Canopies

A canopy is a structure with a connected fabric or metal covering that can give shade or shelter from weather elements such as the sun, hail, snow, and rain. For example, a tent with no floor can be...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article shares important knowledge regarding the creation of protective covers, their use, and much more information on protective covers.
You will learn about:

A protective cover is a specially designed fabric engineered to protect equipment, individuals, surfaces, and enclosures from a variety of environmental conditions. These covers are crafted to defend against threats like UV rays, dust, dirt, moisture, and other harmful elements. They are available in a wide assortment of sizes and styles, ranging from those suitable for small outboard motors to those extensive enough to cover a whole freight train, complete with a semi-truck on top.

Protective covers are tailored to fit the exact dimensions of the objects they are designed to safeguard. The material composition varies based on the intended use, with options including natural fibers and specific types of plastics. During production, the covers are meticulously crafted with secure seams, utilizing advanced stitching and sewing techniques to guarantee a snug and consistent fit around the items they envelop.
Frequently, protective covers are customized to fulfill the unique requirements of their intended environments. Manufacturers tend to offer personalization options, allowing customers to choose suitable fabrics based on environmental challenges and the specific objects in need of coverage.
A diverse range of robust and high-quality fabrics are employed in the creation of protective covers for industrial, commercial, and residential applications. Protective covers, whether custom-made or standard, are essential for shielding equipment, machinery, vehicles, and outdoor furniture from environmental hazards, damage, and premature wear. The choice of protective cover material directly impacts its performance in resisting moisture, UV radiation, chemical exposure, abrasion, and temperature extremes. While all materials serve the same fundamental purpose—to protect valuable assets—they differ in their specific protective properties and ideal use cases. For instance, some fabrics are designed to resist chemical reactions and ultraviolet light, whereas others are engineered to offer protection against moisture, mold, or fire threats.
The range of materials used to manufacture industrial protective covers includes natural fibers like cotton, canvas, and high-performance synthetic plastics such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene, and polypropylene. These materials are meticulously chosen based on the environment and application in which the protective cover will be used—whether for outdoor weather protection, chemical resistance in manufacturing settings, or safeguarding delicate equipment from dust and debris. Selecting the right protective cover material is critical for ensuring durability, longevity, and cost-effectiveness.
Although protective covers are often tailored for particular functions, they commonly exhibit several shared attributes that make them suitable for a broad range of protective solutions. High-quality covers must withstand tough conditions while maintaining their protective integrity. Below are some of these common features, which buyers should evaluate when selecting protective fabric solutions:
Canvas is a widely used material in military, construction, marine, and general industrial applications. This durable, heavy-duty fabric is traditionally made from cotton or linen, valued for its robustness, rigidity, and natural breathability. The production of canvas involves a dense weave of yarns in a simple over-and-under pattern, resulting in a close-knit structure resistant to tearing and abrasion. Canvas fibers are typically thick and range from medium to heavyweight, providing superior strength and longevity where high-stress protection is required.
In industrial settings, canvas covers are used to protect tools, machinery, scaffolding, and outdoor equipment from harsh environmental elements. Industrial canvas tarps are prized for their weatherproof and abrasion-resistant qualities. Cotton canvas, compared to linen canvas, is more flexible and less costly. It stretches more easily and can be enhanced with synthetic fibers or treated with coatings to become water-resistant or mildew-resistant, making it suitable for outdoor equipment protection and custom fitted covers.
Cotton duck, commonly just called “duck,” is a robust, plain-woven fabric made from densely woven cotton. It is a variant of canvas known for its durability, strength, and abrasion resistance due to its tight weave. Cotton duck is more resilient and sturdier than standard canvas and is often finished with water-repellent or flame-retardant coatings, making it an excellent choice for various protective applications.
The term “duck” originates from the Dutch word for cloth, “doek,” rather than the bird. The manufacturing process of cotton duck involves weaving two different fabrics together, with one serving as the warp and the other as the weft. Cotton duck is categorized into grades, from 1 to 12, with 1 being the heaviest and most durable (used for items like hammocks, sandbags, and industrial curtains), and 12 being lighter (suitable for applications such as protective clothing, tool pouches, and dust covers). Buyers looking for durable, reusable protective covers for demanding environments often select heavy-duty cotton duck for its reliability and versatility.

