ISO Standards
Introduction
This article will give a detailed discussion on ISO standards
It is expected that after reading, one should understand:
- ISO Standards: What are ISO Standards and What is ISO Certification?
- How to Obtain ISO Certification
- Common ISO Standards in Different Industries
- Benefits of ISO Certification
- And Much More...
Chapter One: Understanding ISO Standards and Certification
Defining ISO Standards
ISO standards are comprehensive guidelines that cover a variety of management techniques, technological processes, and production procedures, all aimed at enhancing global safety and quality of life. Established in 1947, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) aims to discover best practices for both simple and intricate activities worldwide.
One of ISO's initial tasks was to create a universal measurement system, resulting in the global acceptance of the metric system. Throughout the years, ISO's scope has widened to embrace numerous fields. Today, it comprises standards governing everything from garment manufacturing and wireless connectivity to advanced industrial processes.
The name ISO stems from the Greek word "Isos" (ίσος), signifying "equal." As a global entity, ISO functions to enhance the welfare of people worldwide. It includes 163 member countries, who regularly convene to assess developments in industrial and manufacturing methodologies. During these assemblies, ISO committees and experts propose and deliberate on new standards for ratification.
ISO releases documents containing specifications, guidelines, and standards that companies use to ensure top-tier quality and acceptability in materials, products, processes, and services. Regulatory authorities depend on these standards to evaluate quality. Earning ISO certification communicates to customers, suppliers, and partners that products meet elevated standards of quality, safety, endurance, and eco-friendliness.
The inception of the International Organization for Standardization goes back to a 1946 conference in London, attended by delegates from 25 countries discussing post-war progress and reconstruction. Launching in 1947 with 67 technical and expert committees, ISO has expanded to issue over 24,500 international standards by November 2022, supported by 811 technical committees and subcommittees.

Exploring ISO Certification
ISO certification serves as an official recognition that a company has complied with established quality management benchmarks. For globally-operating companies, ISO certification can help broaden their client reach and improve their brand reputation. Displaying an ISO certification assures stakeholders that the company is reliable, credible, and committed to producing products of superior quality.
The very first ISO standard, ISO/R 1:1951, standardized a reference temperature for industrial measurements. Updated several times, its latest iteration is ISO 1:2002. A pivotal moment in ISO's history occurred in 1987 with ISO 9001's introduction, launching the first quality management standard. With increasing environmental issues in the 1980s and 1990s, ISO also developed ISO 14001 to address environmental pollution and impact concerns.
Numerous industries reap significant benefits from ISO certification. For example, healthcare organizations use it to affirm their commitment to excellent patient care. Likewise, hospitality businesses like hotels and restaurants employ ISO certification to highlight their focus on guest satisfaction.
ISO certification is highly esteemed in fields such as construction, engineering, manufacturing, and technical services, where it demonstrates proof of quality and operational excellence. Customers are more inclined to choose companies with ISO 9001:2015 certification, a standard for quality management systems signaling adherence to stringent quality standards. Such companies often satisfy additional criteria set by regulatory entities.
Obtaining ISO certification involves an extensive evaluation by an outside party to confirm that a company adheres to ISO benchmarks for quality, efficacy, and uniformity. ISO-certified companies are dedicated to delivering high-quality products promptly.
As ISO standards evolve, businesses must adapt their practices accordingly to stay compliant. The core mission of ISO is to elevate safety, quality, and security across various industries, thereby improving both industrial and public welfare.
Chapter Two: How to Receive an ISO Certification?
When a company obtains ISO certification, it has undergone an audit by an independent third party to ensure compliance with the latest quality standards set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The ISO also has a Committee on Conformity Assessment (CASCO) that oversees the certification process and ensures that certification requirements are met.
The Committee on Conformity Assessment creates international standards and guidelines for conformity assessment bodies (CABs) and accreditation bodies (ABs). CABs are responsible for verifying that organizations meet ISO standards through various practices such as testing, inspections, evaluations, audits, and assessments.
An accreditation body is a third-party organization that provides formal recognition of an organization’s capability to perform specific functions. As ISO standards evolve and expand, the number of accreditation bodies has increased to keep pace with the demand. ABs may include laboratories, inspection agencies, and certification organizations, all of which assess the technical competence and reliability of an organization.

