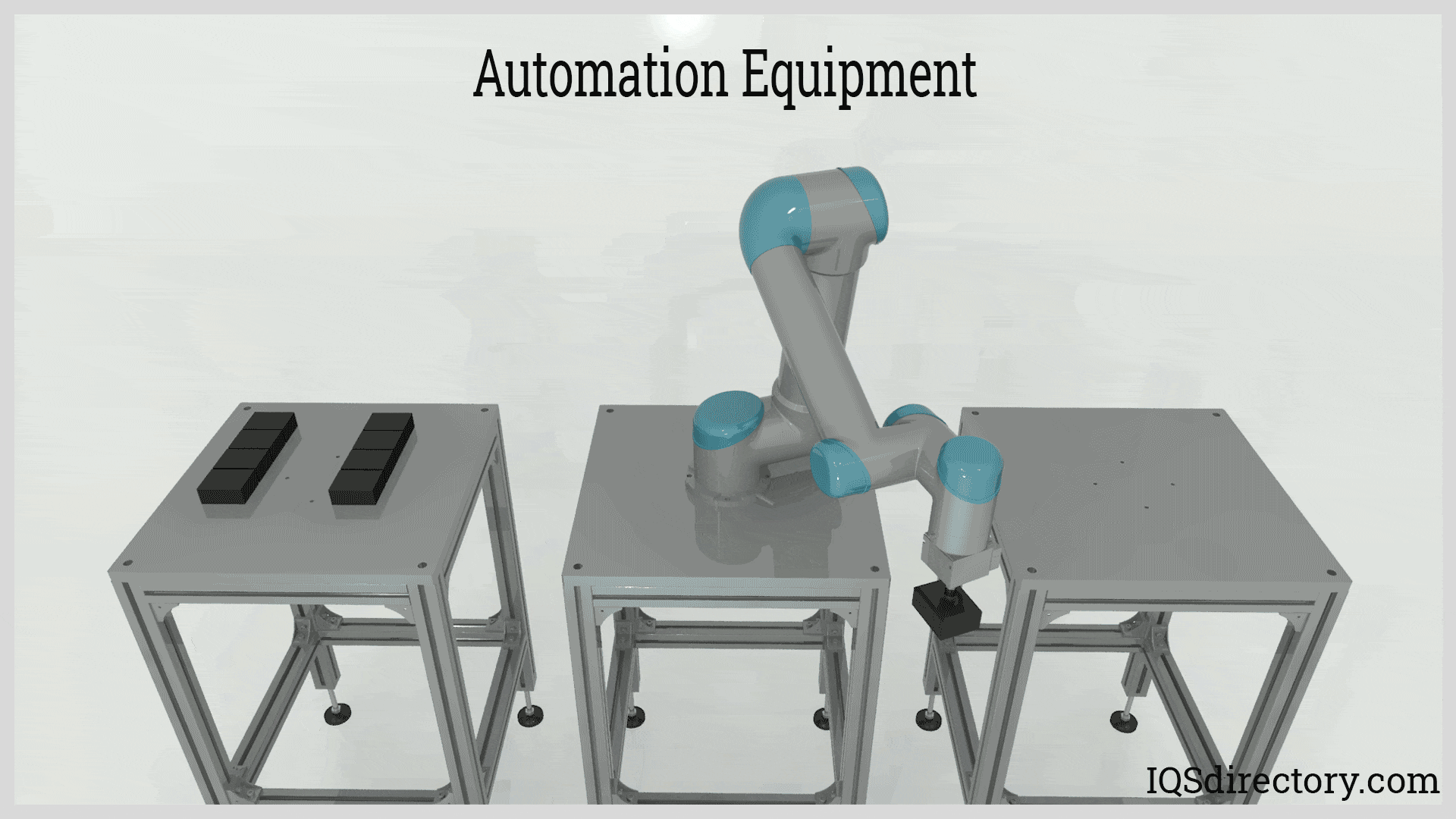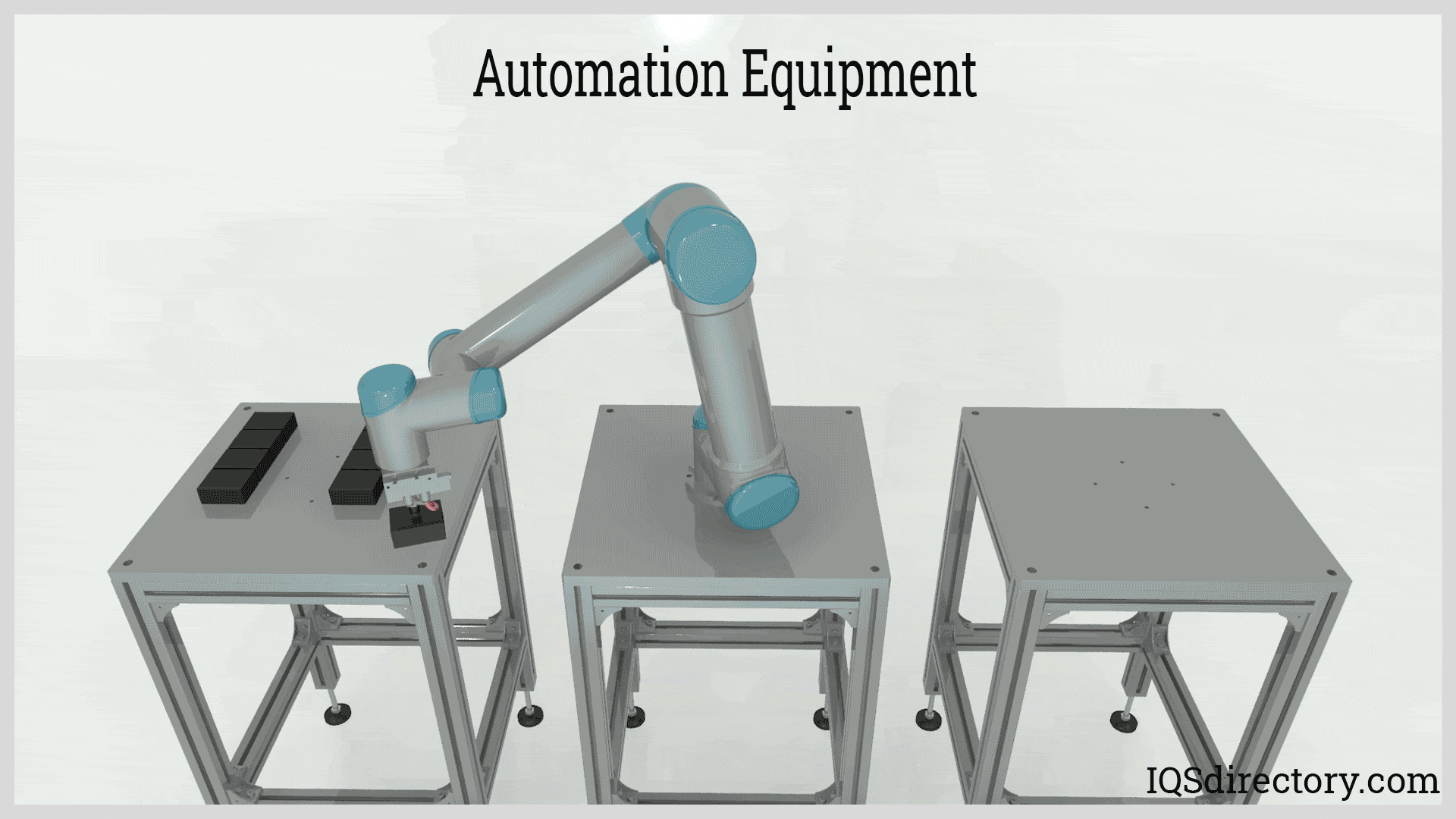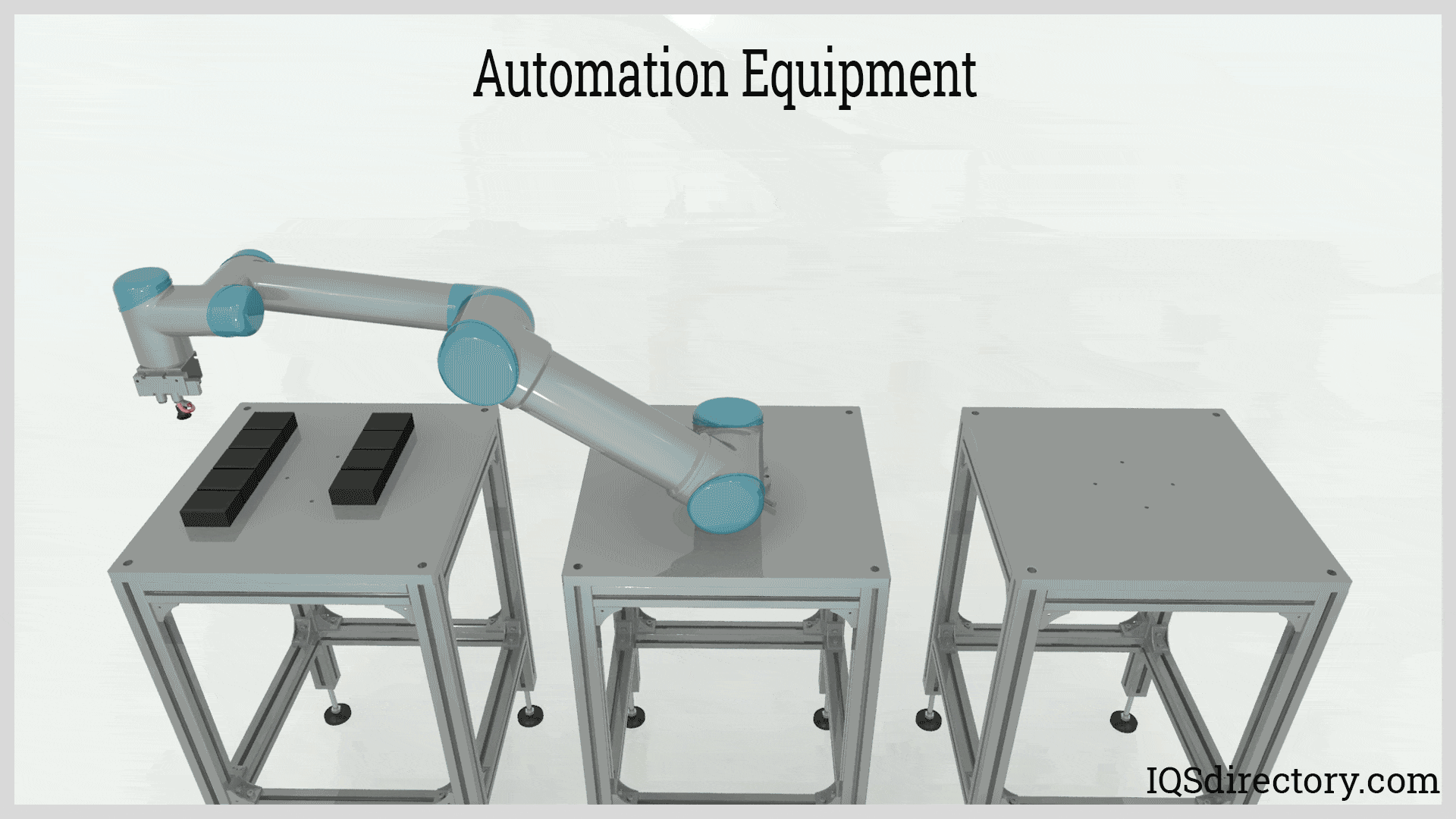
An automation system is an integration of sensors, controls, and actuators designed to perform a function with minimal or no human intervention. The field concerned in this subject is called Mechatronics which is an...