PVC (polyvinyl chloride) fabric is a type of synthetic vinyl commonly used for protective covers in industrial, marine, and construction industries. Known for its superior ease of cleaning, exceptional flexibility, and excellent resistance to fire, oil, grease, and water, PVC fabric offers outstanding durability in harsh operating environments.
Its molecular structure, featuring chlorine atoms bonded to carbon chains, contributes to its remarkable chemical resistance, durability, and resistance to oxidation. PVC is also impervious to sunlight (UV rays) and common industrial chemicals, making it ideal for outdoor covers, containment tarps, and equipment enclosures. Plasticizers are incorporated into PVC fabric to increase its softness and flexibility, enhancing its performance for tailored applications. These properties make PVC fabric easy to cut, shape, and sew, which is why it is preferred for custom-fitted protective covers, machine enclosures, and industrial curtains.
Additionally, the longevity of PVC fabric means it often proves to be more cost-effective over time compared to other materials that may require more frequent replacement, contributing to its widespread use as a protective covering for industrial, automotive, and healthcare applications.

Polyethylene fabric consists of a woven scrim sandwiched between two layers of plastic coating. This low-cost material is widely utilized for its eco-friendly nature and ease of recyclability, along with its strength-to-weight ratio. Made from petroleum-based thermoplastics, polyethylene fabric—sometimes known as PE tarpaulin or poly tarp—is characterized by its crystalline structure, lightweight properties, and impressive resistance to moisture and chemicals.
Polyethylene comes in several densities—including very low density, low density, linear low density, medium density, cross-linked, high density (HDPE), and ultra-high density—each suited for different protective applications. For example, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is favored for heavy-duty truck tarps, industrial container liners, and outdoor storage covers, while lower-density variants are often used for temporary dust covers or lightweight protective sheets.
Polyethylene fabrics are commonly employed in creating protective covers because of their robust strength, long-lasting durability, and resistance to wear, punctures, and UV rays. These water-resistant and weatherproof fabrics are often used to safeguard storage containers, CNC machinery, building materials, agricultural equipment, and temporary structures. Their versatility, affordability, and recyclability make PE covers a leading choice for disposable and reusable protective solutions.
Polypropylene is a synthetic thermoplastic polymer derived from petroleum and is the basis for a notably strong woven fabric called polypropylene yarn. This fabric's durability is attributed to the absence of reactive dyes, which preserves the polymer's integrity, making it resistant to fading, staining, moisture, and mildew. Polypropylene offers superior tensile strength, flexibility, and excellent chemical resistance, which is why it is commonly used in demanding industrial and commercial settings.
The production of polypropylene fabric can vary between woven and nonwoven methods, depending on its intended application. Woven polypropylene is exceptionally strong and ideal for heavyweight protective bags, flood control sandbags, construction site covers, and geotextiles used for ground stabilization. In its nonwoven form, polypropylene fabric is absorbent and effective in uses such as filtration media, painter's drop cloths, dust covers, and wiping cloths. Its popularity stems from its affordability, lightweight nature, flame resistance, and exceptional performance in both wet and dry environments—making it a highly versatile option for protective covering in industrial, agricultural, and medical applications.
Nylon, the pioneering synthetic fiber, is a thermoplastic renowned for its resistance to impact, abrasion, and harsh weather. This material comes in various types, each offering different levels of strength and durability. One of nylon's standout features is its remarkable tensile strength, which rivals that of some metals, making it a popular choice for heavy-duty protective covers and industrial tarps.
Among the many varieties, Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 are especially common, distinguished by the Denier rating system that measures the weight and thickness of fabric threads. Nylon is highly resistant to weather conditions—including rain, sunlight, and temperature fluctuations—as well as biological degradation. It possesses anti-bacterial and anti-mold qualities, making it particularly suitable for long-term outdoor use.
Additionally, nylon is lightweight, easy to manipulate, and highly adaptable, which further enhances its utility in protective covering applications. As a result, nylon fabrics are frequently chosen for outdoor furniture covers, machine and equipment tarps, vehicle covers, and specialty industrial curtains where strength, elasticity, and resistance to the elements are paramount.
When selecting a protective cover for your equipment, machinery, or project site, it's critical to assess the unique requirements of your environment and application. Important considerations include the level of water and moisture resistance needed, exposure to UV and chemicals, temperature extremes, required strength and longevity, fire safety ratings, and whether the cover must meet specific industry certifications (such as OSHA or NFPA). Buyers should also consider factors like breathability, anti-static properties, and the use of antimicrobial finishes if protection from mold and bacteria is essential.
Choosing the right protective cover material can significantly reduce maintenance costs, extend asset lifespans, and ensure compliance with safety standards. Consulting with experienced protective cover manufacturers or suppliers can help you tailor the best material solution for your needs, ensuring maximum performance and cost-efficiency. For large-scale or specialized applications, you may benefit from custom-fabricated covers or engineered textiles designed for your industry's unique challenges.
Industrial sewing is an essential process for manufacturing protective covers, industrial enclosures, and heavy-duty fabric products used in a variety of industries. The fabrication of protective covers—such as equipment covers, machine covers, outdoor furniture covers, and custom-fitted industrial tarps—requires advanced techniques and specialized equipment. Services in this sector include stitching multiple types of materials, precision embroidery for branding or labeling, and embossing which stamps patterns or images onto robust fabrics like cotton duck, canvas, PVC, vinyl, and coated nylon.
Industrial sewing comprises a vast range of highly specialized machines and automated equipment designed to handle the production of virtually any protective cover, weatherproof enclosure, or bulk storage solution. Thanks to this technological variety, manufacturers can deliver custom-designed and precisely fitted protective covers for different brands, machines, and devices—addressing a complete set of customer requirements for both industrial and commercial markets. Below, we explore the most critical types of equipment and technical considerations that define the protective cover manufacturing process, ensuring functionality, durability, and superior product quality.
Industrial sewing machines dedicated to protective cover production are rugged, heavy-duty units engineered to handle dense and high-performance textiles—such as ballistic nylon, Cordura, fire-retardant materials, marine-grade canvas, and UV-resistant fabrics—that are not suitable for standard domestic machines. Built for permanent, high-throughput operation, these machines are made from robust materials and feature strengthened internal mechanisms to minimize downtime due to maintenance.
Unlike their residential counterparts, industrial sewing machines utilize powerful motors and reinforced components, enabling them to operate for extended periods without interruption. This allows for the efficient completion of high-volume production runs, executing tens of thousands of precisely spaced stitches rapidly and accurately—essential for large-scale protective cover manufacturing, custom cover orders, and continuous contract sewing services.
The industrial sector relies on a wide selection of machine styles and functionalities: from single-needle and double-needle lockstitch machines to high-torque walking foot machines, programmable electronic pattern tackers, and flatbed or cylinder-bed configurations. Each machine type is optimized for specific protective cover applications—ranging from flat seams on large tarps to intricate 3D-shaped covers for unique equipment or apparatus. For applications demanding pinpoint accuracy and repeatability, CNC (computer numerical control) sewing technology is increasingly adopted to automate stitches and integrate with digital design files.

