Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard tubes, also known as paper tubes, are cylindrical structures crafted from wood pulp processed into various forms of cardboard, including fiberboard, paperboard, kraft paper, and paper-adhesive composites. These versatile products serve numerous purposes across a range of industries and are typically manufactured by wrapping ribbons of cardboard around a mandrel to achieve the desired dimensions.
Cardboard Tubes FAQ
What are cardboard tubes made from?
Cardboard tubes are made from wood pulp processed into fiberboard, paperboard, kraft paper, or paper-adhesive composites, typically spiral-wound around a mandrel with adhesives for strength and durability.
How are cardboard tubes measured?
Cardboard tubes are classified by their interior diameter in inches, not by exterior size. When exterior dimensions are critical, it is important to specify these clearly with the manufacturer.
What industries commonly use cardboard tubes?
Cardboard tubes are used in shipping, packaging, construction, textiles, automotive, and food industries. Applications range from mailing posters and documents to forming concrete columns and serving as paper cores for consumer products.
What are the advantages of using cardboard tubes?
Cardboard tubes are lightweight, cost-effective, and versatile. They offer strong durability relative to weight, are easy to recycle, and provide an environmentally friendly alternative to metal or plastic tubing.
Can cardboard tubes be customized for specific applications?
Yes, cardboard tubes can be customized by adjusting length, thickness, interior diameter, coatings, and sealants to meet unique performance needs, such as waterproofing or heavy-duty structural use.
How should cardboard tubes be stored to prevent damage?
Cardboard tubes should be stored upright in dry environments, away from moisture, pests, and heat sources. This prevents crushing, bending, and degradation during storage or use.
Are cardboard tubes environmentally friendly?
Yes, cardboard tubes are recyclable, often made from recycled paper, and biodegradable. Their eco-friendly properties make them a preferred choice for sustainable manufacturing and packaging applications.
The History of Cardboard Tubes
The development of cardboard tubes is closely tied to the broader history of cardboard. While the Chinese had used heavy paper for packaging for centuries, the first cardboard box emerged in the late 1800s. By 1903, the production of cardboard tubes and cores was already underway, although cardboard packaging as a whole gained widespread popularity a few years later when the Kellogg brothers began using cardboard boxes for their cornflakes.
Over the following century, the use of cardboard expanded dramatically, driven by advancements in chemistry and industrial manufacturing that enabled the production of stronger, more efficient materials. Today’s manufacturing methods for cardboard tubes remain fundamentally similar to early techniques, with improvements primarily in the quality of raw materials and the degree of automation involved.
Benefits and Advantages of Cardboard Tubes
Lightweight Advantage
Cardboard tubes, being made from paper-based materials, are inherently lightweight, making them easy to handle and transport compared to other structures with similar functionalities.
Strength Relative to Weight
Although cardboard is not the strongest material available, its strength-to-weight ratio is impressive, providing adequate durability for numerous applications while remaining easy to manage.
Versatility of Cardboard
The basic design of cardboard tubes is highly adaptable, making them suitable for a wide range of uses. With only minor modifications, they can be tailored to meet the needs of specialized applications.
Cost-Effective Tubing
Cardboard tubes offer an economical solution for creating cylindrical structures, as few materials can match their properties at such a low production cost.
Ease of Disposal
In applications where disposability is an advantage, the lightweight and degradable nature of cardboard tubes makes them simple to dispose of, particularly when dealing with lighter grades of cardboard.
Environmentally Friendly
Cardboard tubes are relatively easy to recycle and can often be produced from recycled materials. While not all production methods are fully sustainable, cardboard tubes generally offer a more environmentally friendly option compared to many alternatives, supporting efforts toward greener practices.
Design Factors of the Tubes
Strength of a Tube
The strength-to-weight ratio of a cardboard tube is influenced by multiple factors, including the type of base paper, adhesives, layering, resins, curing processes, and the tube's overall length. Each of these elements contributes to the resilience and durability of the final product. Determining specific strength requirements beforehand is essential, allowing collaboration with your manufacturer to ensure the tube meets the desired standards for your application.
Length of Cardboard
Cardboard tubes can be fabricated to virtually any length; however, most common applications require lengths under four feet. For narrower tubes, the appearance may resemble rings rather than traditional tubes, as seen with the cardboard cores used for structural support in tape rolls.