Collaborative robots, also abbreviated as Cobots, are the newest technology in robotics. They have changed the automation world significantly. These robots can work safely together with workers, hence are...

An industrial robot is an autonomous system of sensors, controllers, and actuators that executes specific functions and operations in a manufacturing or processing line. They operate continuously through repetitive...

Warehouse automation is the process of replacing repetitive tasks with systems that are automated. The main goal is to remove labor-intensive duties that consume time. As a result, the workers can focus more on...

An AGV forklift is a driverless self-operating robotic device that has the ability to carry, lift, retrieve, and place loads for easy transfer from one location to another. An automatic guided vehicle (AGV) forklift is a computer controlled mechanism that...
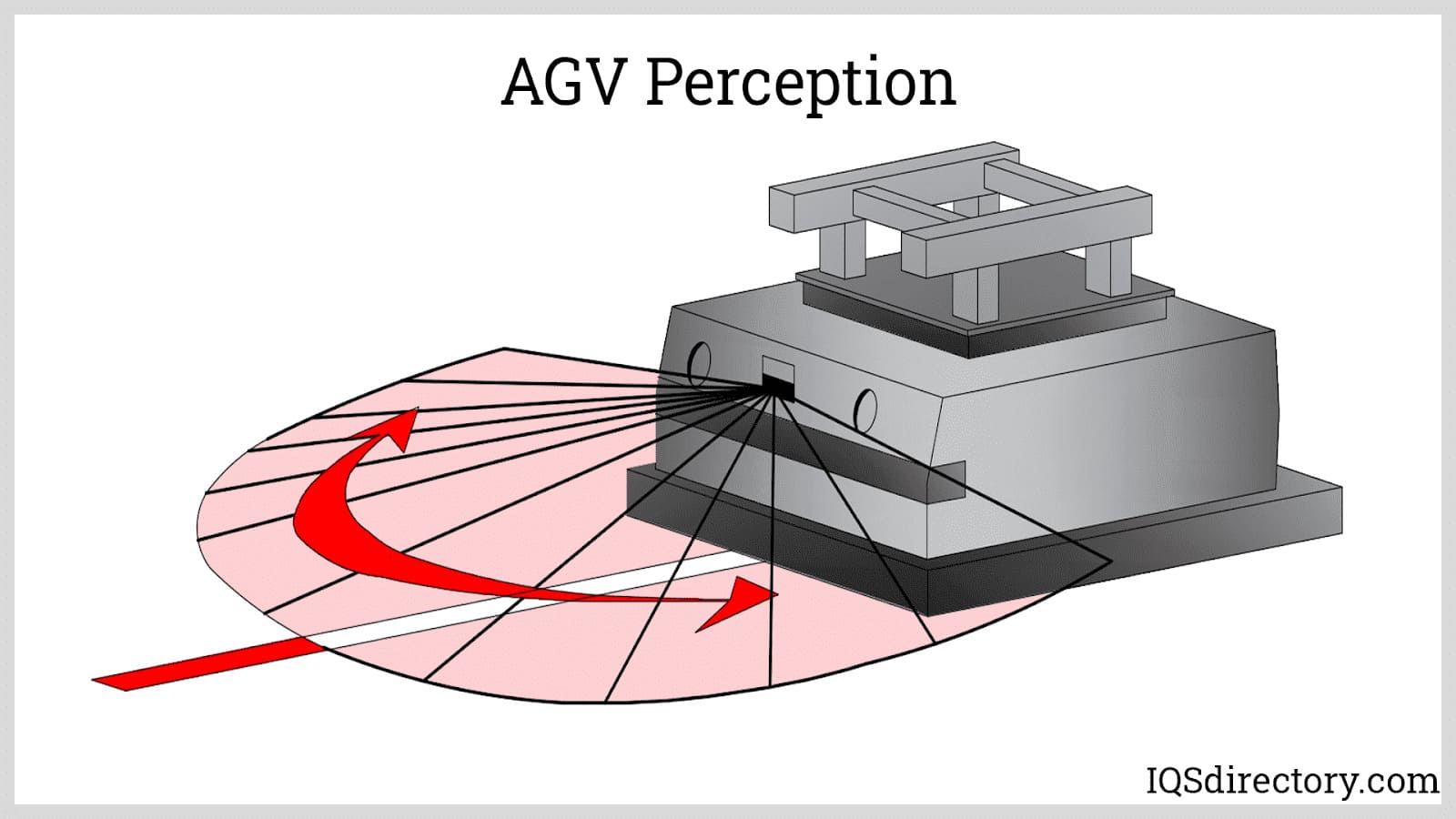
Automated guided vehicles (AGV) or mobile robots are types of guided robotic systems that are not bounded by a fixed range of motion. Rather, it is self-contained and can move along a line, surface, or space...

An autonomous mobile robot (AMR) is a self-propelled self-powered mechanism designed to perform repetitive tasks or organizational functions using an internal guidance system. They are able to navigate their...

A belt conveyor is a system designed to transport or move physical items like materials, goods, even people from one point to another. Unlike other conveying means that employ chains, spirals, hydraulics, etc...
