AC Power Cord

An AC power cord is a detachable way of providing an alternating current of electric energy from a mains power supply to an electrical appliance or equipment. Serving industries like...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article takes an in-depth look at the types of electrical plugs.
Read further and learn more about topics such as:
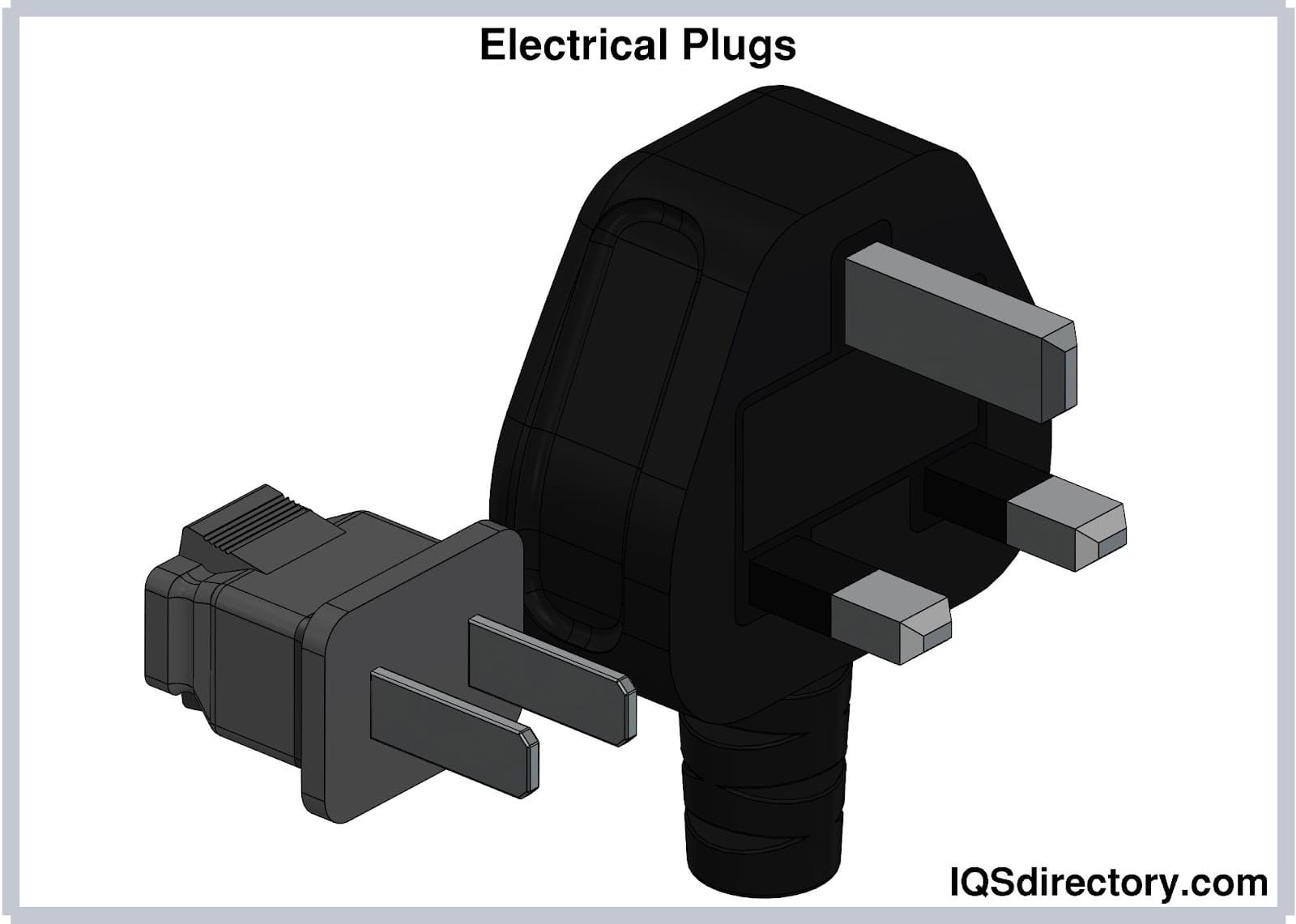
Electrical plugs, commonly known as power plugs, are essential for facilitating the flow of electrical current from a receptacle to an appliance's internal circuits.
Typically composed of prongs or pins housed within a plastic frame or casing, these plugs are designed to fit into outlet sockets or receptacles. This allows for a secure connection between the device and the main electrical supply.
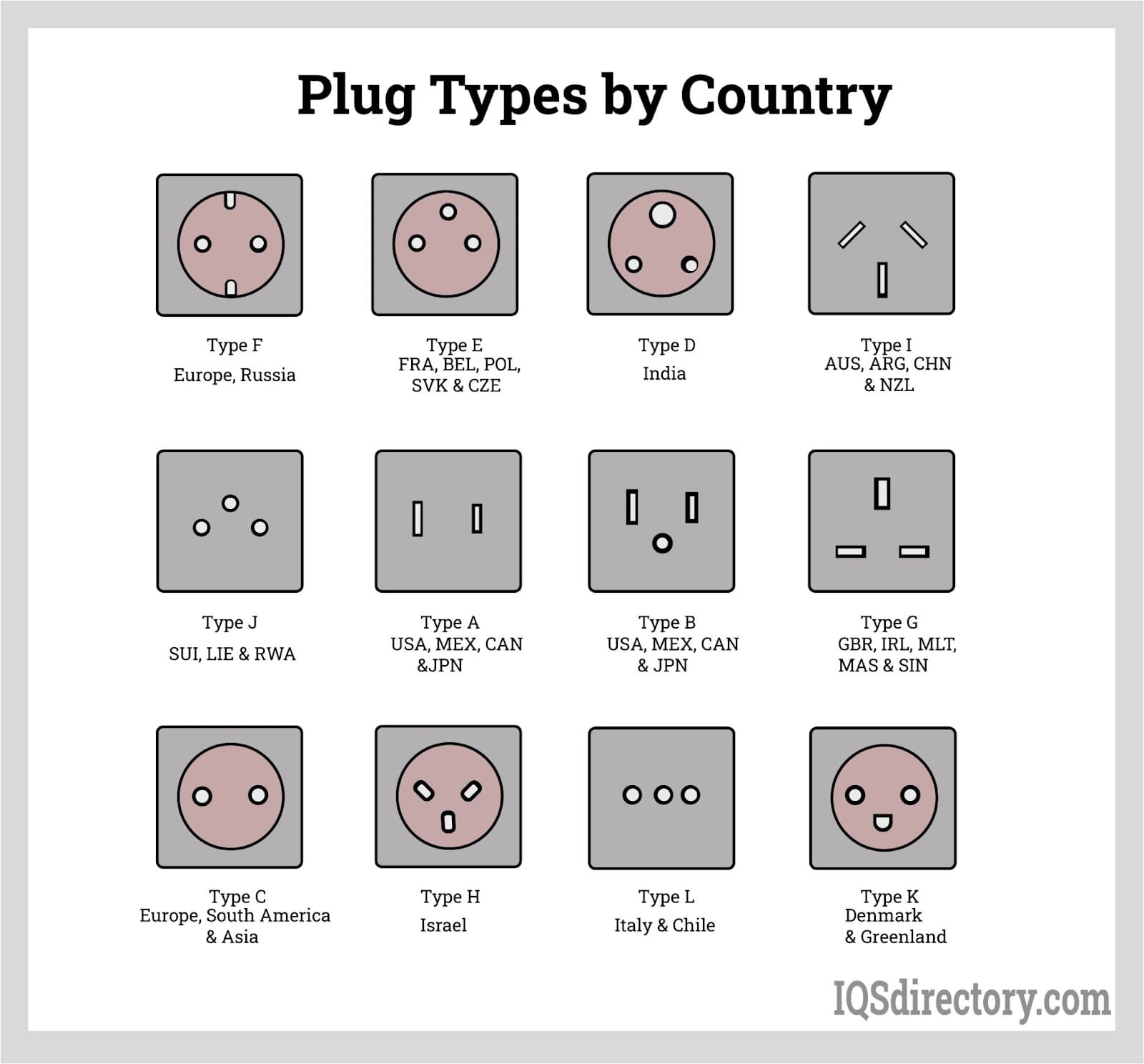
Standard electrical plugs are available in a variety of types globally, suited for residential, industrial, and commercial applications. Their design can differ in the number and size of pins and in voltage and current specifications, which are often dictated by the country of use.
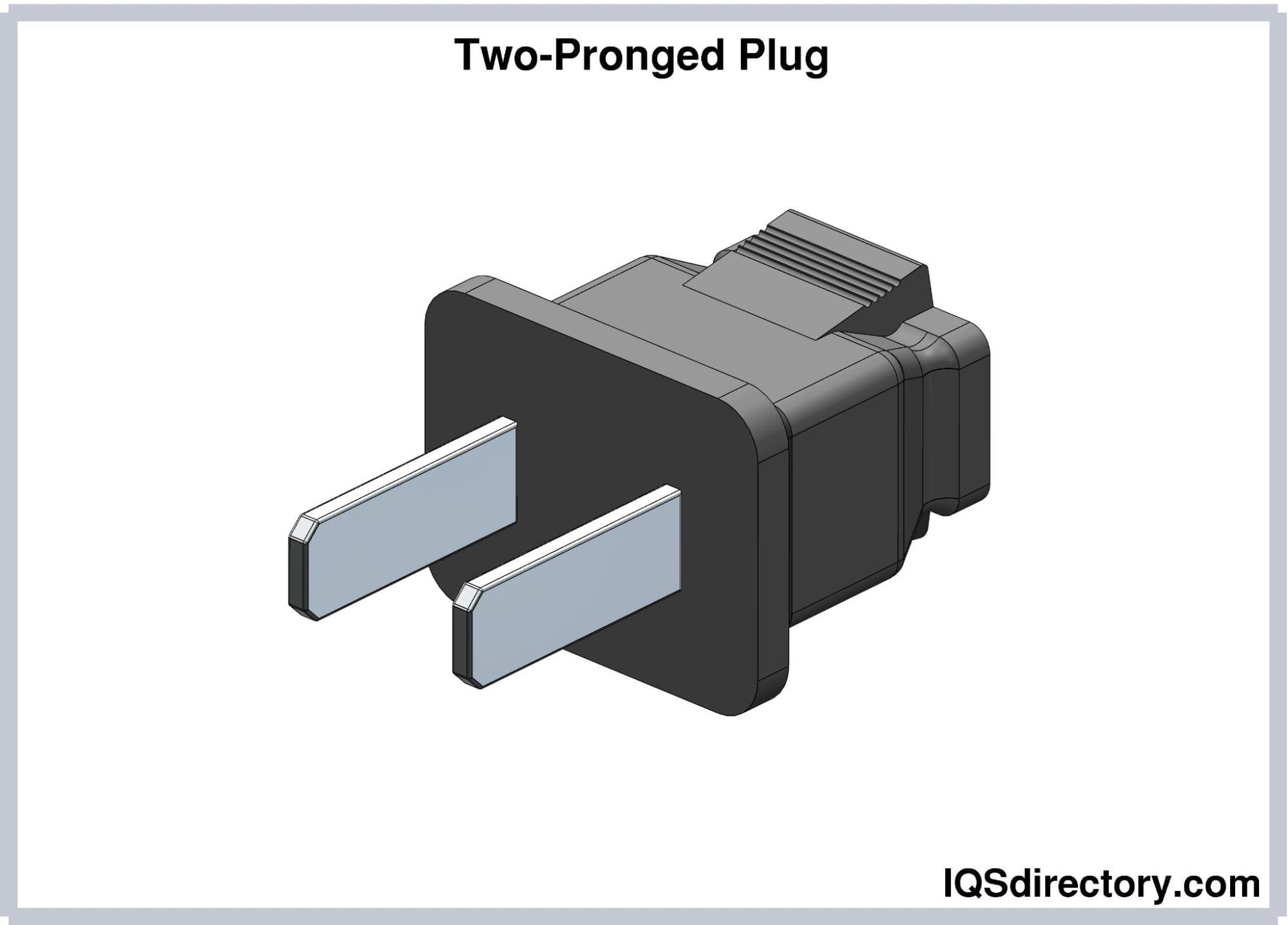
Electrical plugs typically feature either two or three prongs:
Two-pronged plugs feature one prong for the "hot" connection and another for the "neutral" connection. The hot prong connects to the hot slot of the receptacle, drawing current to power the load. The neutral prong connects to the neutral slot, returning the current to the receptacle and completing the circuit. These plugs can be easily inserted into two-slot receptacles.
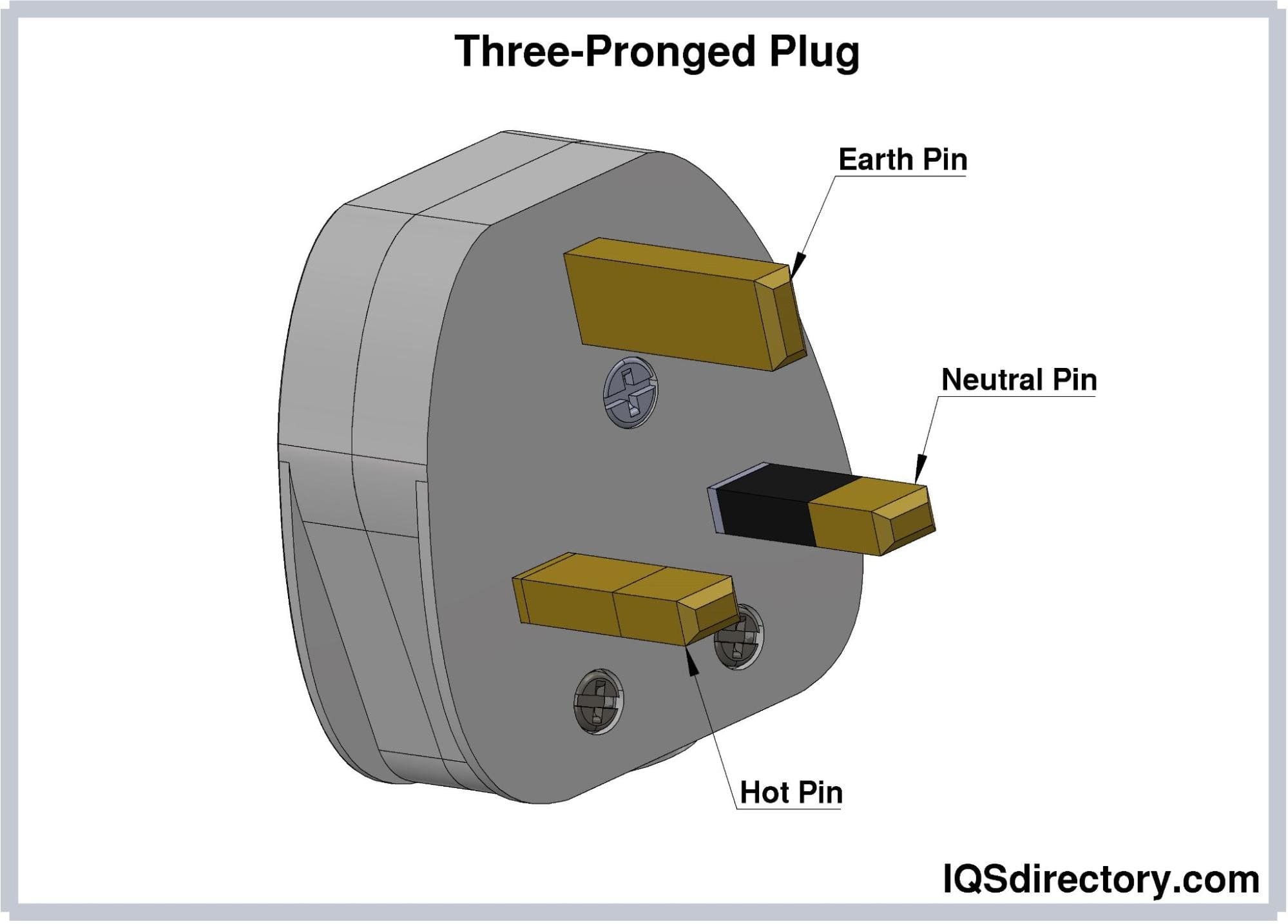
Three-pronged plugs include an additional grounding or earthing pin, which is connected to the electrical system’s ground wire. This pin is positioned below the hot and neutral pins and does not carry current under normal conditions. The grounding pin is a safety feature designed to direct stray electricity away from the appliance in case of a fault, short circuit, or surge. It channels excess current to the ground, preventing electrocution, electrical fires, and damage to the appliance. Today, three-slot receptacles are commonly required in new construction for added safety.
