Hard Cases

A hard case is a type of carrying case that is made from molded plastic, aluminum, veneered or laminated wood, or different types of metals. They are the most secure and durable forms of carrying cases and...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article contains concise information regarding carrying cases and their use.
You will learn:

Carrying cases offer a convenient solution for organizing and transporting various items, regardless of their similarities or differences. They are invaluable for protecting and storing anything from mobile phones to audio systems and technical gadgets, ensuring delicate materials remain secure during transportation.
The design, configuration, and dimensions of carrying cases are specifically tailored to fit the items they are meant to hold. Depending on their intended use, carrying cases can be made from sturdy materials like reinforced fabric, plastic, aluminum, nylon, leather, wood, or a mix thereof.
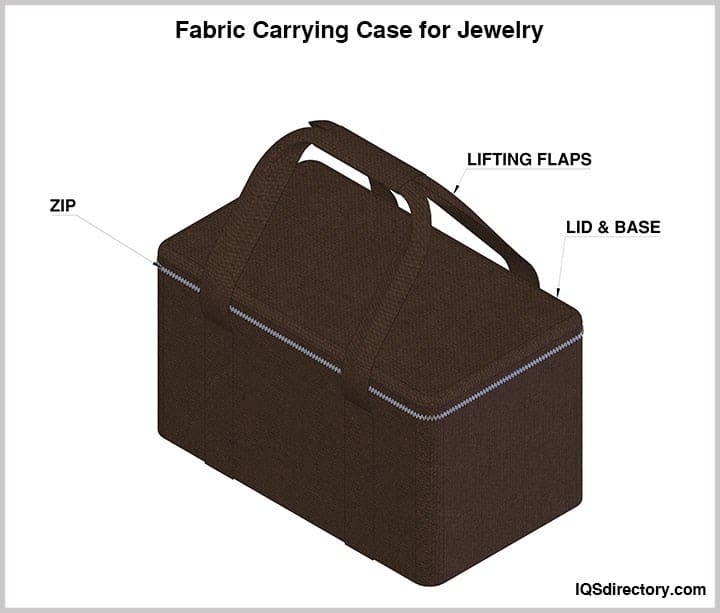
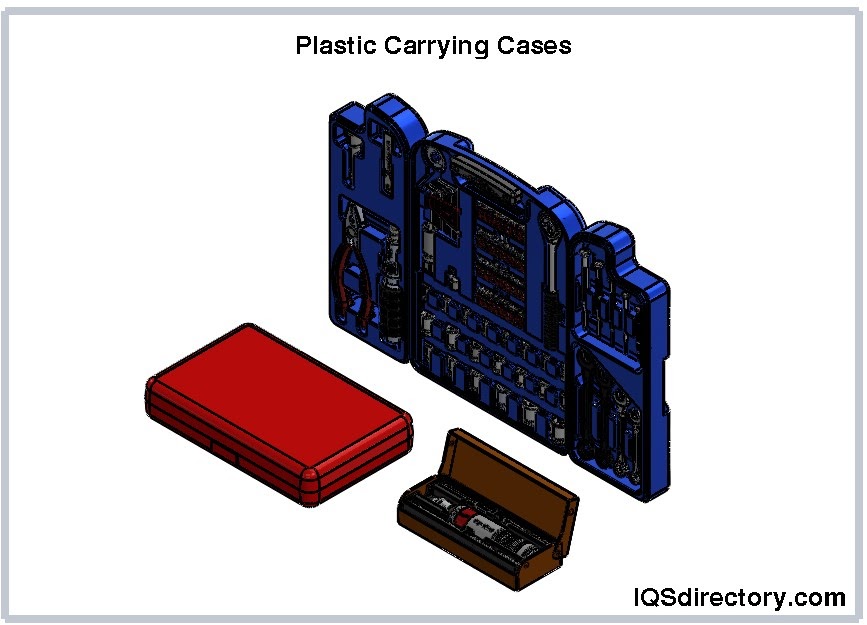
Some carrying cases are specifically designed for unique applications, illustrated in the accompanying image, and are produced to satisfy precise specifications.
Numerous carrying cases include foam inserts that are expertly molded to snugly secure tools, devices, components, and intricate instruments, keeping them firmly in place.
The design and manufacturing of a carrying case depend on its intended use. Standard off-the-shelf cases, available in department stores and online, differ significantly from custom cases designed for specialized applications, such as carrying scientific instruments and delicate equipment.
Carrying cases can be constructed from a range of materials, including aluminum, plastic, wood, sturdy fabrics, lightweight metals, and leather. The key requirements for any carrying case are durability, flexibility, and ease of portability. Some cases use a combination of materials to improve strength and longevity.
The construction of a carrying case is tailored to its intended use. For instance, cases designed for air travel must adhere to specific standards concerning materials, thickness, repairability, and latches. Many manufacturers design cases that exceed these basic requirements to ensure enhanced protection and durability.

Carrying cases are constructed from a variety of materials, including lightweight metals and heavy-duty fabrics such as nylon and neoprene rubber. Plastic cases are often created through blow or rotary molding and may feature cloth or foam padding liners.
Among the various materials used for carrying cases—such as wood, aluminum, fabric, and metals—plastic is the most prevalent due to its ease of formability, availability, and durability. Molded plastic carrying cases are the most common on the market, available in sizes ranging from small, hand-held cases to large, wheeled cases for shipping and transporting substantial equipment.
Plastic's versatility allows designers to shape, configure, and engineer cases to meet various conditions, applications, and aesthetic requirements. This adaptability makes plastic an ideal material for carrying cases that must be rugged and durable enough to withstand demanding environments.
The strength of a carrying case largely depends on the type of plastic used. Plastics, derived from petroleum, are processed into small pellets known as resin or into powder form. These materials are melted before being molded and shaped. The term "plastic" encompasses a range of materials with varying densities and molecular structures. For carrying cases, commonly used plastics include high-density polyethylene (HDPE), fiberglass-reinforced polyester (FRP), carbon fiber, rotationally molded polyethylene, and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE).
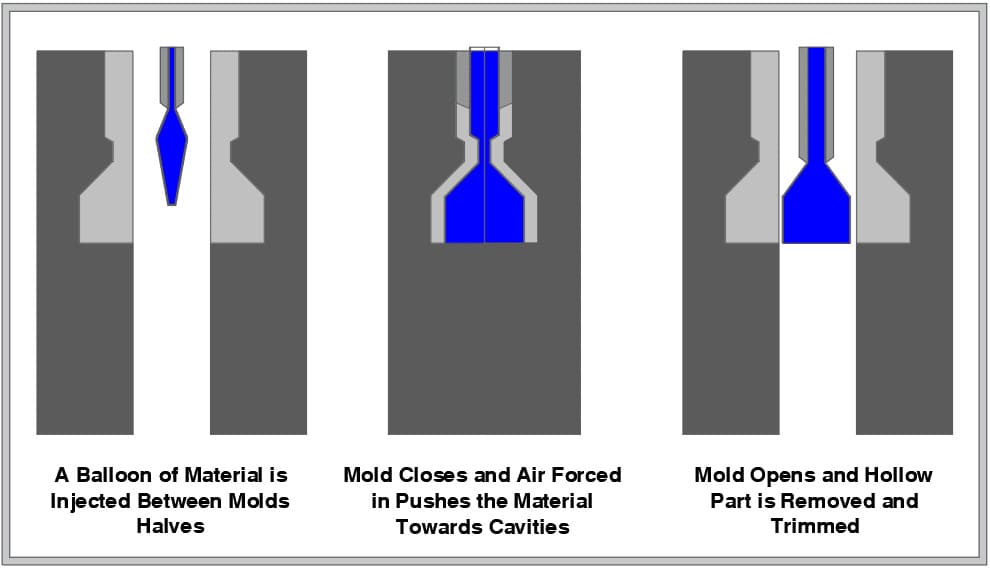
In the blow molding process for plastic cases, plastic is blown into a metal mold. The plastic is forced to evenly cover the surface of the mold as air fills the center of the molten plastic. The final case is uniformly shaped without seams or gaps. Plastic case manufacturers use thermoplastic for its durability, pliability, flexibility, and longevity.
The thermoforming process involves heating plastic sheets and using heat, vacuum, or pressure to shape them into three-dimensional objects. Plastic sheets are fed from rolls into a molding machine where they are heated until they become pliable, but not melted. Molds are then pressed against the heated plastic sheets to create the shape of the carrying cases. After molding, the cases are removed, trimmed, inspected, and prepared for further processing.
Thermoforming can be classified into three types: mechanical, vacuum, and pressure. In vacuum thermoforming, negative pressure pulls the preheated sheet into the mold cavity. Pressure thermoforming, on the other hand, uses positive pressure to push the plastic into the mold. Mechanical thermoforming involves the use of both positive and negative molds that are brought together over the preheated plastic sheet.
Molds used in injection molding are typically crafted from steel to ensure durability and precision for repeated use. In the injection molding process, material is fed into a barrel where it is heated and melted by a helical screw as it progresses along the barrel. The molten plastic is then injected into the mold, as depicted below. Two-shot molding allows for the use of different materials to combine colors and features in the final case. However, injection molding is generally limited to producing cases of certain sizes.