The structural strength and longevity of protective covers depend greatly on the quality and engineering of the stitches. Unique industrial sewing techniques are used because protective covers often face harsh conditions—including UV exposure, moisture, abrasion, and fluctuating temperatures—where seams and stitches are critical weak points. Compared to household sewing, industrial machines generate strong, dense, and uniform stitches such as lockstitch, chainstitch, and overlock, all optimized for high-stress or waterproof seams.
Protective covers may require specialized stitch patterns like double-needle seam reinforcements, waterproof stitch sealing, or heavy-duty zigzag stitching. Modern machinery supports programmable stitch settings to ensure cover specifications such as seam strength, elasticity, and leak-resistance are met. By leveraging a broad palette of stitch options and automated controls, manufacturers can tailor the construction of covers to meet exacting technical requirements for industries like automotive, aerospace, agriculture, and marine.
Due to the complexity of variables—including thread type, stitch density, needle configuration, seam allowance, and fabric layering—the industry follows rigorous standards set by organizations like the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). These standards provide manufacturers with guidelines to ensure consistency, pass durability testing, and guarantee the protective cover performs in the field. For more about stitch and construction specifications, refer directly to the ASTM resource pages.
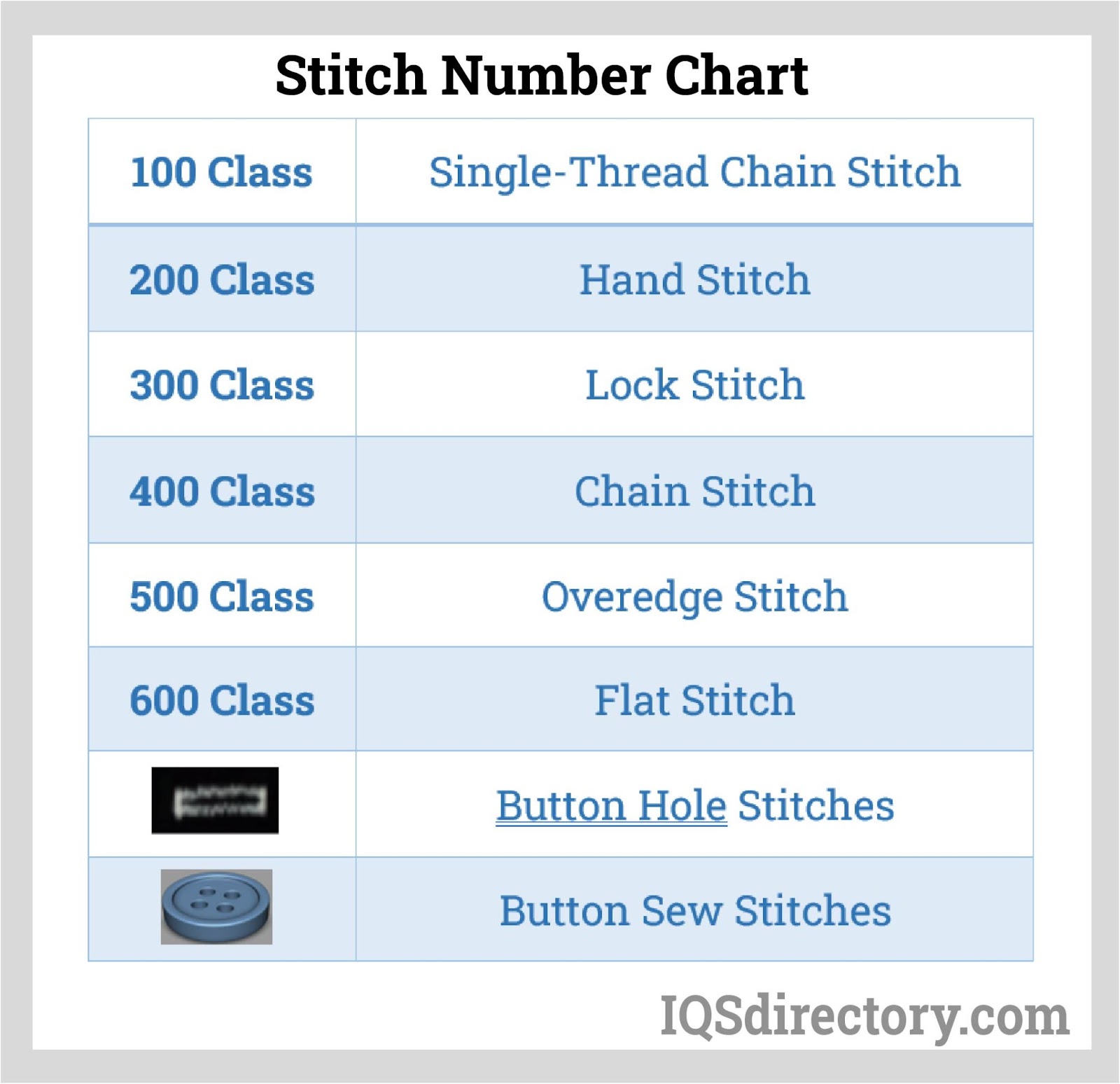
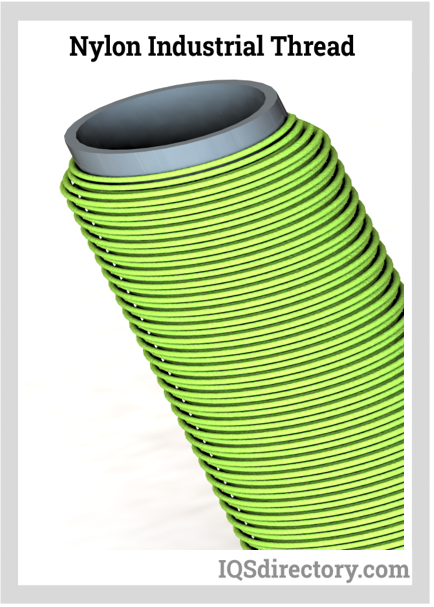
