Blow Molded Plastics
Blow molded plastics are those hollow plastic products that have been created through the process of plastic blow molding.
Quick links to Blow Molded Plastics Information
The History of Plastic Blow Molding
The idea of plastic blow molding originally came from glassblowing, a similar process of earlier origin, and the first blow molding machine was produced around 1938. It was with such a product that, in 1939, plastic bottles were first mass-produced in the United States. However, due to limited resources in the 1940’s, blow molding did not truly become popular until later. Today, blow molded plastics are made from thermoplastics like acetal, polyamide, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), low density polycarbonate (LDPE), high density polycarbonate (HDPE) and polypropylene. Typically, they are characterized by thin walls and durable structures. Blow molded plastic products are quite diverse, including items such as drums, cases, containers, beverage bottles, toys and sports equipment.
Process of Extrusion Blow Molding
To create products such as these, manufacturers use three main processes associated with plastic blow molding: extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding and injection stretch blow molding. In extrusion blow molding (EBM), before the process begins, manufacturers take raw plastic resin, melt it down and form it into a hollow cylinder known as a parison. To kick things off, the parison is clamped into a mold, where a blow pin forces compressed air into it and it expands until it fills out the mold cavity, taking on its shape. Once it reaches its intended shape and size, the plastic is allowed to cool, typically with the aid of conduction, and harden. The last step is to remove it from the mold, which may or may not be done with the help of ejector pins. Extrusion blow molding produces the vast majority of blow molded plastics.
Injection Blow Molding Process