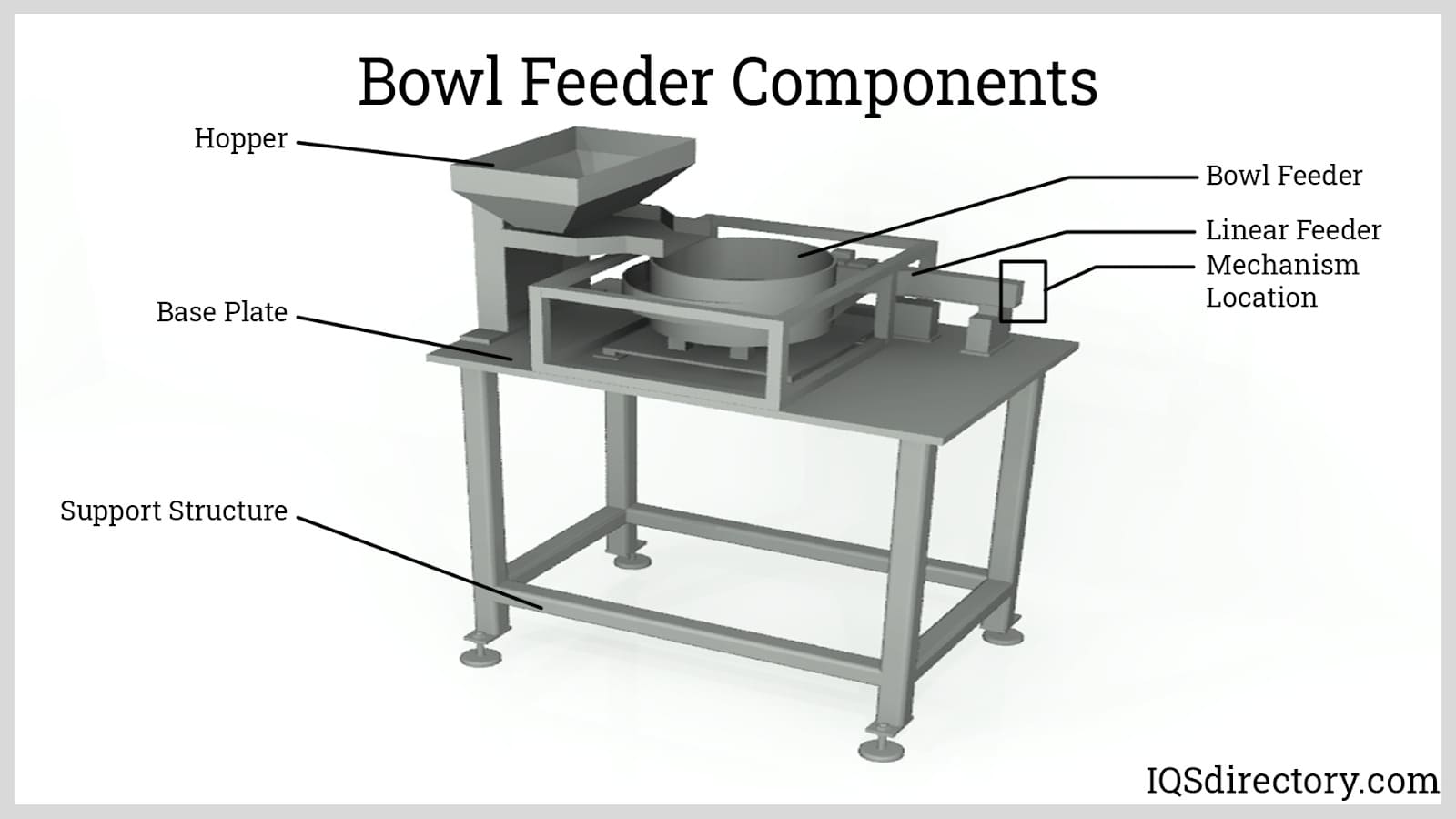

A bowl feeder is a mechanism for supplying small parts and components to a production line or for sorting bulk items for rapid use. A self contained bowl feeder system has a bowl that sets on a spring loaded base that moves vertically...
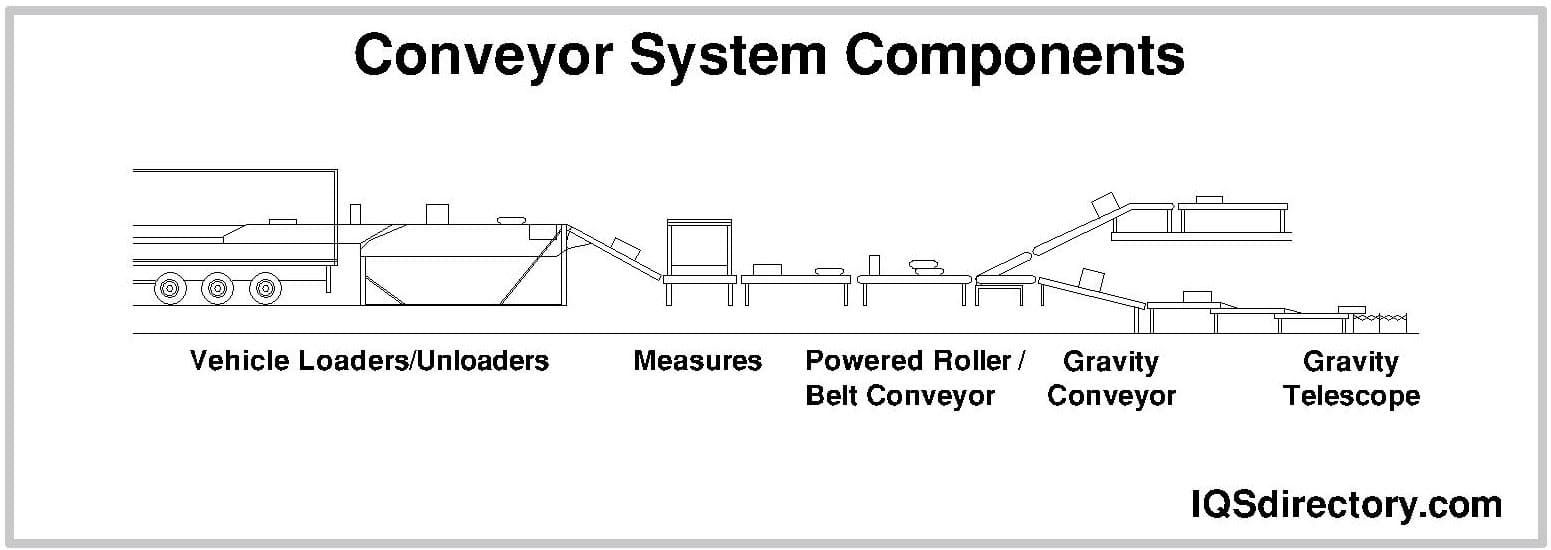
A conveyor system is a method for moving packages, products, supplies, parts, and equipment for production, shipping, or relocation. The different types of conveying systems include pneumatic, screw, belt, and roller. The construction of individual systems depends on the materials...