To achieve ISO certification, a company must first develop and document its management system to ensure it meets quality standards. Often, ISO consultants are engaged to help with this process, providing guidance through each step. The steps involved in obtaining ISO certification include:
Creating a Management System
In a self-assessment, a business will outline and review its procedures to verify improvements. Each management level will document its processes to ensure they meet ISO standards. Once these processes are documented, they should be circulated for approval and acceptance.
Implementation of the System
To implement the system effectively, it's essential to verify that the agreed-upon processes are executed as specified in the documentation. Success relies on providing adequate training to teams on new methods and maintaining them. Comprehensive reporting systems, management review meetings, monitoring objectives, statistical analysis, inspections, testing, corrective measures, and preventive actions are utilized to gather data and evaluate efficiency. During ongoing reviews, necessary steps should be taken to ensure continuous improvement.
Checking the Efficacy of the System
After making adjustments and evaluations, a third-party organization should be engaged to perform an audit to assess the system's effectiveness. This audit will cover all system aspects to identify issues and verify compliance with ISO standards and procedures. The auditor will make observations, conduct interviews, and review documents to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the management system and provide a detailed report. After the report, corrective or proactive measures will be implemented to address any deficiencies.
Identify the System
Following the audit, the management system documentation will be presented for evaluation. The external auditor's assessment will confirm whether the management system has been implemented successfully and meets ISO requirements. ISO accreditation will be granted once the assessment documents are finalized. As ISO standards evolve, the management system must be audited every three years to maintain its certification. Each audit results in recertification of the business.
Selecting an ISO Consultant
Engaging an ISO consultant is a key part of the ISO certification process and requires careful selection. ISO consultants receive extensive training on the requirements and implementation of standards. They review documents and observe procedures to assist companies in achieving ISO compliance.
As they process data, ISO consultants will recommend the most suitable ISO standards for the organization. After identifying these standards, the consultant will perform a gap analysis to assess the difference between current practices and the necessary ones to meet the chosen ISO standards.
Focused on Results
ISO consultants create a detailed implementation timeline for ISO standards, including process enhancements, internal audit schedules, training sessions, and other key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with the organization’s budget and deadlines. Process improvements and implementations are carefully selected and assessed to enhance the organization's chances of successful ISO certification and future success.
Reason to Hire a Consultant
The process of qualifying for ISO certification is complex and involves several new activities for organizations. A consultant acts as a guide to help the management team navigate the process. Using their expertise, consultants analyze all aspects of the organization and develop a timeline to meet ISO requirements. The level of assistance and resources provided depends on the organization's starting position. The consultant's roles include:
- Advisory: interpreting standards and assisting managers on how to implement them
- Management: managing the implementation
- Implementation: adding resources to complete plans
- Ongoing support: planning routine and on-going activities
Individualized Services
The philosophy, concepts, and values of each organization are unique. An ISO consultant's experience and expertise enable them to tailor their services to fit the specific needs of an organization. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to achieving ISO certification. Consultants adapt their methods to address the actual needs of their clients.
Cost and Schedule
The cost of ISO consulting services varies based on factors such as the organization's size, implementation requirements, employee engagement, and project timeline. Smaller businesses may incur lower costs but require more time, while larger enterprises may face higher expenses due to the complexity and duration of ISO training. The cost typically covers training, audits, and other related services.
Consultant Success
An ISO consultant's resume reflects their achievements and qualifications. They assist organizations at various stages and possess training in management, advisory roles, consulting, and internal audits. Their reputation is built on success rates, past projects, client feedback, industry experience, and documented case studies. Consultants present a detailed action plan along with references from other organizations they have supported.
Relevance and Experience
Consultants play a crucial role in guiding management through the implementation process and act as advisors and internal auditors. Each phase of the ISO certification process requires different skills, including initiating and maintaining ISO efforts. An ISO consultant's effectiveness is assessed based on their work quality, client portfolio, and the level of client satisfaction.
Key factors to consider:
- Experience in the industry: This includes a knowledge of the sector of business to be served and its primary activities.
- Knowledge of management systems: All consultants are trained in management systems, which is a requirement of ISO to qualify as a consultant.
- Support for certification bodies: Having knowledge of various certification bodies is the main function of a consultant and is part of their being certified by ISO.
Chapter Three: What are some common ISO standards used in different industries?
Different sectors of ISO standards follow their own numbering systems, with the most commonly referenced being ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Beyond ISO 9001 and ISO 14001, the ISO numbering system becomes highly specialized and detailed.

ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems
Organizations utilize the ISO 9001 standard to enhance the quality of their products and services while meeting customer expectations. This globally recognized standard specifies the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Over a million businesses and organizations across more than 170 countries have achieved ISO 9001 certification.
ISO 9001 is built on core principles such as a strong focus on customer satisfaction, active involvement from top management, a process-based approach, and a commitment to continuous improvement. The principles of quality management in ISO 9001 provide a comprehensive explanation of these concepts, ensuring that customers receive reliable and high-quality products and services.
The ISO 9001 standard offers a framework and guidelines designed to manage a company with effective practices that meet the needs of consumers and stakeholders. Its guidelines lay out a path to success for customers, employees, and management alike.

Industry Specific Applications of ISO 9001
ISO 9001 includes quality management system standards tailored for particular industries and businesses. These encompass:
- ISO 13485: is for companies that design, produce, install and service medical devices and is used for auditing purposes.
- ISO/TS 54001:2019: applies to electoral services provided by an electoral body.
- ISO/IEC/IEEE 90003:2018: software engineering rules for the application of ISO 9001:2015 to computer software.
ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety
ISO 45001 is a global standard that specifies the criteria for an occupational health and safety management system. It aims to protect employees from work-related illnesses and accidents. The certification is designed to help eliminate hazards that could jeopardize the health and safety of workers and organizations. The International Labor Organization (ILO) reports that over 7,600 people die each day due to work-related illnesses or accidents.
A specialized ISO group focused on occupational health and safety is working to establish a global standard with the potential to save three million lives each year. ISO 45001 was developed with input from OHSAS 18001 and various ILO labor standards, conventions, and safety guidelines, among other occupational health and safety frameworks.
ISO 45001 applies to organizations of all sizes and types. By implementing this OH&S management system, companies can incorporate health and safety practices to ensure the wellbeing of their employees. Additionally, organizations must comply with local and national safety and health regulations, such as those specified by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States.


ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems (EMS)
The ISO 14001 standard defines the criteria for creating and maintaining an Environmental Management System (EMS). It includes guidelines for managing environmental impact, reducing adverse effects, and ensuring legal compliance. Research indicates that up to 70% of office waste can be recycled, yet only 7.5% actually gets recycled. Complementing ISO 14001 is ISO 14004, which provides general guidelines for Environmental Management Systems. This includes principles, systems, and supporting procedures related to the development, implementation, maintenance, and enhancement of an EMS.

Private, not-for-profit, and governmental organizations can use ISO 14001. The certification process provides a framework for putting into effect sustainable practices that are beneficial to all businesses in any sector or field. The implementation of ISO 14001 requires that a company consider all environmental issues that are relevant to its operations, such as use of resources, efficiencies, air pollution, water and sewage issues, waste disposal, soil contamination, and issues in regard to climate change. As with all ISO management system standards, ISO 14001 stresses the need for on-going development of environmental policies and procedures.
Recent updates to ISO 14001 have enhanced the role of environmental management in an organization's strategic planning. These revisions emphasize greater leadership engagement and a stronger commitment to proactively enhancing environmental performance.
Following the practices outlined in ISO 14001 has been effective for businesses in reducing water and energy consumption, improving compliance with regulations, and boosting overall environmental performance. ISO 14001 focuses on identifying, managing, monitoring, and controlling environmental issues. Its objective is to promote environmental conservation by recommending the use of renewable energy sources over fossil fuels.

ISO 13485: Quality Management Systems for Medical Device Manufacturing
ISO 13485 addresses the production of products intended for diagnosing, preventing, or treating medical conditions, including devices, machines, implants, and in vitro reagents. It is a management system standard tailored specifically for medical device manufacturing and is based on the ISO 9001 process model. The primary aim of ISO 13485 is to standardize regulatory requirements for medical devices, including their production, installation, and maintenance.
ISO 13485 is targeted at organizations involved in the development, manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of medical devices. It is also utilized by certification bodies to support their auditing processes. Organizations holding ISO 13485 certification are viewed as more reliable and credible. The standard is revised and updated every five years to reflect new standards and industry needs.

ISO 22000: Food Safety Management Systems
ISO 22000 aims to enhance food safety management systems across the food industry, helping organizations improve their performance in ensuring food safety. The standard is designed to provide a framework for maintaining food safety on a global scale.
ISO 22000 is applicable to any organization within the food industry, ranging from farms and producers to restaurants. Obtaining ISO 22000 certification demonstrates to clients and customers that the business has a robust food safety management system in place, assuring them of their protection.

