Ball Valves
Ball valves offer a straightforward and highly effective method for controlling the flow of gases or liquids through a pipe, relying on a secure seal to ensure efficient operation. The defining feature of these valves is their handle, which operates within a 90-degree range of motion, commonly referred to as a "quarter-turn." This simple yet precise mechanism allows for quick and reliable shutoff or flow activation.
At the core of a ball valve’s design is a durable metal joint housing that encases a spherical ball with a hole drilled through its center. This hole serves as the passageway for fluid or gas when aligned with the pipe. A slot at the top of the ball connects to the stem of the external handle, enabling smooth rotation and effortless control over flow regulation.
Although ball valves and ball check valves may appear similar, they serve distinct functions and should not be confused. A ball check valve is specifically designed to prevent backflow and differs in construction by utilizing a solid interior sphere rather than one with a bored passage. Since ball check valves operate on a different principle, this article focuses exclusively on conventional ball valves and their applications.
Ball Valve History
Sometimes referred to as a "spherical plug" valve, the ball valve is a relatively recent innovation in fluid control technology. The earliest ball valves were developed by aviation engineers working for the United States government during World War II, where they were integrated into Allied aircraft systems to regulate fluid and gas flow with precision and reliability. While the concept of a ball-type valve can be traced back to a patent issued in 1871 to inventor John Warren, it was not until the wartime era that this design was refined into the modern ball valve.
Following the end of World War II, the use of ball valves expanded rapidly across various industries. As engineers and manufacturers continued to refine and enhance the design, these valves became increasingly versatile and efficient. Advances in materials, machining techniques, and sealing technologies have allowed ball valves to serve an ever-growing range of applications, making them an essential component in industries such as plumbing, chemical processing, manufacturing, and energy production. Today, ongoing innovation in ball valve technology continues to drive improvements in durability, performance, and adaptability across multiple economic sectors.
The Benefits of Using a Ball Valve
- Reliable Tight Seal
- Ball valves provide numerous advantages, with one of the most significant being their ability to establish a dependable, tight seal for shutting off gas flow. These valves effectively regulate material movement and can even facilitate multi-directional flow through specialized designs, such as three-way ball valves. Additionally, ball valves exhibit low-pressure drop characteristics, making them particularly valuable in applications where quick and efficient flow control is required. Their ability to swiftly stop or resume gas flow enhances their practicality in both industrial and residential settings.
- Cost Effectiveness
- Another key benefit of ball valves is their affordability. Modern manufacturing techniques allow for the production of these valves in a variety of materials, including brass and steel, ensuring cost-effective solutions for numerous engineering challenges. Their simple yet effective design makes them widely accessible, requiring no technical expertise for operation. Furthermore, ball valves are easy to maintain and repair, reducing long-term costs while ensuring reliable performance over extended periods of use.
- Attractive Design
- In addition to their functional advantages, ball valves often feature visually appealing design elements, particularly in consumer applications. Available in materials such as stainless steel, brass, and copper, they are commonly incorporated into faucets and fixtures that combine durability with aesthetic appeal. Many models feature stylish lever handles that complement modern and classic décor alike. Due to their versatility and sleek appearance, ball valves have gained widespread popularity for use in both industrial systems and residential plumbing applications.
Common Ball Valve Applications
Ball valves are widely utilized in factory and manufacturing settings, where they play an essential role in mechanical and industrial systems. Frequently integrated as components within machinery, these valves provide efficient flow control. Engineers often incorporate actuators —typically electric or pneumatic—to automate the opening and closing of ball valves, ensuring precision and reliability in mechanical designs.
Within complex mechanical assemblies, both the valve and actuator contribute to seamless operation. A more advanced variation, known as a "globe valve," is sometimes used as a control valve in automotive transmissions, allowing for precise regulation of fluid flow.
Beyond industrial applications, ball valves are also prevalent in commercial and residential infrastructure. These valves provide an easy and effective method for controlling the flow of water, heating oil, and natural gas. By simply turning a lever handle at a right angle, operators can quickly shut off or resume flow, much like solenoid valves. Their user-friendly operation makes them an essential component in plumbing, HVAC systems, and gas delivery networks.
Engineers have developed numerous variations of ball valves to accommodate different applications. This highly versatile "quarter-turn" valve design is used worldwide in a vast array of industries. Ball valve manufacturers featured in the Industrial Quick Search Directory offer an extensive selection of these valves, including specialized models designed for unique operational requirements. The directory provides valuable contact information for suppliers, making it easy for businesses to source the right ball valve for their needs.
