Foam Fabrication
Foam fabricating involves the production of a lightweight and highly versatile material derived from polymers. During the manufacturing process, substances like plastic or polyurethane are aerated while in a molten state, creating a frothy consistency. As the material cools, it solidifies while retaining countless tiny air pockets throughout its structure, resulting in a texture and appearance reminiscent of a sponge.
Foam Fabrication FAQ
What is foam fabrication?
Foam fabrication is the process of creating lightweight, versatile materials by aerating polymers such as plastic or polyurethane. The material solidifies with air pockets, giving it strength, flexibility, or insulation depending on the formulation.
What are the main benefits of foam fabrication?
Foam fabrication offers advantages such as lightweight performance, cost efficiency, versatility across industries, and strong insulation properties. These benefits make foam ideal for applications in construction, shipping, automotive, and consumer goods.
What industries use fabricated foam?
Fabricated foam is used in construction, automotive manufacturing, medical products, shipping and logistics, furniture, bedding, and acoustic applications. Its adaptability makes it an essential material across industrial and consumer markets nationwide.
What is the difference between open-cell and closed-cell foam?
Open-cell foam has interconnected cells that allow airflow, making it soft and excellent for sound absorption. Closed-cell foam has sealed cells, providing high strength, moisture resistance, and superior insulation for construction and protective uses.
How is foam cut and shaped during fabrication?
Foam can be cut with methods such as die cutting, water jet cutting, hot wire cutting, or laser cutting. Each process offers different precision levels, enabling custom shapes for packaging, insulation, or automotive parts.
Is foam fabrication cost-effective for large projects?
Yes, foam fabrication is especially cost-effective at scale. It reduces waste, repurposes scrap into secondary products, and lowers handling and shipping costs due to its lightweight nature, making it ideal for large industrial projects.
Can fabricated foam be recycled?
Yes, many foam scraps are rebonded into products like carpet padding, cushions, or fillers. While recycling requires sorting and processing, it offers a sustainable alternative to incineration and helps reduce environmental impact.
History of Foam Fabricating
Foam fabrication spans a vast array of technologies and products, making its historical development a topic that could easily fill an entire textbook. The origins of polymeric foam science and manufacturing date back to the 1920s and 1930s, when the Talalay and Dunlop processes were pioneered for producing latex foam. These early breakthroughs laid the groundwork for an industry that would rapidly expand alongside advancements in chemistry and materials science.
From this foundation, the history of foam fabrication closely parallels the broader evolution of chemical engineering over the following decades. The discoveries made during and after World War I introduced new substances and chemical principles that gradually found their way into industrial applications, shaping the development of various foam materials.
A major milestone arrived in 1947 when researchers at Dow Chemical Company’s industrial labs invented foamed polystyrene, commonly recognized today as Styrofoam. Other modern foams emerged from independent research efforts conducted by numerous scientists and corporations, each developing unique formulations and fabrication techniques. As a result, different types of foam evolved simultaneously, each with distinct properties tailored to specific applications.
Today, foam fabrication reflects nearly a century of accumulated knowledge, experimentation, and innovation contributed by countless engineers and material scientists. The fundamental principles governing foam production continue to advance, influenced by both scientific discovery and practical manufacturing requirements. Recent developments, such as Nano cellular polymer foams, demonstrate how the field is still evolving, with new breakthroughs pushing the boundaries of what foam materials can achieve.
Benefits of Foam Fabrication
Given the sheer variety of foam types and applications, defining the benefits of foam fabrication as a single process is challenging. Some foams are remarkably strong, while others prioritize flexibility and pliability. Certain formulations are brittle yet highly resistant to pressure, whereas others maintain a soft composition while exhibiting exceptional tear resistance. If there is one overarching advantage to foam fabrication, it is the extraordinary range of customization available to achieve specific performance requirements.
- Lightweight Advantage
- Foam-based products consistently weigh less than comparable alternatives, making them particularly valuable in industries where reducing weight is a key priority. Applications in shipping, automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and consumer packaging all benefit from foam’s low-density properties. Beyond performance considerations, the reduced weight also simplifies handling and transportation logistics across a variety of industries.