Interior Diameter Tube
Cardboard tubes are classified exclusively by their interior diameter in inches, not by their exterior dimensions. When specific exterior measurements are crucial for your application, it is vital to communicate these requirements clearly with your manufacturer to avoid misunderstandings about how dimensions are described.
Cardboard Tube Thickness
The thickness of a cardboard tube depends primarily on the base material and the number of layers applied during production. Additional factors, such as resins, adhesives, and coatings, can further influence the final thickness, impacting both functionality and suitability for specific applications.
Production Cost
Stronger cardboard tubes generally come with higher production costs. Additionally, the weight of these tubes can impact shipping expenses, which should be considered in your budget. For this reason, it is often more cost-effective to aim for tubes that are "strong enough" for your specific application, rather than opting for maximum strength unnecessarily.
Weight of Cardboard Tubes
For applications where minimizing weight is critical, working closely with your manufacturer is essential. Together, you can identify the ideal combination of materials and manufacturing processes to create a lightweight tube that meets your requirements for strength and other physical properties. A list of reliable cardboard tubing manufacturers can be found at the top of this page to assist in your search.
Sealants or Cures
If your cardboard tubes require enhanced resilience, such as moisture resistance, waterproofing, or durability beyond the properties of standard paper materials, specialized sealants and treatments will need to be applied during manufacturing. These treatments create a non-porous finish, ensuring the tubes meet the demands of more challenging environments.
Tube Characteristics
Cardboard tubes are distinguished by their impressive strength-to-weight ratio, making them durable yet lightweight. Their cylindrical shape is highly functional for a wide range of purposes, and their low production and shipping costs add to their appeal. In numerous applications, the ease of disassembly further enhances their value. For instance, cardboard tubes used as structural supports can be quickly removed once concrete has set. The discarded material can then be shredded using special equipment and recycled into new products, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Cardboard Creation Process
The majority of cardboard tubes are spiral-wound and reinforced with adhesive additives. The process begins with large sheets of cardboard or paperboard, which are cut into thin ribbons. These ribbons are coated in adhesive and wrapped at an angle around a mandrel shaped to the desired dimensions. To achieve the required strength, multiple layers of cardboard can be applied to the forming mandrel. Cardboard tubes are always measured and defined by their interior dimensions rather than their exterior, and most tubes are limited to a maximum length of 48 inches to maintain structural integrity.
For heavy-duty applications requiring high strength, waterproofing, or resistance to environmental factors, additional adhesives or interior sealing layers can be integrated into the fabrication process. The wood pulp-resin mixture is formed and cured, often followed by further curing in an oven. During this heat treatment, the pulp and adhesives bond together, resulting in a product with enhanced strength and durability. This process ensures that the finished tubes retain their shape and structural integrity, even in humid conditions or adverse weather. These characteristics are particularly crucial for applications involving storage or transportation, where products are exposed to risks from moisture, air, or typical transit-related damage.
Cardboard Tube Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts

Paper tubes consist of paper or paperboard sheet layers wound together to for a cylindrical shape and bonded with adhesives.
The different varieties that pape tubes are used for.

Different methods used for storing paper tubes to prevent damage.
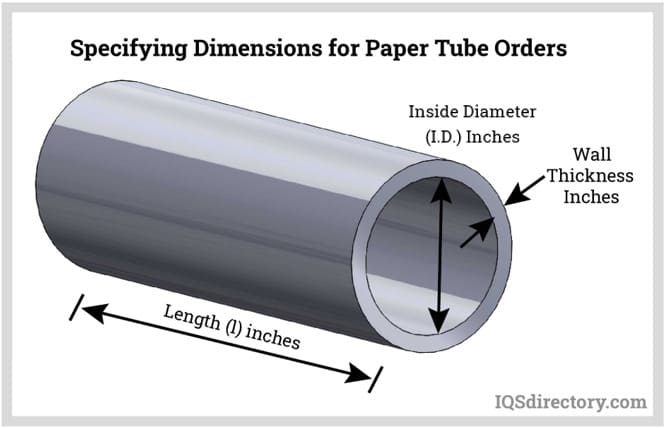
Paper tubes are measured according to the inner diameter (ID), wall thickness and length, which should be based on the products dimensions.