A wide range of industries depend on ball valves for their durability and efficiency. Economic sectors that rely extensively on these industrial valves include mining, agriculture, oil and gas, construction, transportation, consumer goods, and chemical processing. The adaptability of ball valves has led to the development of specialized designs such as float ball valves and trunnion ball valves, further expanding their functionality across diverse applications.
The Design and Engineering of Ball Valves
Ball valves have become essential across numerous applications due to their ability to efficiently shut off the transmission of gases and liquids within distribution systems. Their widespread use stems from their straightforward operation and reliable performance. These valves are available in a variety of fittings and housings, providing customers with an extensive selection to meet specific needs. Today, ball valves come in multiple dimensions, designs, and materials, including stainless steel, ductile iron, carbon steel, bronze, and brass, ensuring compatibility with a range of industrial and commercial requirements.
While some ball valves incorporate a valve body and gear operator, their primary function remains limited to basic "on/off" flow control. Unlike globe valves, which offer precise flow regulation, ball valves are primarily designed for efficient shutoff applications. However, their simplicity and cost-effectiveness make them an ideal solution for many engineering challenges, particularly when rapid and reliable fluid control is required.
The mechanics of a ball valve are straightforward yet highly effective. When in the "open" position, the cavity running through the center of the ball aligns precisely with the input and output pipes, allowing unrestricted flow of the transported material. Rotating the handle to the "closed" position causes the ball to turn, positioning its solid side perpendicular to the flow path and completely shutting off the transmission of gases or liquids. This secure sealing mechanism makes ball valves a preferred choice for controlling the flow of natural gas, oil, water, and other fluids. Compared to cumbersome gate valves, ball valves offer a more user-friendly handle, making them particularly convenient for residential applications.
Ball valve manufacturers offer two primary design options: floating ball and trunnion-mounted ball valves. A floating ball valve features a freely moving ball that shifts into place against the seat, creating a tight seal. This design is simple and effective for many standard applications. In contrast, a trunnion-mounted ball valve utilizes a fixed ball held in place by additional mechanical supports, making it suitable for more complex applications. Due to its enhanced design, the trunnion-mounted valve is typically more expensive.
The operation of a ball valve is controlled by a handle, which can be manually operated, motorized, or actuated for automated control. The handle rotates the ball by a quarter turn, determining whether the flow is open or restricted. When the hole in the ball aligns with the pipe opening, the flow is restored, while rotating the handle away from the opening shuts off the flow entirely. One of the advantages of ball valves is their intuitive design—the position of the handle immediately indicates whether the valve is open or closed.
Manufacturers produce ball valves in a range of materials, with stainless steel, brass, cast iron, and plastic, such as PVC, being the most common. The size of ball valves varies significantly based on application needs. Mini ball valves, typically less than an inch in diameter, are ideal for installations in confined spaces or hard-to-reach areas. Additional variations in ball valve design include 3-way ball valves, which allow for multi-directional flow control, and flanged ball valves, which provide secure connections in piping systems. Specialized designs such as ball check valves ensure that liquids flow in only one direction, while high-pressure ball valves can withstand extreme pressure and temperature conditions. For those seeking high-quality ball valves, IQS Directory offers an extensive listing of ball valve manufacturers, including suppliers specializing in check valves and high-performance flow control solutions.
Features of Ball Valves
The technical specifications for the interior ball within a ball valve often necessitate the use of specific metals or a combination of metal and ceramic materials, particularly when the valve operates in high-pressure environments. Depending on the intended application, manufacturers offer ball valves with either metal or plastic interior balls. The choice of material can significantly impact the valve’s durability, longevity, and performance, making it essential for customers to carefully review these requirements before selecting a ball valve.
In some cases, a design specification may mandate the use of a stainless steel ball valve to ensure optimal strength and corrosion resistance. Additionally, manufacturers have developed specialized ball valves in which the interior metal ball is coated with nickel or chrome plating.
These coatings enhance the valve’s ability to endure heavy use while offering improved resistance to wear and corrosion, making them particularly valuable in demanding industrial environments.
Modern ball valves are designed to integrate seamlessly into a variety of piping and tubing systems, with numerous fitting options available to facilitate secure connections. Common fittings include socket welds and double ferrule designs, allowing for compatibility with different industrial applications. Many design standards now incorporate high-quality ball valves as essential components between connecting pipes or tubes to regulate fluid flow efficiently. However, the exact specifications of any given ball valve can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, industry standards, and the testing criteria established by oversight bodies. When procuring customized ball valves, purchasers should ensure that rigorous inspection and quality control measures are in place to verify product reliability and compliance with performance standards.