- Cost Effective Benefit
- Foam fabrication enables the efficient production of bulk materials, with cost-effectiveness becoming even more pronounced at larger scales. The economic advantages of foam over alternative materials become increasingly evident as production volumes grow. Additionally, skilled foam fabricators can further optimize costs by minimizing waste and repurposing scrap materials for secondary applications, ensuring that resources are used as efficiently as possible.
- Versatility of Foam
- While companies may initially require foam for a singular purpose, the adaptability of foam materials extends their usefulness across multiple applications. Establishing a partnership with an experienced foam fabricator can provide long-term benefits, simplifying procurement for future needs such as protective packaging, soundproofing, or thermal insulation. Having a trusted supplier in place streamlines sourcing and enhances efficiency when additional foam-based solutions become necessary.
- General Insulation of Foam
- Foam’s insulating properties vary depending on its composition and manufacturing process, but it consistently outperforms many competing materials in thermal, acoustic, and vibration insulation. In this regard, foam is not just a viable option but often the superior choice. Its ability to deliver high-performance insulation at lower weights and densities makes it an optimal solution in construction, automotive applications, and industrial environments where maintaining controlled temperatures, reducing noise, or dampening vibrations is essential.
Applications of Foam Fabricating
Foams serve a vast range of purposes across numerous industries, making them an indispensable material in both everyday and specialized applications. It would be difficult to find an industry or field where fabricated foam does not play either a major or minor role. The adaptability of foam materials ensures their presence in everything from essential construction components to advanced medical solutions.
- Uses in Construction
- Rigid foams and sprayed polyurethane foam provide highly effective insulation and sealing solutions, contributing to reduced construction costs and improved energy efficiency. Their ability to fill gaps and create air-tight seals makes them an essential component in modern building projects.
- Household Applications
- Foam is a key material in a variety of household products, including sponges, filters, and mats. These everyday items benefit from foam’s unique properties, such as absorbency, flexibility, and durability, enhancing their functionality in domestic environments.
- Automotive Foam
- Custom foam components play a crucial role in the automotive industry, improving vehicle performance, comfort, and safety. Noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) seals, gaskets, padding, and pillar stuffers all rely on foam materials to optimize the driving experience by reducing noise and increasing structural efficiency.
- Medical Foam
- Foam is an essential material in medical applications, manufactured for a wide range of purposes, from surgical sponges and wound dressings to orthopedic foam inserts and prosthetic padding. Its ability to provide cushioning, support, and sterility makes it invaluable in healthcare settings.
- Fabricating Foam for Shipping
- Foam plays a fundamental role in shipping and logistics, offering protective cushioning and shock absorption for transported goods. Foam-based packaging solutions include shipping containers, packing inserts, and cushioning mats, ensuring fragile items remain intact during transit.
- Acoustic Applications
- Many foam materials excel in soundproofing and acoustic management, absorbing and dampening sound waves to improve noise control. This makes foam a preferred choice for recording studios, offices, theaters, and industrial facilities where managing sound levels is a priority.
- Bedding
- Memory foam mattresses and pillows are prime examples of how foam fabrication enhances comfort and ergonomics. Designed to conform to body contours, these foam products provide superior support and pressure relief, improving sleep quality and overall well-being.
- Uses in Furniture
- Polymeric foams form the foundation of modern furniture cushioning and upholstery, providing the perfect balance of support and softness. Whether in sofas, chairs, or mattresses, foam ensures long-lasting comfort and durability in residential and commercial furniture applications.
- Using Foam for Filtration
- Open-celled foams are widely used in filtration systems, forming the primary structure of air filters that remove particulates and contaminants. Their porous nature allows for efficient airflow while capturing unwanted particles, making them essential in HVAC systems, appliances, and industrial air purification.
- Absorption Applications
- Foam’s ability to absorb liquids and impacts makes it ideal for a variety of custom absorption applications. From kitchen sponges and bath mats to large-scale industrial absorption pads, foam is designed to handle everything from minor spills to major fluid containment needs.