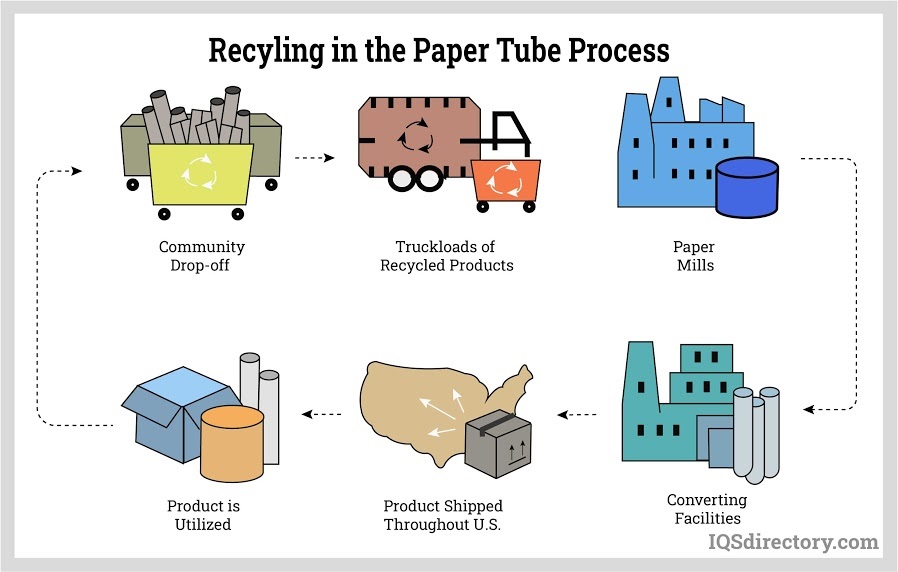
The recycling process used to recycle paper tubes for new usage.
Cardboard Tube Types
Cardboard Tubes
These are any tubes crafted from spiral-wound cardboard materials. Their applications are diverse, ranging from cores for various products to storage containers and shipping purposes.
Coin Bank
Small cardboard tubes specifically designed to hold precise monetary amounts of coins of the same denomination, serving as convenient storage and organization tools.
Corrugated Tubes
Constructed from composite paperboard, these tubes feature a layer of fluted material sandwiched between two layers of linerboard, providing additional strength and rigidity.
Construction Tubes
Often referred to as construction cores, these tubes are essential in forming and creating concrete construction components. They are most commonly used to fabricate concrete columns for load-bearing applications, though they are also suited for various other industrial and commercial uses.
Convolute Tubes
These tubes are made by rolling cardboard longitudinally upon itself to form a coiled, twisted, or rolled shape. The result is a unique structure with specialized applications.
Fiber Tubes
Made from fiberboard, these tubes are versatile in their use. They can store individual rolls, protect sensitive fabrics from crushing, separate and secure small lots, provide a location for returning goods, and make "bottom" rolls accessible when a full roll is not needed.
Mailing Tubes
Cardboard tubes designed for rolling up paper products to enable compact shipping while preventing bending or creasing of the material being sent.
Shipping Tubes
Also known as mailing tubes, these are cylindrical containers used explicitly for shipping items that fit conveniently in a tube. They may feature graphic advertisements printed on the exterior. End caps for these tubes can be made from wood, metal, or paper, depending on the application.
Sonotube
Large, water-resistant cylindrical forms made of paper, primarily used in concrete pouring applications to shape and support structures during the curing process.
Paper Tube Cores
Typically spiral-wound, these tubes serve as the center for various materials, including paper towels, fax paper rolls, tape, and film products, providing structural support and easy handling.
Paper Cans
Composite containers made primarily from paperboard, featuring an inner liner that acts as a protective barrier. These cans come in various thicknesses and sizes, with customizable closures and label options to meet specific requirements.
Spiral Wound Paper Tubes
These tubes are known for their longer cores, offering durability and versatility in applications where extended lengths are necessary.
Uses for Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard tubes are incredibly versatile and can be tailored to accommodate a wide range of products. Their structural strength and thickness are adjustable, depending on the level of protection required. Commonly, they serve as mailing and shipping tubes, ideal for transporting papers, posters, documents, and artwork that can be rolled into a cylindrical shape. These tubes, often made from high-quality kraft paper, are designed to endure the stress and pressure of transit. Kraft tubes, known for their durability, are widely used in shipping and packaging applications.