When evaluating ball valves, several key factors should be taken into account, including the constituent materials of the valve, its dimensions, pressure capacity, lining material, body composition, expected lifespan, and intended function—specifically, the types of gases or liquids it will regulate. While most ball valves are designed to function at room temperature, special considerations must be made for those intended to operate in extreme high or low-temperature conditions. Manufacturers typically provide customers with detailed product specifications and performance data, offering guidance on selecting the most suitable ball valve for their needs. Additionally, they may supply valuable insights into the anticipated lifespan of different ball valve models, helping customers make informed decisions based on their specific operational requirements.
Ball Valves Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts
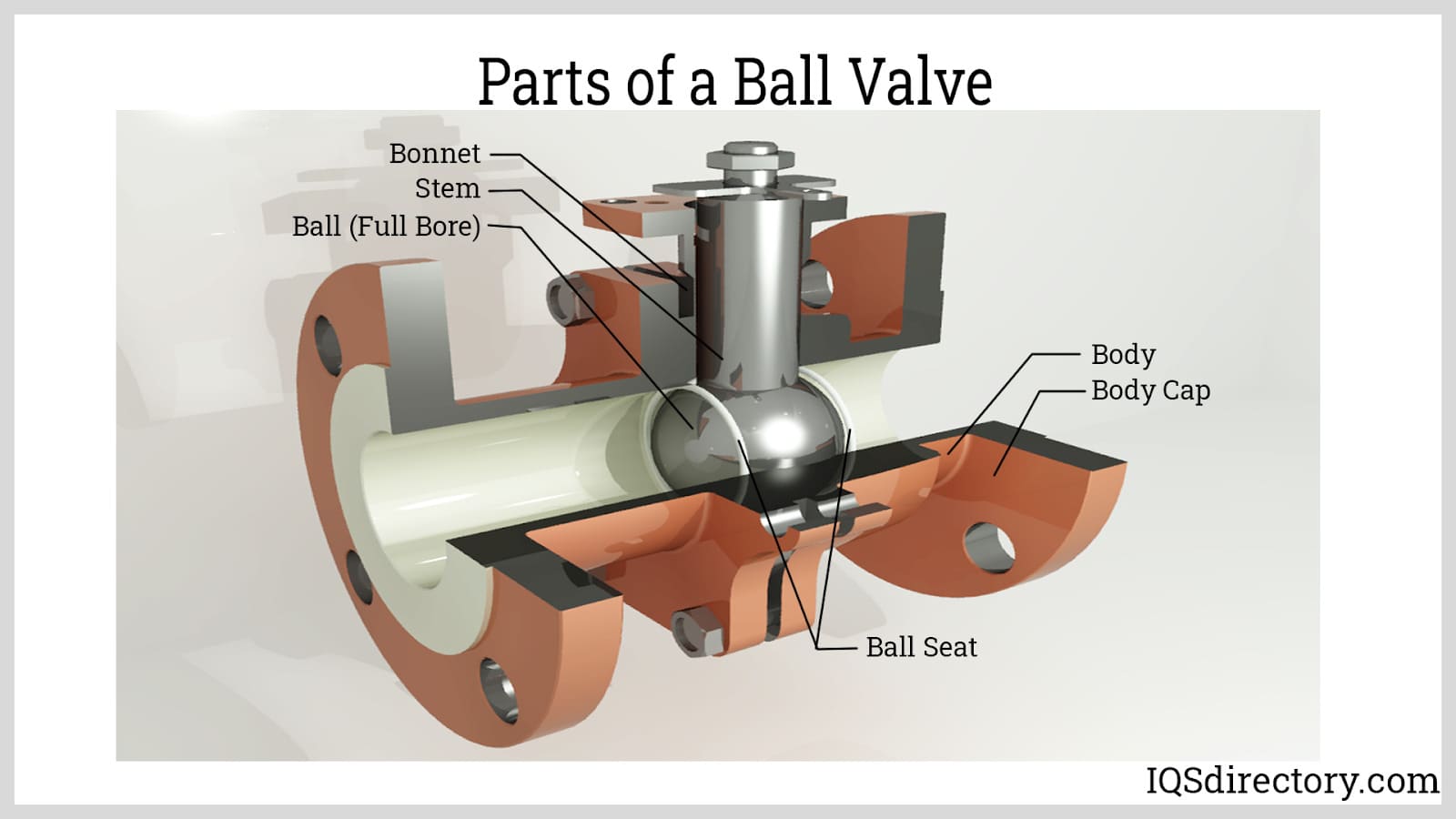 The internal components of a ball valve inside the valve housing.