- Seals
- Foam-based seals take advantage of the material’s flexibility and compressibility, ensuring secure closures in various applications. From industrial machinery to consumer products, foam seals provide airtight and watertight barriers that enhance product reliability and performance.
Fabricated Foam Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts
 Products made by polyurethane foam allowing for flexibility, low density, and high force absorption.
Products made by polyurethane foam allowing for flexibility, low density, and high force absorption.
 Flexible polyurethane foams can be made from either polyether or polyester polyols and have lower bulk densities, higher sag factors, and permeable structures.
Flexible polyurethane foams can be made from either polyether or polyester polyols and have lower bulk densities, higher sag factors, and permeable structures.
 Polyurethane foams are used for packaging materials, furniture, thermal insulations, car seats, and mattresses.
Polyurethane foams are used for packaging materials, furniture, thermal insulations, car seats, and mattresses.
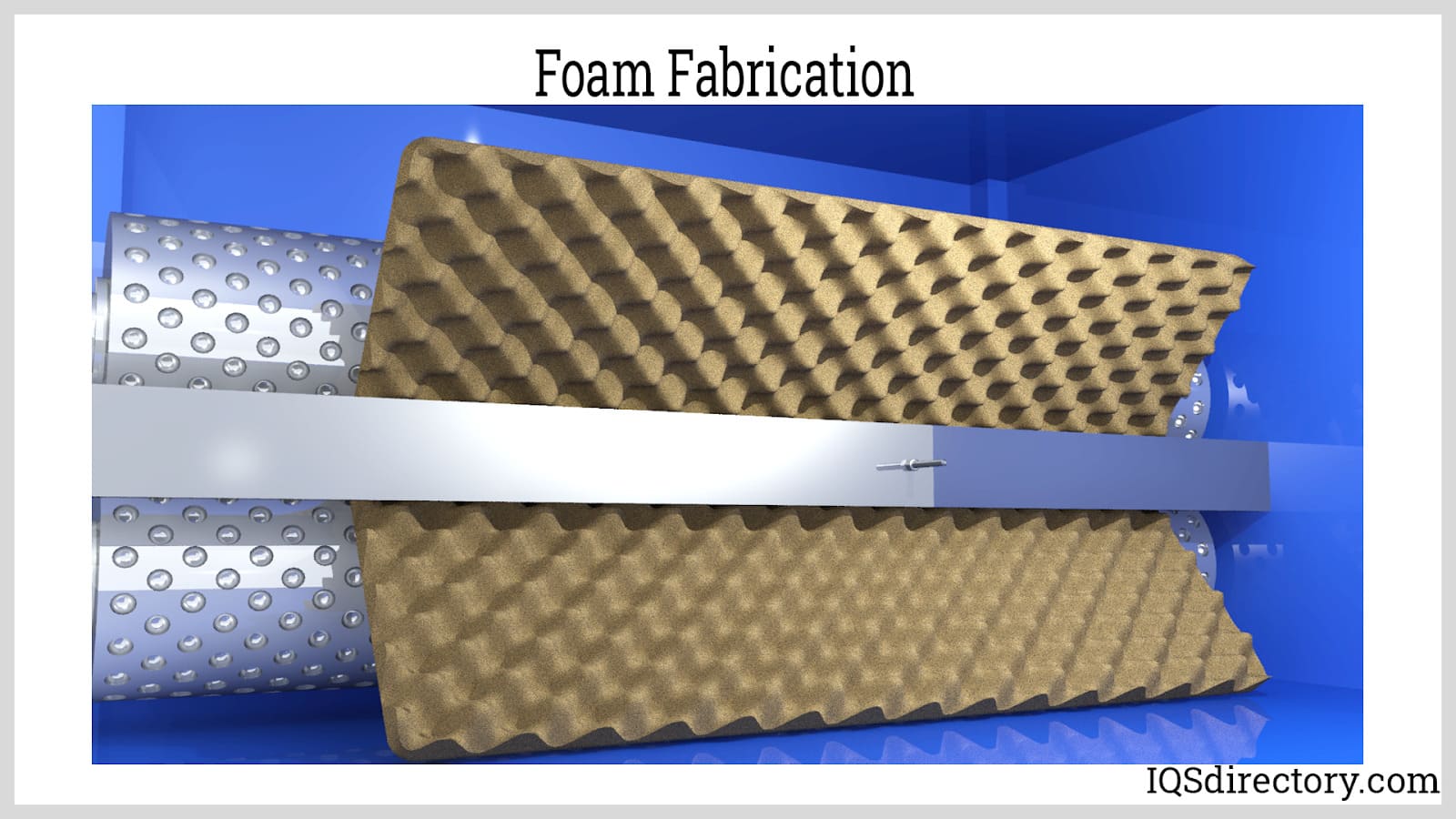
 The production process can be divided into the polymer system preparation and the foam production process.