Next, injection blow molding (IBM) is performed in three main segments: injection, blowing and ejection. First, a molten polymer is fed into a hot runner manifold and injected via nozzles into a heated cavity and onto a core pin. The polymer surrounding the pin takes on the shape of the cavity, forming an exterior, while the core pin ensures that it remains hollow. Second, this pin rotates its way to a blow molding station, where the mold is clamped around a core rod, inflated inside a preform and cooled. Lastly, once hardened, the finished product is moved into the ejection position and stripped off the core rod. Note that injection blow molding is the least commonly utilized plastic blow molding process and is only used to create small capacity bottles and jars. Its infrequent usage is due to the fact that it is difficult to control the base center during the blowing process. Also, using this method, handles cannot be added and barrier strength cannot be increased.
Plastic Blow Molding Images and Illustrations
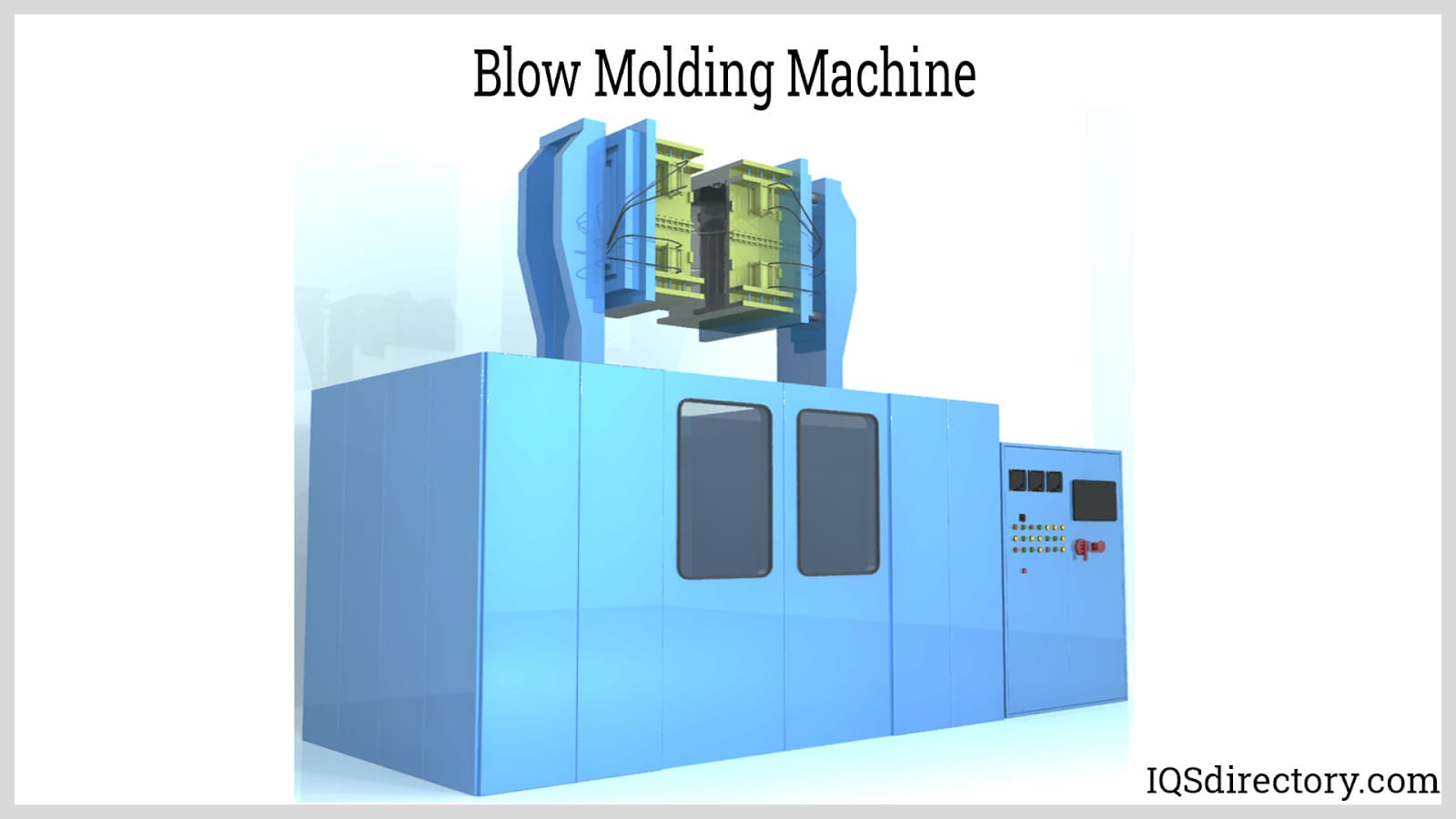
The blow molding machine compresses the air then inflates the preform until the plastic is molded according to the profile.
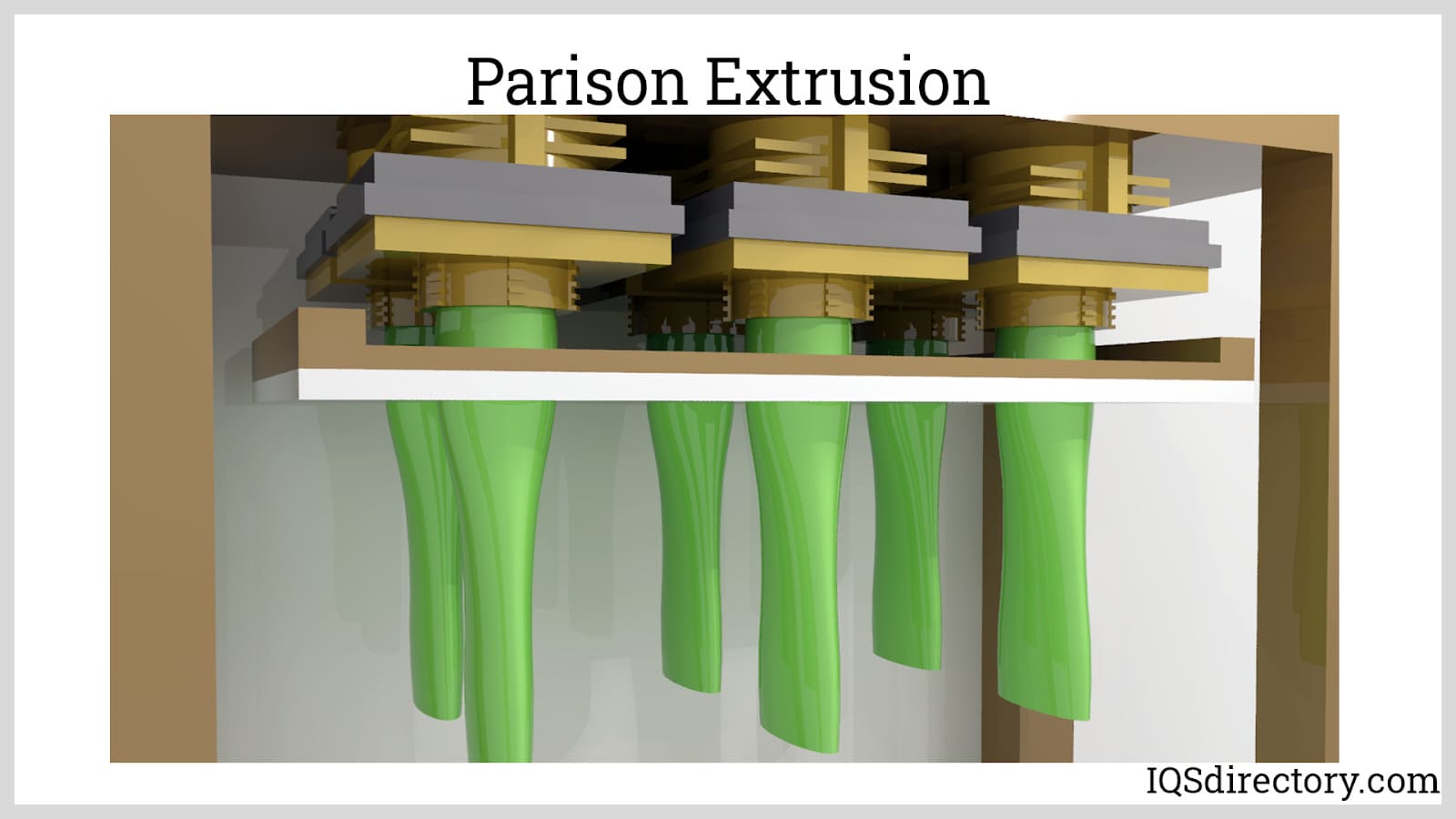
This process is the preparation of the parison or preform to be inflated
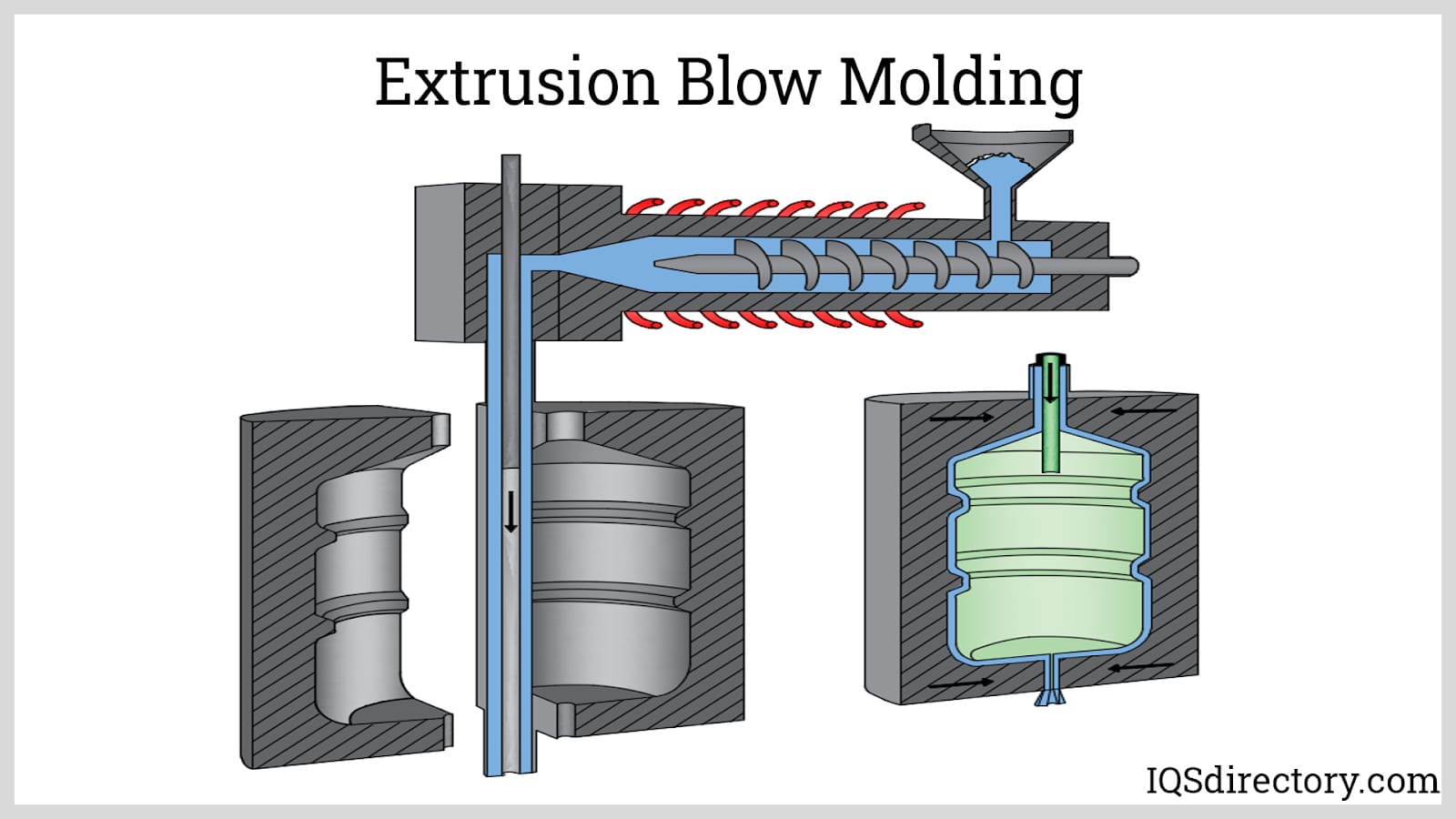
Extrusion blow molding involves the extrusion of a parison with a predetermined length which is held by a split the die on the ends, which is sealed on one end while the other end is fitted to an air supply.
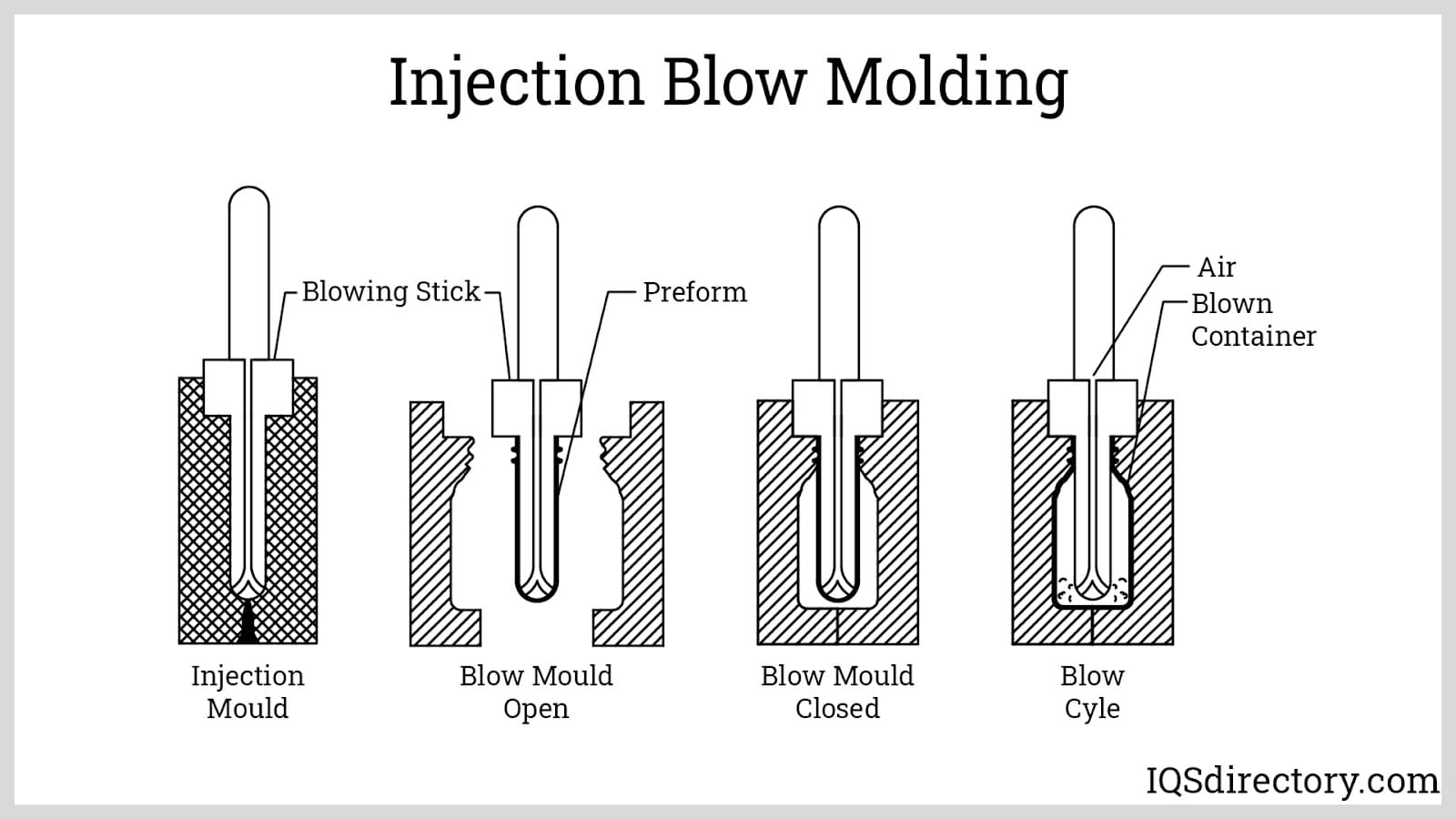
Injection blow molding combines the same attributes for injection molding and blow molding by using the injection molding then blowing the plastic into shape.
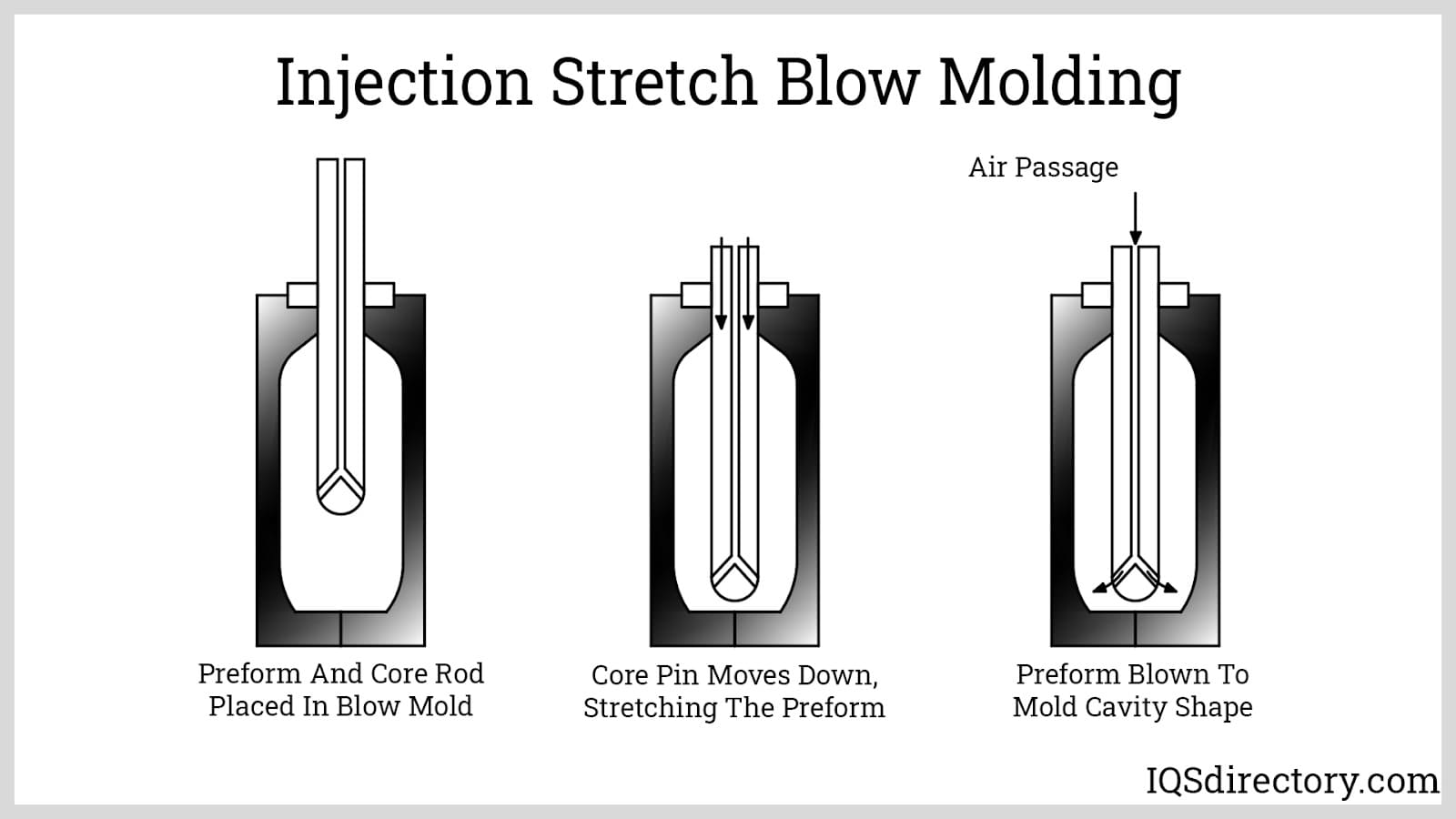
A modified version of the injection blow molding process involving stretching the plastic with a pull rod, enclose the plastic with a die, and then is inflated to the shape.