The internal components of a ball valve inside the valve housing.
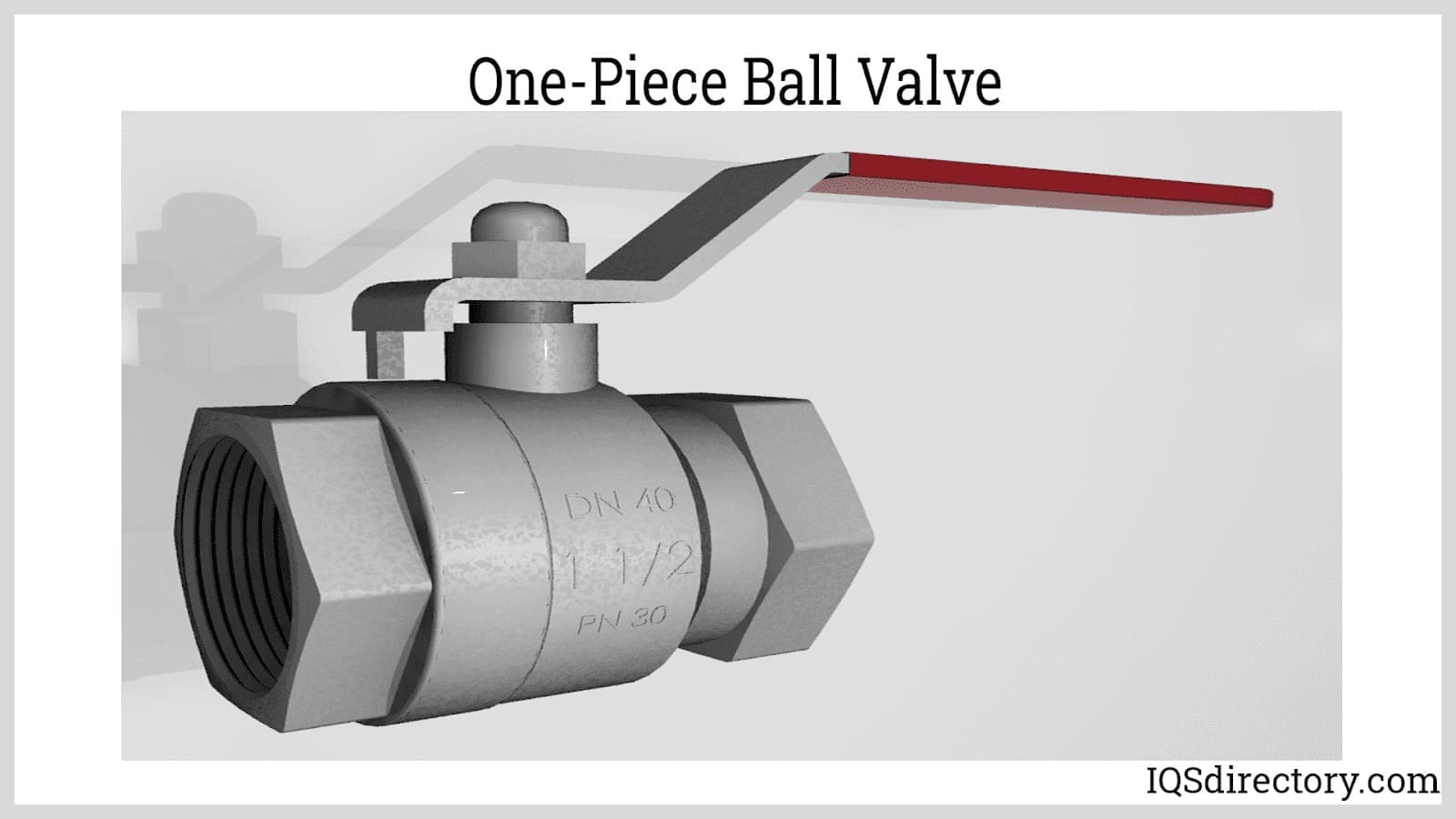 A one-piece ball valve has a single-piece cast body that houses the internal components and eliminates the risk of leakage.