Cardboard tubes also find extensive use as paper cores, providing structural support for products like rolls of fabric, paper towels, toilet paper, and electrical wires. They function as coin banks for collecting donations, caulking tubes in construction projects, grease cartridges for automotive and mechanical applications, and paper cans for packaging food, cosmetics, and merchandise. Contractors and the construction industry rely on heavy-duty, durable cardboard tubes like Sonotubes® for forming concrete pillars, ensuring reliable performance in demanding applications.
For transporting, storing, or mailing fragile items, thicker cardboard tubes offer optimal protection. Mailing tubes are specifically designed to resist denting, bumping, and breaking during transit. Choosing the correct tube size is essential to prevent excessive movement of contents inside. Shipping tubes are typically sealed at both ends with plastic plugs, one of which is removable but may be sealed for security purposes, such as for confidential documents or medical and scientific products. Some tubes feature fold-in closures at each end. Measurements used to classify these tubes are based on their interior dimensions, accounting for wall thickness and the space required for end closures.
Shipping and mailing tubes often outperform boxes or other containers in strength and durability. Their cylindrical shape makes them particularly suitable for items that should not be folded, such as posters, artwork, large maps, or blueprints. They can also be customized with colorful, printed paper or foil for decorative or promotional purposes. For food packaging, product information and branding can be printed directly on the tube. Gift packaging and holiday-themed postal tubes often incorporate vibrant colors, patterns, and designs.
Cardboard tubes are frequently manufactured from recycled paper, and those made from durable board can be reused, offering a cost-efficient alternative to materials like metal, plastic, glass, and wood. Cardboard is easier for manufacturers to cut, purchase, and dispose of than most other materials. With a comparable strength-to-weight ratio, cardboard rivals plastic and metal tubes, making it an ideal choice for mailing, shipping, storing, and distributing various materials.
Heavy-duty cardboard tubes are particularly resistant to denting and breaking, offering excellent protection against rough handling. However, as a porous material, cardboard may require additional non-porous layers for specific applications, such as electrical wiring or food processing, to act as a moisture barrier. Despite this limitation, cardboard tubes are tough, flexible, and renewable, making them an excellent solution for commercial and industrial tubing needs.
Cardboard Applications
While the simplicity of cardboard tubes might suggest limited uses, their versatility makes them valuable across numerous industries and fields.
Shipping Tubes
Cardboard mailing tubes, postal tubes, and shipping tubes are widely used for securely transporting documents, posters, and other small items, offering protection against bending and damage during transit.
Structural Cores as Support
Paper cores play a crucial role as structural supports for various materials, including paper towels, wrapping paper, issue paper, textiles, and similar products.
Grease Cartridges
In mechanical and automotive fields, certain grease cartridges are crafted from durable cardboard tubes, serving as an economical and functional solution.
Paper Cans
Cardboard tubes are used to create paper cans for packaging foodstuffs, cosmetics, and a variety of other goods, often incorporating protective liners for added durability.
Construction Cardboard
Heavy-duty cardboard tubes are employed as structural supports in construction projects, such as forming concrete pillars and other load-bearing structures.
Support in Horticulture
Cardboard tubes are frequently used in horticulture as plant supports, cost-effective alternatives to pots, and containers for garden supplies and goods.
Cardboard Storage
Cardboard tubes provide inexpensive storage solutions for a wide array of goods and materials, making them a practical choice in various settings.
How Cardboard Tubes are Made
The production of cardboard tubes typically begins with the creation of cardboard in ribbon form. This base material may consist of paperboard, fiberboard, kraft paper, or a variety of composites and laminates. These ribbons are coated with strengthening adhesives and then wrapped in a spiral around a mandrel to form the desired cylindrical shape.
Specialized tubes often undergo additional treatments during or shortly after this process. These may include the application of specific adhesives, coatings, or sealants to enhance performance. For the most demanding applications, the process may incorporate resin coating, oven curing, or other heat treatments. These steps produce cardboard tubes with improved water resistance, chemical resistance, and overall tolerance to moisture, making them suitable for more rigorous or specialized uses.