Implementing ISO 22000 involves establishing interactive communication, managing systems, and applying prerequisite programs alongside Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles. This ensures that all potential food safety risks are identified and controlled at each stage of food processing, with ongoing communication throughout the process.
Effective communication helps both customers and suppliers understand the requirements for proper food handling. ISO 22000 builds upon and complements the key elements of ISO 9001, providing a comprehensive framework for developing, implementing, monitoring, and enhancing a documented Food Safety Management System (FSMS).
ISO 22000 certification requires adherence to proven HACCP practices and good manufacturing principles, which are essential for maintaining food safety. HACCP is internationally recognized for its effectiveness in addressing safety concerns within production environments and ensuring the production of safe food products. The standard mandates that food producers integrate all relevant statutory and regulatory food safety requirements into their systems.

ISO 27001: Information Security Management Systems
The ISO 27001 standard provides a framework for safeguarding an organization's confidentiality, integrity, and privacy while complying with local and national regulations. It covers the protection of sensitive information, including customer and employee data, confidential brand information, and proprietary processes. This accreditation is based on a process-oriented approach for establishing, implementing, managing, and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
With increasing concerns about the security of detailed information and data held by businesses, companies, and medical organizations, stringent legislation is being enacted to prevent unauthorized data releases. ISO 27001 addresses these concerns by aligning with government-imposed guidelines and regulations.

Implementing ISO 27001 is an effective strategy for addressing consumer concerns and meeting legal obligations, especially in preparation for potential security threats like cybercrime and data breaches. Achieving ISO 27001 accreditation showcases a company's dedication to adhering to industry best practices in information security. The accreditation process offers a professional evaluation of a company's information security measures.
ISO 50001: Energy Management Systems
ISO 50001 was developed to focus on optimizing energy usage, conserving resources, and enhancing financial performance through effective energy management. The ISO 50001 framework supports the creation of policies for more efficient energy use, establishing objectives and methods to meet those objectives, analyzing data to guide energy decisions, measuring outcomes, evaluating implemented policies, and fostering ongoing improvements in energy management.
Obtaining ISO 50001 certification demonstrates an organization's dedication to continuous improvement in energy management. This certification process allows companies to significantly advance their energy management strategies and ensures adherence to local, national, and international regulatory standards.

The ISO 50001 standard benefits organizations of any size by providing a practical approach to reducing energy consumption through the establishment of an energy management system (EnMS). Enhanced resource management leads to fewer regulatory reporting requirements by reducing claims, returns, reprocesses, and rejections.
Depending on the business type and energy requirements, implementing ISO 50001 may necessitate the use of energy monitoring systems. While the primary objective of ISO 50001 is to achieve energy savings, it also offers substantial cost savings through enhanced energy efficiency.