Rotational molding is utilized to create very large cases with precise tolerances. The process starts with a mold, typically several feet wide, long, and high. Raw plastic resin is placed into a closed mold that shapes the top and bottom of the case.
The mold is mounted on a frame that can rotate along multiple axes. This assembly is then heated in a chamber until the plastic resin melts. As the frame rotates, the melting resin evenly coats all sections of the mold, forming a consistent layer.
This technique allows for the production of various case designs, including those with double-entry, lift-off, and hinged lids. Most cases produced by rotational molding are custom or special orders. The entire process is illustrated in the image below.
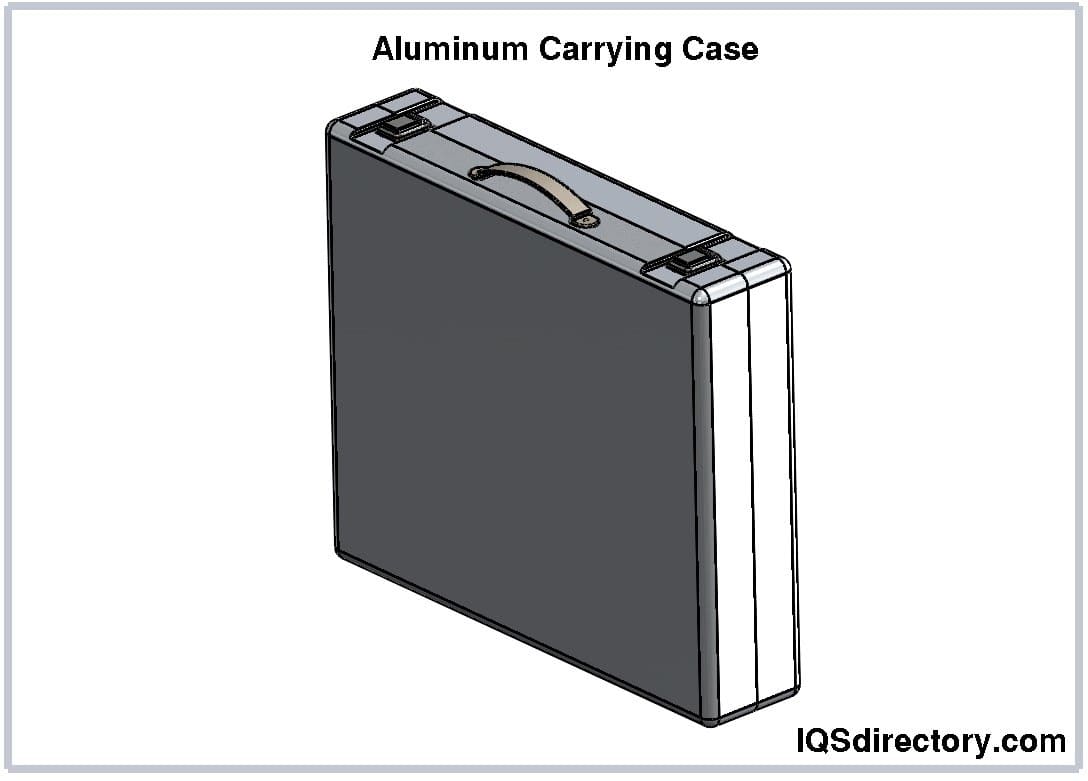
The manufacturing process for aluminum cases resembles thermoforming. It begins with flat aluminum sheets, which are either rolled or extruded to form the case's exterior. These textured aluminum sheets are then bent, shaped, and formed to create the top and bottom parts of the case. A frame is added around the edges of the top and bottom to ensure uniform proportions and a tight seal when the case is closed.
Handles, hinges, and corners are either riveted or welded to ensure strong, secure connections. For medium to large cases, wheels are often included to enhance portability and ease of handling. The primary goal of aluminum carrying cases is to ensure they can endure harsh and demanding conditions.
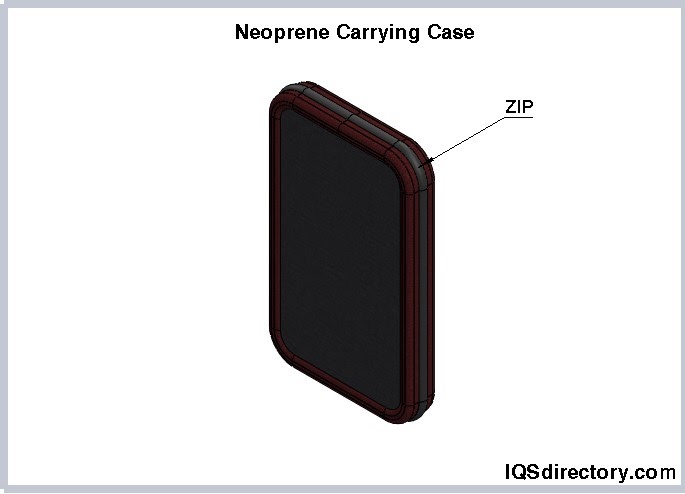
Neoprene, also known as polychloroprene rubber, is a highly durable, non-conductive, and waterproof material. Its thickness and flexible, cushioned surface make it an excellent choice for protection against punctures, weather conditions, and various types of wear and tear.
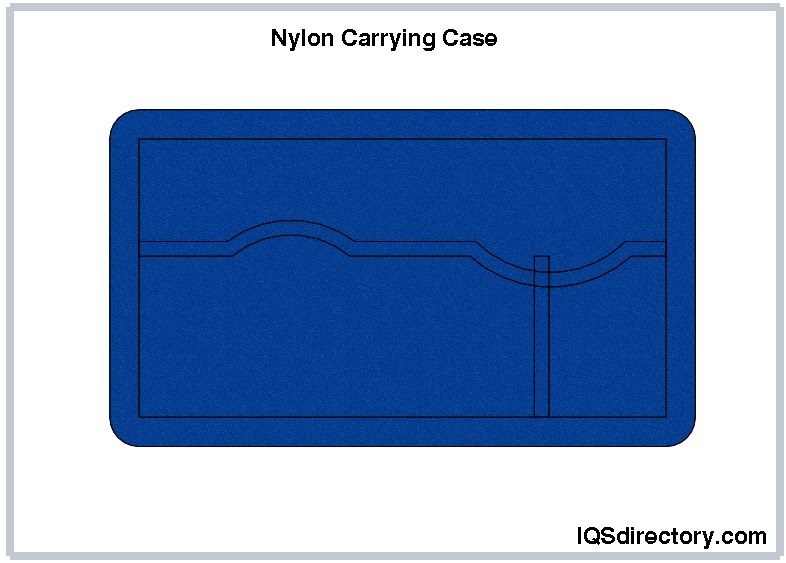
Nylon carrying cases are designed for transporting audio and visual equipment, featuring padded interiors to safeguard items such as speakers, mixers, and other gear. Available in various shapes, colors, and sizes, these cases are known for their exceptional durability. They offer tear resistance and retain their shape under diverse conditions, even after years of use.

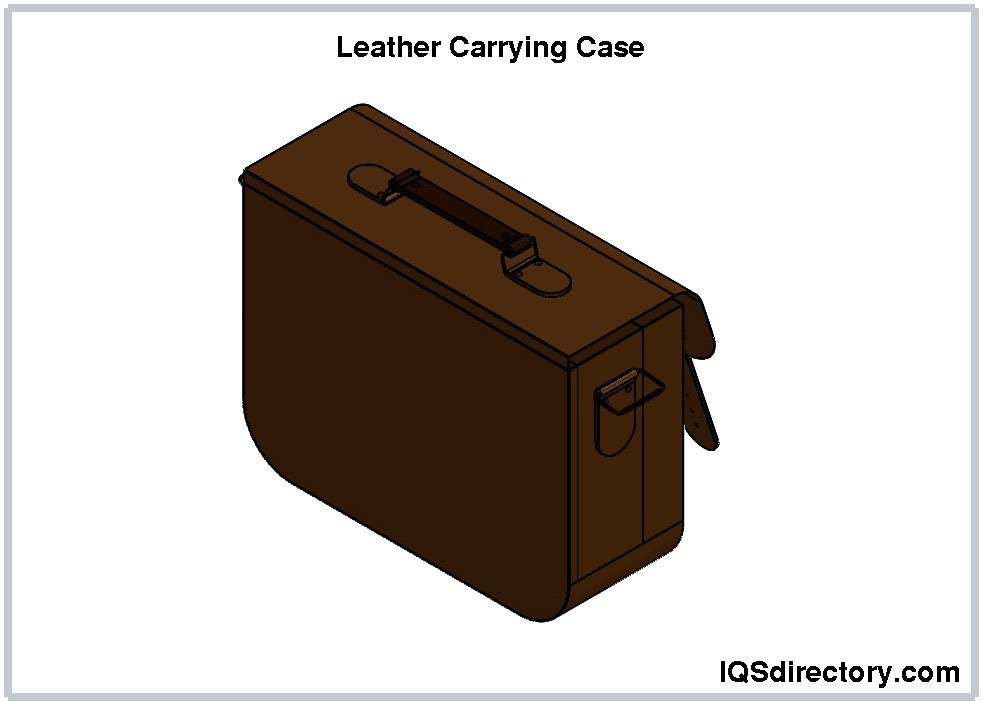
Leather carrying cases differ based on the grade of leather used. Full-grain leather, which is the hide of an animal after the hair has been removed, maintains its natural texture and durability without any alterations. Although full-grain leather cases are highly durable, they are also more expensive. In contrast, lower-grade leathers are more affordable but offer less durability.
Wooden carrying cases are crafted from durable woods such as pine, cherry, birch, or mahogany. They are known for their sturdiness and reusability. The interiors of these cases can be lined with wood, plastic, foam, or fabric, while the exteriors are often finished with leather, plastic veneer, or fabric for added protection and aesthetic appeal.
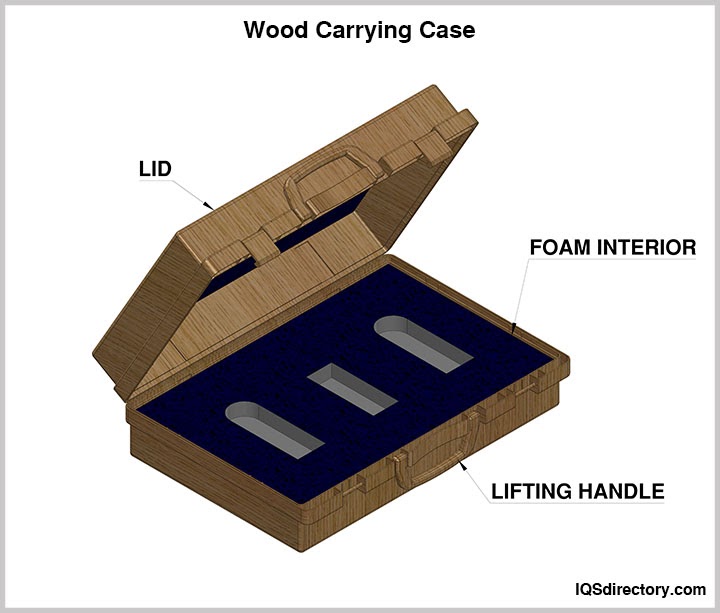
Designing a carrying case is tailored to meet the specific needs of the customer. Manufacturers work closely with clients to develop prototypes or proposed solutions until the final design aligns with the customer’s requirements. Even seemingly minor details—such as handles, types of hinges, locking mechanisms, material durability, and other small components—are crucial in the design process. Attention to these details is essential for ensuring that the carrying case is both functional and durable.
American Transportation Association (ATA) cases are subject to rigorous design standards. To comply with ATA requirements, these cases must be vibration and shock resistant and can be constructed from various materials, including wood with a plastic veneer, plastic board, aluminum, and certain sheet metals. Handles and latches are often recessed to protect them from damage. The ATA provides a set of standards that determine a case’s classification and durability, ensuring that it meets the necessary performance criteria.