Three-pronged plugs are typically used for high-power appliances such as flat irons, toasters, HVAC systems, industrial machinery, and sensitive electronics. They are also essential for devices housed in metal casings, like computers and game consoles, where stray electricity could potentially cause shock. The grounding pin helps to safely redirect any stray current away from users.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) recognizes fifteen (15) standard types of mains electrical plugs globally, as outlined in the IEC 60083 standard. Each plug type is assigned a letter designation, and we will explore these types in detail in the following sections.
NEMA plugs adhere to the standards and specifications established by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), a leading trade association for electrical and medical imaging equipment. While NEMA standards are widely used in North and Central America, they are also adopted in other regions. NEMA designates several plug types, including Type A and Type B.
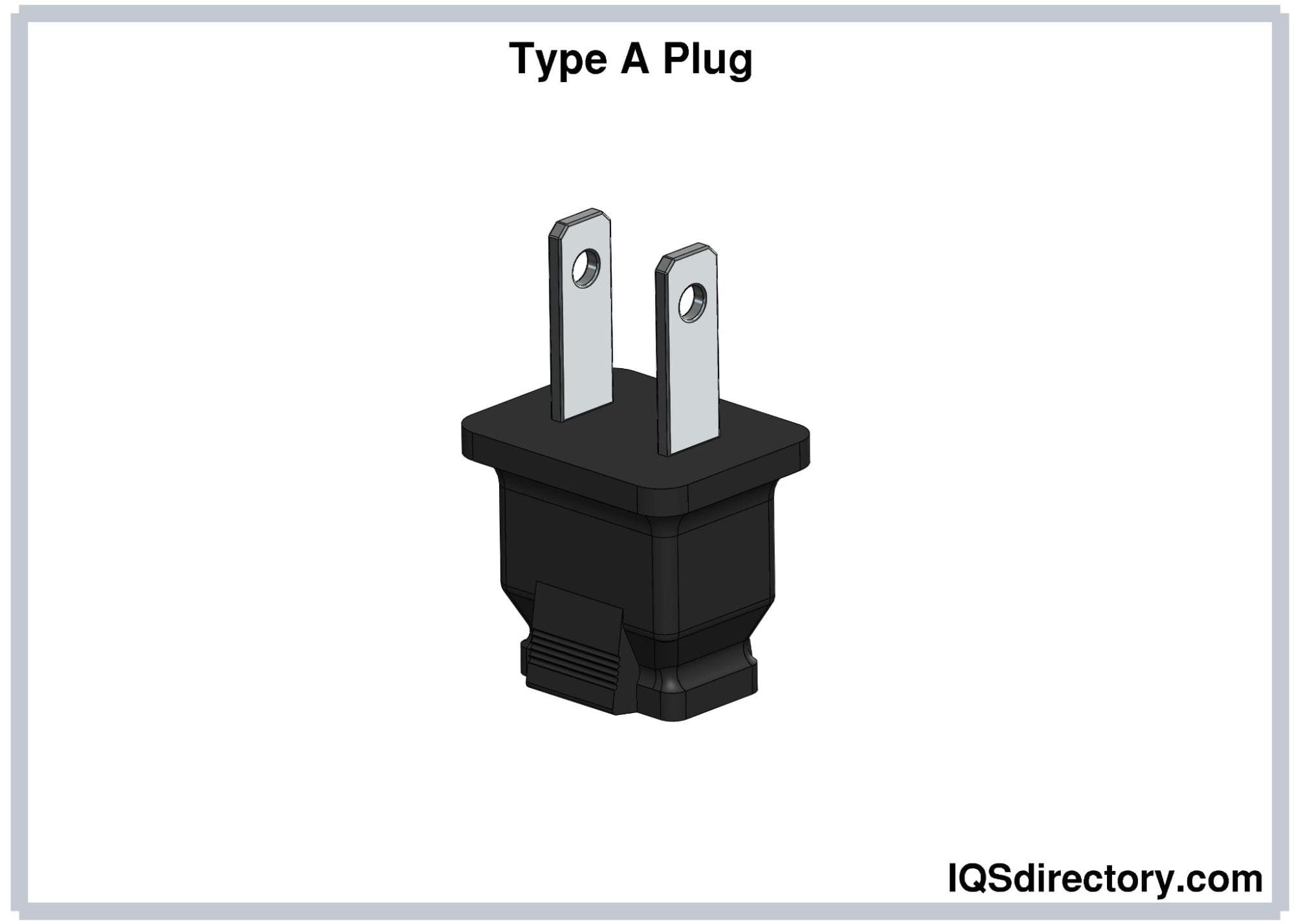
Type A electrical plugs are ungrounded and feature two flat parallel prongs. They have a current rating of 15A and a voltage rating of 125V. The prong length ranges from 15.9 to 18.3 mm, with a spacing of 12.7 mm between the prongs.
Type A plugs come in both polarized and non-polarized versions. Polarized plugs feature a neutral pin that is wider than the hot pin, ensuring they can only be inserted in one orientation. These are commonly used in North America and Mexico, with the neutral and hot pins measuring 7.9 mm and 6.3 mm in width, respectively. Non-polarized plugs, which have prongs of equal width, are prevalent in Japan. While non-polarized plugs can fit into polarized sockets, the reverse is not true. Type A plugs are compatible with both Type A and Type B sockets.
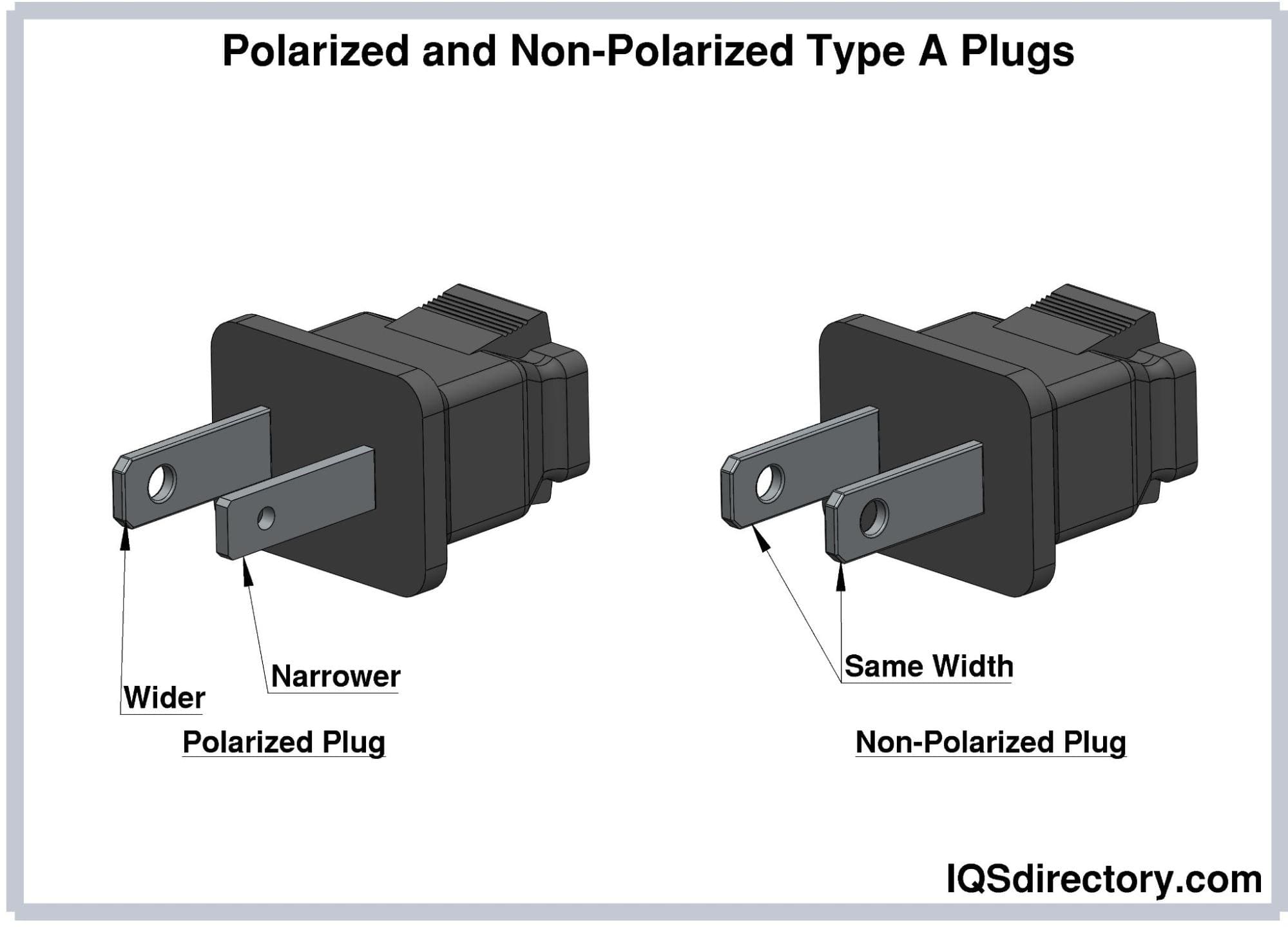
Type A plugs feature holes near the tips of the prongs. When the prongs are inserted into the receptacle, bumps on the outlet’s contact wiper fill these holes, ensuring a secure connection and preventing the plug from dislodging due to its weight. In certain specialized sockets, a rod can be inserted into these holes to lock the plug in place. Additionally, these holes can be used for factory sealing purposes.
Some sockets use spring-action blades instead of a contact wiper. These blades grip the sides of the prongs, making the holes in the prongs unnecessary for securing the plug.
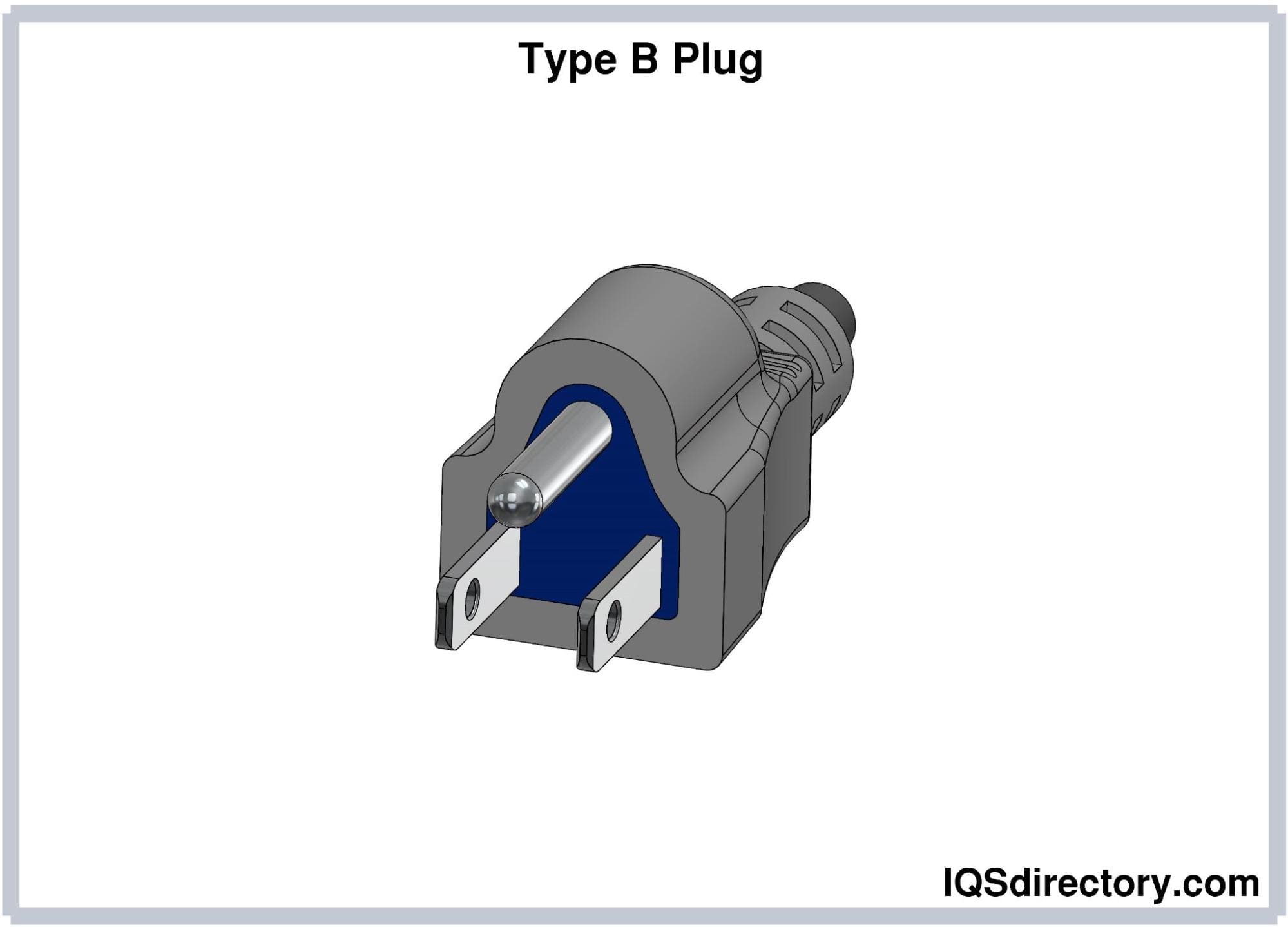
Type B electrical plugs, also known as the North American 3-pin plug, are grounded and feature two flat parallel prongs along with a round grounding pin. The ground pin is longer than the hot and neutral pins to ensure that the ground connection is established before the voltage connection. The hot and neutral prongs are 1.5 mm thick, 15.9-18.3 mm long, and 6.3 mm wide, while the ground pin has a diameter of 4.8 mm and extends 3.22 mm longer than the flat prongs.
Type B plugs are rated for 15A and 125V and are commonly used in North America, Mexico, China, Japan, and other countries that use Type A plugs. In Japan, Type B plugs have slight design variations compared to those used in the United States.
CEE Publication 7 is the standard titled "Specification for plugs and socket-outlets for domestic and similar uses." Maintained by the IECEE, this standard regulates domestic electrical connectors used across Europe. Notably, countries such as the United Kingdom, Ireland, Malta, Cyprus, Switzerland, and Italy do not use CEE 7 plugs and sockets as their primary power connectors.