A one-piece ball valve has a single-piece cast body that houses the internal components and eliminates the risk of leakage.
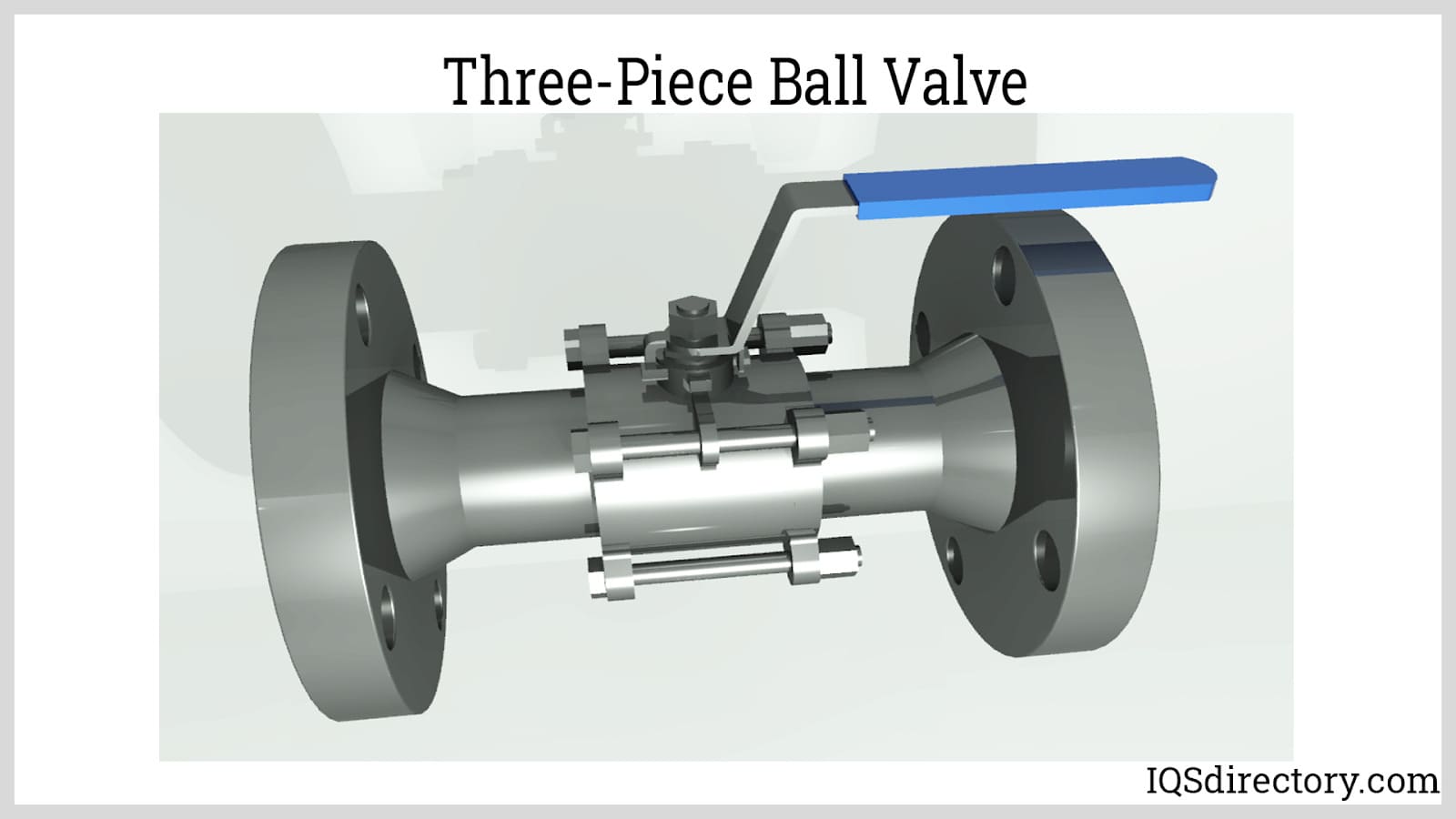 A three-piece ball valve, the internal components are fitted and held together by bolt connections.
A three-piece ball valve, the internal components are fitted and held together by bolt connections.