Carrying cases have a wide range of uses and are continually evolving, with new designs emerging each year. As more commercial activities take place at customer locations, carrying cases are being developed to address these dynamic needs.
The types of carrying cases are diverse and adapt to new items and technological advancements. Continuous innovations, inventions, and prototypes drive the creation of new carrying case solutions.
Instrument cases are designed to protect sensitive and delicate instruments during transit. Electronic devices that measure readings, fluctuations, and collect data are particularly vulnerable to impact and mishandling, which can easily disrupt their calibration.
Musical instruments, while not as sensitive as technical devices, can still be severely damaged if shipped in inadequate or poorly constructed cases. Repairing such damage can be difficult and costly, sometimes rendering the instrument unusable.
Instrument cases are engineered to safeguard delicate items by featuring both padded exteriors and interiors that match the shape and dimensions of the instrument. These cases also include hard or soft exteriors to shield against environmental and weather conditions.
Instrument cases designed for technical equipment, such as calculators or chronometers, come in various styles, sizes, and configurations to ensure easy access while providing complete protection. Larger cases for instruments with multiple components are crafted to fit the specific size, shape, and complexity of the items they hold.
A crucial component in the manufacturing of instrument cases is the foam insert, which is cut to precisely match the instrument’s shape. Methods for creating these inserts include die cutting, contour cutting, and compression cutting for round equipment. Additionally, a layer of flocked foam may be added for extra protection.
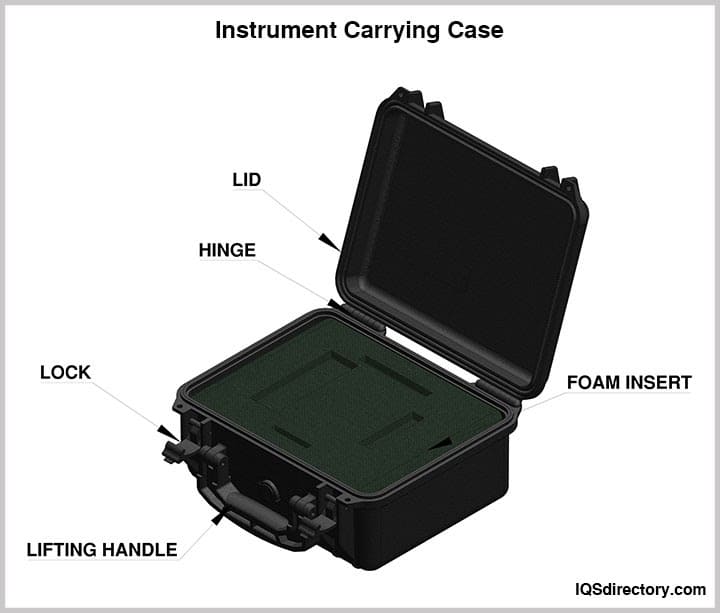

Divider carrying cases are designed with sections to securely hold parts, components, and instruments. These cases use dividers made from tightly packed rubber or polyethylene foam to ensure the safe transportation of technical or fragile equipment. The customizable multiformat dividers allow the case to be tailored to fit the specific needs of the equipment, providing a snug and secure fit.
The dividers in these cases typically feature a stiff plastic core covered with a durable, soft material. These cores can be trimmed, cut, and shaped to fit the design of the case. The number of dividers varies depending on the interior size and intended use of the case, ranging from two or three up to more than ten. For electronic technicians and small equipment repair specialists, cases may include 20 or more dividers due to the compact nature of their tools.
Custom-designed divider cases are often necessary to meet the specialized requirements of certain instrumentation and equipment. This is particularly true for repair personnel working in confined spaces with small equipment. Their cases must be compact for easy access while being robust enough to withstand regular use.

Equipment carrying cases are designed to protect various devices and equipment, including tools, monitors, computers, and more. They come in different sizes to accommodate specific items. Transporting sensitive and delicate equipment poses challenges, as any damage can lead to serious issues. Beyond protecting the equipment from damage, these cases also safeguard against mishandling by baggage handlers and others during transit.
The outer shells of equipment carrying cases are constructed from durable, hard materials to ensure safety and security. For equipment that is crucial to a job, the case must be robust enough to withstand the rigors of travel while protecting its contents. These cases are designed to resist impacts and scratches, be airtight to prevent water damage, and include padding to keep the equipment stable.
While equipment carrying cases may seem similar to other types of cases, they are specifically tailored for carrying equipment samples, medical instruments, delicate measuring devices, and fragile electronics. Each application requires cases with precise dimensions and features to meet the specific needs of the equipment and its usage.
Transit cases are built for durability and longevity, offering robust protection for instruments and equipment. Their primary functions are to shield against impacts and provide a stable, reusable container that withstands repeated use. These hard-sided cases ensure that their contents are safeguarded during shipping.
The exterior of a transit case serves as the first line of defense, designed to resist mechanical damage. Inside, most transit cases are lined with foam, polymer materials, or cushioning, and often feature molded inserts tailored to fit technical equipment and instruments. These inserts provide a secondary layer of protection against shocks, vibrations, and temperature fluctuations.
Transit cases may earn ATA certification based on their durability and frequency of use. Advanced cases might also receive MIL-SPEC certification if they meet the MIL-STD-810 standards, which test for airtightness, waterproofing, drop resistance, and corrosion protection. Achieving these certifications requires rigorous testing of the cases.
Transit cases are designed to be sealed against environmental conditions and to protect contents under harsh circumstances. Their latches, handles, and locks are engineered to remain secure and often require significant force to open. The corners and edges are reinforced with extruded plastic, aluminum, or metal to enhance durability.
Foam insert carrying cases are similar to divider cases but use soft foam to create custom sections tailored to the precise shape of the items being transported. Each foam insert case is custom-designed to fit its specific application, with foam cut to exact specifications. This level of customization is particularly beneficial for protecting delicate and sensitive equipment during rough handling.

Pouch carrying cases are designed for transporting small instruments and tools. Unlike divider and foam insert cases, pouches are typically smaller and can be carried on a belt or like a briefcase. They can also be attached to the side of larger cases to provide additional storage for small items.
The term "pouch" broadly refers to a small, envelope-like case used to carry specialty items, documents, tools, or art supplies. Pouches are often used as supplementary accessories to main carrying cases, offering protection for delicate small instruments. They are usually crafted from soft, pliable fabrics using commercial sewing techniques.
The choice of fabric for pouches affects their protective qualities. Neoprene and Hypalon are known for their chemical and abrasion resistance, making them suitable for harsh environments. Vinyl and nylon offer weather resistance, making them ideal for outdoor use. While less common today, leather pouches were historically used to carry items like tobacco and gunpowder but have since been largely replaced by modern materials such as cotton and polyester.