Injection Stretch Blow Molding Process
The final blow molding process, injection stretch blow molding, works quite similarly to injection blow molding. The main way in which it differs from the former is its use of bottle-shaped preforms. Note that injection stretch blow molding can be carried out using one of two methods: single-stage or two-stage. In the first method, both the preform and the bottle are blown in the same machine. In the second method, the preforms are created first, using the injection molding process, then they are later reheated and stretched into their intended shape and size. The latter step is done using pressurized air and core rods, which help the preforms stretch properly. Stretch blow molding is known for producing very high volumes of oval, rectangular or cylindrical bottles. Also, generally speaking, this process impedes bottle design very little. However, it does create somewhat high costs and it requires a larger amount of floor space than most.
Air Flow and Blow Molding
When performed properly, plastic blow molding processes yield plastic products with fairly long lifespans. The key to well-made blow molded plastics is air flow: in order to create strong, uniform walls, manufacturers must take care to apply pressurized air in a controlled and constant stream. This ensures even expansion. The inconsistent application of air would lead to varying wall thicknesses, which would likely result in products with diminished durability and strength. Per the request of their customers, manufacturers can affordably create products of different shapes, sizes and capabilities. They can even inject colors into the plastic before it is formed, without compromising their fast turnaround times. Plastic manufacturers are eager to collaborate; reach out to them today to find out more.
More Blow Molded Plastics Information
Blow Molded Plastics Informational Video