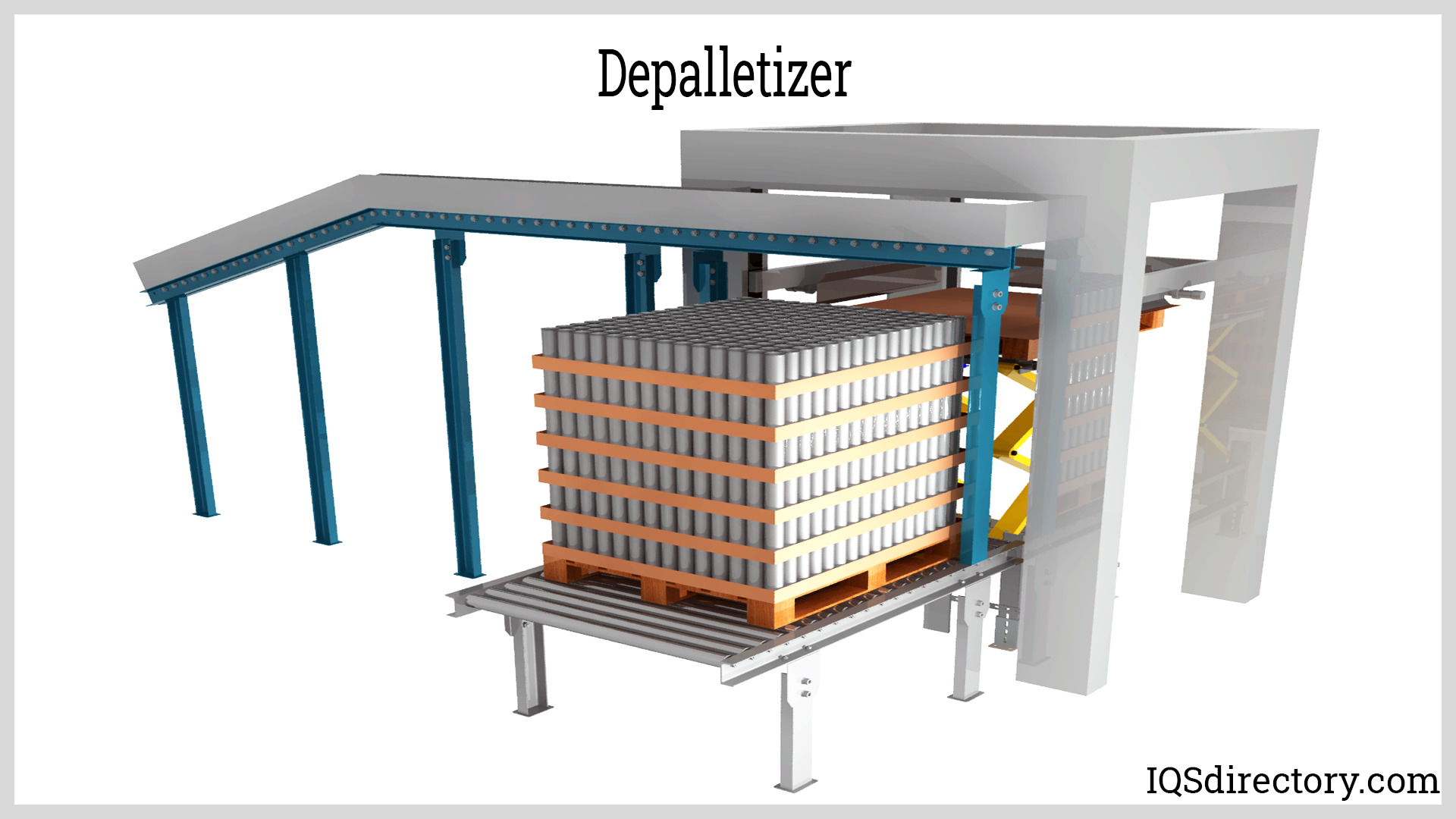
Palletizing is the process of putting items on a pallet. The process of emptying the loaded objects in the reverse pattern is known as depalletizing. A pallet is a flat, square-shaped platform used to transport and...