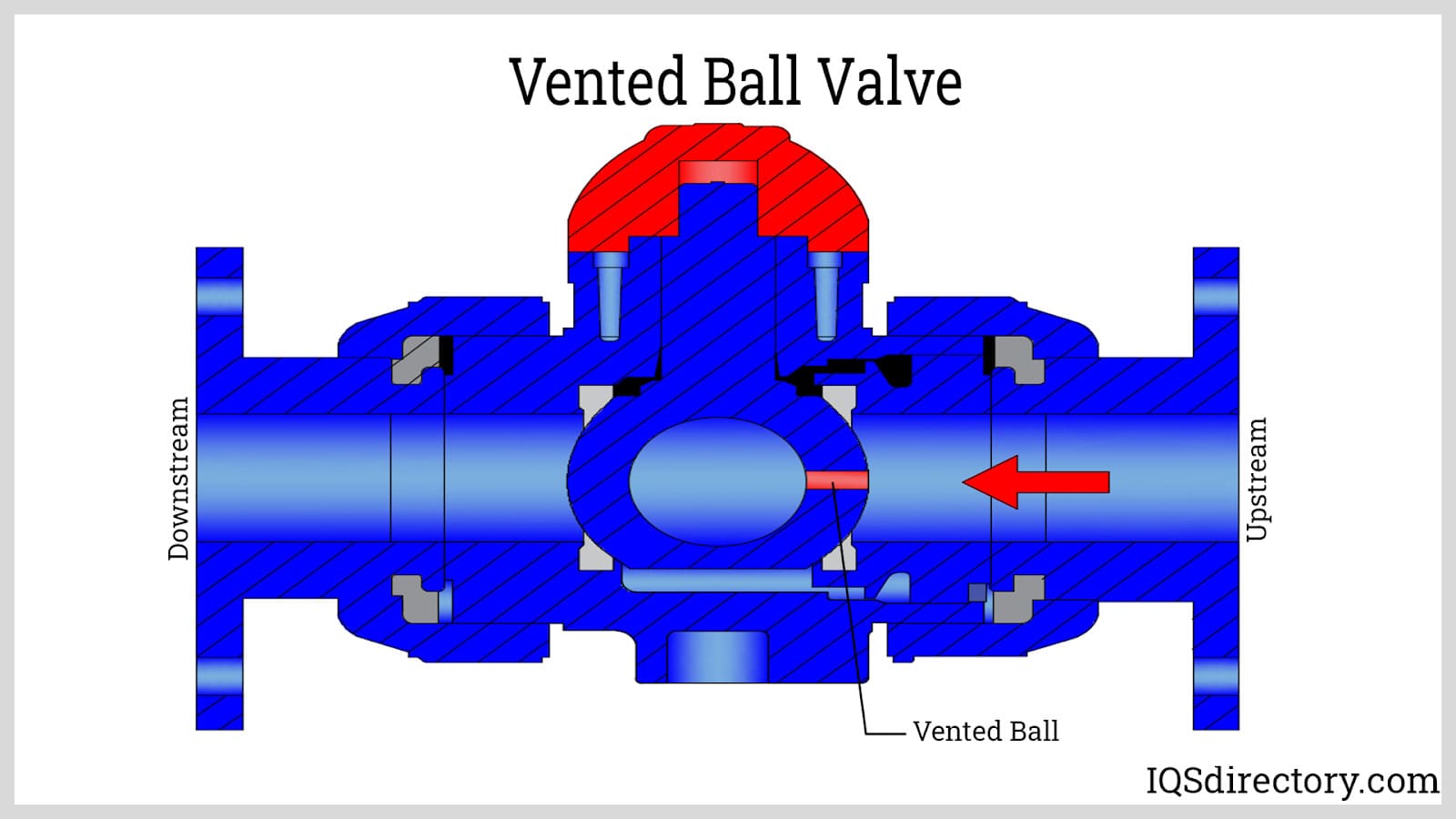 Vented ball valves are constructed and operates the same as a standard ball valve, except that the vented ball has small orifices drilled into its side.
Vented ball valves are constructed and operates the same as a standard ball valve, except that the vented ball has small orifices drilled into its side.
Types of Ball Valves
Manufacturers typically classify ball valves based on two primary criteria: the movement of the interior ball and the depth of the bore. Bore types include full bore, reduced bore, or specialized bore, each affecting the flow capacity and pressure characteristics of the valve. Additionally, the ball within the valve may either receive extra anchoring for stability or remain connected solely to the stem, allowing it to float slightly. Some specialized ball valves incorporate moveable stems for enhanced functionality. Engineers have designed several widely used variations of ball valves to accommodate different operational needs and industrial applications.