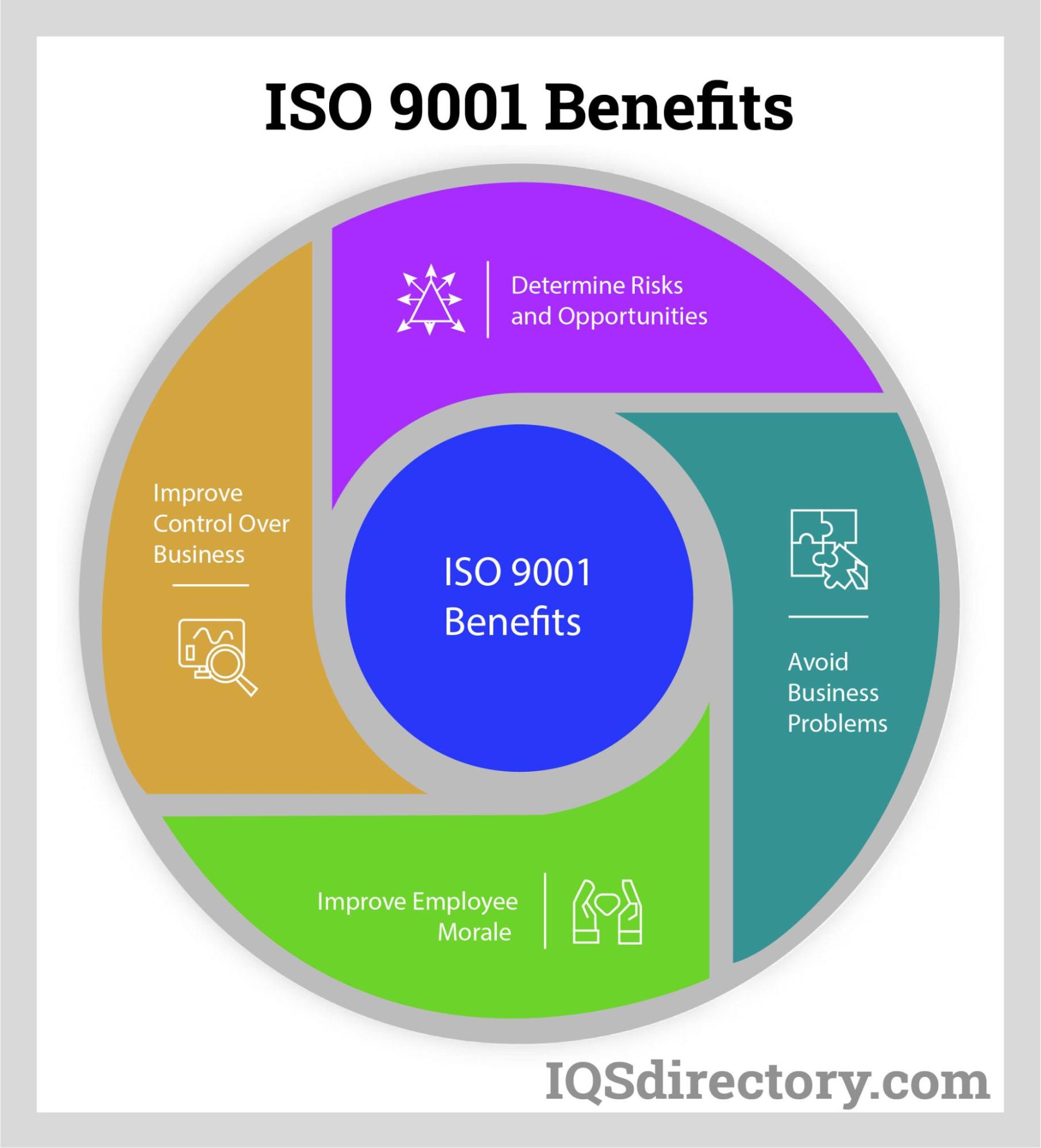
Chapter Four: What are the benefits of ISO certification?
ISO documentation provides specifications, guidelines, practices, and processes that organizations can utilize to guarantee that materials, products, procedures, and services meet the highest quality standards. Guidelines for information security, food safety, risk management, environmental performance, and quality management contribute to enhancing a company's reputation and credibility. Adhering to ISO standards ensures excellence, consistency, and safety.
The benefits of ISO accreditation:
- Reliability: An ISO accreditation shows a company’s dependability to customers, suppliers, business partners, and the government as well as its dedication to the quality, safety, and durability of its goods and services. Included in ISO accreditation is a demonstration of adherence to and meeting the requirements of international laws and regulations as well as a commitment to excellence.
- Enhanced efficiency: To adhere to ISO standards, companies describe, record, and track their processes to determine their goals and track their development. ISO accreditation provides companies with the knowledge to optimize their operations and boost performance. Following the ISO process helps people to work effectively and efficiently, as well as to adopt new working methods quickly and successfully.
- Superior quality: ISO standards enable companies to improve the quality of their services and manage projects efficiently to reach new markets. The display of the ISO emblem promotes consumer confidence since it is associated with reliability and high quality. Compliance with ISO standards gives clients faith and confidence in a company’s goods and services.
- Better quality control: ISO complaint management and client satisfaction monitoring standards keeps clients and customers happy and reduces consumer complaints, an important advantage of ISO certification, according to research.
- Increased income: ISO certification allows a company to market its quality, which leads to an increase in revenue and sales. Large businesses demand that suppliers have an ISO certification, which is crucial for businesses looking to expand into international markets. ISO standards have become more important as world markets become more interconnected in regard to the movement of goods, services, and logistical technologies. The finest performance outcomes occur in businesses that consistently strive to enhance operations.
- Risk mitigation: The ability to anticipate hazards and turn them into opportunities is a key advantage of ISO standards. The requirements guarantee and awareness of methods for risk management and risk reduction. When issues do develop, businesses are prepared to handle them and recover quickly.
- Sustainability: In recent years, sustainability has become a major concern for companies as they focus on how their operations will affect future generations. ISO standards assist by showing an organization's commitment to addressing environmental and social issues. Businesses save money, boost their reputation, and address environmental issues by examining how they use their resources and energy as well as the quality of their waste management practices.
- Innovation: A practical outcome of ISO certification is a business’ ability to see its processes and develop new and innovative ways to approach problems. The energy and system improvement provided by ISO certification opens communications and empowers all members of an organization.
- Applies to all business sizes and types: A primary goal of the ISO is to help companies improve, regardless of their size, function, and sector. If the world is to properly deal with the issues of climate change and industrial pollution, it needs a set of standards as a guide and touchstone, which is what the ISO provides.