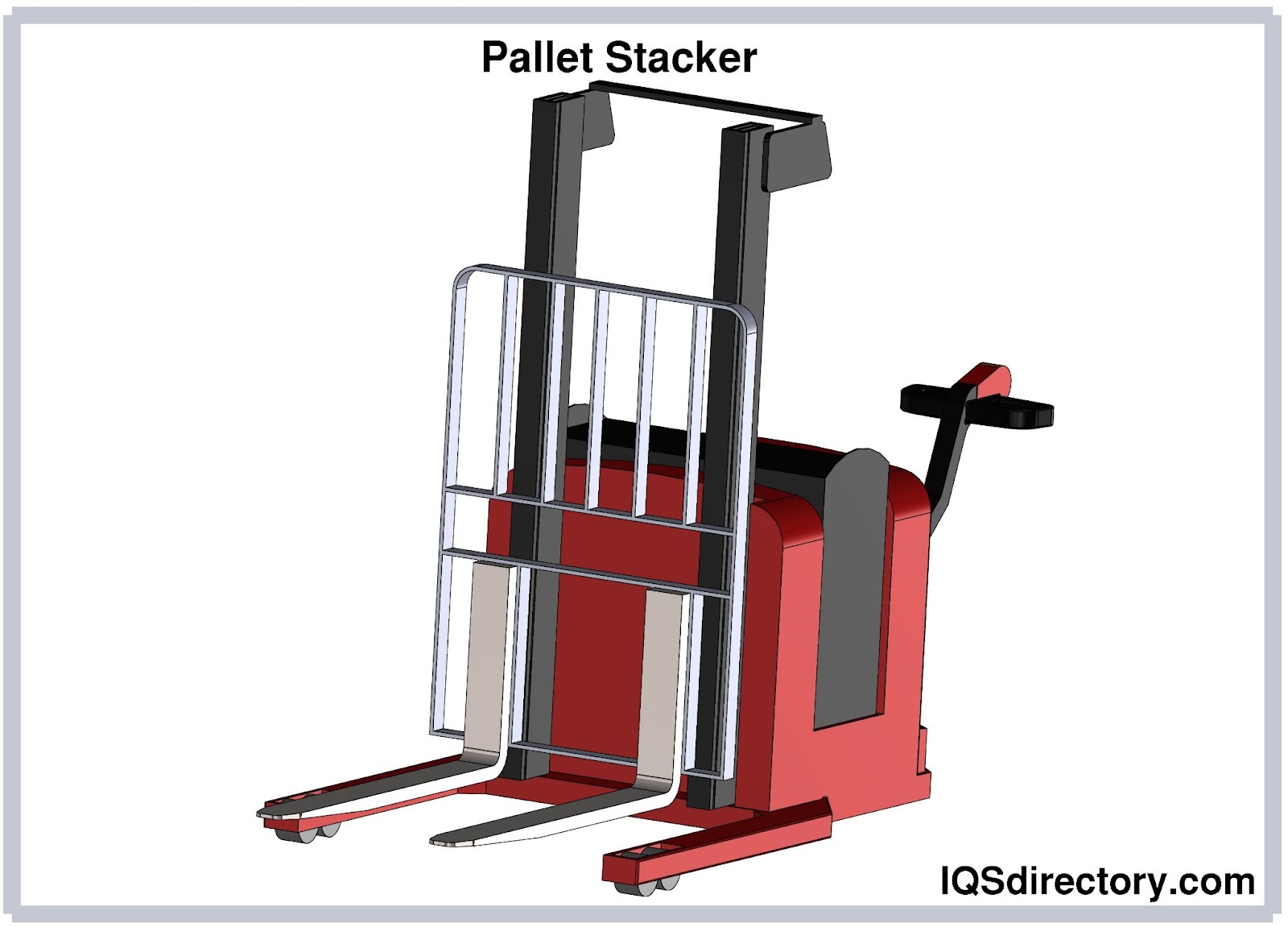
A pallet stacker is a machine designed to assist the user in lifting, moving and handling palletized materials with ease. A pallet itself is a flat and horizontal structure used to support goods in a sturdy fashion...
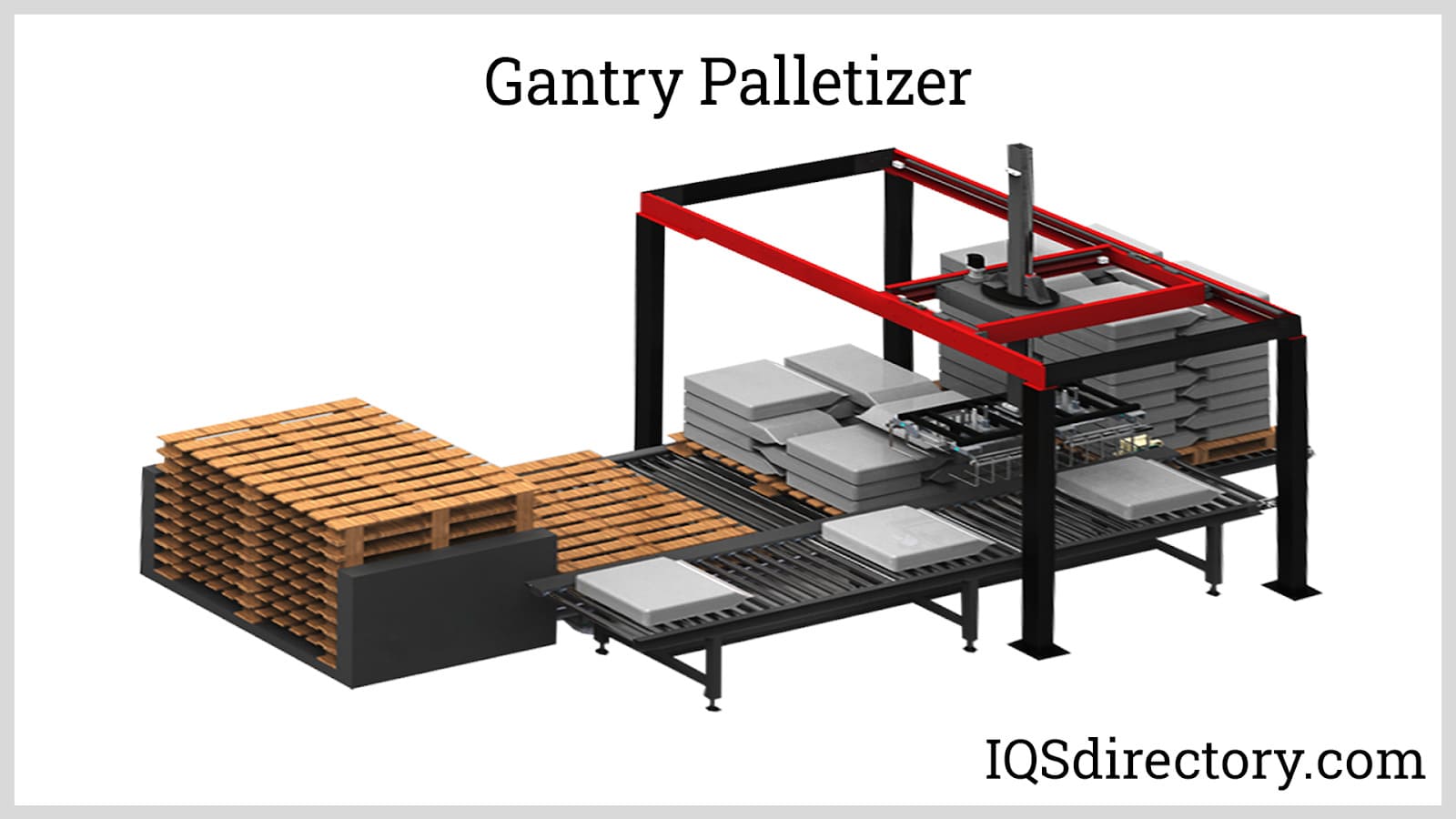
A palletizer is an automated material handling machine used to stack and orient several individual products into a single load for a more convenient and economical method of handling, storage, and shipment. Palletizers are usually part of a bigger packaging process...