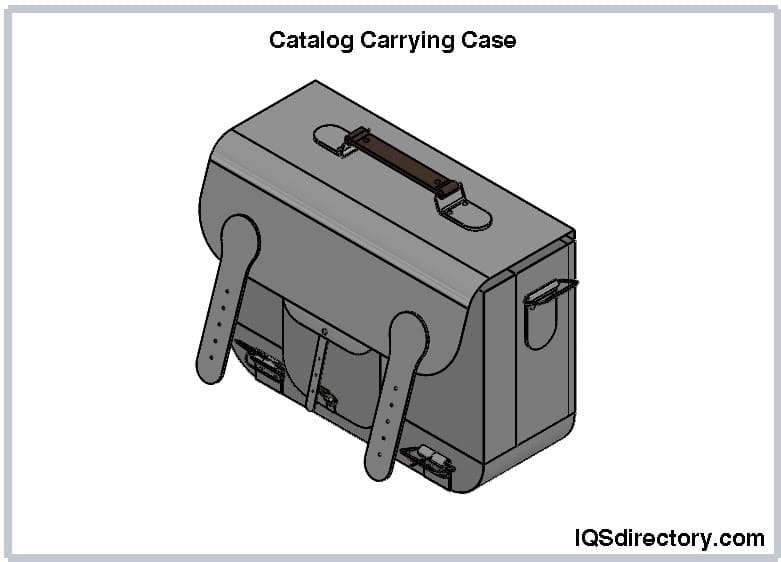
Catalog carrying cases feature a firm outer shell, typically made of vinyl-coated fabric or plastic. The vinyl coating mimics the appearance of leather, providing an attractive look and enhancing durability for heavy use. These cases are washable and resistant to cracking, peeling, and stains. The firm lids are equipped with piano-style hinges, allowing for easy opening and closing.
The interiors of catalog cases vary. Some cases have an open space with an accordion pocket on one side, while others include dividers to organize papers, brochures, and catalogs. Many designs feature additional exterior pockets and small compartments in the lid for items like pens and writing instruments. Modern catalog cases often include a dedicated section for a laptop or tablet.
Catalog cases are designed to hold, organize, and protect important paperwork and documents, making transport and distribution of informational brochures more efficient. Although similar to briefcases, catalog cases are generally more robust and heavy-duty. They include features like interior accordion files for categorizing documents and metal hanging file frames for file suspension, similar to a file cabinet.
With the rapid evolution of computer types and models, innovative computer carrying cases are continually being introduced. The primary purpose of a computer case is to protect the device from damage caused by drops or impacts. These cases come in a vast array of styles, sizes, shapes, and configurations, designed to accommodate the diverse range of computer brands available.
There are two main types of laptop computer carrying cases: soft-side and hard-side. Soft-side cases resemble a padded briefcase, with thick, cushioned sides and a dedicated compartment shaped to fit the computer. They often include additional sections for books, papers, and other materials.
Hard-side cases, on the other hand, are made from blow-molded plastic and feature a robust, molded exterior. The interior is lined with thick padding to safeguard the computer, and these cases can be custom-fitted to the exact dimensions of the device, offering enhanced protection.
Both soft and hard computer cases typically include compartments for accessories such as a mouse, speakers, and cameras. These storage options can include pouches, pockets, zipper compartments, and accordion files. Additionally, they provide space for paperwork, books, and other materials.
Computer carrying cases are designed to meet specific durability standards. They are often watertight, impact-resistant, and resistant to corrosion and dust. The cases can feature hard exteriors made from materials like plastic, aluminum, vinyl, or leather. Specialized cases may also include foam inserts to securely hold and protect the computer.

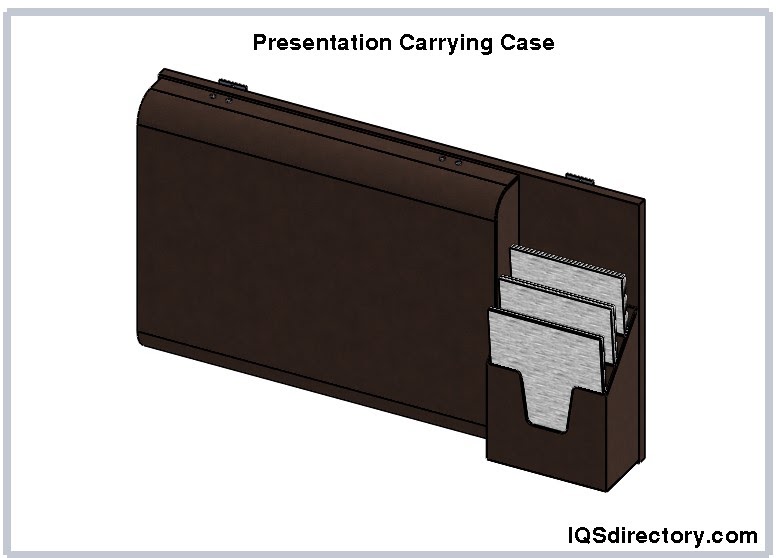
Portfolio carrying cases are designed to carry materials for presentations and exhibition. They are made from a variety of materials that include aluminum, leather, or various types of soft sturdy fabrics. There is some confusion regarding portfolio cases since there are so many varying definitions. For manufacturers, a portfolio case is made to carry graphics, artwork, or items for display. They are made of materials that protect the contents and keep it from being damaged.

Presentation cases feature a hard exterior and are securely closed with latches. They may also include a collapsible handle and wheels for easier transport. The interior is lined or padded to protect materials from scratches and damage. Custom-shaped foam inserts can be added to provide extra protection by securely holding the contents. Cut foam interiors are commonly used for delicate equipment and instruments, such as cameras, calculators, and computers.
Presentation cases come in various sizes, shapes, and configurations, including ATA cases, catalog cases, and pouch cases. They are designed to accommodate the items needed for an effective presentation of products, programs, companies, or agencies. Contents may include flyers, brochures, paperwork, equipment, blueprints, and tools. Regardless of the type, these cases ensure that the contents remain in pristine condition and are securely stored.
Securing the contents is a key function of presentation cases, which is why they are equipped with latches and locks. The items in a presentation case are often valuable representations of an organization, requiring robust protection. Thus, presentation cases are designed to be tightly sealed and securely locked.
Sample cases are a marketing tool for carrying samples of products, presentation materials, product literature, and documents. Depending on the products to be presented and the weight of the materials, they can be designed with rollers and a telescoping handle. Sample carrying cases are an important asset for salespeople since they offer the ability to bring office materials to a client meeting.

Shipping cases are designed to safeguard their contents from shock, vibrations, moisture, dust, and damage. Constructed from robust materials like aluminum, wood, steel, fiberglass-reinforced polyester, or high-density plastic, these cases come in a wide range of sizes to suit various applications.
Choosing the appropriate shipping case depends on the type of materials being shipped and the conditions they will encounter. Aluminum cases are lightweight and ideal for applications where weight is a concern, but they are more expensive and less durable compared to other materials.
Roto-molded cases, made from high-density polymers, are known for their strength, ruggedness, and durability. These cases are designed to endure tough conditions and are commonly used to ship sensitive devices, communication equipment, and valuable items. They often come with custom-formed foam inserts for added protection and can be ATA certified, ensuring the safety of equipment during long-distance transport.
Reinforced wood shipping cases are a cost-effective option. Made from composite wood or plywood, which is coated or laminated, these cases are built to withstand the rigors of long-distance shipping. Their durable exterior retains its shape even after multiple trips, providing reliable protection for shipped items.

Tool carrying cases can be either standard or custom-designed to suit any size or configuration. They are built to protect their contents from moisture, salt spray, dust, and even immersion. These cases are made from a range of materials including aluminum, high-density polyethylene, reinforced polyester, carbon fiber, and low-density polyethylene. Additionally, tool carrying cases can be equipped with various features such as wheels, zipper closures, compartments, and shelves to enhance functionality and convenience.
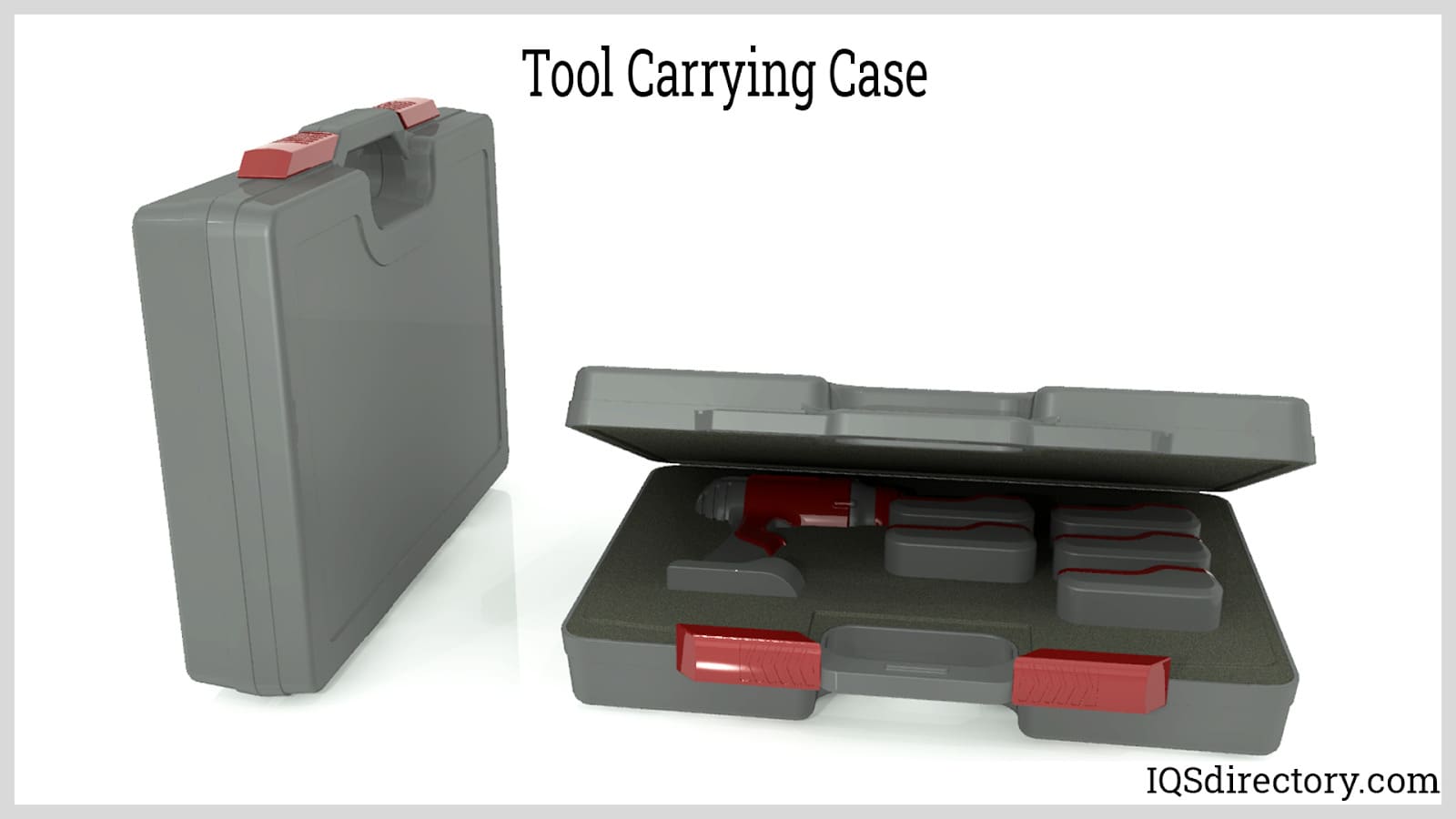