The production process can be divided into the polymer system preparation and the foam production process.
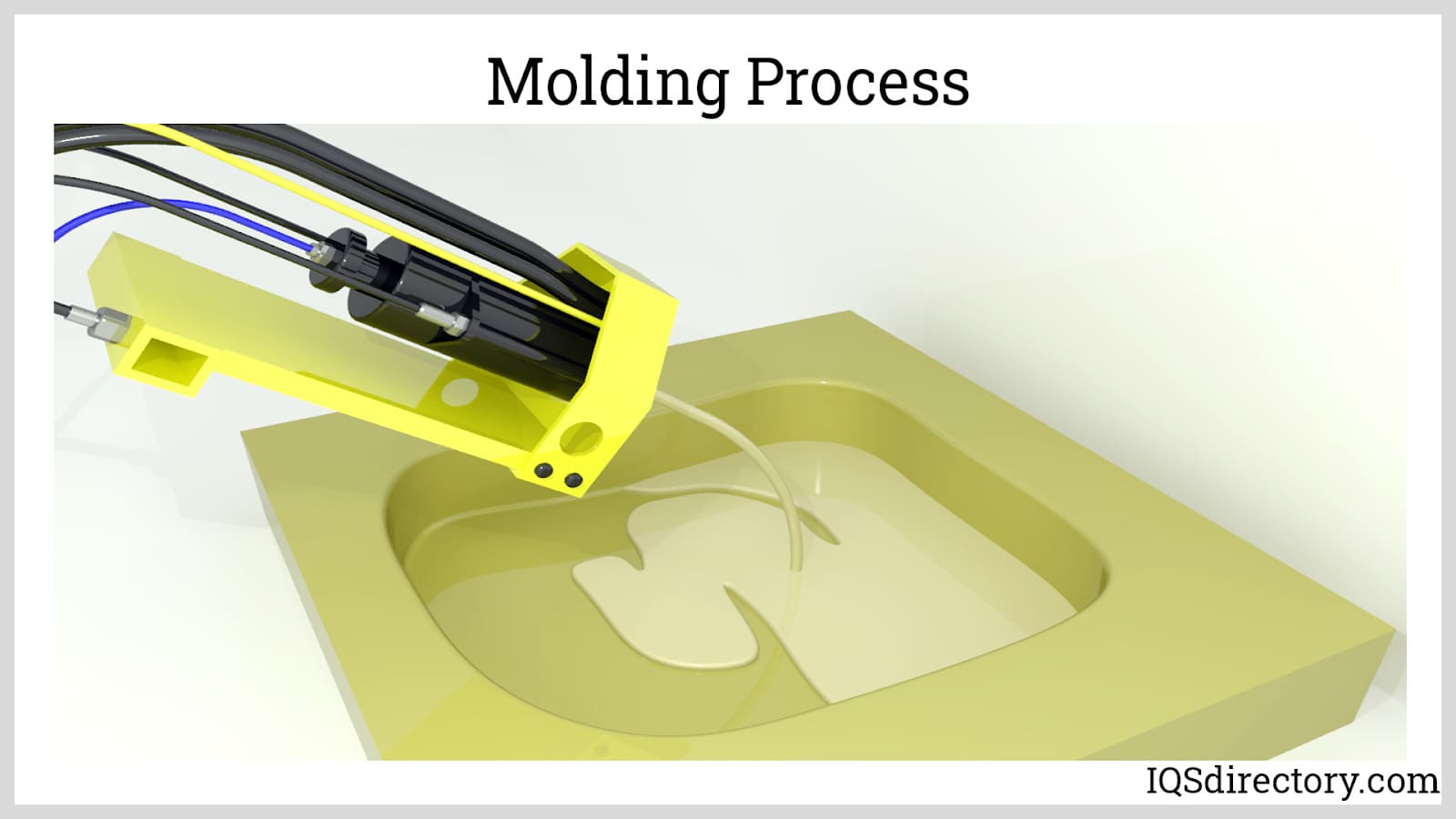 Molding foam process involves pouring or injecting the components through a mixing head and into a preheated mold, where the components react inside the mold causing the foam to rise.