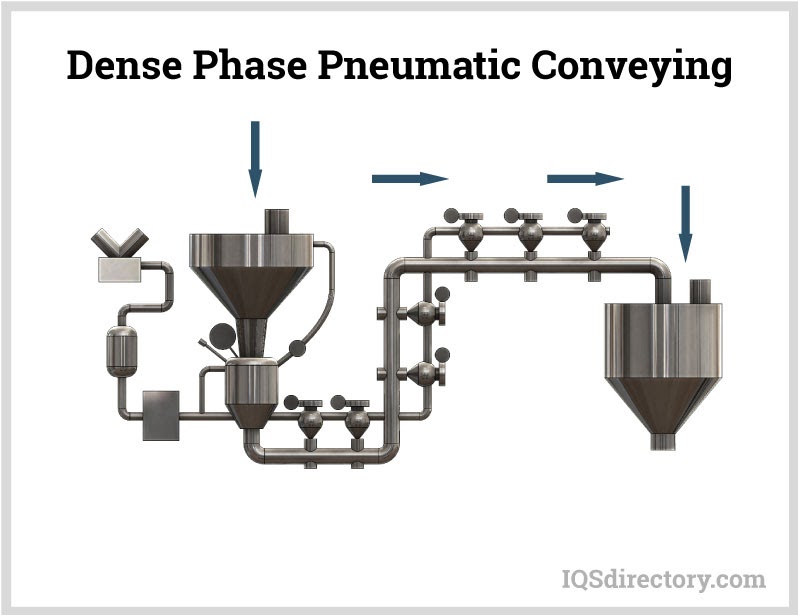
Pneumatic conveying is a method for transferring bulk materials, like powders and granules, using compressed gas or air, from one processing center to another. Material is moved through an enclosed conveying line or tube using a combination of pressure differential and airflow from a blower or fan...
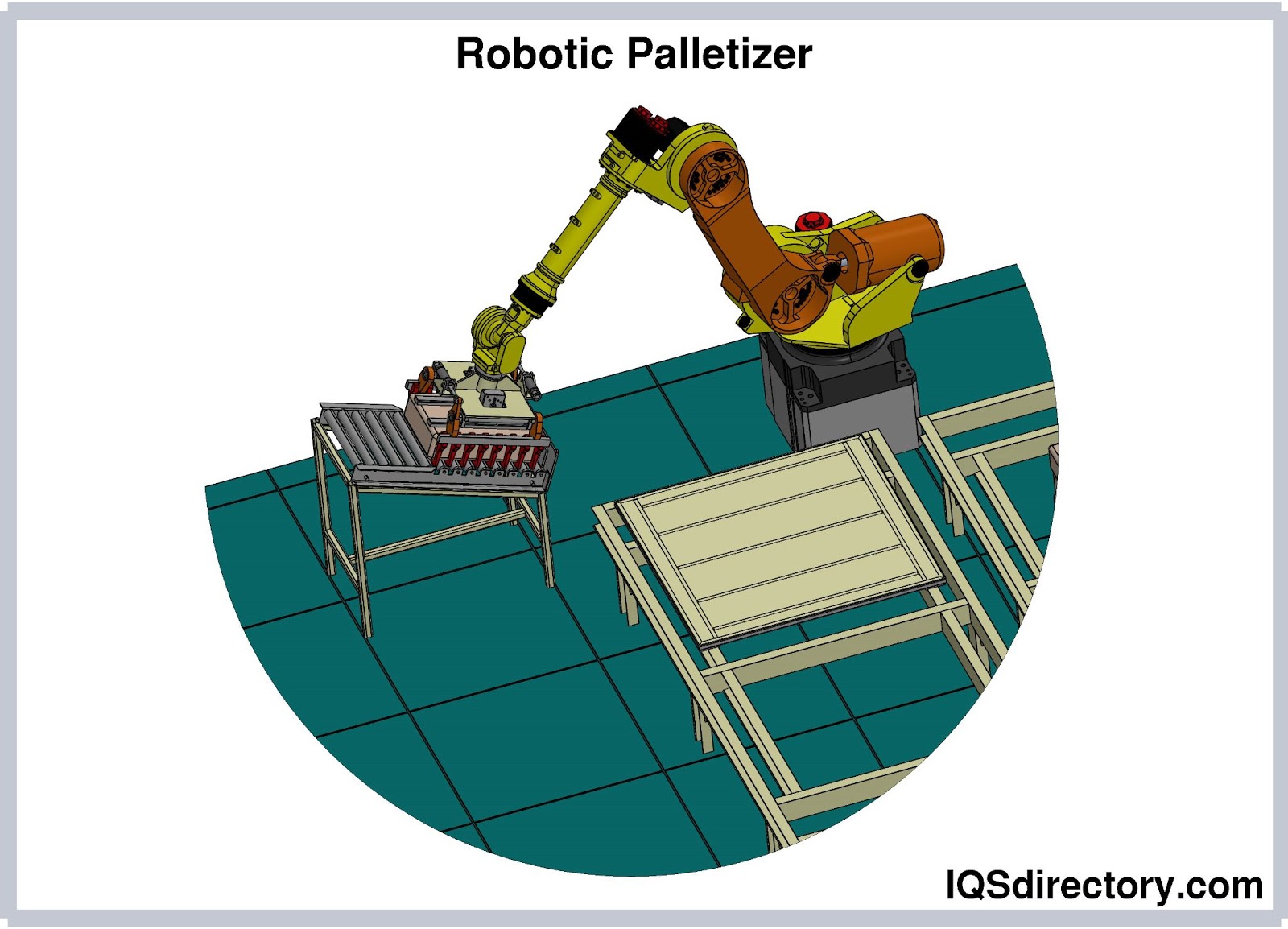
A robotic palletizer is a type of palletizer that employs a robotic arm to pick, orient, and place individual products and arrange them into a single stack of load. They are the next generation of palletizers, and they will supersede conventional palletizers...