Tool carrying cases can be either standard or custom-designed, available in various sizes and configurations. They offer protection against moisture, salt spray, dust, and immersion. These cases are crafted from materials such as aluminum, high-density polyethylene, reinforced polyester, carbon fiber, and low-density polyethylene. They can also feature additional elements like wheels, zipper enclosures, compartments, and shelves for enhanced functionality.
Over the years, tool cases have evolved and specialized to meet the needs of various professions, driven by technological advancements. For example, copier repair technicians use tool cases tailored for the specific adjustments of copier machines, while computer repair specialists require cases for monitors, calculators, and error-detection devices. The diverse requirements of different repair fields have led to a wide range of tool cases beyond the traditional screwdriver, drill, or saw.
Initially, tool cases, or toolboxes, were made of wood, reflecting the materials available at the time. Nowadays, tool cases are predominantly constructed from molded plastics with foam inserts, designed to accommodate specific tools and withstand various conditions. The design and manufacturing of tool cases have become a specialized industry, catering to the needs of unique and specialized tools and instruments.

A personal utility case is designed to offer robust protection for items that need to be safeguarded from damage. It features an exterior layer capable of withstanding bumps, shocks, and vibrations. The interior is sealed to prevent dust and particulate matter from contaminating the contents. Personal utility cases provide an effective and cost-efficient solution for protecting sensitive items such as credit cards, phones, and other personal belongings.
Carrying cases come in a wide variety of types, each tailored to specific needs and uses. While some designs adhere to traditional, foundational styles that are universally valued, the differences among carrying cases are influenced by factors such as the materials used in their construction, industry standards and regulations, and their intended purpose.
Heavy-duty carrying cases are constructed from the same robust materials used for shipping containers but are designed to be lightweight and user-friendly. They are built to meet or exceed American Transport Association (ATA) standards and are reinforced with ribs for added protection and durability. These cases are typically made from materials such as aluminum, high-grade plastics, stainless steel, and certain gauges of steel.
While heavy-duty carrying cases serve similar functions to shipping cases, they are manufactured from smaller molds, making them easier to load and transport. The primary advantage of heavy-duty carrying cases is the enhanced protection they offer for sensitive instrumentation and valuable components. These cases must also adhere to military standards for carrying cases to ensure reliability and durability.
Due to the weight of their contents, heavy-duty carrying cases are designed with ergonomic considerations in mind. Despite their exceptional protection and durability, they need to be convenient to carry, accommodating various modes of transportation such as airplanes, cars, trains, and trucks.
Most heavy-duty carrying cases feature vertical or horizontal ribbing, similar to briefcases, to enhance their strength and stability. This ribbing not only makes the cases easier to stack but also increases their overall durability.

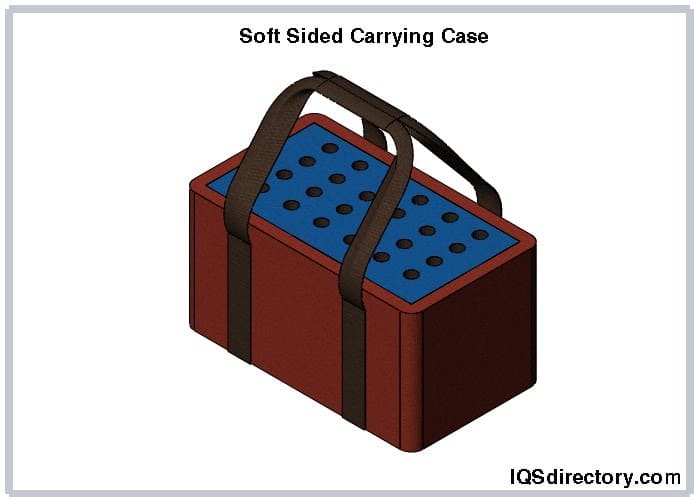
Soft-sided cases are made from materials such as neoprene, canvas, nylon, leather, or vinyl, available in a range of colors, sizes, and designs. They are both water and dust resistant, designed to withstand harsh conditions and inclement weather. The soft, pliable interior provides added protection for instruments, components, equipment, and technical devices. Soft-sided carrying cases are lightweight, ergonomically designed, and flexible, allowing them to adapt to various environments and conditions.
Key features of soft-sided carrying cases include their flexibility, convenience, and durability. They are capable of carrying sample trays, instruments, fold-away boxes, and small tools. The soft sides offer exceptional protection against environmental factors and harsh conditions. When not in use, a soft-sided case can be easily folded and stored, making it a practical choice for diverse applications.
Several processes are used to produce soft-sided carrying cases, with the method selected depending on the type of raw material used.
In high-volume production, soft-sided carrying cases are typically sewn using automated machines. For specialty and custom cases, however, experienced craftspeople may sew them by hand to ensure precise assembly and quality.
Gun carrying cases come in various types and sizes, tailored to the specific weapon they are designed to protect. These cases can be either soft-sided or hard-sided, but typically feature a soft interior layer for added protection. Strict regulations govern the use of gun carrying cases, and informed gun owners are well aware of these rules. Enthusiasts of guns, handguns, shotguns, and rifles often take extra precautions when traveling with their weapons, and gun carrying cases play a crucial role in ensuring safety during transit.
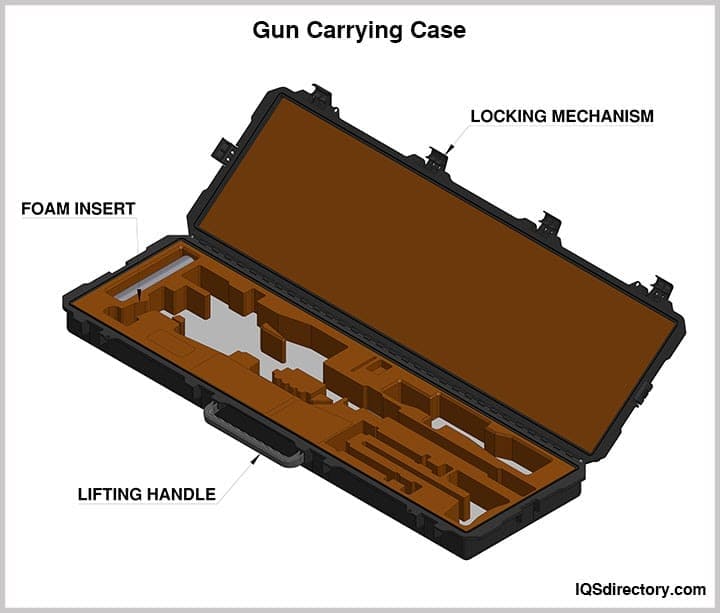
ATA cases are a specific specialty case that is designed to withstand being frequently shipped and meets the standards of the ATA. To be categorized as an ATA case, a case has to be able to endure being shipped over 100 times and maintain its structure. They are well known for their durability, ease of use, ability to be easily loaded and unloaded, and reusability.
ATA cases are constructed using fiberboard for the exterior walls, which is typically coated for added durability. The interior features protective foam or a honeycomb design to safeguard the contents. The corners and edges are reinforced with extrusions made from plastic, aluminum, stainless steel, or steel, and are often equipped with metal or plastic corner brackets for additional protection.
The latches and handles of ATA cases are made from steel to ensure extra strength and stability. The edges of the lids are also reinforced with aluminum, steel, plastic, or stainless steel extrusions. For ease of movement, ATA cases are equipped with locking casters. Common latch types for ATA cases include spring-loaded twist latches and draw latches.
ATA cases must meet the standards outlined in ATA-300 Category I, which specifies the durability required for a case to be classified as an ATA case. ATA-300 approval signifies that a case can withstand rough handling for up to 100 trips without compromising its integrity. The primary characteristic of an ATA case is its ability to endure harsh conditions typically encountered during transport by train, air, or sea.
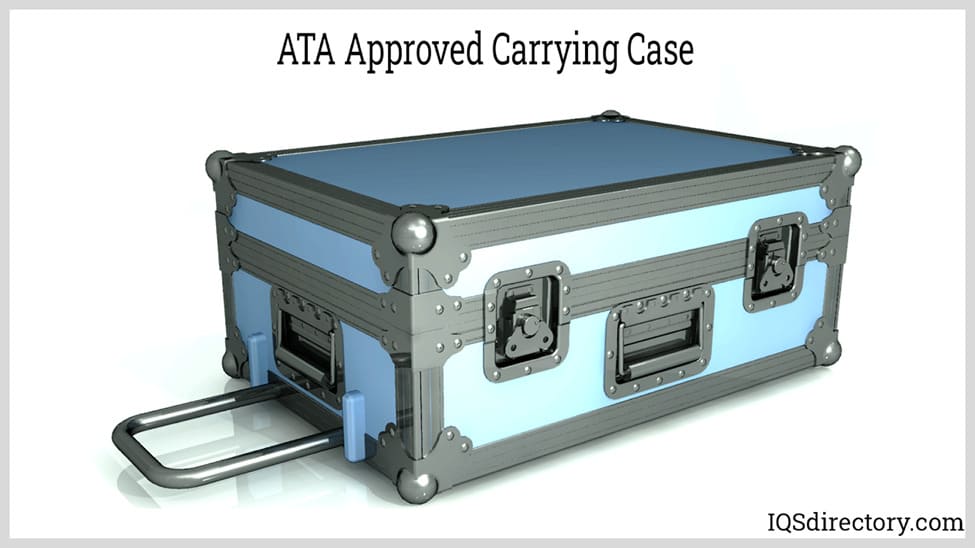