Molding foam process involves pouring or injecting the components through a mixing head and into a preheated mold, where the components react inside the mold causing the foam to rise.
 Spraying polyurethane projects and impinges the blended polymer system on a surface or inside the cavity.
Spraying polyurethane projects and impinges the blended polymer system on a surface or inside the cavity.
Types of Fabricated Foam
When exploring fabricated foam, you will encounter a vast range of descriptors and classifications. Some foams are defined by their base materials, others by their manufacturing methods, and many by their post-processing treatments. Even an extensive list cannot capture every possible variation due to the sheer diversity of foam types available in modern applications.
- Closed-Cell Foam
- This high-density foam consists of individual, sealed cells that are physically separated from one another. Closed-cell foam exhibits remarkable compressive strength and resistance to moisture infiltration, making it ideal for insulation and protective applications. Because gas and liquid molecules cannot freely pass between the cells, heated gases cause expansion within the material, enhancing its thermal insulation properties. Spray foam is a common example, widely used for energy-efficient building insulation.
- Open-Cell Foam
- Unlike closed-cell foam, open-cell foam consists of interconnected cells that allow air to flow freely throughout the structure. This results in a lightweight, soft, and highly flexible material with excellent sound absorption properties. Open-cell foams are commonly used for foam padding products, foam cushions, and acoustic treatments, offering nearly twice the sound resistance of their closed-cell counterparts.
- Polyethylene Foam
- One of the most commonly used foam materials, polyethylene foam provides superior shock absorption, insulation, and vibration dampening. As a closed-cell, extruded plastic foam, it offers predictable impact resistance, making it an excellent choice for protective packaging. Products such as computer components, furniture, frozen foods, sporting goods, and clothing often rely on polyethylene foam for safe transport. Ethafoam, a specific type of polyethylene foam, enhances shock absorption and is widely used for cushioning and bracing in material handling and shipping applications. Polyether foam, a low-cost polyurethane variant, offers good cushioning with additional acoustic and packaging benefits.
- Cross-linked Polyethylene
- This fine-celled, resilient foam is known for its thick, smooth texture and superior physical and chemical durability. XLPE foam provides excellent impact resistance, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, making it a preferred material in medical, industrial, and packaging applications.
- Flexible Polyurethane Foam
- A highly versatile category that includes both polyether and polyester foams, flexible polyurethane foam is widely used in commercial applications due to its exceptional resilience and cushioning properties. This foam serves as a foundational material for bedding, furniture, automotive interiors, and packaging solutions.
- Foam for Acoustics
- Primarily composed of flexible polyurethane foam, acoustic foam is engineered to absorb and shape sound. Depending on its design, it can either attenuate sound waves for noise reduction or modify acoustic properties for specific applications, such as in recording studios and home theaters.
- Adhesive-Backed Foam
-
Designed to provide secure and even pressure distribution, adhesive-backed foam is commonly used in medical applications, including wound care, orthopedic supports, and protective padding. This foam maintains its structural integrity while adhering to surfaces for extended periods.
- Bonded Foam
- Formed by binding together shredded foam particles, bonded foam is an economical solution for carpet cushioning, padding, and support applications. Its durability and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for flooring underlayment and upholstered furniture.
- Cushion Foam
- A broad category encompassing foams specifically designed for padding in athletic gear, furniture, and impact-absorbing applications. Cushion foams provide enhanced comfort and shock absorption across a wide range of industries.
