Die Cutting
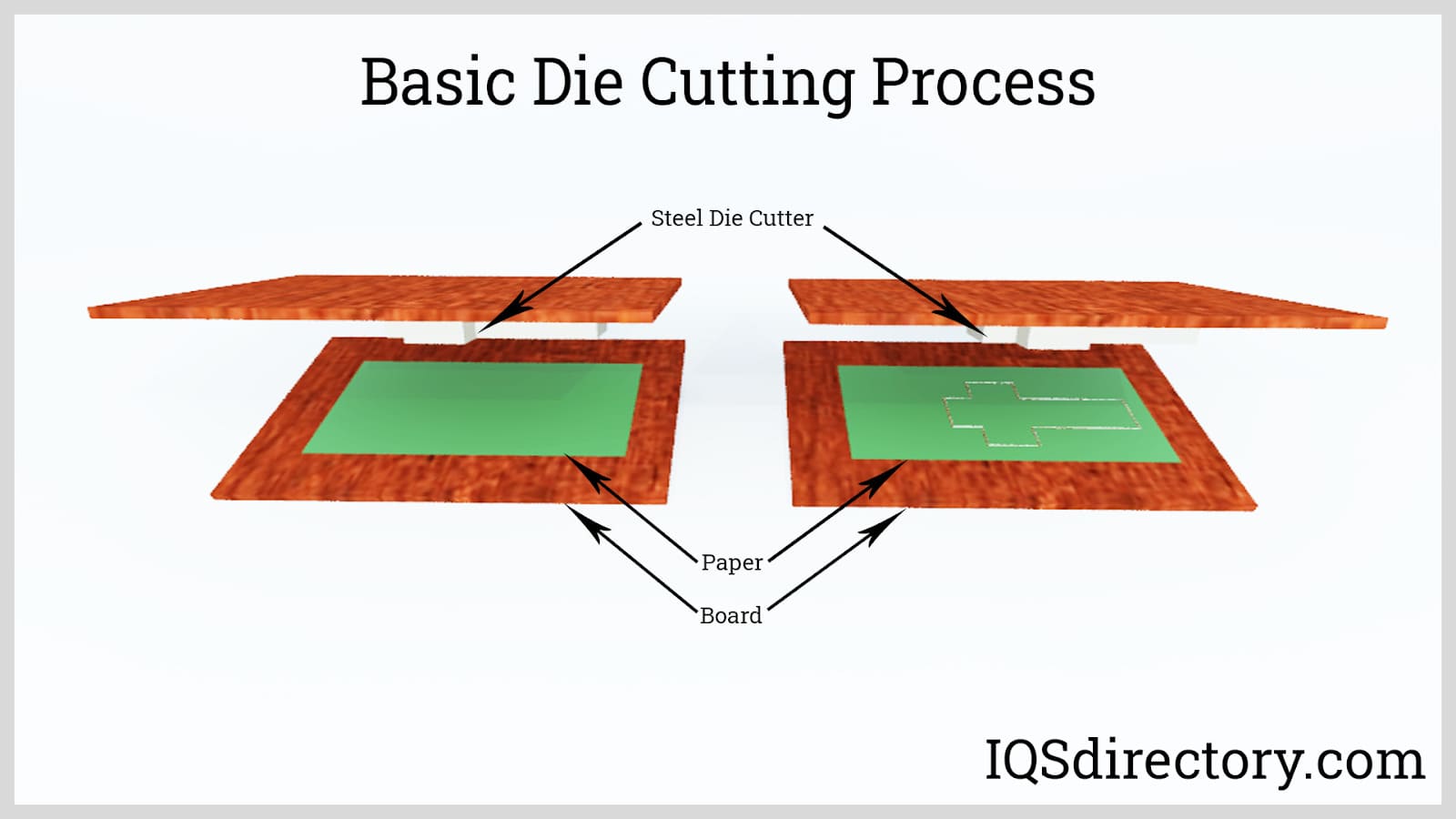
Die cutting is a mass production method of cutting parts, components, and materials efficiently and quickly using specially designed equipment and tools that cut, shear, and shape fabrics such as paper, rubber, fiber, and metals. It is a widely used method for the production of gaskets from neoprene and foam materials.
The term die cutting is a descriptor used for several cutting processes. Each of the different methods fulfills a specific need or configuration. The most common forms of die cutting are flatbed, rotary, and digital. The process chosen for cutting is in accordance with the material to be cut as well as the required efficiency and accuracy.
Flatbed die cutting is the simplest and least complex of the different methods. It is mainly used in production situations where several parts have to be processed in a short period of time. It is selected as a method of cutting for its ease of operation, low cost, versatility, and flexibility. Any type of material can be shaped, configured, or cut using this process.
An exceptional feature of flatbed die presses is their ability to apply extreme pressure on sheet or rolled stock. The factors that determine the use of flatbed die cutting is the type of material, design, and calculated geometries. The process can be used to cut through thin light materials as well as hard thick surfaces.
Rotary die cutting is a highly productive method of die cutting that can produce high volumes of parts and products rapidly. It is an exceptionally accurate process that uses dies that are attached to a cylinder in a press. A benefit of rotary die cutting is the multiple layers that can be cut with precision and exactness at very high speeds.
Much like the flatbed process, rotary die cutting is able to have the pressure of its cut set to the type of material to be fabricated with few limitations. Unlike flatbed die cutting, rotary die cutting is limited to web materials.