Cardboard Innovations: Emergency Road Signs
Cardboard tubes, traditionally limited to uses like packaging, serving as cores for materials such as paper and plastic, forming concrete structures, and even acting as flower pots, have found a novel application through recent innovations. While these conventional uses have long defined their purpose, a new design showcases the potential of cardboard as an inexpensive yet sturdy material for a completely different function: emergency road signs.
This innovative application uses a cardboard tube to house a compact, flexible plastic emergency sign, designed for doctors, emergency personnel, and travelers in need. The sign, neatly stored within the tube, serves as a highly visible indicator of car trouble. Reflective green with white lettering, the sign ensures maximum visibility, even at night, functioning similarly to traditional road signs. Users can customize the message on the sign, making it adaptable to a wide range of industries and personal needs.
The concept originated in the United Kingdom, inspired by an incident where a doctor’s car broke down on a highway, leaving her unable to reach her destination. Despite her predicament, no one stopped to assist because there was no indication that the vehicle belonged to a doctor. This situation led to the development of the emergency road sign, aiming to prevent similar occurrences in the future.
To keep the product lightweight, portable, and cost-effective, a cardboard tube manufacturer was commissioned to create the casing for the sign. The compact design allows the tube to fit conveniently into small spaces within a vehicle, ensuring it is readily accessible in emergencies. While the standard sign is green and white for high visibility, users can choose from a range of color combinations to suit their preferences. This innovation highlights the versatility of cardboard and demonstrates its value beyond traditional applications.
Cardboard Standards and Specifications
Due to the broad range of applications for cardboard tubes, there are few universal standards or compliance factors that govern their production. Instead, the requirements for a given tube are largely dictated by its intended use. This makes it essential to thoroughly research and understand the specific regulations or standards relevant to your application before reaching out to a manufacturer.
Collaborating with a manufacturer experienced in your specific application can significantly streamline this process. Their expertise often includes a deep understanding of the unique needs and specifications required to meet compliance requirements, ensuring that the final product aligns with both functional and regulatory expectations.
Things to Consider When Purchasing Cardboard Tubes
Choosing the Right Manufacturer
Selecting the best cardboard tube manufacturing team isn’t just about finding the highest-rated or cheapest option—it’s about finding the right fit for your specific project. A manufacturer that aligns with your needs will save you more time, money, and resources than any other factor, ensuring a smoother and more efficient production process.
Specific Applications of Tubes
With the vast array of applications for cardboard tubes, it’s crucial to choose a manufacturer familiar with your specific use case. Researching their experience or obtaining references from similar production jobs will help you identify a team that understands your requirements. A knowledgeable manufacturer minimizes the risk of mistakes, missteps, waste, or inefficiency during production.
Manufacturer Flexibility
Working with a manufacturer that offers customization is key. Avoid companies that impose one-size-fits-all solutions to simplify their own processes at your expense. Instead, seek a partner willing to adapt their production methods to meet your exact needs, helping you optimize efficiency and achieve the best results for your project.
Scheduling Delivery
Early in your negotiations, establish clear delivery schedules to ensure you receive your cardboard tubes when needed. A realistic schedule, based on an in-depth understanding of your project requirements, shipping logistics, and other factors, is critical to avoid delays and disruptions.
Product Transparency
Know exactly what you’re getting for your money. When ordering cardboard tubes for a specific purpose, clarify what’s included in the quote, such as caps, storage solutions, sealants, or other secondary items. Failing to address these details upfront can lead to budget overruns or production issues, making transparency a vital aspect of the purchasing process.
Proper Care for Cardboard Tubes
While cardboard tubes are often chosen for their cost-effective and disposable nature, it is still essential to protect them from damage before and during use to ensure they serve their purpose effectively. Pay close attention to the following considerations:
Effects of Moisture
Moisture can compromise the integrity of almost any cardboard tube, except for specially treated heavy-duty varieties made with non-porous materials. To avoid damage, store your tubes in a dry environment or wrap them in protective plastic or insulating barriers if they are to be used in moist or wet conditions.
Upright Storage
Cardboard tubes lack the structural strength to withstand excessive weight or pressure. To prevent crushing or bending, store them upright rather than stacking them horizontally. This minimizes the risk of deformation during storage.