- 3-Way Ball Valves
- These ball valves feature three distinct ports, allowing for multiple flow configurations. Some models enable all three ports to remain open simultaneously, while others permit selective control, closing one or more ports as needed to regulate fluid direction.
- Actuated Ball Valves
- Unlike manually operated ball valves, actuated ball valves utilize automatic power actuators—such as electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic systems—to control the opening and closing of the valve, improving efficiency and automation in industrial processes.
- Ball Check Valves
- Designed to ensure unidirectional flow, ball check valves use internal pressure to move the ball, allowing fluid to pass through. When pressure decreases or stops, the ball returns to its seat, closing the valve and preventing backflow.
- Brass Ball Valves
- Constructed from brass, one of the most commonly used materials for ball valves, these valves provide durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for both residential and industrial applications.
- Flanged Ball Valve
- These ball valves incorporate a body that joins along a central rib or flange. While the flanged design often simplifies maintenance by providing easy access to internal components, it may also introduce a greater risk of leakage if not properly sealed.
- Floating Ball Valve
- Featuring a design where the ball is attached only to the stem, these valves allow slight movement within the pipeline. This floating action helps maintain a secure seal against the valve seats, although some wear may occur over time due to constant stem contact.
- Full Port Ball Valve
- Widely utilized in refineries and chemical plants, full port ball valves have a bore diameter identical to the connected pipeline. This design minimizes flow restrictions and reduces pressure loss, making them ideal for applications requiring maximum flow efficiency.
- High Pressure Ball Valves
- Engineered to handle both small and large flow capacities under extreme pressure conditions, high-pressure ball valves are built with reinforced components to withstand demanding environments.
- Mini Ball Valves
- Compact in size, mini ball valves function similarly to standard ball valves but are designed for confined spaces or precise flow control in smaller piping systems. They rely on a rotating ball to create a secure seal.
- Motorized Ball Valves
- These ball valves utilize an electric motor to automate valve actuation, eliminating the need for manual operation. They are commonly used in industrial automation systems, remote-controlled fluid networks, and HVAC applications.
- Multiport Ball Valves
- Designed to connect multiple pipelines to a single valve, multiport ball valves facilitate fluid mixing, redirection, and distribution. They play a crucial role in industrial manufacturing, chemical processing, and gas blending applications.
- Plug Valves
- A variation of quarter-turn valves, plug valves use a cylindrical or tapered plug with a central hole to regulate flow. Their simple yet robust design ensures reliable performance in various fluid control systems.
- PVC Ball Valves
- Constructed from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), these ball valves offer excellent resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and moisture, making them ideal for water treatment, irrigation, and chemical processing applications.
- Stainless Steel Ball Valves
- Manufactured from stainless steel, these ball valves provide superior corrosion resistance, strength, and longevity, making them suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature, and chemically aggressive environments.
- Swing Check Valves
- Unlike standard ball check valves, swing check valves use external levers to control the rate of flow reduction. The lever mechanism gradually moves the ball into the flow, ensuring smoother shutoff and preventing sudden pressure spikes in the system.
- Trunnion Ball Valve
- Designed for high-pressure pipelines, trunnion ball valves feature additional mechanical support for the ball at both the top and bottom. This design enhances stability and reduces operational torque, making them ideal for large-diameter applications.
- Two Way Valves
- These ball valves have a straightforward configuration with one inlet and one outlet connection, allowing fluid to flow in a single direction. They are among the most commonly used ball valve designs.
- V-Port Ball Valve
- Manufacturers sometimes shape the bore or internal ball in a "V" pattern to enhance flow control precision. This design allows for finer regulation of fluid speed, making V-port ball valves highly effective for throttling applications.
Installing a Ball Valve
Always adhere to manufacturer guidelines to guarantee the proper installation of ball valves. In addition to these instructions, specific industry protocols may also apply, depending on the application. Certain work environments require adherence to specialized safety procedures to mitigate job hazards, ensuring that ball valves function safely and efficiently in their intended settings.
Ball valves are known for their reliability and user-friendly operation, making them an ideal choice for various industries. Their manual functionality is easy to learn, requiring minimal training for effective use. Even when left unused for extended periods, these valves maintain their performance without significant degradation. Their straightforward design, combined with their durability and ease of installation, has contributed to their widespread popularity across industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
Ball Valve Standards and Specifications
Ball valve manufacturers and customers must carefully adhere to industry standards governing the production and use of pipes and valve products. These regulations often define specific testing requirements to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance within various applications. For instance, 49 CFR 195.116 outlines federal standards for the transportation of hazardous liquids by pipeline, setting minimum requirements for valves—including ball valves—used in such operations.