Selecting the right thread is a fundamental aspect of protective cover fabrication, directly impacting product strength, durability, weatherproofing, and chemical resistance. Industrial sewing threads for protective covers are manufactured from advanced materials such as bonded polyester, continuous filament nylon, Kevlar®, or PTFE thread for maximum resistance to UV degradation, moisture, or harsh chemicals. Thread thickness— determined by tex or Denier rating—affects both the structural integrity of stitch lines and their compatibility with high-speed sewing machines.
Threads are classified by their tex number (weight in grams per 1000 meters), where higher numbers indicate thicker, more robust thread suitable for stress-bearing seams or outdoor use. Most heavy-duty applications specify threads above 69 tex for extended service life. The Denier system (weight in grams per 9000 meters) and manufacturer ticket numbers are additional measurements commonly referenced. Government specifications may also apply for defense, public safety, or specialty-industry covers.
Thread selection further considers the operational requirements: high-speed, multi-directional industrial sewing typically uses bonded thread with a resin coating to minimize friction, heat, and fraying during continuous operation. In lower-speed or specialty processes, non-bonded thread, known for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness, may be ideal. Ultimately, optimal thread choice ensures that custom protective covers withstand applications ranging from indoor dust covers to exterior weatherproof enclosures for construction equipment or agricultural machinery.