Road cases, also known as ATA cases, are designed to transport various types of instruments and sensitive equipment. While they share the same rugged design principles as ATA cases, they may not necessarily have ATA certification. The term "road case" implies that the case is built from durable materials capable of withstanding the demands of frequent travel.
Road cases are typically constructed with plywood panels covered in fiberglass. The panels are joined with metal or plastic connectors and reinforced with solid metal corner brackets. The interior configuration of a road case varies depending on its intended use. Basic road cases often feature a raw wood interior for general transport and storage, while more advanced versions include padded interiors with polymer foam, which can be custom cut and shaped to fit specific equipment.
Although road cases serve a similar purpose as shipping containers, they are distinguished by their specialized construction, including reinforced metal edges and corners. Due to their large and bulky nature, road cases often come equipped with casters for easy maneuverability, while smaller models may include convenient recessed handles.
Hard cases are constructed from high-density molded plastics, aluminum, veneered or laminated wood, and other non-ferrous metals. They offer exceptional protection and are known for their durability and security. Hard cases are commonly used for shipping and storing military equipment, sensitive instruments, and emergency gear for police and first responders.
There are four primary plastic shaping methods used in the manufacture of hard cases: blow molding, injection molding, roto molding, and thermoforming. Blow molding involves blowing molten plastic into a two-sided mold to form the shape of the hard case. Similarly, injection molding injects molten plastic into a two-sided mold to create the case.
Roto molding, suitable for larger cases, involves placing plastic resin in a two-sided mold connected to a rotational machine. As the machine rotates and heats the mold, the molten plastic spreads evenly across the mold's surface. After the plastic has fully coated the mold, the machine enters a cooling phase where the plastic solidifies. The finished hard case is then removed from the mold.
Thermoforming, a vacuum molding process, involves heating a plastic sheet and drawing it into a two-sided mold to form the case's lid and base. After cooling and setting, the plastic is removed, and additional components such as latches, hinges, and handles are added.
Each molding technique produces hard cases with thick, impenetrable walls made from high-density plastic, designed to withstand the rigorous conditions they face. Manufacturers of hard cases focus on ensuring that their products deliver the durability, strength, and longevity needed to protect valuable equipment, instruments, and tools.

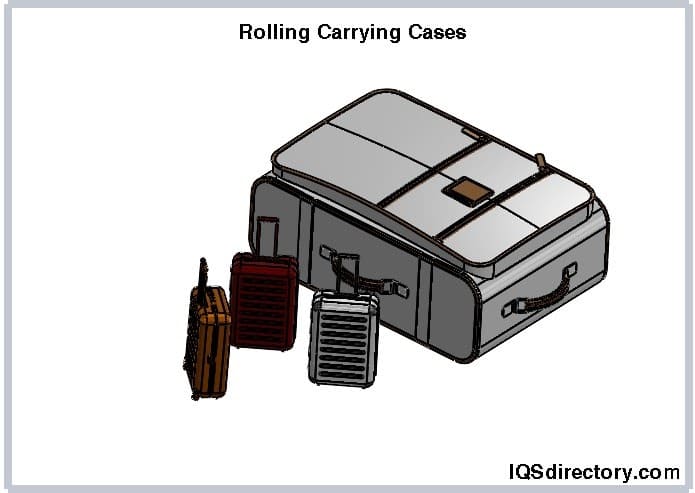
Rolling carrying cases feature small wheels on the bottom, allowing for easy transportation without the need to carry them. They are particularly suited for large or bulky instruments and devices. These cases are equipped with telescoping handles for effortless maneuverability and are available in various sizes with multiple interior padding options to suit different needs.
Storm carrying cases are built to withstand severe conditions, featuring an exceptionally tough exterior crafted from highly durable materials. These cases are designed to safeguard fragile or sensitive instruments and equipment from damage. When not in use, storm carrying cases also serve as excellent storage containers, protecting contents from contaminants and harsh environments. The interior is lined with soft fabric or foam for added protection.

Protector cases are built from exceptionally robust materials, designed to endure hostile environments and challenging conditions. These cases are essential for safeguarding delicate and complex technical instruments, whether they are used for data recording, team communication, or memory storage. When not in use, protector cases offer enhanced protection and secure storage for these vital tools.
Protector cases are watertight, crushproof, dustproof, and resistant to vibrations and impacts. They feature solid, thick walls made from lightweight materials. Designed with double latches to prevent accidental openings due to impact, protector cases are ideal for protecting handheld electronics.
Air cases are a type of protective case crafted from sturdy yet lightweight materials, designed to withstand impacts and shocks. These cases feature an airtight design to keep out air and dust, making them suitable for a variety of applications. Air cases come in various configurations to meet different needs.
Available for traveling, hiking, or simply keeping electronics safe, air cases share common features regardless of their size. They can include dividers for additional protection and security.
Backpacks have been used for centuries to conveniently carry a wide range of items, including clothing, books, tools, weapons, and hiking gear. They have long been a staple in military gear and are now common in schools. Backpacks are made from various materials, with canvas, cotton, and nylon being particularly prevalent. Depending on their intended use, backpacks can be crafted from soft, pliable materials for comfort or from tougher materials for enhanced durability and strength.
Backpacks are typically sewn from pre-cut fabric pieces. The pattern is laid out on the fabric, pressed, and cut electronically. The pieces are then assembled using heavy-duty commercial sewing machines with strong nylon thread and a 301-type stitch, although other thread types are weaker.
After the main components are sewn together, additional features such as zippers, snaps, and buckles are added. These components are also sewn on with nylon thread. The design and features of a backpack depend on its intended use. For military backpacks, quick and easy access is crucial, with secure snaps and zippers that can be opened with minimal effort.
Purses come in countless styles, sizes, and types, each serving specific functions. They can be practical for carrying daily necessities or serve as a decorative fashion statement. Regardless of the variety, all purses function as pouches for carrying items, whether they are elaborate and adorned or simple leather bags with flaps. Purses have been a convenience and necessity for all genders for centuries.
Manufacturing methods for purses vary, producing distinctive personal items. Purses can be woven from yarn, cut from fabric, pieced together like a backpack, or adorned with glued and sewn jewels. The method chosen depends on the material, purpose, and design of the purse.
Leather is often the material of choice due to its durability and longevity, although synthetic fabrics are increasingly used for their ease of sewing and cost-effectiveness. Mass-produced purses are sewn using industrial machines, while designer purses are hand-sewn with fine thread to ensure high quality.
The production of custom-designed carrying cases is continually evolving as new and unique equipment emerges. These specially crafted cases are engineered to serve specific functions and are created through advanced planning and sophisticated engineering techniques.
The rigorous demands of military operations necessitate equipment and materials that can endure extreme conditions. Military carrying cases must not only be durable but also watertight, shockproof, corrosion-resistant, and dustproof. They are designed for ease of handling, including loading and stacking.
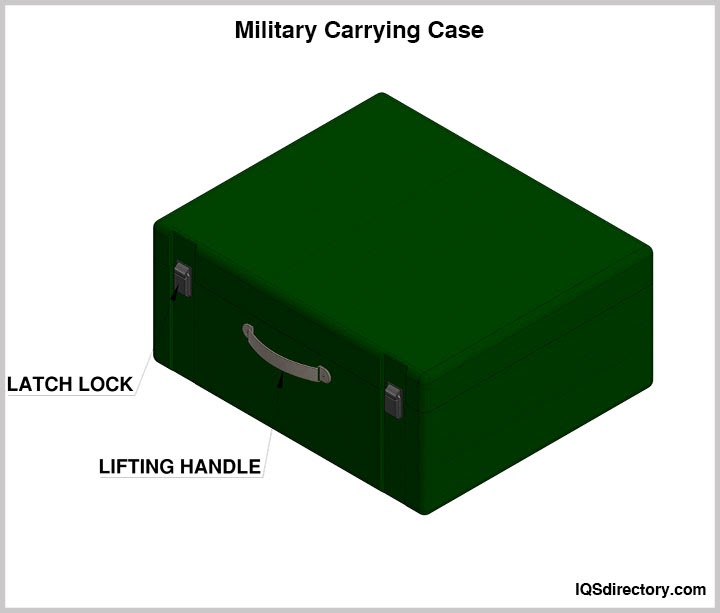
Medical equipment is both delicate and costly, requiring robust cases to prevent damage and ensure it remains effective in life-saving situations. The primary requirement for medical carrying cases is exceptional protection and reliability during emergencies. These cases come in various forms, designed to hold equipment, medications, and supplies needed for wound care and other medical treatments.

Similar to medical carrying cases, fire and rescue operations demand equipment that remains reliable under extreme conditions. Fire and rescue carrying cases must be both portable and lightweight while offering the durability needed to endure hazardous environments. These cases come in various designs and often feature organizational inserts, ensuring quick and efficient access to essential life-saving equipment.

Just like in human care, veterinary carrying cases come with specific requirements. They must facilitate the hygienic transport of diagnostic supplies, medications, and other essentials. These cases should feature document pouches and be constructed from highly durable materials such as aluminum or synthetic leather. Given the diverse environments in which veterinarians operate, the cases need to offer ample storage space for collecting samples and other necessary items.

Shipping and moving hazardous materials necessitate cases that comply with stringent government regulations for handling such materials. Hazmat carrying cases are custom-designed to meet specific application needs while adhering to legal requirements and safety standards.