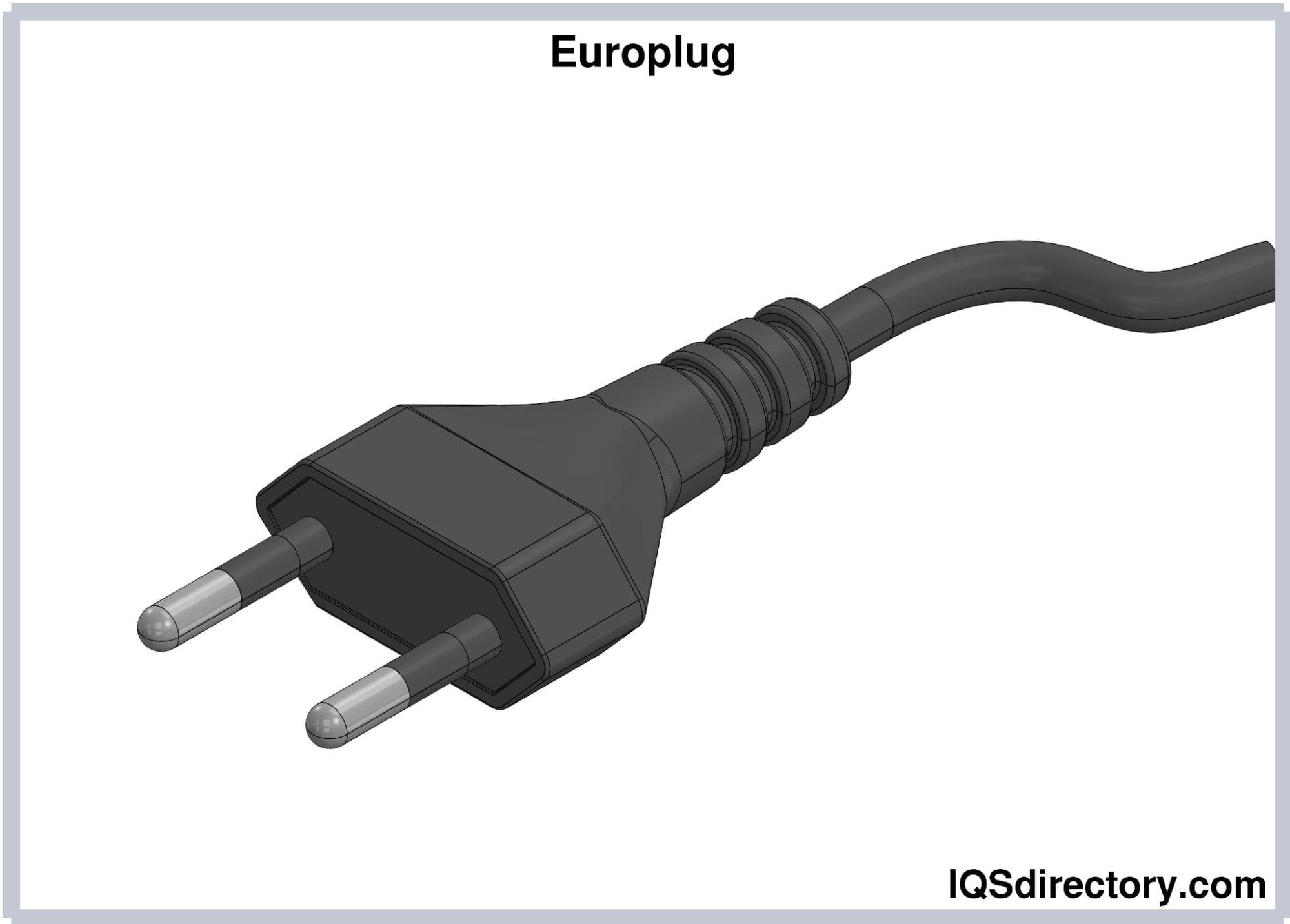
Type C is the most widely used electrical plug globally. It is an ungrounded and unpolarized plug featuring two round pins. There are two variations of Type C plugs:
Europlug (CEE 7/16). Europlugs have two pins measuring 19 mm long and 4 mm in diameter. The pins are 18.6 mm apart from the base and 17.5 mm from the tip. They have an insulated covering 10 mm of their length from the base. The pins are relatively flexible, which allows them to fit in sockets that support rounded pins from 4.0 to 4.8 mm in diameter and whose slots are 17.5-19 mm apart. Europlugs are rated with 2.5A; the low current rating limits the Europlug to low energy applications.
Europlugs are the more popular type of Type C plugs.
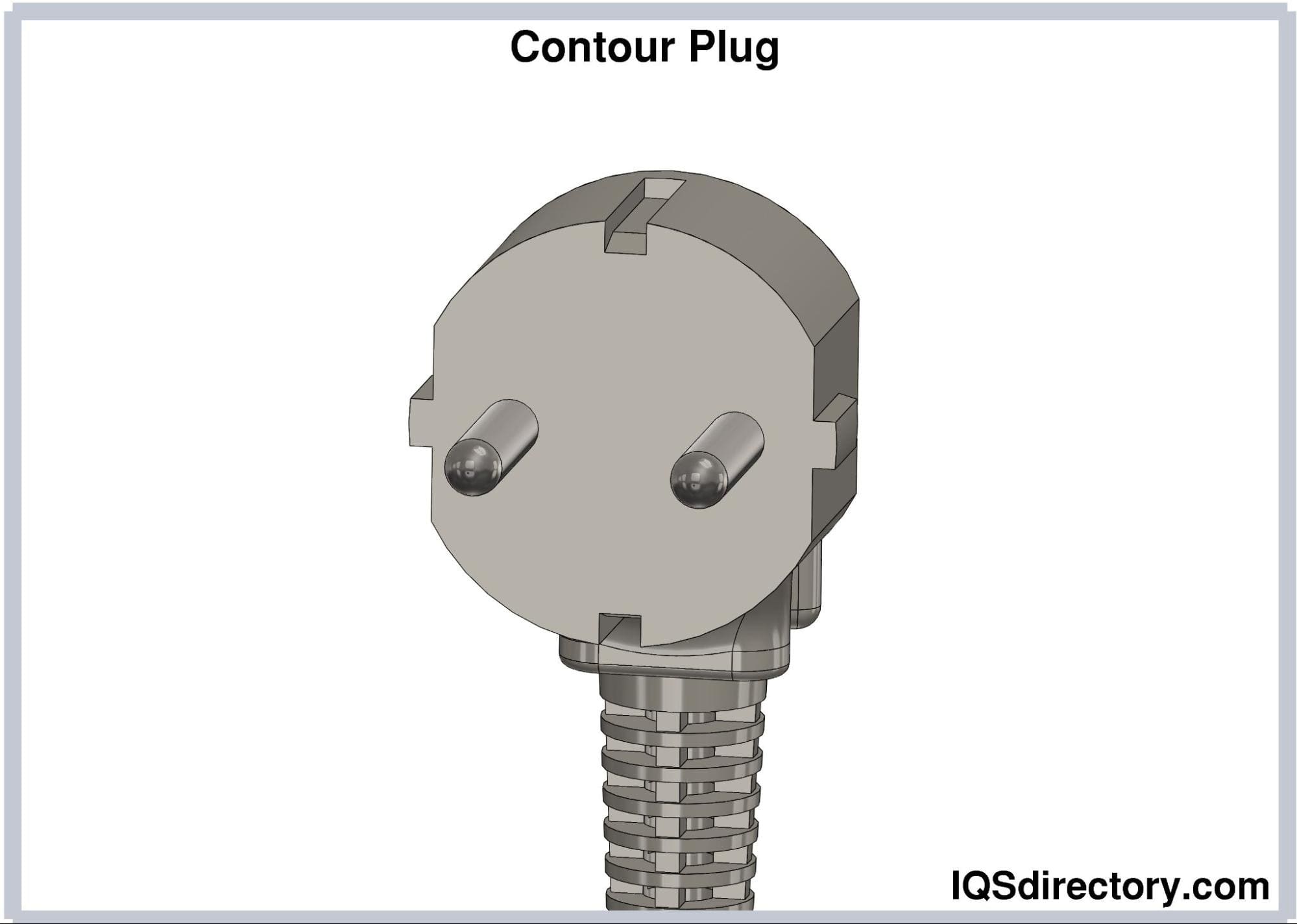
Contour Plug (CEE 7/17). Contour plugs have two pins measuring 19 mm long and 4.8 mm in diameter. The pins are spaced 10 mm apart. Unlike Europlugs, contour plugs do not have an insulated sleeve. The insulated sleeve in electrical plugs makes their operation safer.
Contour plugs are rated at either 10A or 16A; thus, they can be used in high energy appliances.
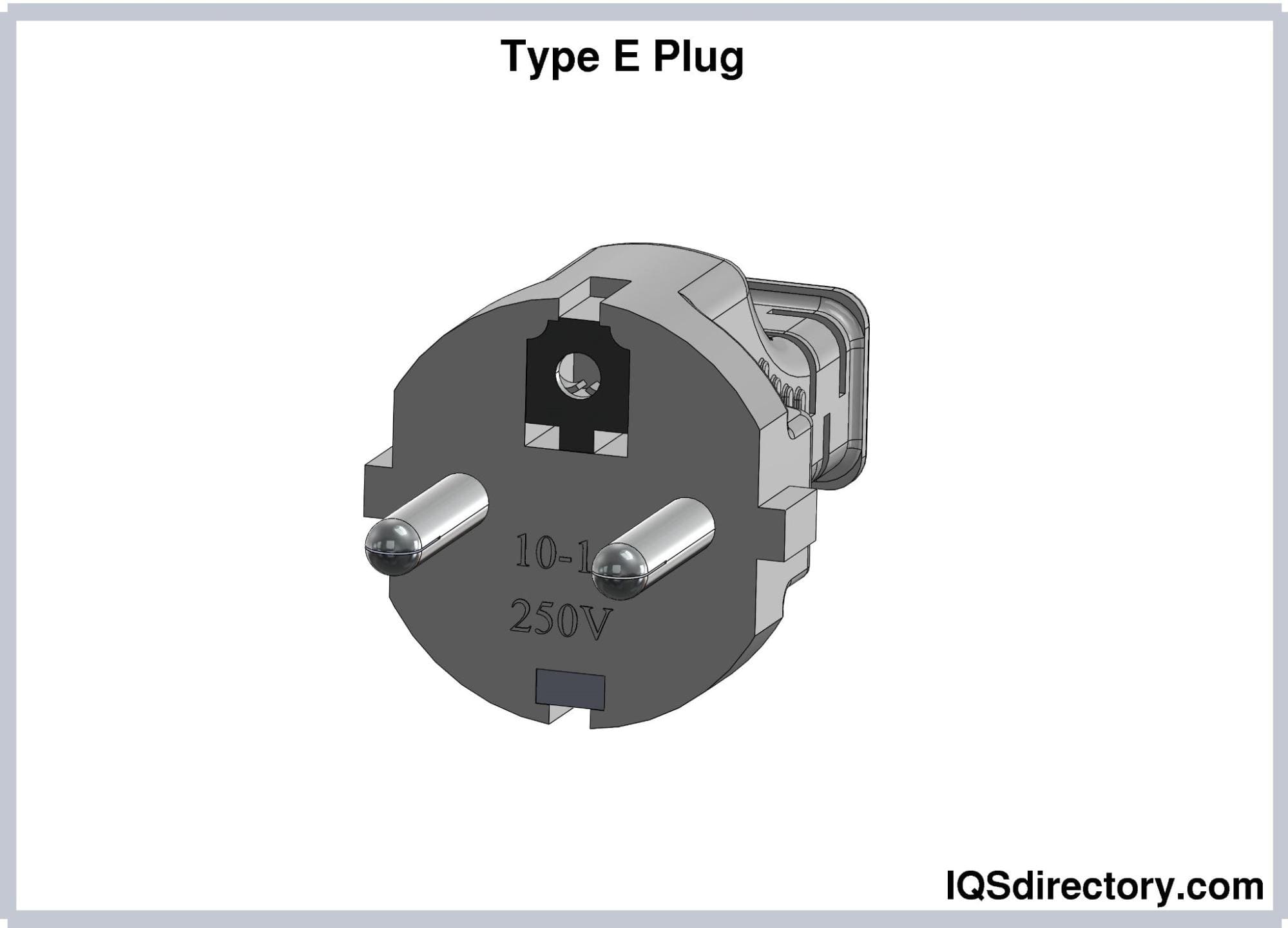
Type E electrical plugs feature two round pins that are 19 mm long, 4.8 mm in diameter, and spaced 19 mm apart. They include a female contact or hole designed to fit the socket’s earthing pin, which is 14 mm long and 4.8 mm in diameter, located beneath the plug pins. The asymmetrical pin arrangement in Type E plugs prevents polarity reversal.
With a current rating of 16A, Type E plugs are compatible with both Type E and Type F sockets. Commonly referred to as “French plugs,” they are widely used in France, Belgium, Slovakia, and Tunisia.
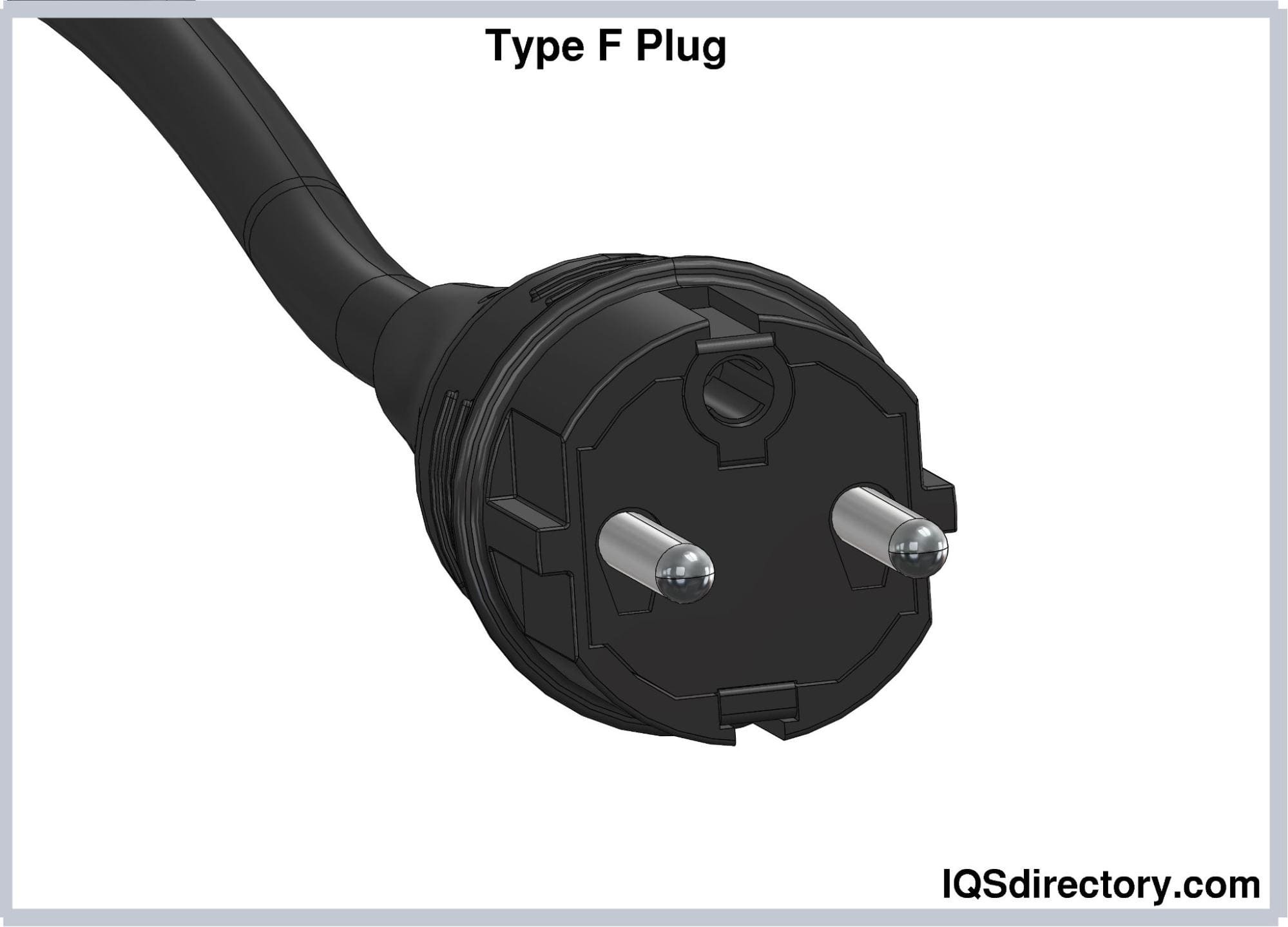
Type F electrical plugs are similar in pin dimensions to Type E plugs, but their pins are not perfectly rounded. Instead of a female earthing contact, Type F plugs feature two earthing clips located on the upper and lower sides of the plug housing, which are positioned 16 mm from the midpoint between the pins. Additionally, these plugs include plastic notches on the left and right sides to enhance stability when used as a built-in plug.