Roller conveyors are a type of conveyor belt that allows objects to skate on its surface by using rollers, which are equally spaced revolving cylinders. They transport stuff from one location to another...

Screw conveyors, or auger conveyors, are industrial equipment used in transporting bulk quantities of granular solids (e.g., powder, grains, granules), semi-solids, liquids, and even non-flowing materials from one point to another...
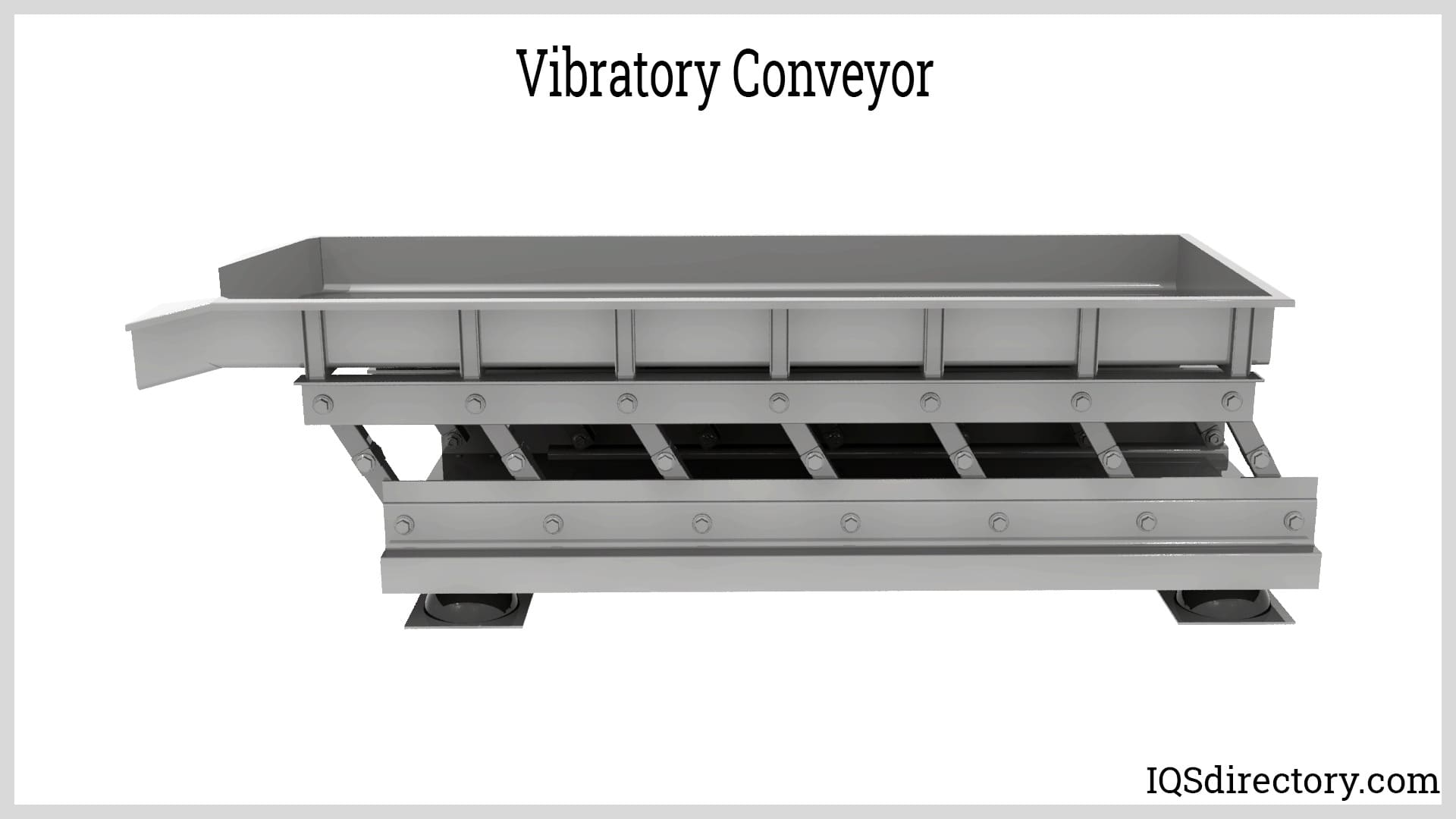

Vibratory conveyors are material-handling equipment used to transport fine to coarse-grained bulk materials. These vibratory conveyors are strong conveying equipment utilized for bulk commodities with fine to coarse graininess...
A vertical conveyor is an engineered mechanical method for moving goods, products, supplies, parts, and components from a lower level to a higher level or from a higher level to a lower level. They are...
Vibratory feeders are short conveyors used to transport bulk materials utilizing a controlled vibratory force system and gravity. The vibrations impart a combination of horizontal and vertical acceleration through tossing, hopping, or sliding-type of action to the materials being handled...
In 1954, when Arthur "Mac" Barrett, of Barrett Electronics Corporation, unveiled the first AGV, he named it Guide-o-Matic and described it as a driverless vehicle...