A popular method of die cutting is digital, which uses CNC programmed lasers, blades, and a variety of tools to cut materials without the use of a die. The process is capable of producing all of the various shapes and designs of the other die cutting methods with more precision at a lower cost.
Die cutting is a widely used method of fabrication and shaping due to its ability to be adapted to a variety of applications. Every die cutting machine can produce multiple shapes and forms from an endless number of dies. Dies can be easily changed and customized to fit the material. There are innumerable die cutting operations that vary from bending, coining, embossing, and perforating to name a few.
There are several benefits to using the die cutting process, which include speed, uniformity, and cost. Though die cutting produces parts at a rapid rate, every part is exactly the same from the first to the last. This is one of the main reasons die cutting is used for the fabrication of so many components and parts. Another of its benefits is its ability to be customized and programmed to perform specialized functions to create unique and unusual parts.
Die cutting services developed in the 19th Century to assist shoe manufacturers improve the production of their products. Since its introduction, it has grown to be an essential part of a variety of industries and industrial processes.
 Die cutting is the manufacturing process of stamping or cutting two dimensional parts out of flat sheets of materials like rubber, fiber, paper, or metals.
This process, often used in conjunction with laminating services, is a crucial finishing service for a wide range of parts and products.
Die cutting is the manufacturing process of stamping or cutting two dimensional parts out of flat sheets of materials like rubber, fiber, paper, or metals.
This process, often used in conjunction with laminating services, is a crucial finishing service for a wide range of parts and products.
Sometimes the term die cutting stems confusion, as it is quite ambiguous and its meaning differs in different fields. Other than cutting a material, a die can perform other functions as well, such as, forming, which involves compression and other stressing method for producing desired shapes. Learn more about die cutting.
 For many centuries, the same materials have remained as the base structural support for any structure.
These materials include concrete, wood, and steel. However, new research has created the potential for new structural support systems manufactured from fiber-reinforced polymer composites (FRP).
For many centuries, the same materials have remained as the base structural support for any structure.
These materials include concrete, wood, and steel. However, new research has created the potential for new structural support systems manufactured from fiber-reinforced polymer composites (FRP).
A FRP structure uses a combination of high-performance polymer resins, carbon and glass reinforcement fibers, and a foam core to create a highly stable, yet still flexible structural support system that is inexpensive and highly useful. The structures have been used successfully in the marine, renewable energy, and aerospace markets. FRP has been used in these markets for 40 years with favorable results.
Now, the FRP structures are available for use in architectural and civil structures. There are many benefits to using FRP, including the ability to form unique shapes, the freedom to use structural elements to create design freedom, and a simpler way to create curved forms. FRP is also resistant to structural damage, corrosion, fire, and environmental damage. The cost of FRP is also less than some materials, like steel, and the strength of the material is just as high.
Because of these benefits, the structure requires less maintenance, which cuts down on maintenance time and expenses. Buildings that use the foam structural cores will find that the chances of the structural support catching on fire is much less, and the structure is impervious to flooding. FRP is not invincible, as it can still be damaged by earthquakes and other shifts in the ground. The benefits of the material far outweigh any downsides, however. Learn more about foam fabricating.
 In industrial terms, a gasket, or an industrial gasket, is a mechanical seal used to bridge the gap between two surfaces.
Gaskets are used to create high-pressure seals between parts or surfaces. They put an end to the potential for leaks from or into products or areas. They ensure the smooth and proper functioning of many of the gadgets and equipment we use in our everyday lives.
Learn more about gaskets.
In industrial terms, a gasket, or an industrial gasket, is a mechanical seal used to bridge the gap between two surfaces.
Gaskets are used to create high-pressure seals between parts or surfaces. They put an end to the potential for leaks from or into products or areas. They ensure the smooth and proper functioning of many of the gadgets and equipment we use in our everyday lives.
Learn more about gaskets.
 O-rings are round, ring-shaped mechanical seals used to prevent leakage of media in and from mechanical parts.
Examples of the types of media these flexible mechanisms seal include gas, air, liquid and chemicals.
Learn more about o-rings.
O-rings are round, ring-shaped mechanical seals used to prevent leakage of media in and from mechanical parts.
Examples of the types of media these flexible mechanisms seal include gas, air, liquid and chemicals.
Learn more about o-rings.
 Plastic fabrication is the process by which manufacturers develop plastic products.
Plastic fabrication processes include thermoforming methods like extrusion and molding, as well as mechanical forming processes like plastic machining and stamping. It even includes joining processes like welding. Note: the terms "plastic fabrication," "plastic machining" and "plastic manufacturing" can be used interchangeably.
Learn more about plastic fabrication.
Plastic fabrication is the process by which manufacturers develop plastic products.
Plastic fabrication processes include thermoforming methods like extrusion and molding, as well as mechanical forming processes like plastic machining and stamping. It even includes joining processes like welding. Note: the terms "plastic fabrication," "plastic machining" and "plastic manufacturing" can be used interchangeably.
Learn more about plastic fabrication.
 Tape suppliers refers to both tape manufacturers and distributing tape companies that supply tape for a number of industries.
Tape is a long strip of sticky or otherwise adhesive material.
Learn more about tape suppliers.
Tape suppliers refers to both tape manufacturers and distributing tape companies that supply tape for a number of industries.
Tape is a long strip of sticky or otherwise adhesive material.
Learn more about tape suppliers.