The choice of thread for manufacturing protective covers also depends on the following factors:
In addition, manufacturers must account for environmental factors when selecting sewing thread for protective covers. For example, high-UV or outdoor applications often require UV-resistant or waterproof threads. Specialty threads like anti-microbial or flame-retardant types are also used for protective covers in sensitive environments such as laboratories, food processing, or hazardous material storage.
The industrial sewing process for protective covers demands precision in needle selection and system configuration. Key attributes include needle size, overall length, point configuration, and construction alloy—each matching both the machine model and the precise characteristics of the cover fabric. Proper needle and thread pairing prevents thread breakage, skipped stitches, and fabric damage, ensuring optimal cover quality and seam strength.
Needle systems are identified by a coding convention typically illustrated as two sets of numbers separated by "X" and are further declared on packaging with corresponding size and point specifics. The numeric sizes are available in both metric (35 to 250, corresponding to diameter in 1/100 mm) and US standards (6 to 28), formatted as NM metric size/US size (e.g., 110/18). Choice of a larger needle with an appropriate point type is essential for handling heavyweight or coated fabrics—ensuring consistent stitch penetration and integrity through multiple fabric plies.
Needle points are marked with specific letter codes to indicate the tip’s shape and purpose. The correct needle point ensures the seam structure is compatible with the targeted application, be it for high-strength lockstitch, decorative finishes, or cut-and-sewn waterproof seams. Proper selection optimizes production speed and product reliability, key drivers in industrial sewing for high-performance protective covers.
Some examples of needle points include:

Precision cutting sets the foundation for successful protective cover manufacturing, determining not only the finished product’s fit but also its material efficiency and production speed. Cutting requirements—such as single-ply or multi-layer stacking, complex 3D patterns, or integration of technical reinforcements—are dictated by the end-use application, cover geometry, and type of technical textile.
The market features advanced cutting equipment including automated multilayer cutting beds, CNC digital knife cutters, high-speed CO₂ laser cutting systems, and industrial die-cutting presses. Each technology offers unique advantages: multilayer cutters allow for mass production with minimal waste, digital cutters provide unparalleled accuracy for custom or irregular shapes, laser cutters produce clean, sealed edges (crucial for waterproof covers or synthetic fabrics), and die cutters enable rapid repetition of standardized cover parts.
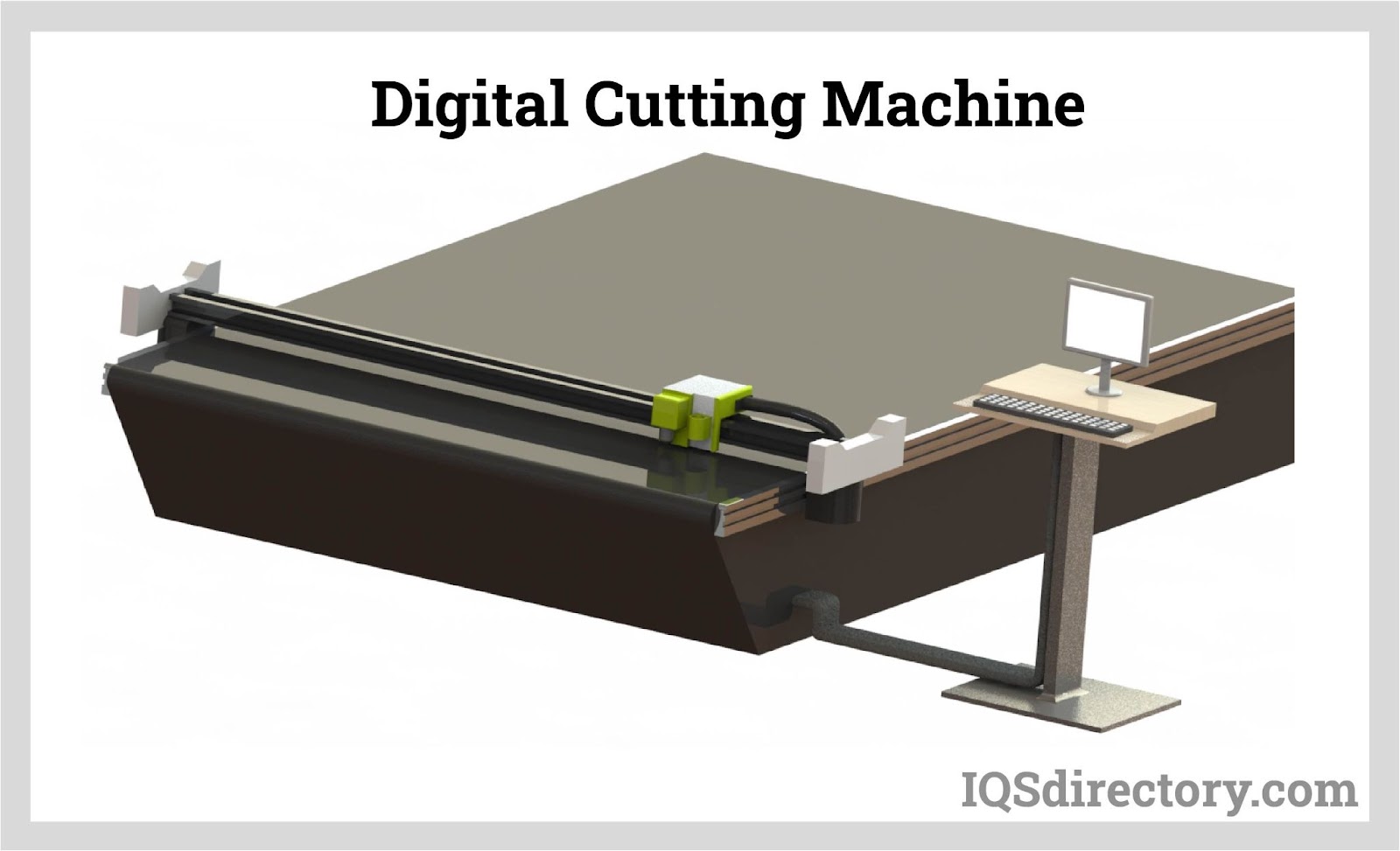
Throughout the manufacturing process, quality assurance protocols—including material inspection, dimensional verification, and seam strength testing—are implemented to guarantee each protective cover meets performance, durability, and safety standards. Custom-made protective covers can include additional features such as reinforced corners, weatherproof zippers, Velcro closures, drawstring hems, and industrial grommets for ease of use and extended life in demanding work environments.
Ultimately, the combination of cutting-edge industrial sewing equipment, quality materials, and strict adherence to engineering standards enables manufacturers to produce protective covers that are reliable, durable, and perfectly suited to their intended applications.
Protective covers play a crucial role in safeguarding inventory, assets, and machinery across various industries and manufacturing processes. Their effectiveness hinges on their design, which must be tailored specifically to ensure comprehensive protection for the equipment.
Design patterns are developed using computer-aided design (CAD) software, which incorporates the specifications of the items to be shielded. A 3D visualization of the proposed design provides an initial view of the protective cover and its final look. This digital model guides the cutting, sewing, and production of the cover material. Below are examples of items that typically require such protection.
The technical nature of CNC machines requires that they be protected from liquids and potentially-harmful particulates. The natural inclination to protect such delicate equipment is to use shrink wrap fit comfortably over a CNC machine. Due to where CNC machines are located and the industrial environment they operate in, however, shrink wrap is not sturdy enough to offer the best protection.
To enhance security and durability, CNC machines should be equipped with covers made from materials that precisely match the machine’s configuration and include a zipper for easy access. The chosen material for the cover needs to be robust, durable, and resistant to abrasion. It should be able to endure the challenging conditions typical of a manufacturing environment.
It is essential to keep woodworking tools free from debris, dust, and moisture during storage. Exposure to these elements can cause significant wear and tear, ultimately reducing the lifespan of your tools. Sturdy protective covers crafted from tough, breathable materials are ideal for safeguarding your woodworking equipment and minimizing potential damage.
The breathable nature of these covers helps prevent rust by using durable, coated cotton duck fabric that effectively reduces moisture build-up and condensation. These adaptable covers are perfect for protecting saws, planes, sanders, drill presses, and lathes.