Type F plugs are rated for 16A and are not compatible with Type E sockets. Known as “Schuko plugs,” they are commonly used in Germany, Austria, the Netherlands, and Spain.
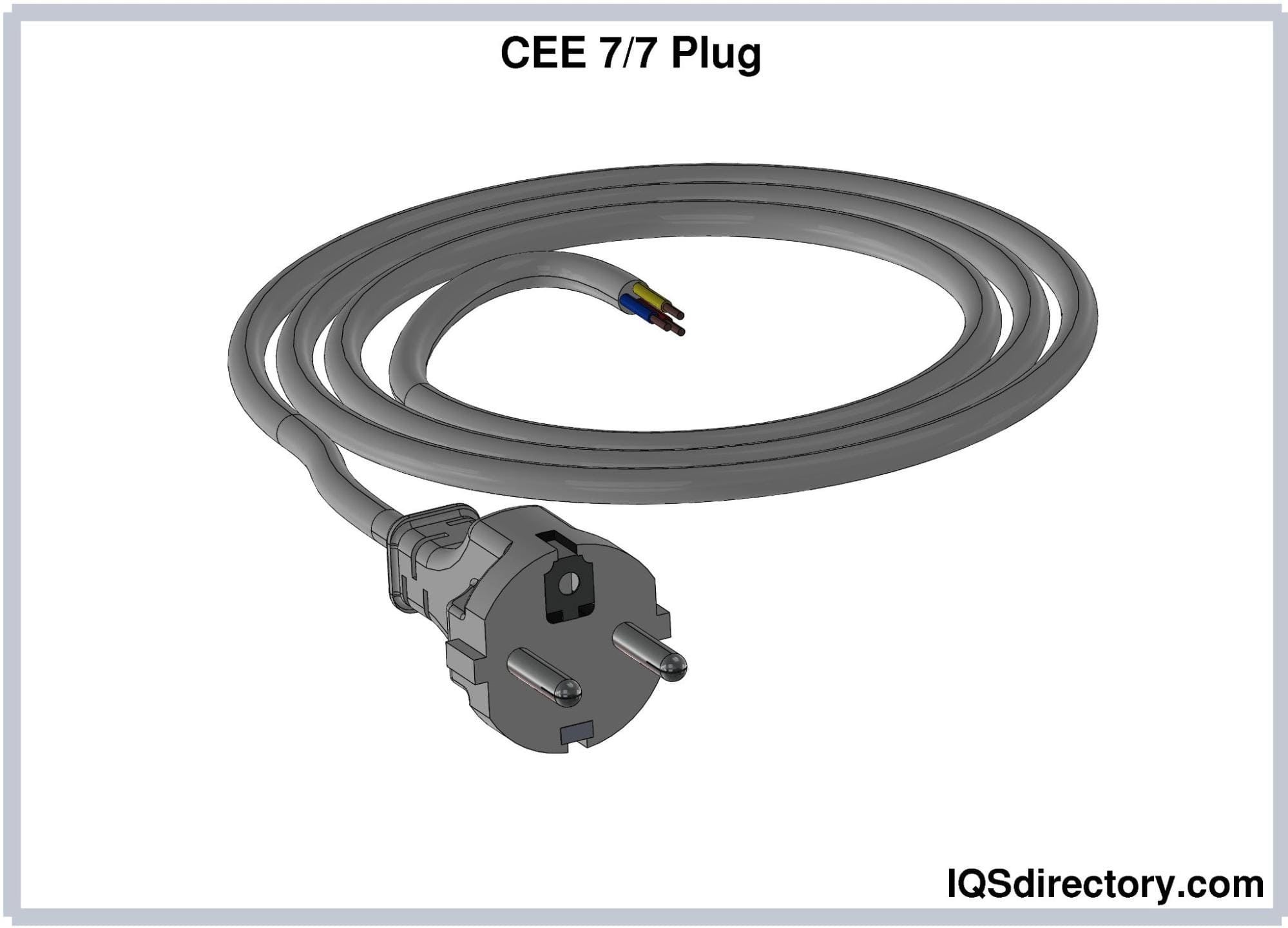
The CEE 7/7 plug is a hybrid design combining features of Type E and Type F plugs, making it compatible with both socket types. It includes a female earthing contact for Type E sockets and two earthing clips on the plug housing for Type F sockets. CEE 7/7 plugs are commonly used in countries where both Type E and Type F plugs are standard.

BS 1363 is a British standard outlining the safety, construction, electrical and mechanical testing, dimensional accuracy, and marking requirements for plug and socket systems in the UK. This standard has also been adopted by other countries, including India, Malta, and South Africa.
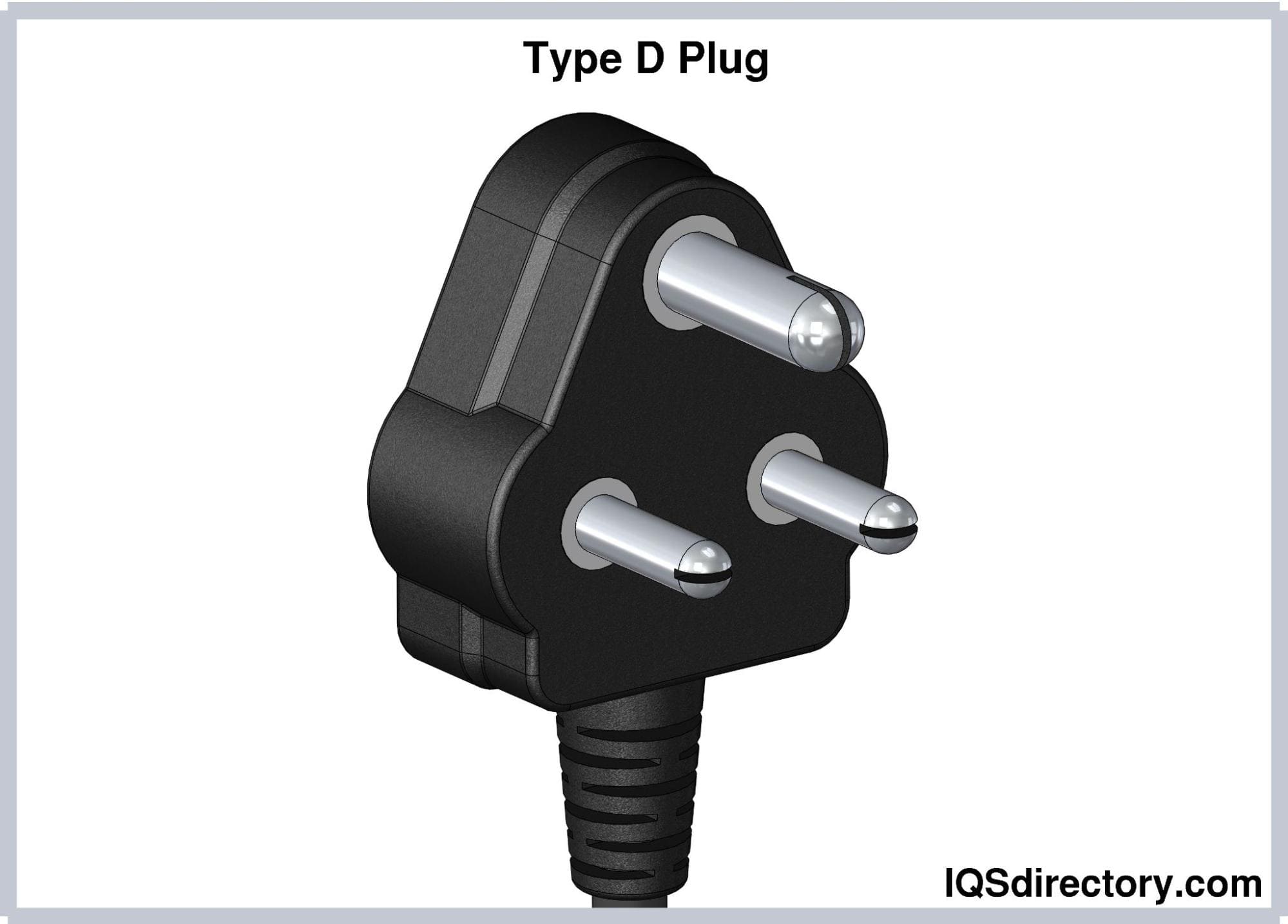
Type D electrical plugs feature three round pins arranged in a triangular pattern. The central earthing pin measures 20.6 mm in length and 7.06 mm in diameter, while the hot and neutral pins are 14.9 mm long, 5.08 mm in diameter, and spaced 19.1 mm apart. The asymmetrical pin arrangement in Type D plugs prevents polarity reversal. These plugs are rated for 5A and are commonly used in India, Sri Lanka, Namibia, and Nepal.
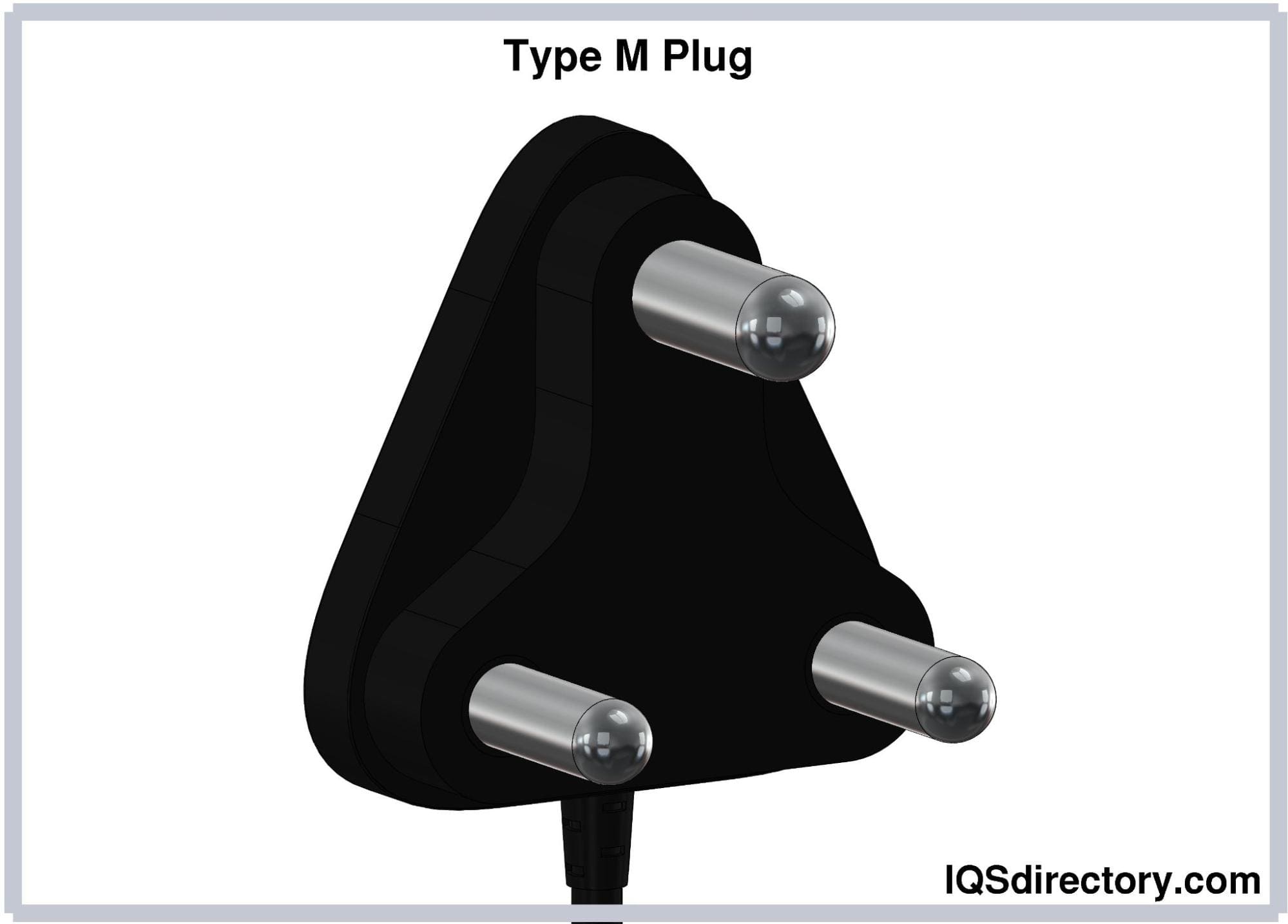
Type M electrical plugs share the same pin arrangement as Type D plugs but are designed with larger pins and a higher current rating of 15A. The central earthing pin measures 28.89 mm in length and 8.71 mm in diameter, while the hot and neutral pins are 18.94 mm long, 7.06 mm in diameter, and spaced 25.4 mm apart. Due to their higher current rating, Type M plugs are used alongside Type D plugs for appliances with higher power needs. Type M plugs are commonly used in South Africa, Swaziland, Lesotho, the UK, Israel, and the UAE. The South African version includes an insulated sleeve and a bare connector on both pins.
Type G electrical plugs feature three rectangular pins arranged in a triangular pattern, along with an integrated fuse. The central earthing pin measures 4 mm by 8 mm by 22.7 mm. The hot and neutral pins are 4 mm by 6.35 mm by 17.7 mm long, with a center-to-center distance of 22.2 mm. These pins are partially covered by an insulated sleeve, while the earthing pin remains uninsulated. British sockets are equipped with shutters that prevent foreign objects from contacting the hot and neutral pins.
Type G plugs incorporate a fuse rated either at 3A or 13A, with the higher rating used for more demanding appliances. This design makes the Type G plug and socket system one of the safest options available for users and equipment. Type G plugs are specifically designed for Type G sockets and are not compatible with other plug types.
Also known as the “Commonwealth Plug,” Type G plugs are widely used in the UK, Ireland, Hong Kong, Singapore, Cyprus, and Malta.