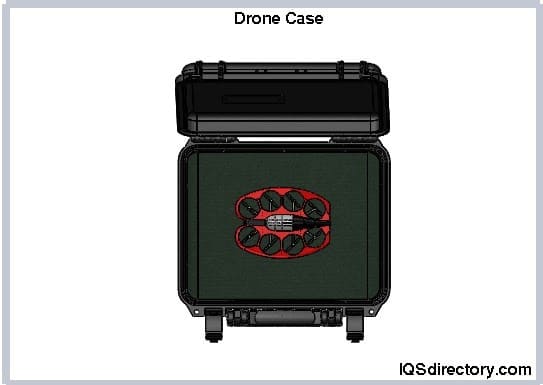
Drones, which serve various purposes beyond personal use—such as exploring terrain, inspecting oil fields, or surveying battlefields—are valuable and require meticulous care. Given their expense and delicate nature, they must be handled with the utmost caution.
Bel-Air Cases is a prominent plastic case manufacturer that provides solutions for a variety of applications and situations. Their rugged and durable cases are engineered to endure the challenges of transportation and frequent use. Bel-Air offers medium-duty cases for less frequent use and heavy-duty cases for regular shipping. The company takes pride in crafting cases that are appropriately sized, competitively priced, and aesthetically pleasing, all while being built to last. For specific needs, they also offer custom-designed cases to meet their customers' exact requirements.
Tetrafab is a leading custom case manufacturer with facilities in Asia, South America, and the United States. They collaborate closely with clients to create the ideal case tailored to the specific conditions and applications required. Tetrafab's success is rooted in the meticulous effort they invest in ensuring their products are of the highest quality. Their designers work with clients to produce computer-generated renderings of cases that align perfectly with customer specifications.
Pelican's success is built on its dedication to producing cases that endure even the harshest and most demanding environments. Whether used for personal travel or industrial applications, Pelican cases are designed to withstand rigorous conditions. The company's mission is to ensure that the contents of their cases remain protected under extreme stress and strain. Pelican offers a comprehensive range of cases to suit various needs, from family vacations to industrial operations.
Royal Case Company provides an extensive range of cases, including injection and blow-molded plastic cases as well as soft-sided carrying cases. Their team of designers and engineers transforms customer concepts and designs into professionally crafted and durable cases. As a national leader in case manufacturing, Royal Case Company excels in producing both hard and soft cases for well-known brands, focusing on safeguarding critical and life-saving equipment.
Shell-Case specializes in producing both soft and hard cases for diverse applications such as medical devices, electronic equipment, measuring instruments, and optics. They bring customer visions to life through innovative and original design techniques. Each case is meticulously planned and constructed with the highest quality materials, ensuring a precise fit from the inner structure to the outer shell.
Carrying cases are constructed from materials chosen for their durability and ability to withstand harsh conditions. Plastic is a popular choice due to its resistance to various environmental factors. Other materials include aluminum, valued for its corrosion resistance; leather, known for its durability; sturdy fabrics, which offer flexibility; rubber, which maintains its shape; and wood, appreciated for its protective qualities and reliability.
Plastic is the most commonly used material for manufacturing carrying cases due to its versatile properties. It is airtight, water-resistant, and resistant to crushing and dust, often exceeding ATA specifications. Plastic carrying cases can be blow-molded into various shapes and feature smooth, seamless surfaces.
Aluminum cases are valued for their lightweight, durability, and resistance to corrosion and dust. The inherent strength and endurance of aluminum make it an ideal material for carrying cases. These cases come in various sizes, ranging from compact briefcases to large shipping containers.
Certain types of wood are well-suited for crafting carrying cases, often serving as the core frame and structure. These wooden frames are typically covered with additional materials such as vinyl, plastic, or heavy fabric to enhance durability and functionality.

Nylon is a highly versatile and durable material, known for its expandability and self-healing properties. Available in various colors and thread sizes, it is ideal for both the interior and exterior of carrying cases. Nylon cases are well-suited for heavy use due to their tear resistance and long-lasting color that does not fade over time.
Leather is known for its durability and comes in a variety of grains. The strongest type is natural leather, which is tanned directly from animal hides. Over 24 different animal skins can be used in the production of leather cases, each offering unique qualities and strengths.
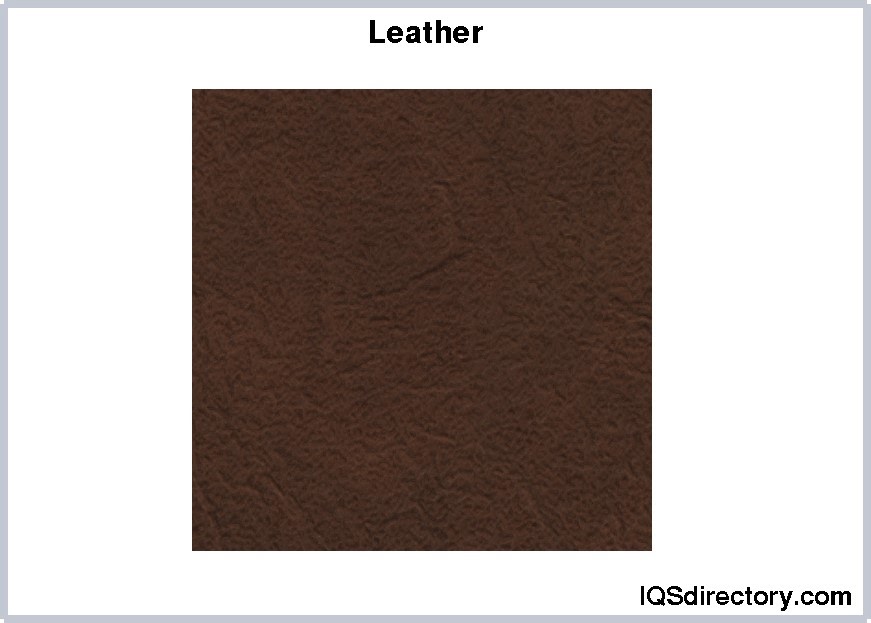

Neoprene is a highly durable and resilient synthetic rubber, available in both solid and soft, flexible latex forms. It retains its strength and durability even under harsh conditions, making it an excellent choice for manufacturing carrying cases. A notable characteristic of neoprene is its resistance to oils, which enhances its suitability for various applications.


A hard case is a type of carrying case that is made from molded plastic, aluminum, veneered or laminated wood, or different types of metals. They are the most secure and durable forms of carrying cases and...
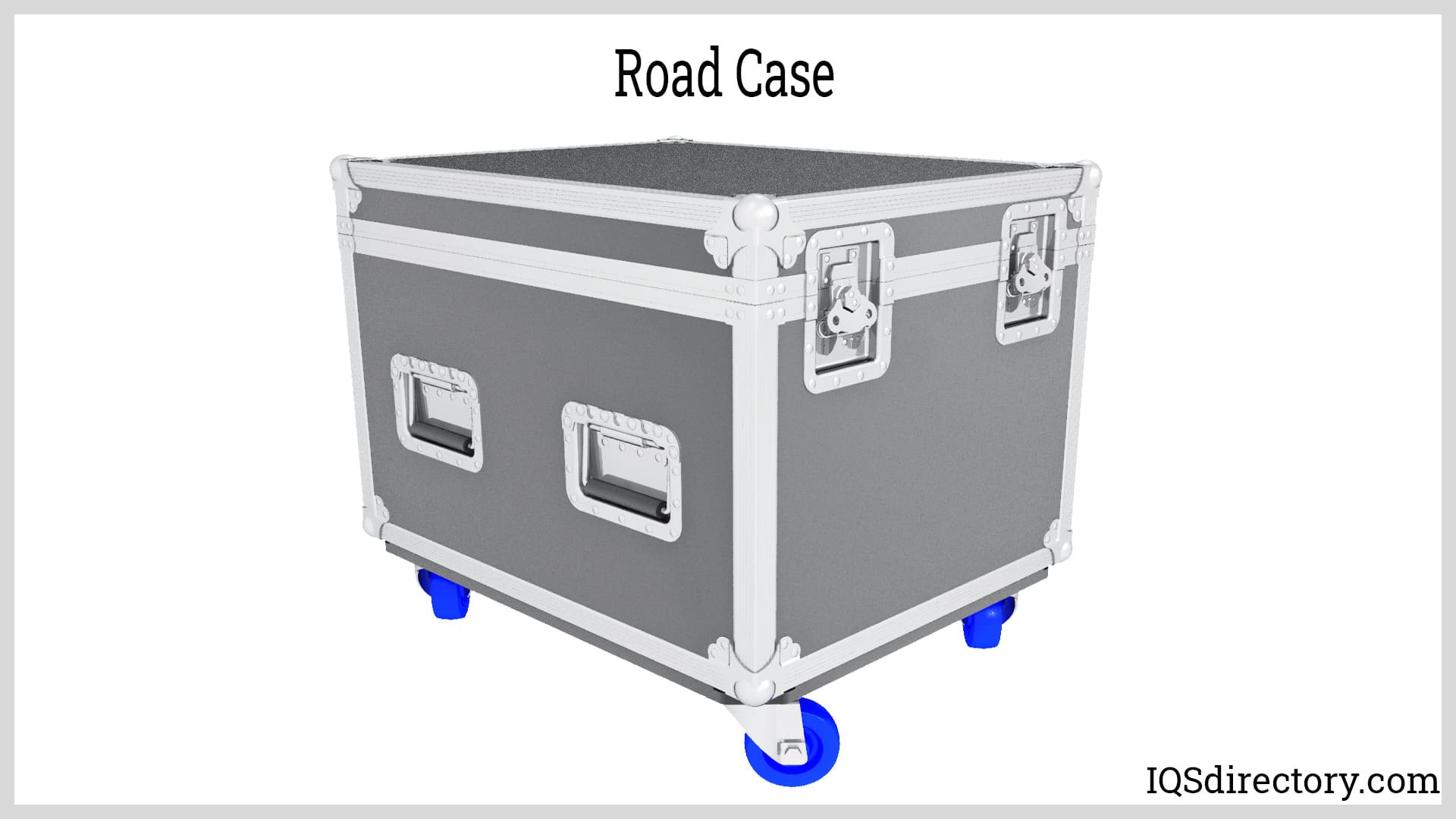