A protective boat cover serves to shield the vessel from moisture accumulation and debris, while also offering protection against harmful UV rays. By using a boat cover, you can help preserve the boat's condition and extend its lifespan. There are different types of boat covers available, from those designed to cover key areas of the boat to options that provide full coverage. Most boat covers are crafted from polymer fabrics, which allow for a snug and even fit over the boat.

Car covers have gained significant popularity as an effective way to safeguard a vehicle's finish in various weather conditions. Over time, exposure to the elements can lead to noticeable wear and tear on both the exterior and interior of a car. Car covers offer a convenient and efficient means of protecting a vehicle, helping to preserve its appearance and extend its lifespan.
One of the main concerns for car owners is rust, making a protective car cover an essential item. Covers made from polymer materials offer excellent moisture resistance. Similar to boat covers, these car covers are crafted from polymers and are designed to be weatherproof.

Protective covers for equipment are among the most specialized, as each piece of equipment requires a uniquely tailored cover based on its specific needs and usage conditions. These covers are essential for safeguarding delicate equipment from environmental factors and varying atmospheric conditions. Given the diversity of equipment, these covers must be custom-designed using materials that match the exact specifications and environmental demands of the equipment they protect.
Key features for these protective covers include tear resistance, high tensile strength, strong adhesion, waterproofing, and resistance to low temperatures, decay, mildew, and acids. The durability and robustness of these covers are critical, given the harsh conditions they often face and the high value of the equipment they protect. Consequently, these covers are typically constructed from highly durable polyolefin fabrics.