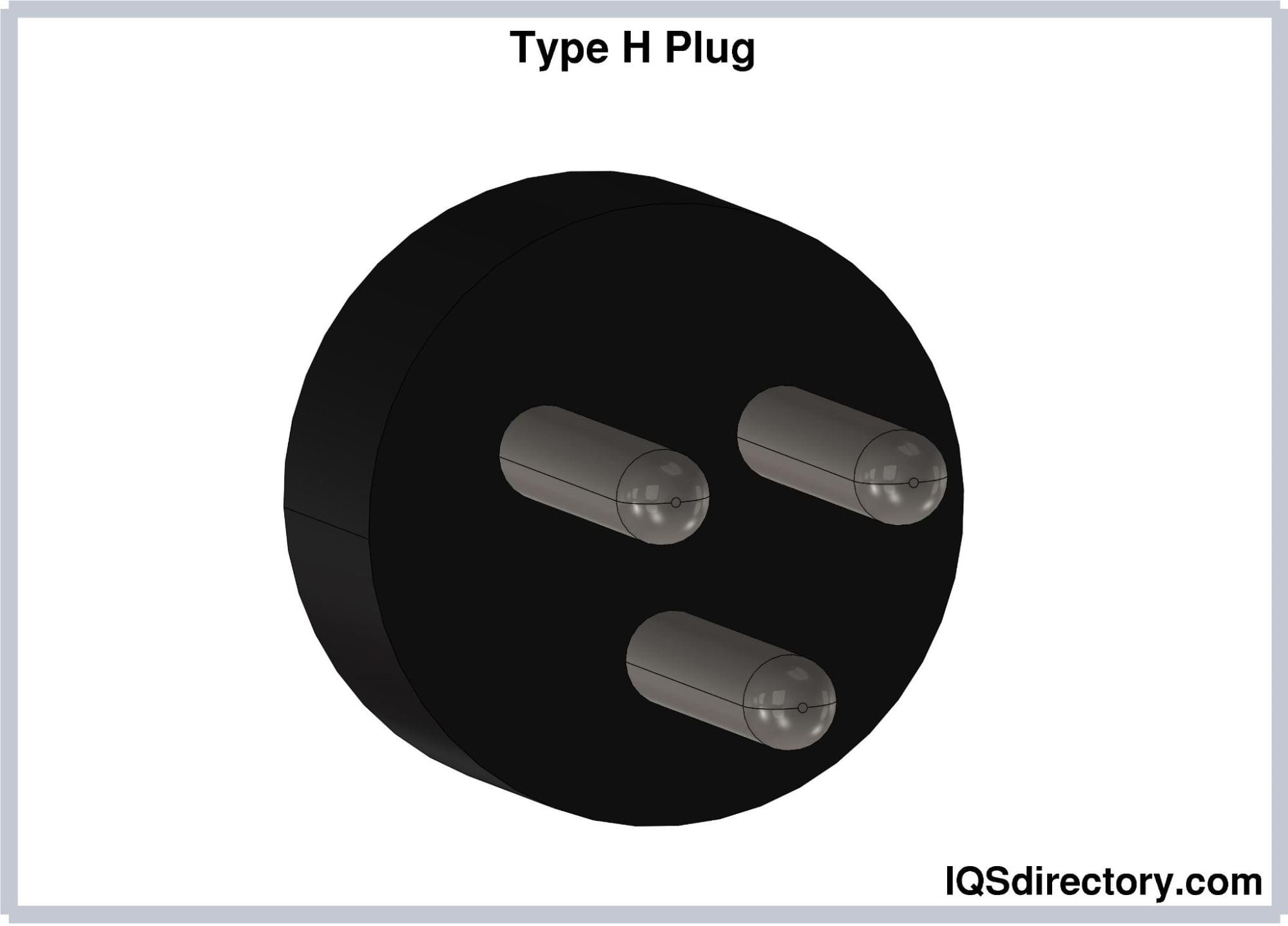
Type H electrical plugs feature three round pins arranged in a triangular pattern, with each pin having a diameter of 4.5 mm and a length of 19 mm. The distance between the hot and neutral pins is 19 mm, and the earthing pin is positioned 9.5 mm from the midpoint between the hot and neutral pins. Type H plugs are grounded and rated for 16A.
Type H plugs are designed to fit only Type H sockets. Although Type H sockets can accommodate Type C plugs, they are not safe for Type E or Type F plugs. Additionally, Type H plugs lack an insulated sleeve, which can pose a hazard when the plug is partially inserted.
Type H plugs are used exclusively in Israel and Palestine.
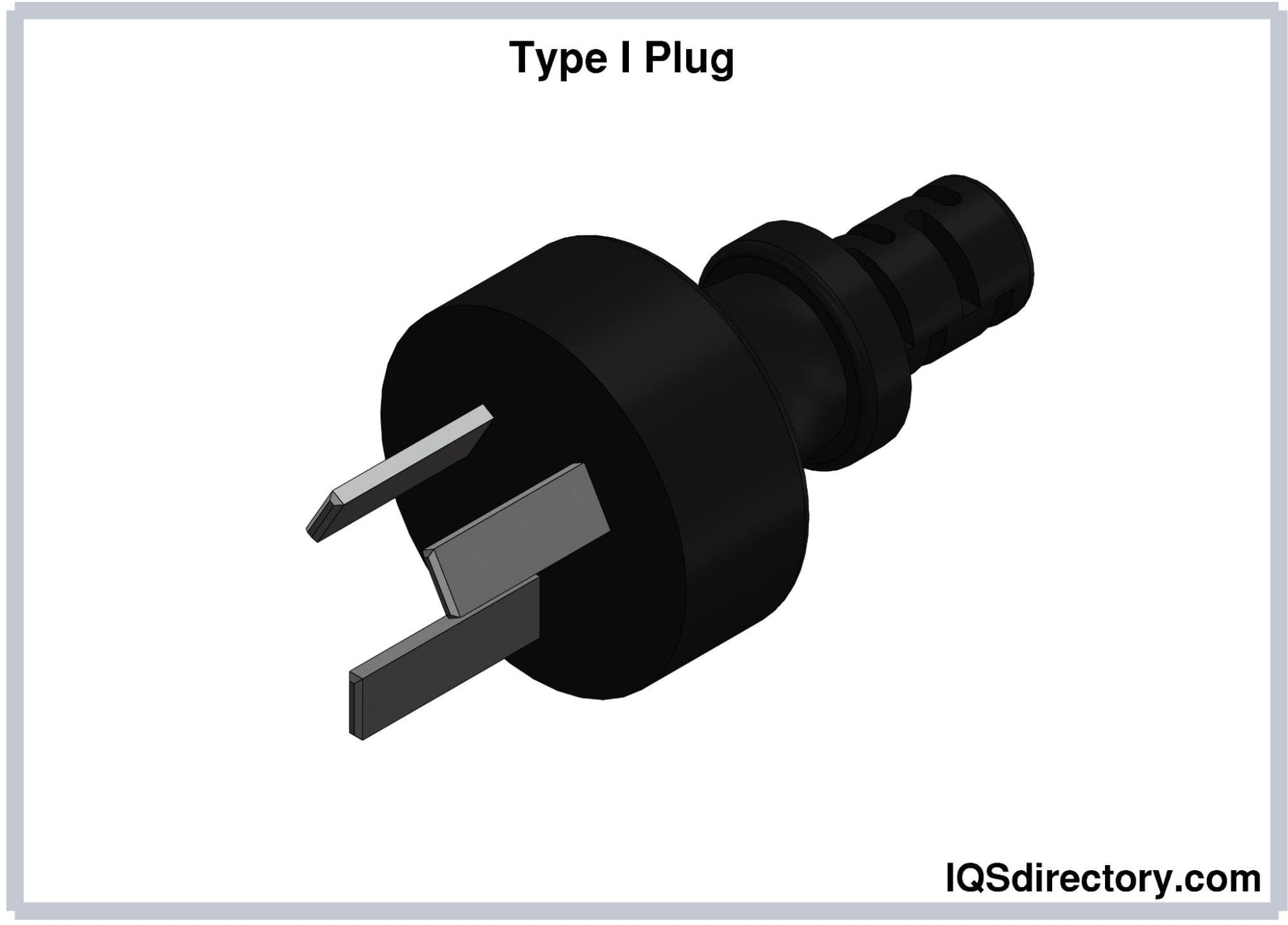
Type I electrical plugs feature two flat pins angled at 30 degrees from the vertical, creating an inverted-V configuration, along with a flat earthing pin. The hot and neutral pins are 17.3 mm long, 6.3 mm wide, and spaced 13.7 mm apart. These pins are insulated, while the earthing pin is 20 mm long and positioned 10.3 mm from the center of the plug. The width of the earthing pin varies with the current rating: 6.3 mm for 10A plugs and 8 mm for 15A plugs. There are also 20A Type I plugs with wider prongs. Plugs with a lower current rating can fit into sockets with a higher rating. Ungrounded versions of Type I plugs are also available.
Type I plugs are commonly used in Argentina, Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, China, and other Pacific Island nations. In China, Type I plugs have the earthing pin above the other two pins, and all pins are 1 mm longer than the standard. Type I plugs from Australia are compatible with Type I sockets in China.
Type I plugs are specified in AS/NZS 3112, the Australian and New Zealand standard for plug and socket systems.
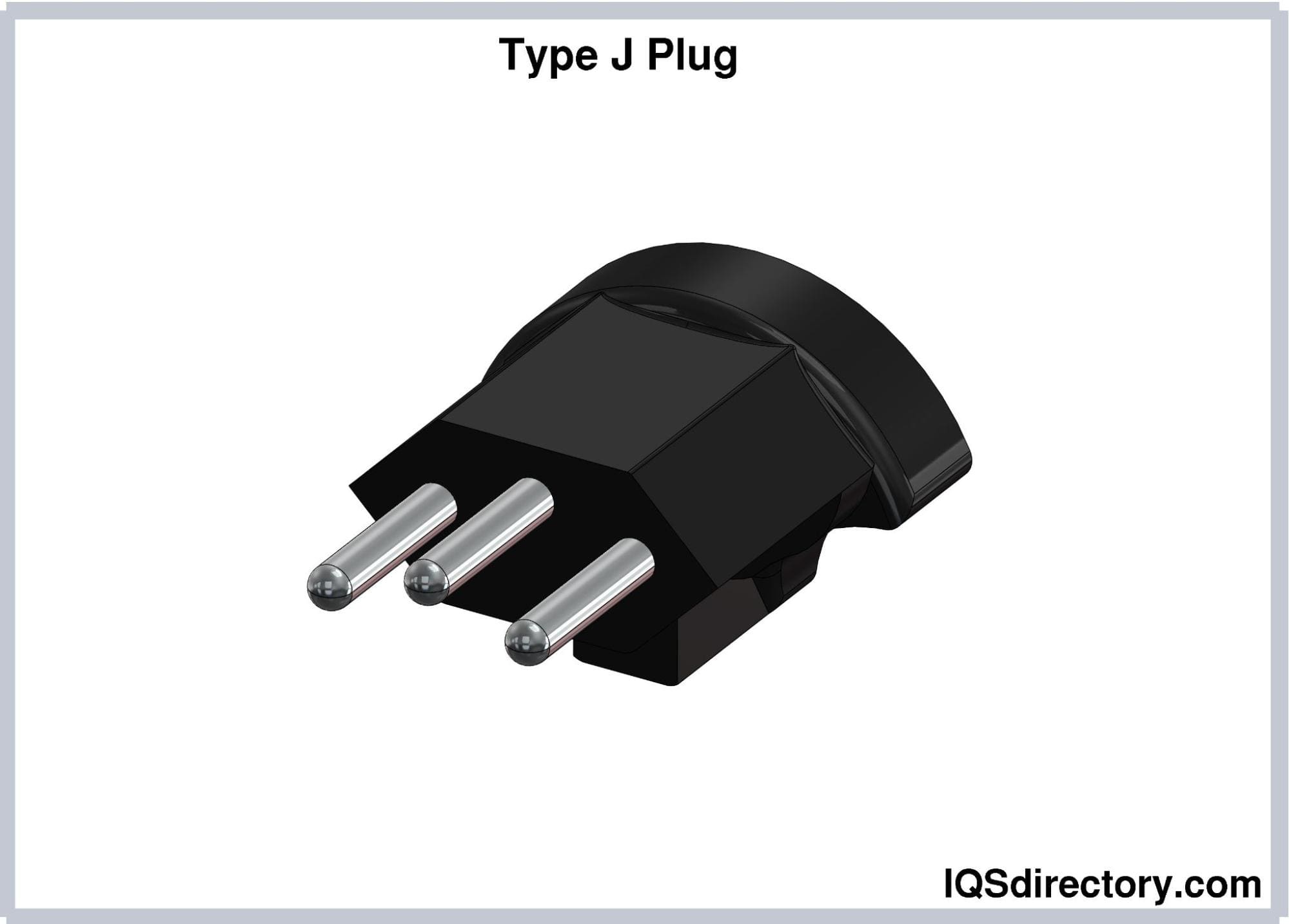
Type J electrical plugs feature three round pins, similar in size to those of Type C plugs. The hot and neutral pins are spaced 19 mm apart, while the earthing pin is offset by 5 mm from the centerline between the hot and neutral pins. All pins have a length of 19 mm and a diameter of 4 mm, and they are fully insulated. The design of Type J plugs ensures polarity cannot be reversed. These plugs are rated for 10A.
Although Type J plugs resemble the Brazilian Type N plugs, they are not compatible with Type N sockets due to the different positioning of the earthing pins.
Type J plugs are used in Switzerland and Liechtenstein. They are listed as Type 13 plugs in SEV 1011, the Swiss standard for domestic plug and socket systems.
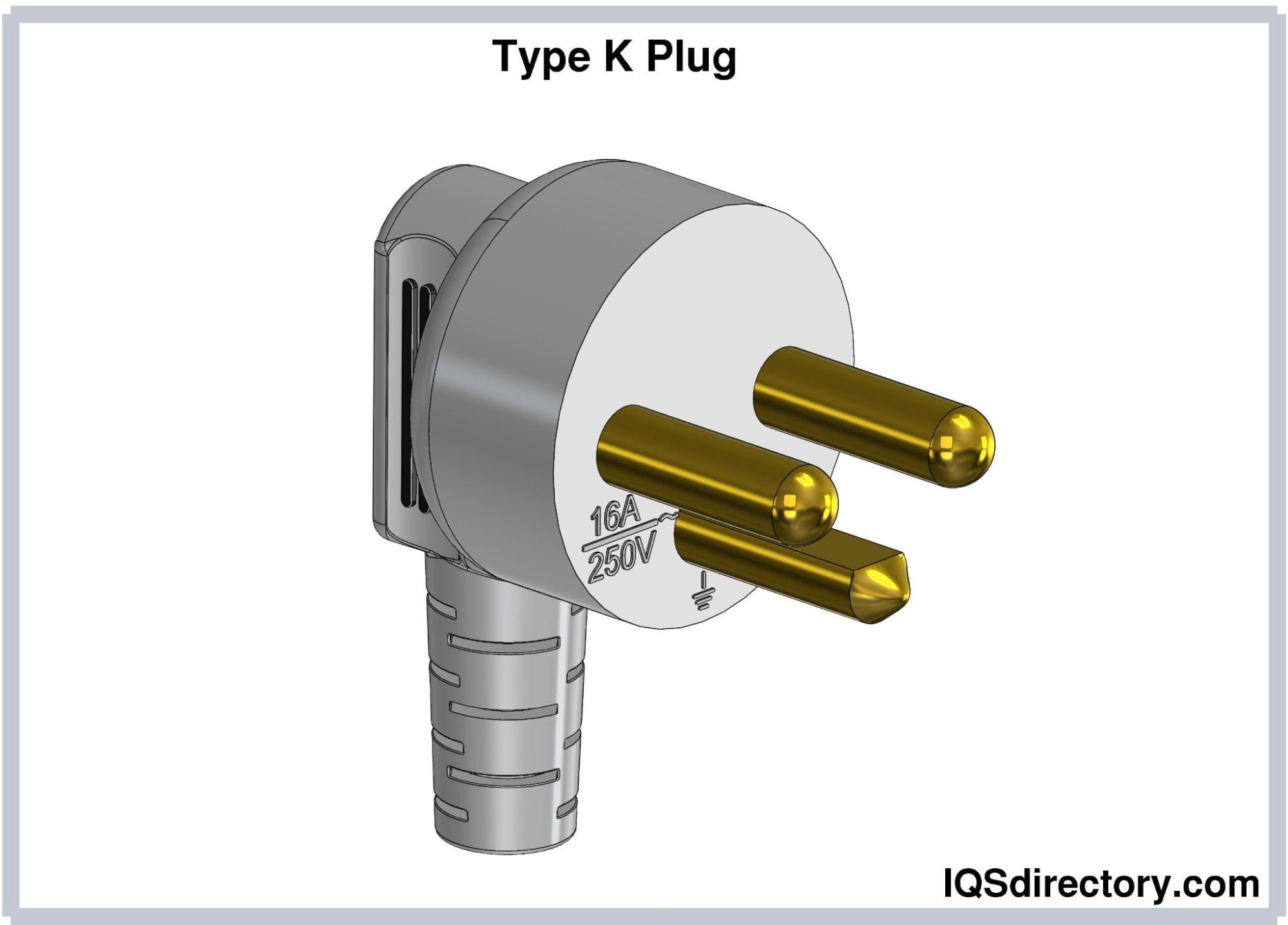
Type K electrical plugs feature two round pins and a U-shaped earthing pin. The hot and neutral pins each have a diameter of 4.8 mm, a length of 19 mm, and are spaced 19 mm apart. The U-shaped earthing pin has a diameter of 6.5 mm, a length of 14 mm, and a thickness of 4 mm. While similar to Type E plugs, Type K plugs differ in the design and gender of the earthing contact. The configuration of Type K plugs prevents polarity reversal. They are rated for 16A.