Heat Sources
Cardboard tubes are primarily composed of paper, wood fibers, and glue, making them highly flammable. Keep them away from sparks, open flames, or other high-heat sources to avoid potential hazards.
Secure From Pests
The paper and glue used in cardboard tubes can attract pests, such as insects and rodents. To prevent infestation, store your tubes in a secure location and consider applying protective sprays if necessary.
Use and Installation of Tubes
Cardboard tubes are among the simplest products to handle and use for various purposes. However, their relative fragility should always be considered during handling and management to avoid accidental damage. For cardboard tubes intended for high-speed manufacturing or sorting machinery, ensure they are specifically engineered to withstand the demands of those applications. Properly designed tubes will ensure seamless operation and reduce the risk of failure.
Cardboard Tube Accessories
End Caps
Cardboard tubes used for shipping, storage, or similar applications require proper fittings to securely seal their ends. Caps, plugs, or seals designed to match the specific dimensions of your tube are essential for ensuring the contents are protected and contained.
Sealants
Although cardboard tubes can be reinforced and strengthened during their production, additional sealants and coatings can be applied post-production to enhance their performance. These treatments provide insulation against moisture, chemicals, pests, or other environmental factors, extending the durability and functionality of the tube in various applications.
Cardboard Tube Terms
Composite or Paperboard Can
A packaging solution consisting of a body and two end closures, made from a variety of materials and available in numerous shapes and sizes. The container body is typically formed from paper tubes with various liners to meet barrier requirements and is often finished with a printed label for branding and package graphics.
Corrugating Medium
The fluted middle layer used in corrugated boxes or paper tubes, crafted from paperboard. This material is typically produced on a Fourdrinier machine as a single layer, utilizing a mix of virgin and recycled fibers to achieve the desired strength and structure.
Cylinder Paperboard
A type of paperboard produced from recycled fibers on a cylinder machine. It consists of multiple plies bonded together during the papermaking process, creating a sturdy material suitable for various applications.
End Closure
Rigid caps made from metal, plastic, or paper, or flexible structures such as layered plastic film, foil, or paper membranes, used to seal the ends of a package. End closures may be mechanically attached or heat-sealed, ensuring a secure and functional seal for the package.
Engineered Carriers
Highly specialized paper tubes, cardboard tubes, or cores made from paper or plastic, designed as carriers for products such as film, paper, tape, textiles, and metals. These carrier tubes are engineered to withstand extreme speeds and stress during material take-up, ensuring optimal performance in demanding applications.
Fiberboard
A composite material composed of compressed wood fibers and adhesive, fiberboard offers strength and durability for various applications.
Fourdrinier Machine
A machine used in the production of all grades of paper tubes and board, divided into distinct sections: a wet end, a press section, a drying section, and often a calendar section. This equipment is critical for manufacturing high-quality paper products.
Kraft Paper tube
Crafted from a chemically processed wood pulp, kraft paper is a coarse material known for its dark brown color, though it can be bleached to lighter shades. Derived from the German word for "strong," kraft paper is commonly used for wrapping and packaging.
Mandrel
An elongated core or mold around which materials such as resin-impregnated fiber, paper, fabric, tape, or filaments are wound to create pipes, tubes, or structural shell shapes.
Membrane Closure
A flexible material used to seal the end of a rigid package, typically attached with a peelable heat seal. This closure may consist of coextruded plastic film or layered materials such as plastic film, foil, or paper with a heat-seal coating for secure and functional sealing.
Paperboard
A category of paper characterized by its heavier weight, increased thickness, and rigidity. Generally, sheets with a thickness of 12 points (0.012 inches) or more are classified as paperboard, with exceptions like blotting papers, felts, and drawing paper, as well as certain thinner materials such as corrugating medium and linerboard.
Recovered Paper
Paper and its derivatives that are separated, removed, or diverted from solid waste for the purposes of reuse, sale, or recycling. This includes materials requiring further processing to meet specifications for their intended applications.
Spiral Winding
A manufacturing process where a ribbon of adhesive-coated cardboard is wrapped in a helix pattern around a round mandrel. This method creates spiral-wound paper tubes, producing a continuous product that can be cut to custom lengths and specifications.
More Cardboard Tubes Information
Paper Tubes Information