Protective covers are essential for safeguarding valuable equipment and tools from potential damage. Exposure to dust, dirt, moisture, UV rays, and temperature fluctuations can severely impact the condition and lifespan of materials and equipment. By using protective covers, you can shield these items from harmful elements, thereby extending their longevity. Below, we explore some of the key benefits and protective features that these covers offer.
Prolonged exposure to environmental factors like water and salt can lead to rust and corrosion, weakening metals and rendering machinery inoperable. Moreover, UV radiation from the sun can deteriorate plastics and composite materials, leading to fading and cracking.
Heavy-duty protective covers are specifically engineered to shield against sunlight, repel moisture, and create a robust barrier against environmental damage. Their strength and resilience help extend the life of materials and equipment, ensuring they remain in good condition for longer.
Temperature fluctuations can have a detrimental impact on machinery and equipment. Repeated cycles of expansion and contraction can lead to warping, cracking, and other forms of material damage. Sensitive instruments and electronic components are particularly vulnerable to extreme heat.
A protective cover acts as an insulating layer, helping to stabilize the temperature around the equipment and reducing the adverse effects of temperature variations and climatic changes.
Among the various threats to machinery, particulates pose one of the greatest risks, often because they are so small and difficult to detect. These fine particles and dust can penetrate electronic controls and instruments, leading to scratches, etching, and damage to control boards. An accumulation of these tiny particles can also increase the risk of fire hazards.
To protect against particulate damage, a protective cover acts as a shield for the equipment, blocking out external elements and safeguarding against potential harm.
During transportation, equipment faces exposure to flying debris, moisture, road grime, and various environmental conditions. These uncontrolled factors can inflict significant and lasting damage on equipment, making it essential to use strong, secure, and fully sealed coverings to protect it.
Storing equipment, whether in a warehouse or outdoors, carries a substantial risk of causing permanent damage. Protective covers offer a cost-effective, preventative measure against these risks, crafted from lightweight, durable, flexible, and securely fitted fabric.
Protective covers are constructed from durable fabrics engineered for longevity. They are highly resistant to chemicals and can effectively prevent degradation, corrosion, wear, and mildew accumulation.
The synthetic fabrics used in making protective covers are designed to stretch and adapt to the contours of the equipment while maintaining their original strength and durability.
A primary purpose of protective covers is to guard against water damage and prevent water accumulation. Often, this is the main reason for their use.
Protective covers are available for virtually any set of conditions, no matter how extreme or potentially harmful. This versatility is what makes them an essential tool. They are user-friendly, simple to clean, and highly durable. Designed to withstand years of use without tearing, rupturing, or cracking, their resilience makes them an ideal solution for safeguarding products.


A canopy is a structure with a connected fabric or metal covering that can give shade or shelter from weather elements such as the sun, hail, snow, and rain. For example, a tent with no floor can be...

Contract sewing is a specialized industry that provides services to manufacturers for production of a wide range of products using highly skilled workers and technologically advanced sewing machines. The strength of the contract sewing industry is its ability to perform any type of sewing services...

Cut and sew is a process for the manufacture of clothing where the design and pattern are printed on the raw cloth from which the garment is cut, ensuring full color, edge to edge print of the design and color...

A carrying case is a way of conveniently organizing and transporting a collection of similar or dissimilar items for future use. There is a type and kind of carrying case to fit every possible application from protecting and storing cell phones to cases for speaking systems and technical equipment...
Contract manufacturing is a business model in which a company hires a contract manufacturer to produce its products or components of its products. It is a strategic action widely adopted by companies to save extensive resources and...

A hard case is a type of carrying case that is made from molded plastic, aluminum, veneered or laminated wood, or different types of metals. They are the most secure and durable forms of carrying cases and...

A road case is a ruggedly built, highly functional protective container with varying wall thicknesses that is capable of withstanding the riggers and handling of shipping. They are designed to meet...

A tool case is a portable case designed to organize and protect tools and allow easy access and convenient availability. Standard tool cases can be used when working on a project. In addition, specialty and custom-designed tool cases are...
Cases designed to carry special valuables have been part of society throughout history back to the time of the Egyptians and before. Carrying cases are commonly found in any house stored in a garage, tucked away in a basement, or setting on a shelf...