- Flexible Foam
- Often referring to polyurethane foams used in bedding and furniture, flexible foam provides a combination of softness, resilience, and breathability. This foam type is integral to mattresses, seating cushions, and ergonomic support products.
- Molded Foam
- A structured cellular foam that retains the precise shape of its mold after production, molded foam is utilized in applications requiring consistent dimensional accuracy. Automotive components, medical supports, and ergonomic seating often rely on this technology for custom-shaped foam products.
- Foam Used in Packaging
- A general term encompassing various foam types designed for shipping, handling, and product protection. Packaging foams ensure the safety of fragile items by providing cushioning and impact resistance during transit.
- Plastic Foam
- Characterized by a high strength-to-weight ratio, plastic foams feature tiny gas bubbles dispersed within a polymer matrix. These foams balance durability and lightweight properties, making them suitable for insulation, flotation devices, and protective enclosures.
- PVC Foam
- A rot-proof, self-extinguishing closed-cell foam with minimal moisture absorption, PVC foam adheres well to various materials using standard adhesive techniques. Its structural stability and flame-retardant nature make it ideal for marine, automotive, and industrial applications.
- Rigid Foam
- Composed of tightly packed cells, rigid foam offers outstanding thermal insulation and moisture resistance. Its structural strength makes it a preferred material for construction insulation panels, flotation devices, and lightweight composite materials.
- Microcellular Foam
- Manufactured with microscopic cell structures, microcellular foam exhibits superior compression resistance and enhanced mechanical properties. This advanced foam is used in applications requiring fine-tuned performance, such as automotive components, impact-resistant padding, and high-precision industrial parts.
- Nanocellular Foam
- A cutting-edge innovation in foam technology, nanocellular foams feature cell sizes measured in nanometers rather than micrometers or millimeters. These ultra-fine foams offer unprecedented strength, thermal insulation, and weight reduction, making them a promising material for aerospace, biomedical, and high-performance engineering applications.
Process and Materials of Foam Fabrication
Foam can be created from a diverse range of materials, including plastic, low-density elastomers, and rubber. Most commonly derived from polymers, foam production begins with the careful blending of chemical compounds, followed by the introduction of a gassing agent. This agent triggers expansion within the material, forming a foam strip composed of numerous gas bubbles trapped within the polymer structure. Once the foam has been created, various fabrication processes can be applied to shape and refine it for specific applications.
Several foam cutting techniques allow for precise modifications to foam materials. One of the most widely used methods is die cutting, where foam strips, blocks, or sheets are stamped into designated shapes using a press or rotary die. For applications requiring greater precision, water jet cutting employs a fine stream of water under ultra-high pressure to achieve exceptionally close tolerances that traditional die cutting cannot match. Hot wire cutting, another specialized method, utilizes a heated wire to create smooth, straight cuts, making it ideal for shaping foam into clean and uniform sections.
In addition to cutting, various foam forming techniques are used to manipulate bulk foam into different configurations. Thermal-forming is a common approach in which foam materials are heated and reshaped into desired forms, such as foam sheets. Another widely used technique, foam felting, compresses and cures thick, soft foam materials to produce denser, more compact structures.
Once foam is initially produced through chemical processing, it can be shaped into countless forms. A standard production method often results in a simple slab of foam, which can then be cut or refined using one of several major cutting techniques:
- Water Jet Cutting
- Ultra-high-pressure jets of water slice through foam materials with remarkable efficiency and accuracy. This method excels in creating precise cuts but is somewhat limited in the complexity of shapes it can produce.
- Die Cut Foam
- A specialized cutting instrument, typically incorporated into a press or rotary system, cuts foam into specific shapes. Die cutting is a cost-effective and straightforward approach, making it a popular choice for high-volume production.
- Hot Wire Foam Cutting
- By passing foam through a heated wire, this method enables smooth, clean cuts with excellent accuracy. While well-suited for detailed shaping, hot wire cutting becomes less efficient at larger scales.