Type K plugs are utilized in Denmark and Greenland. They are specified in DS-60884-2-D1, the Danish Standard for plugs and sockets designed for household and similar uses.
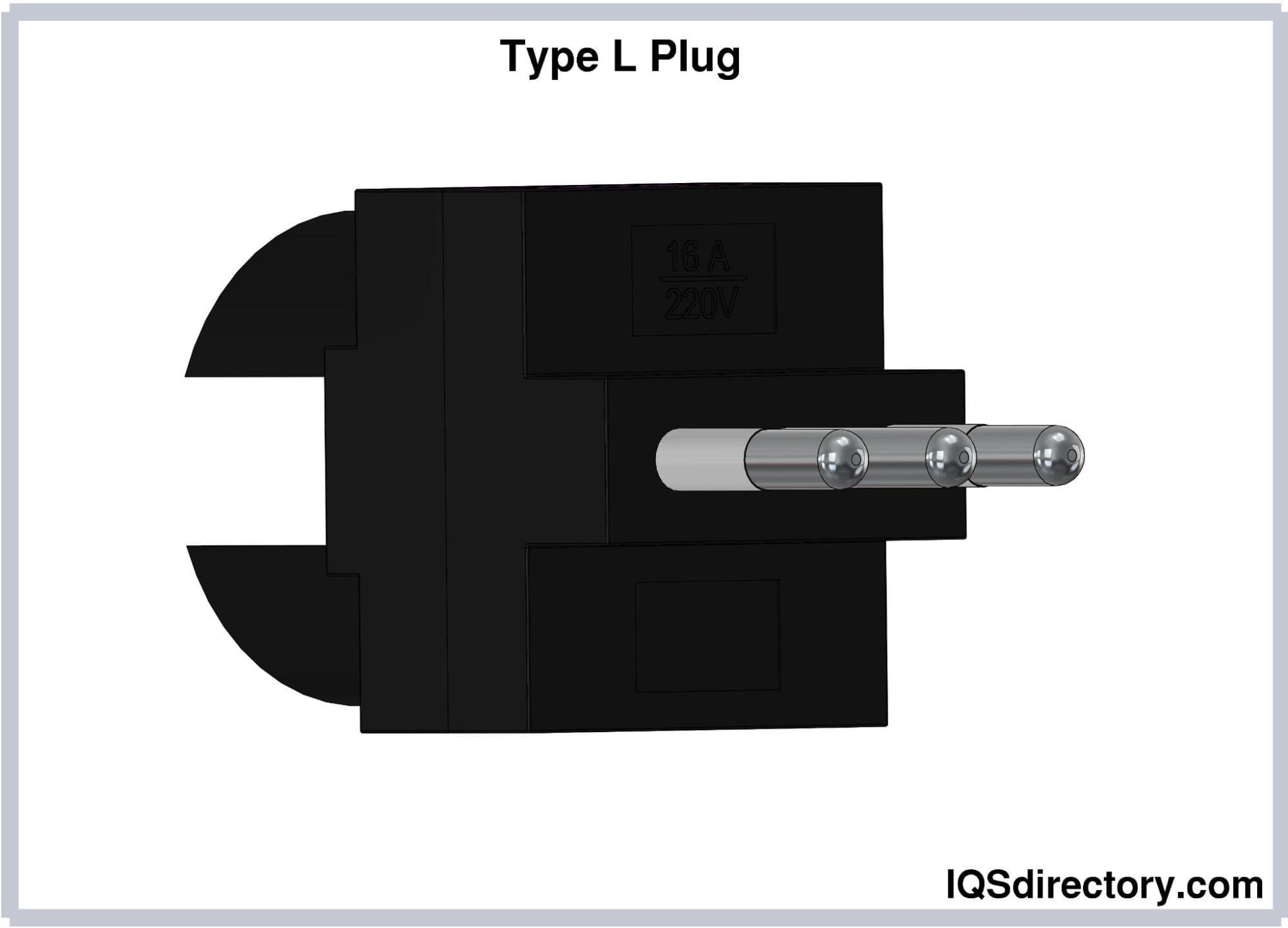
Type L electrical plugs are characterized by three round pins arranged in a straight line, with the earthing pin positioned between the hot and neutral pins. There are two versions of Type L plugs, differing in current rating and pin dimensions:
The 10A and 16A Type L plugs are not interchangeable due to differences in their dimensions. The symmetrical design of Type L plugs means they can be inserted in any orientation, making them unpolarized.
Type L plugs are utilized in Italy, Chile, Uruguay, and some countries in North Africa.
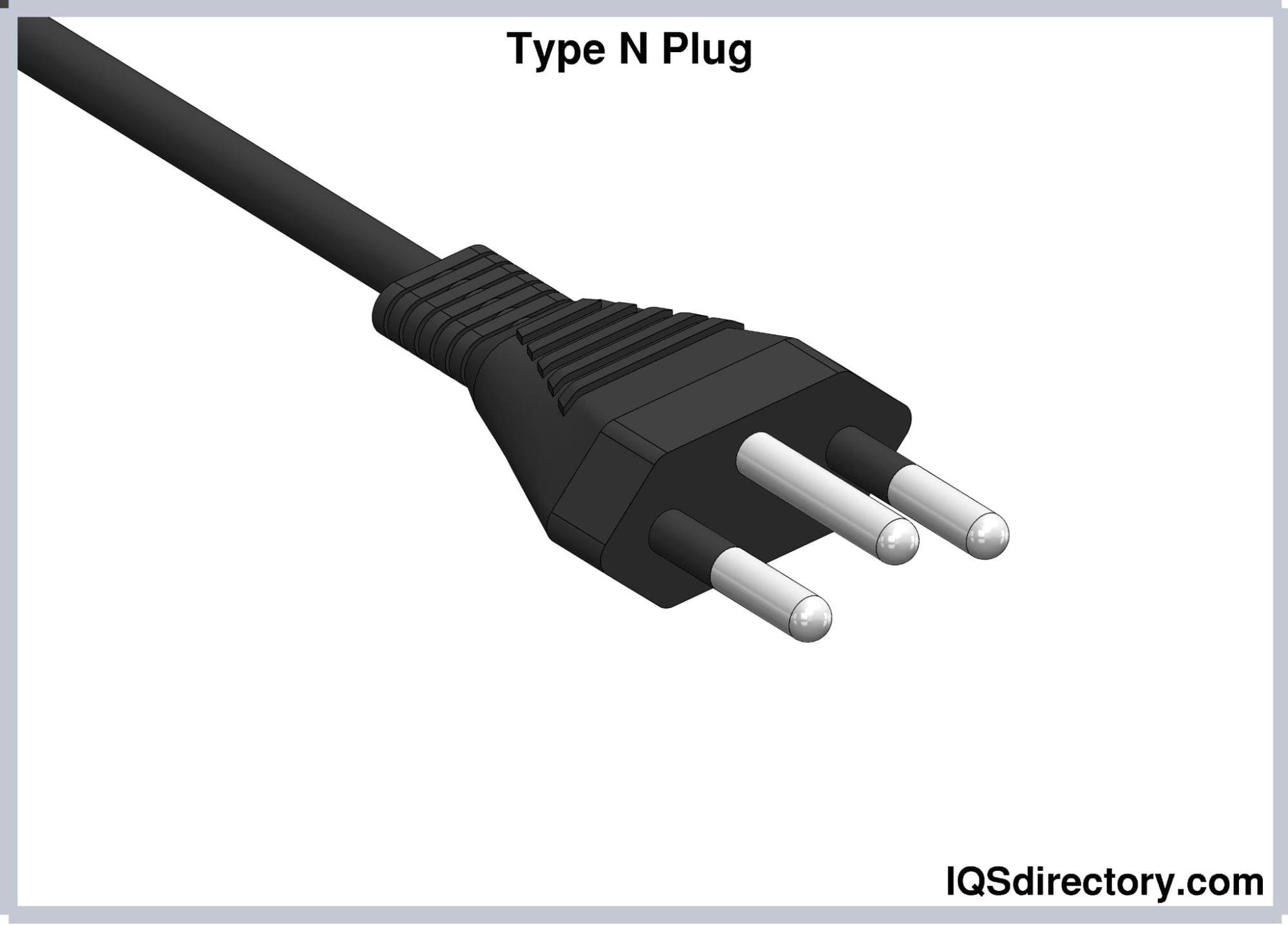
Type N electrical plugs consist of three round pins arranged in a triangular configuration. This type has three variants rated at 10A, 16A, and 20A. The pins of all variants are 19 mm long. However, the diameters are 4 mm, 4.5 mm, and 4.8 mm for the 10A, 16A, and 20A versions, respectively. The pins are covered with an insulated sleeve measuring 10 mm of their length. The center-to-center distance of the hot and neutral pins is 19 mm apart. The center of the earthing pin measures 3 mm away from the midpoint of the imaginary line connecting the hot and neutral pins. Hence, Type N plugs are not compatible with Type J plugs because this measurement is smaller compared to the latter (5mm).
The 10A and 20A Type N plugs are used in Brazil, while the 16A version is used in South Africa.
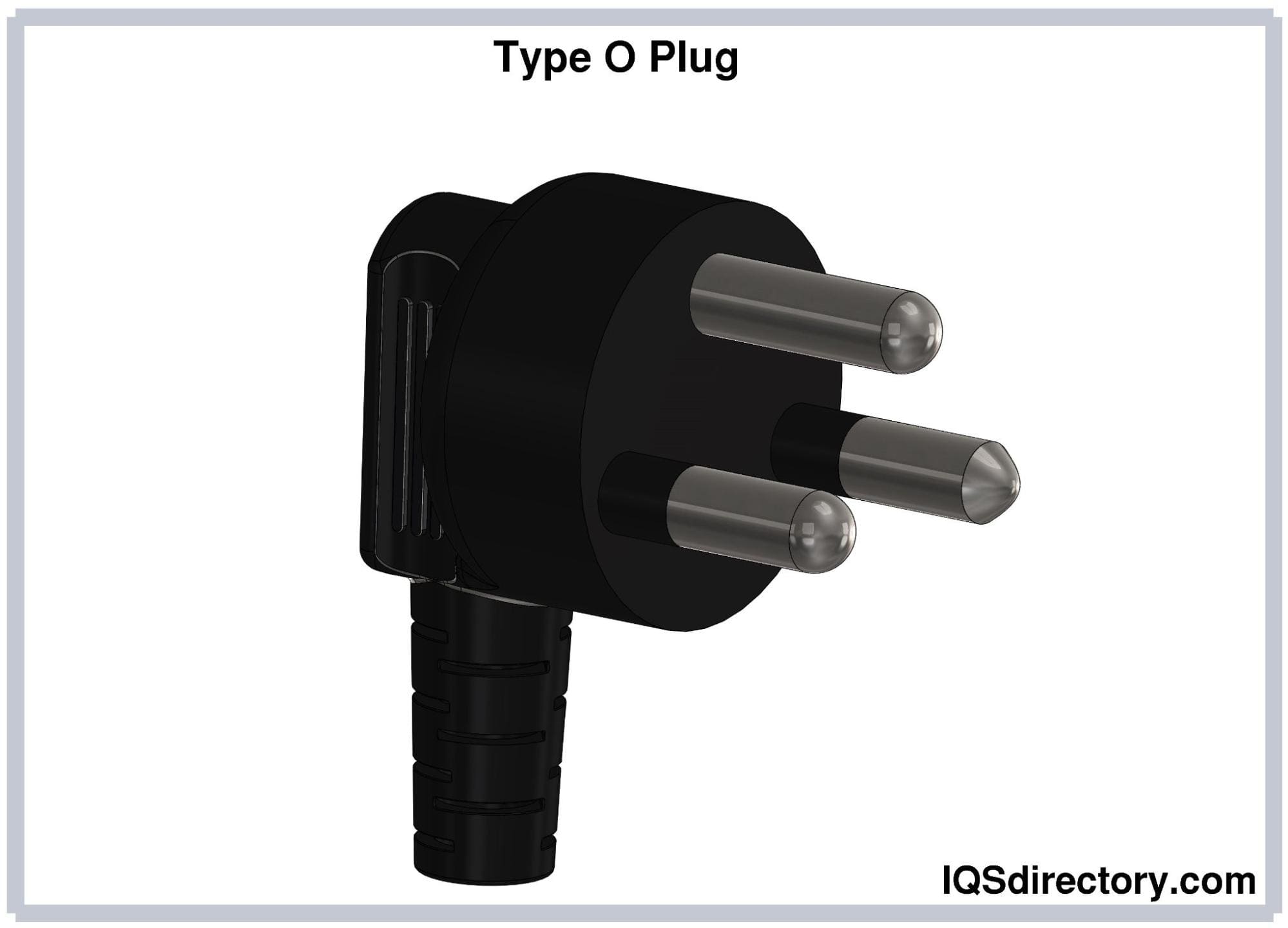
Type O electrical plugs feature three round pins, each with a diameter of 4.8 mm. The hot and neutral pins are 19 mm long and have an insulated sleeve extending 10 mm along their length. The earthing pin measures 21.4 mm in length. The spacing between the hot and neutral pins is 19 mm, while the earthing pin is offset by 11.89 mm from the centerline of the hot and neutral pins. Type O plugs are rated for 16A.
Type O plugs are used exclusively in Thailand and are specified in the TIS 166-2549 standard. Introduced in 2006, this plug and socket system is currently in the process of being phased in.