A road case is a ruggedly built, highly functional protective container with varying wall thicknesses that is capable of withstanding the riggers and handling of shipping. They are designed to meet...
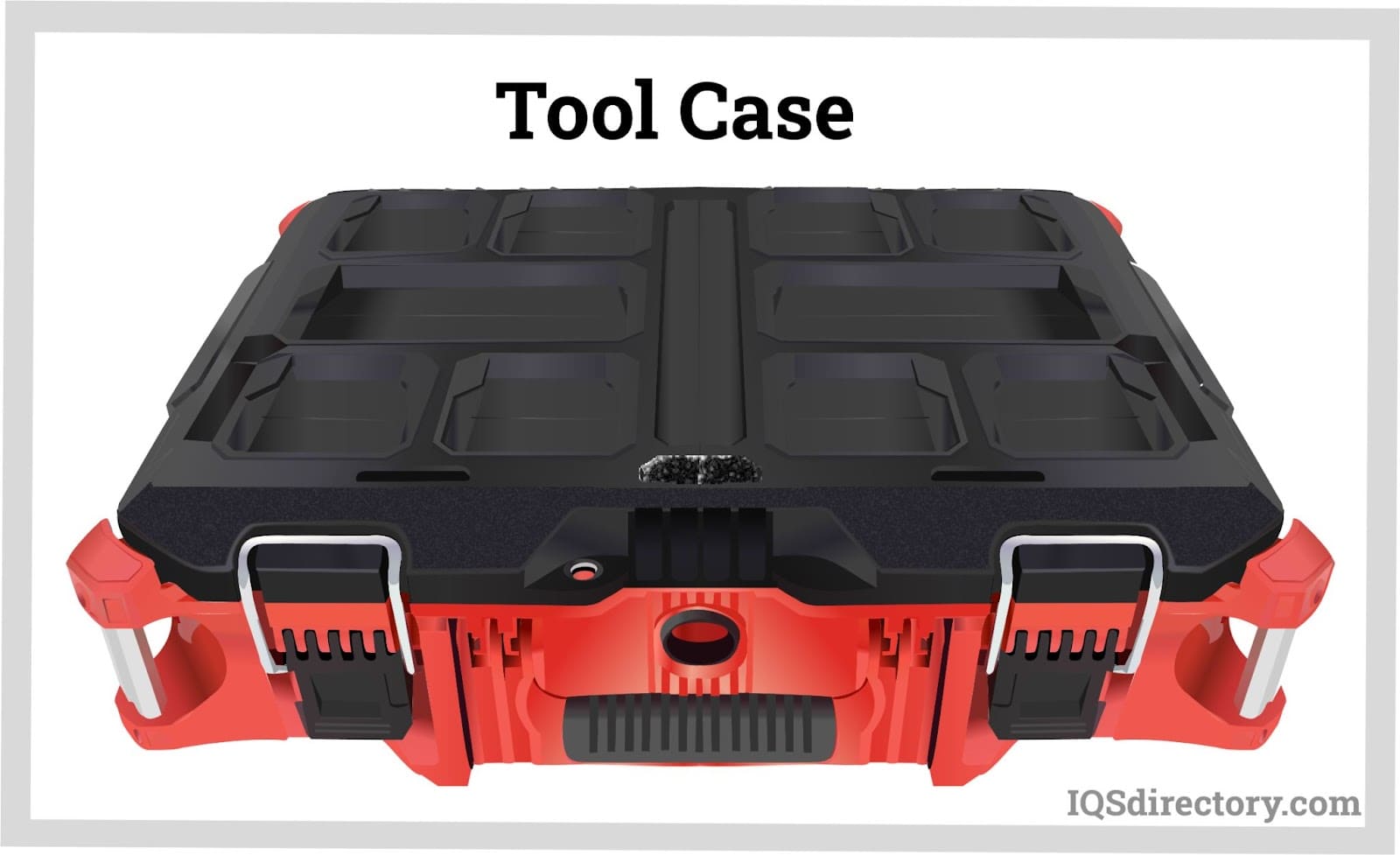

A tool case is a portable case designed to organize and protect tools and allow easy access and convenient availability. Standard tool cases can be used when working on a project. In addition, specialty and custom-designed tool cases are...

Cases designed to carry special valuables have been part of society throughout history back to the time of the Egyptians and before. Carrying cases are commonly found in any house stored in a garage, tucked away in a basement, or setting on a shelf...
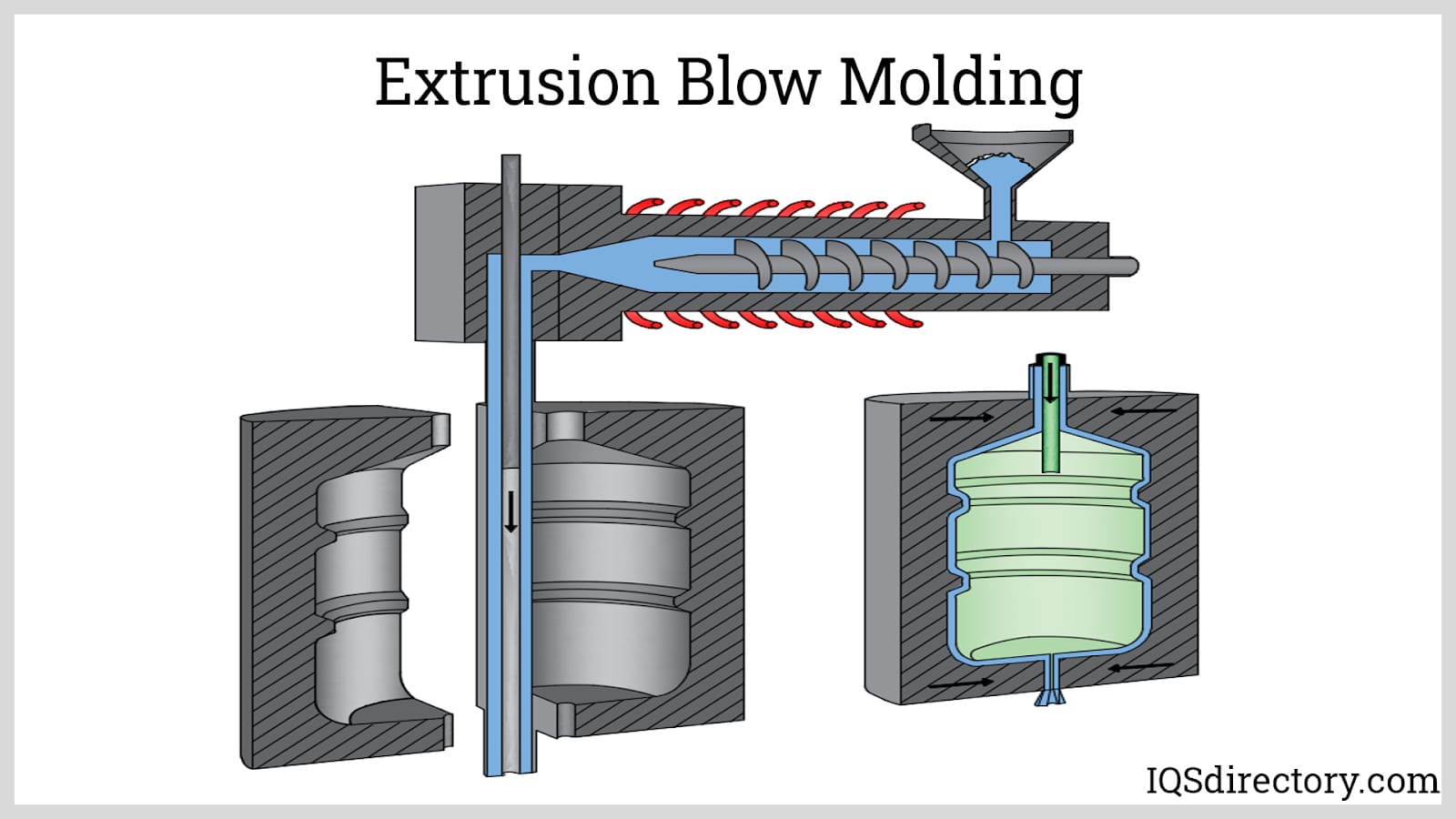
Blow molding is a type of plastic forming process for creating hollow plastic products made from thermoplastic materials. The process involves heating and inflating a plastic tube known as a parison or preform. The parison is placed between two dies that contain the desired shape of the product...

A canopy is a structure with a connected fabric or metal covering that can give shade or shelter from weather elements such as the sun, hail, snow, and rain. For example, a tent with no floor can be...

Contract sewing is a specialized industry that provides services to manufacturers for production of a wide range of products using highly skilled workers and technologically advanced sewing machines. The strength of the contract sewing industry is its ability to perform any type of sewing services...

Cut and sew is a process for the manufacture of clothing where the design and pattern are printed on the raw cloth from which the garment is cut, ensuring full color, edge to edge print of the design and color...

A protective cover is a sewn fabric that is specifically designed and used for protecting equipment, people, surfaces, and enclosures. Protective covers provide protection from the elements, UV rays, dirt, dust, moisture, and...