- Laser Foam Cutting
- A high-intensity laser, often controlled by advanced programming, precisely cuts foam into intricate designs. This method allows for highly complex shapes and fine details, making it ideal for specialized applications.
- Other Foam Cutting Options
- Beyond these primary techniques, foam fabrication encompasses a broad spectrum of custom cutting and post-processing methods. The sheer variety of approaches allows for extensive customization in foam shaping, with nearly as many cutting and forming techniques as there are base foam materials.
- More advanced foam products may also involve various unique approaches to combining or layering foam via adhesives, heat treatments, lamination, and other joining techniques.
Machinery Used for Foam Fabricating
The vast diversity of foam types and applications makes it difficult to define a single set of machinery used in foam fabrication. The production of two different foam materials—such as flexible polyurethane foam and cross-linked polyethylene foam—may require entirely distinct equipment. Furthermore, after the initial formation, these foams can undergo additional shaping, treatment, or combination processes, each requiring specialized machinery.
Because foam fabricators often specialize in particular materials and techniques, those seeking custom foam fabrication must carefully evaluate their options. Discussing specific needs with fabricators is crucial, as capabilities and equipment vary significantly across the industry. Selecting the right foam fabricator ensures compatibility with project requirements and maximizes the potential of the final product.
Things to Consider When Choosing Foam Fabrication
There are quite a few factors to consider when finding the right manufacturer for your needs. Because foam fabrication encompasses such a wide range of end products and applications, you're best served looking for a fabrication team that matches your specific needs rather than one that's simply 'good' in a generic sense. In particular, you'll want to look for these factors.
- Equipped for the Right Foam Type
- The first and most crucial factor is ensuring that the manufacturer is properly equipped to produce the exact type of foam required for your project. While some manufacturers maintain the tools and expertise to handle a broad spectrum of foam types, others specialize in a narrower range of production methods. Verifying that a fabricator can meet your material specifications prevents costly delays and ensures that the end product performs as expected.
- Familiar With Your Usage
- Beyond possessing the necessary equipment, an ideal foam fabricator should have direct experience working with applications similar to yours. A manufacturer familiar with your specific industry or product standards will be better equipped to optimize production, reduce waste, and meet compliance requirements efficiently. The more specialized your needs, the more critical it becomes to partner with a team that understands the unique demands of your application.
- Transparency With the Consumer
- Given the numerous variables in foam fabrication, working with a manufacturer that values transparency is essential. Clear communication regarding production methods, costs, and logistics helps prevent unexpected setbacks that could disrupt your timeline and budget. Ensuring that a fabricator openly shares details about material sourcing, lead times, and quality control procedures allows for better planning and smoother execution.
- Versatility in Foam Fabrication
- While specialized fabricators offer deep expertise in certain areas, it is often beneficial to work with a manufacturer capable of handling multiple foam-related projects. Establishing a long-term relationship with a versatile fabricator simplifies procurement and coordination, reducing the need to source different foam producers for separate projects. A flexible fabricator can adapt to evolving requirements, making them a valuable long-term partner.
New Foam Fabrication for Structural Support
For centuries, traditional materials such as concrete, wood, and steel have served as the foundation for structural support in construction. However, advancements in materials science have introduced new structural solutions, including fiber-reinforced polymer composites (FRP). These innovative structures combine high-performance polymer resins, carbon and glass reinforcement fibers, and a foam core to create a support system that is both highly stable and flexible.
FRP structures have been successfully implemented in industries such as marine engineering, renewable energy, and aerospace for over four decades, demonstrating their reliability in demanding environments. Now, this technology is increasingly being applied to architectural and civil structures, offering numerous benefits over traditional materials.
One of the key advantages of FRP is its ability to form unique, customized shapes, providing greater design freedom for architects and engineers. The material’s corrosion resistance, fire resistance, and environmental durability make it an attractive alternative to conventional building materials. Additionally, FRP is lighter and often more cost-effective than steel, yet it maintains comparable strength and load-bearing capacity.