Industry associations play a valuable role in assisting companies seeking guidance on compliance and testing procedures. Standards such as ASME B31.3, which provides piping codes for various ball valve categories, help establish uniform quality and performance benchmarks across different industries. Whether manufacturing or purchasing ball valves for a particular application, it is essential to thoroughly research and understand these regulations to ensure the valves meet all necessary operational and safety standards.
Ball Valve Care and Maintenance
In certain situations, technicians must periodically inspect the interior ball within the ball valve to confirm that it remains free of blockages or corrosion. Ensuring the integrity of this component is essential for maintaining smooth operation and preventing flow disruptions. Because the valve’s functionality depends on continuous contact between the ball and the stem of the valve handle, any significant wear or breakage in the stem may compromise performance. If the stem becomes damaged or excessively worn, repair or replacement of the valve may be necessary to restore proper operation.
How to Select a Ball Valve Manufacturer
Businesses often seek guidance on the most effective approach to selecting a reliable ball valve manufacturer. Above, we have provided a list of outstanding companies specializing in ball valve production. The ideal manufacturer for your business will be one that can meet your specific product requirements, ensuring quality, durability, and compatibility with your applications. To assist in this process, our web pages offer a wealth of valuable information on ball valves and trusted ball valve suppliers, providing the insights needed to make an informed decision.
Ball Valve Accessories
Some vendors provide ball valve accessories, including stem extension devices, to enhance functionality and accessibility. However, because many ball valves operate in highly regulated environments, it is essential to review industry safety and legal code requirements before incorporating any accessories. Additionally, some manufacturers produce original equipment manufacturer (OEM) components designed specifically for use with their customized ball valves. Using non-OEM or unauthorized spare parts may lead to compatibility issues and, in some cases, void manufacturer warranties. Ensuring compliance with recommended accessories helps maintain valve performance, safety, and regulatory adherence.
Ball Valve Terms
- Actuator
- A device used to operate a ball valve by controlling the flow of materials. Actuators can be manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic, depending on the application.
- Ball
- The central closure component of the valve that regulates or restricts the flow of liquid or gas by rotating within the valve body.
- Butterfly Valve
-
A type of valve that uses a circular disc or vane to control flow by pivoting at a 90-degree angle to the direction of the pipe’s flow.
- Flange
- A projecting rim or edge designed to reinforce, secure, or connect one object to another, often used to attach pipes, valves, or fittings.
- Full Bore Value
- A ball valve where the interior ball’s bore diameter matches the pipeline’s diameter, ensuring unrestricted flow. This is also known as a full port valve.
- Globe Valve
- A globular-shaped valve consisting of a disk, valve stem, and handwheel. The internal structure allows for precise flow control, typically used in throttling applications.
- Poppet Valve
- A valve that moves perpendicularly to its seat, opening and closing to regulate flow. It generally provides higher flow capacity than a ball valve.
- Port
- The designated flow path within a valve through which liquid or gas moves.
- Pressure Control Valve
- A valve designed to regulate pressure by closing when a predetermined threshold is reached, preventing excessive force within a system.
- Pressure Relief Valve
- A self-operating valve that automatically releases pressure when it exceeds safe levels, ensuring system protection and preventing potential damage.
- PSI (Pounds Per Square Inch)
- A unit of pressure measurement equivalent to kilonewtons per square centimeter in the metric system, commonly used to quantify pressure in fluid systems.
- Reduced Bore Value
- A ball valve where the internal ball’s bore is smaller than the pipe opening, allowing for controlled flow restriction. Also referred to as a standard bore or standard port valve.
- Relief Valve
- A valve that opens to discharge excess pressure or temperature, protecting equipment and ensuring safe operation in high-pressure environments.
- Slurry
- A thick mixture of liquid, typically water, combined with solid materials, forming a semi-fluid substance similar to mud or plaster of Paris.
- Trunnion
- A structural support system consisting of upper and lower supports that help stabilize the ball within the valve, ensuring smooth operation under high-pressure conditions.
- Valve Seat
- A stationary component of the valve that forms a seal against the movable closure mechanism, preventing or restricting liquid or gas flow when engaged.