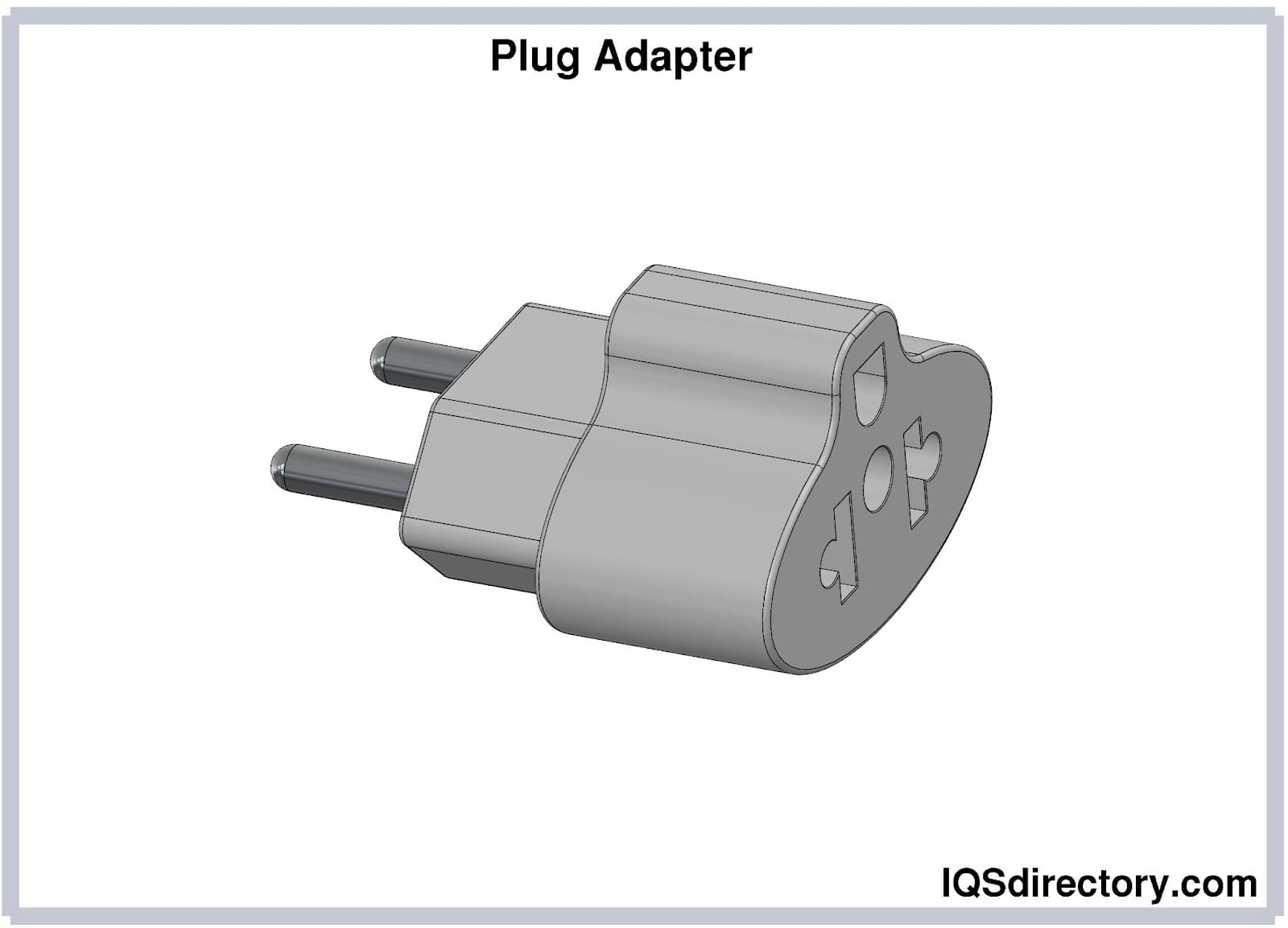
Plug adapters are compact tools that allow you to connect a plug to a socket with a different configuration of prongs or shapes. They are especially useful when traveling internationally, as they help fit plugs into various types of receptacles. It's important to note that these adapters do not alter voltage or current. These devices are sometimes referred to as power converters, travel plugs, or grounding adapters.
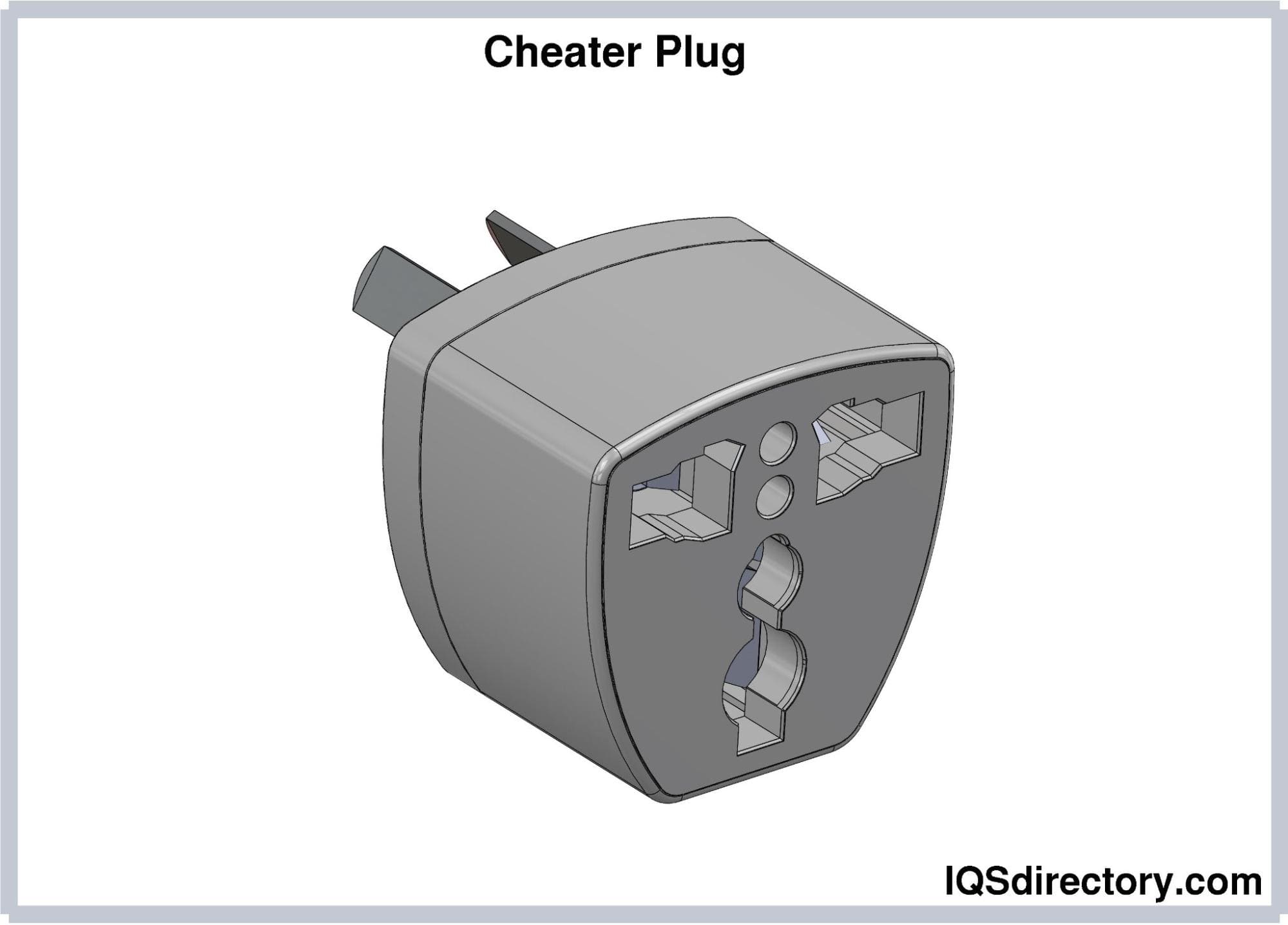
Cheater plugs, also known as three-to-two prong adapters, enable the connection of a three-pronged plug to a two-slot outlet. While they allow your electrical device to function, they bypass the grounding feature of the original three-pronged outlet. As a result, these adapters should be used cautiously and only for short periods.
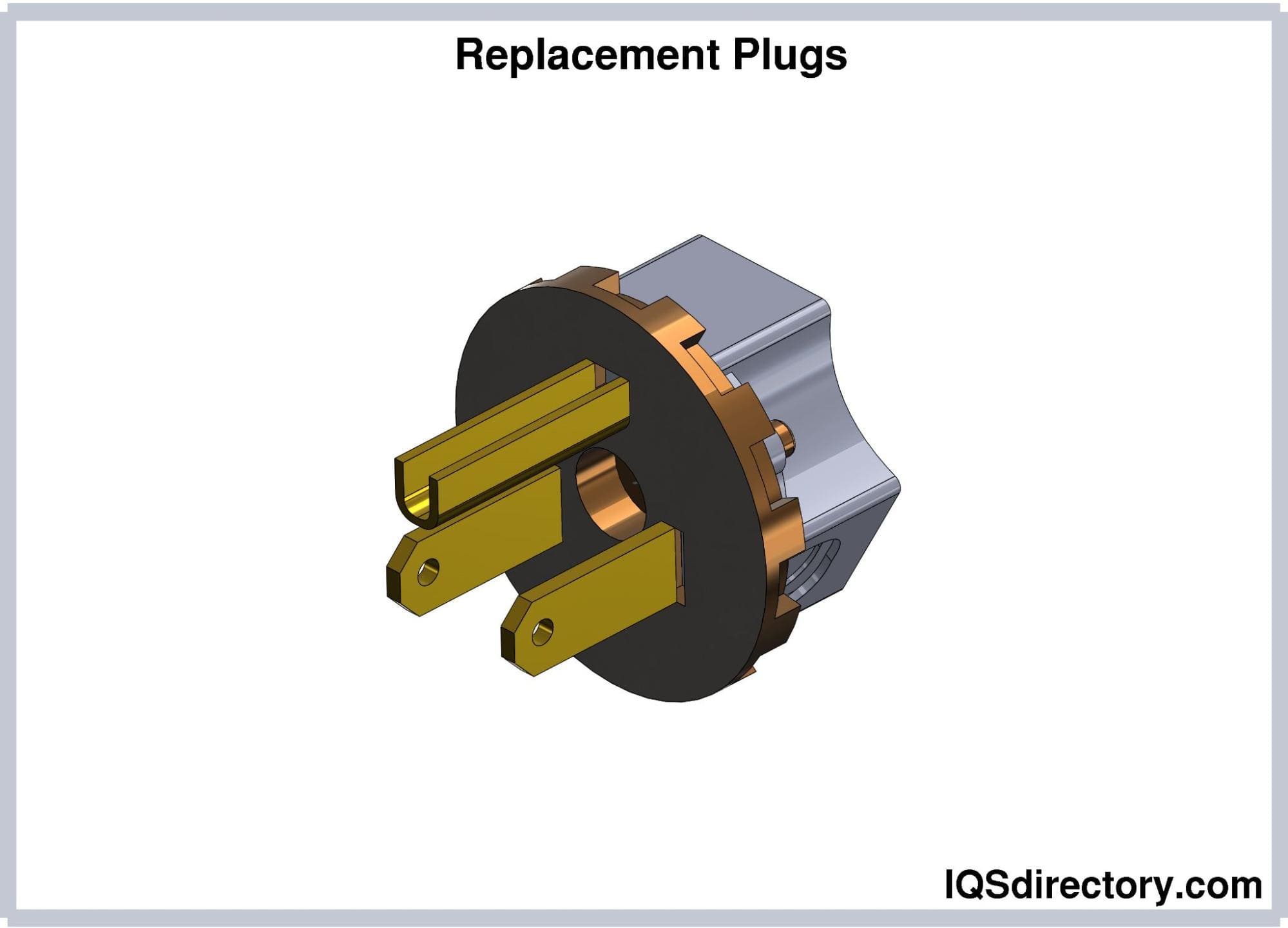
Replacement plugs are designed to substitute damaged or worn plugs on electrical cords. They feature terminals for hot, neutral, and ground connections, all encased within a plastic shell. These plugs do not come with attached appliances or cords.
When replacing a plug, ensure the new one matches the type and rating of the original. Before installation, disconnect the cord from the power source. Cut off the old plug, then strip the outer jacket and insulation to reveal the wires. Connect these bare wires to the appropriate terminals on the new plug, secure them, and reassemble the housing.

An AC power cord is a detachable way of providing an alternating current of electric energy from a mains power supply to an electrical appliance or equipment. Serving industries like...
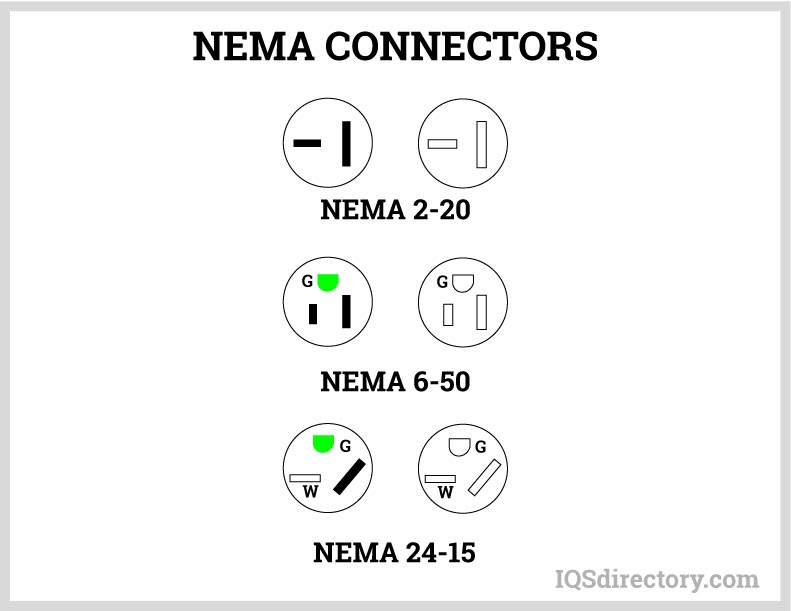
A NEMA connector is a method for connecting electronic devices to power outlets. They can carry alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). AC current is the typical current found in homes, offices, stores, or businesses...
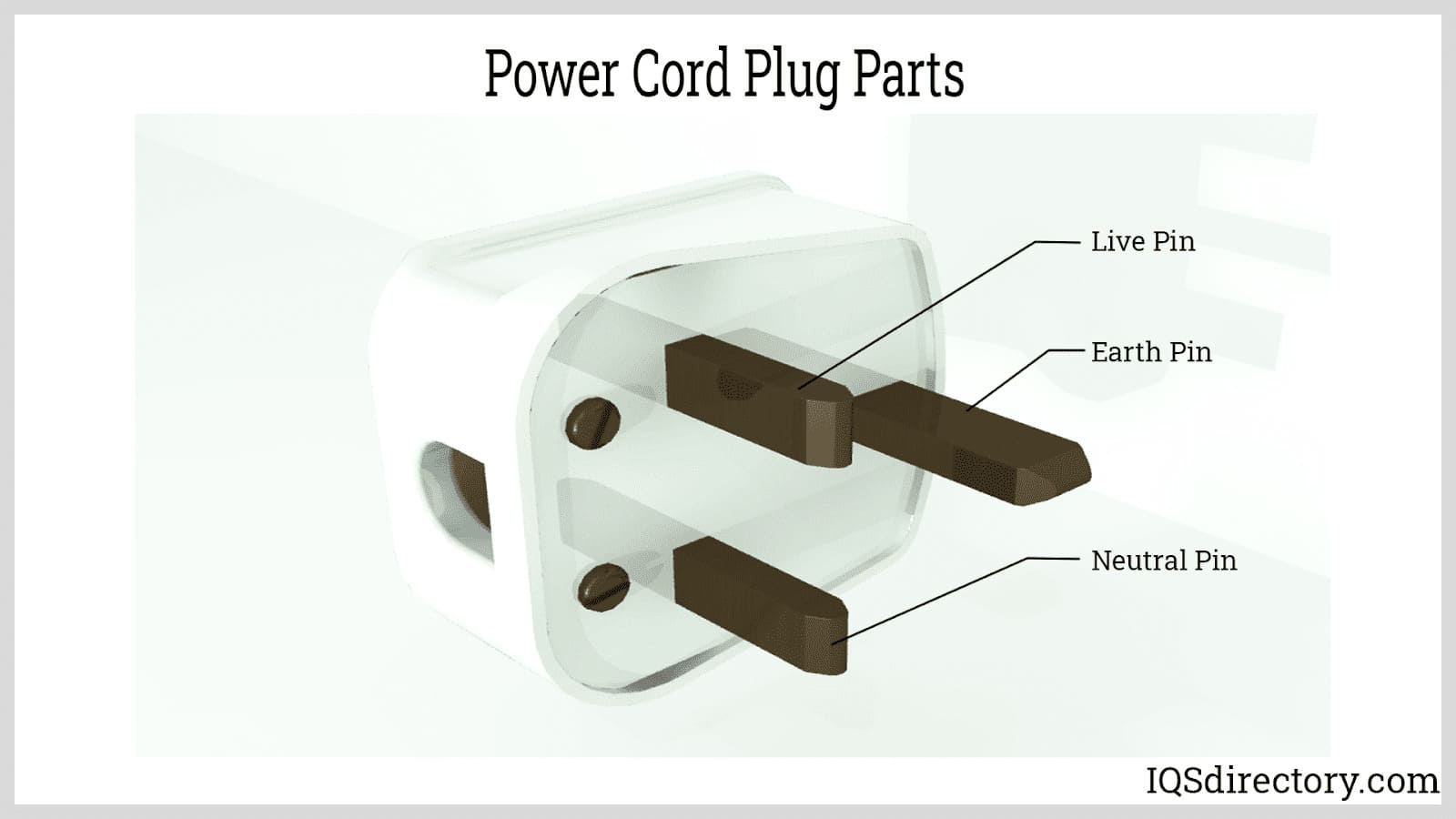
A power cord is an electrical component used for connecting appliances to an electrical utility or power supply. It is made from an insulated electrical cable with one or both ends molded with connectors...
Thomas Edison developed the power distribution system in 1882. He wrapped a copper rod in jute, a soft shiny fiber from plants, as an insulator. The jute wrapped copper rod was placed in a pipe with a bituminous compound...

Power supplies are electrical circuits and devices that are designed to convert mains power or electricity from any electric source to specific values of voltage and current for the target device...
An AC power supply is a type of power supply used to supply alternating current (AC) power to a load. The power input may be in an AC or DC form. The power supplied from wall outlets (mains supply) and...
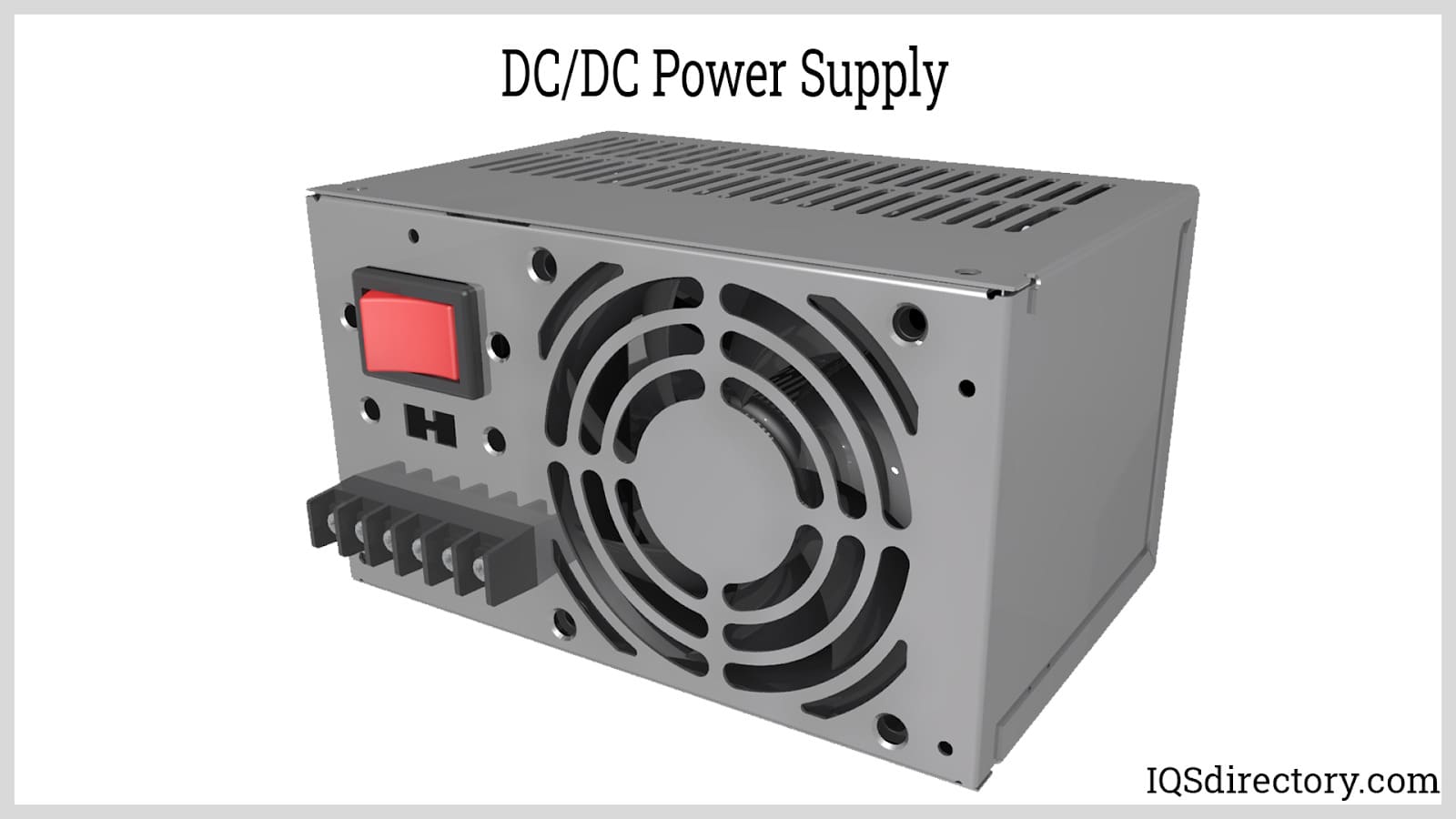

A DC DC power supply (also known as DC DC Converter) is a kind of DC power supply that uses DC voltage as input instead of AC/DC power supplies that rely on AC mains supply voltage as an input...

A DC power supply is a type of power supply that gives direct current (DC) voltage to power a device. Because DC power supply is commonly used on an engineer‘s or technician‘s bench for a ton of power tests...
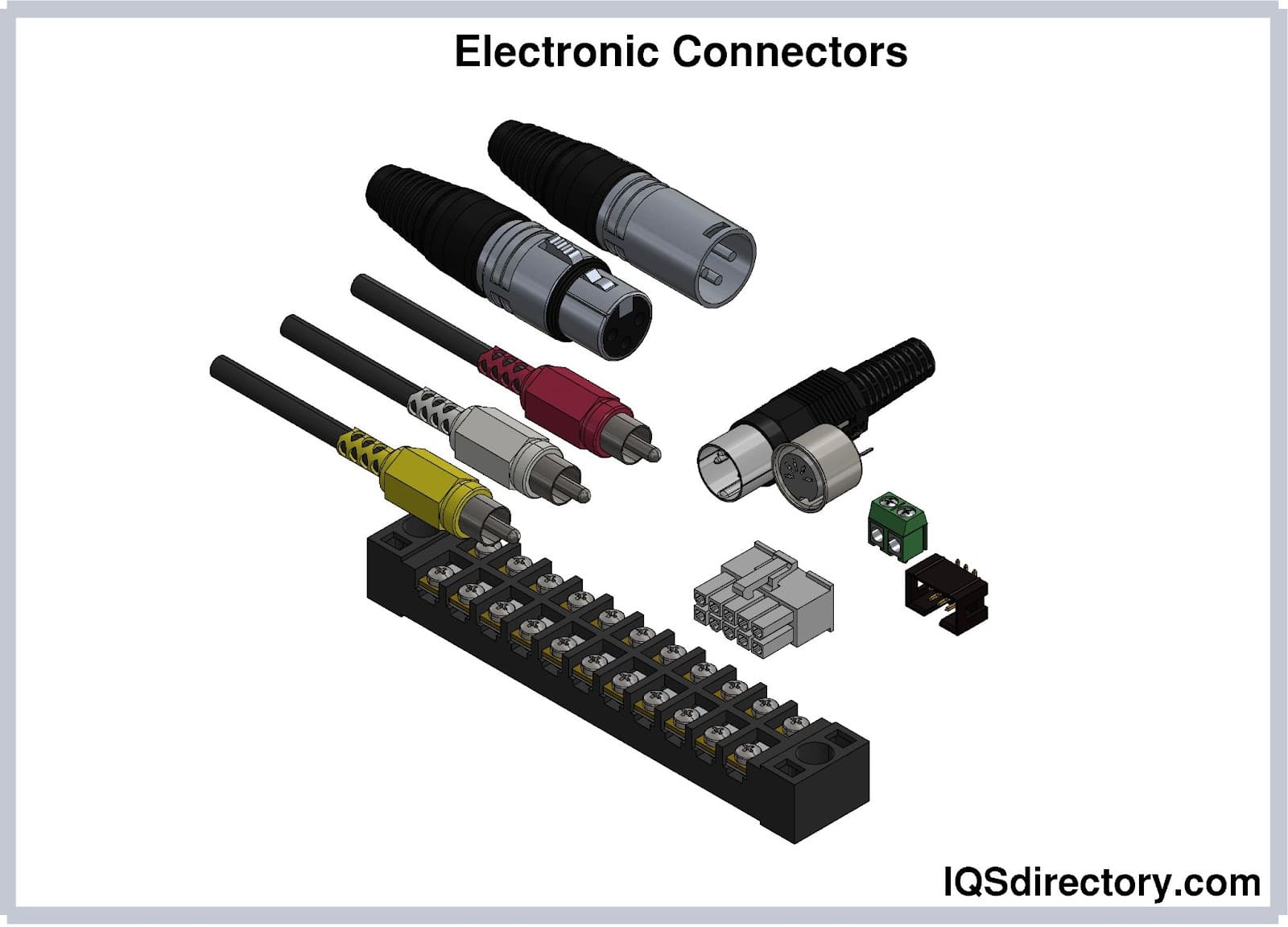
Electronic connectors are devices that join electronic circuits. They are used in assembling, installing, and supplying power to electrical devices. Connectors are an important component of every electronic equipment used in...
An electric switch is a device – usually electromechanical – that is used to open and close an electric circuit. This disables and enables the flow of electric current, respectively...

By definition a power supply is a device that is designed to supply electric power to an electrical load. An electrical load refers to an electrical device that uses up electric power. Such a device can be anything from...

A programmable power supply is a method for controlling output voltage using an analog or digitally controlled signal using a keypad or rotary switch from the front panel of the power supply...
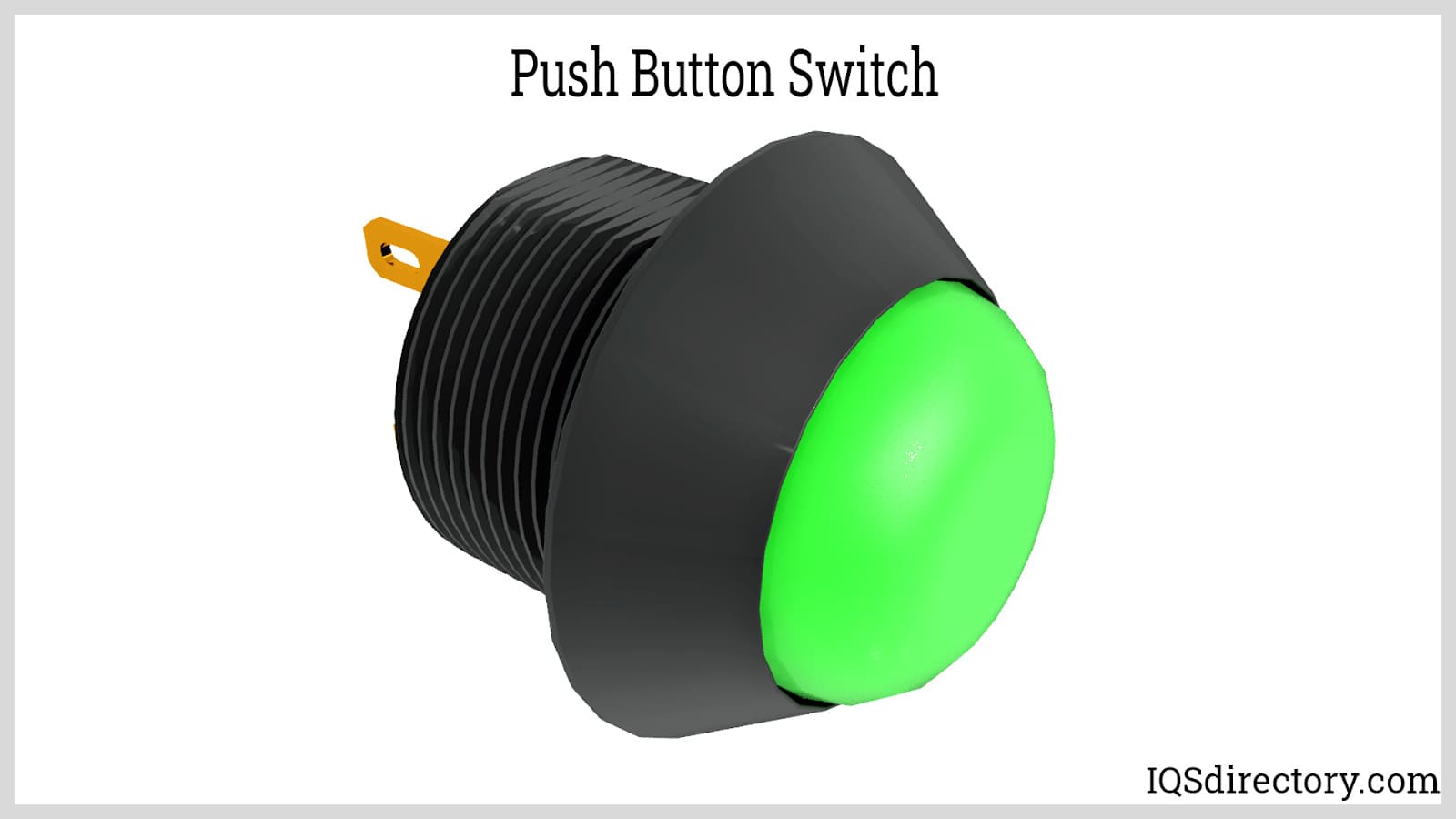
Push button switches are electrical actuators that, when pressed, either close or open the electrical circuits to which they are attached. They are capable of controlling a wide range of electronic gadgets...