Because of these inherent advantages, FRP structures require less maintenance over time, significantly reducing upkeep costs and extending the lifespan of buildings and infrastructure. Structures incorporating foam-based FRP cores benefit from improved fire resistance and flood protection, minimizing risks associated with common environmental hazards. While FRP is not immune to damage from extreme seismic activity or ground shifts, its benefits overwhelmingly outweigh its limitations.
As advancements in foam fabrication and composite engineering continue, FRP structures are expected to become a more widespread and economically viable option for modern construction projects, infrastructure development, and specialized industrial applications.
Handling Foam Waste
Foam fabrication processes generate significant amounts of scrap material. The first major source of foam waste occurs during production and cutting processes, particularly foam die cutting. Scrap is generated during startup and shutdown procedures, production line changeovers, and when foam blocks are trimmed and shaped into final products. The second primary source of foam waste comes from discarded foam products that have reached the end of their usable life.
To minimize waste, shredded foam is often rebonded and repurposed into secondary products such as carpet padding, pillow and furniture fillers, and other cushioning materials. While burning foam to reduce bulk was once a widely used disposal method, this practice has declined due to increasing environmental concerns and stricter carbon dioxide emission regulations. Although U.S. government agencies classify foam burning as non-toxic, many manufacturers have shifted toward recycling as a more sustainable waste management strategy.
Recycling offers manufacturers an opportunity to recover value from foam waste that would otherwise be lost through incineration. However, the recycling process involves several challenges, including foam collection, contaminant separation, and cost-effective transportation. While the use of recyclable foam materials continues to expand, the economic feasibility of foam recycling depends on advancements in sorting and processing technologies that make the effort more efficient and cost-effective.
Alternatives to Foam
Because foam serves diverse functions across various industries, alternative materials vary significantly depending on the application. For insulation, materials such as fiberglass insulation and cellulose boards provide effective substitutes. In bedding applications, natural fillings like down or textiles can be used in place of foam. For protective shipping solutions, alternatives include bubble wrap, cardboard padding, and molded pulp packaging.
Despite the availability of substitutes, foam remains a preferred choice in many industries due to its versatility, cost efficiency, and ease of fabrication. The best material for any given application depends on specific performance requirements, environmental considerations, and cost-effectiveness. Instead of making a broad decision between “foam” and “non-foam” materials, evaluating the unique needs of each application ensures the most effective solution is selected.
Foam Fabricating Terms
- Additive
- A material used to modify the properties, processing, or final application of a base polymer. The amount of additive is typically measured in parts per hundred of the total resin within the polymer formulation.
- Air Flow
- The volume of air passing through a two-foot by two-foot by one-foot foam sample under a five-inch water pressure differential, expressed in cubic feet per minute.
- Air Traps
- Voids found in molded foam parts caused by air pockets trapped during mold fill-out. These air traps are characterized by smooth, shiny surfaces.
- Amine
- A category of compounds that serve as catalysts in polyurethane foam reactions.
- Anti-Static Flexible Polyurethane Foam
A foam containing electrically conductive material designed to prevent static electricity buildup or facilitate static discharge, primarily used for packaging electronic components.
- Auxiliary Blowing Agent (ABA)
- An additive that enhances the primary blowing agent, typically water, in foam production. It can contribute to the creation of softer or lighter foam.
- Ball Rebound
- A test method measuring the surface resilience of flexible polyurethane foam by dropping a steel ball of a specified weight from a set height onto the foam. The ball rebound value is expressed as a percentage of the original drop height.
- Basal Cells
- Large, irregular cells located just beneath the surface of a molded foam part.
- Blowing
- The foaming process in polyurethane production, where toluene diisocyanate reacts with water to generate carbon dioxide, expanding the material.
- Bonding
- The process of combining two or more components into a composite. Foam is often bonded to other foam grades or polyester fiber.
- Buffed
- A shaping or contouring method where foam is refined using abrasives to achieve the desired form.
- Bun
- A section of foam cut from continuously produced slab stock.
- Cells
- Hollow spaces within polyurethane foam, enclosed by polymer membranes or a polymer skeleton, created during the blowing process.
- CFC-Free Foams
- Flexible polyurethane foams manufactured without chlorofluorocarbons as auxiliary blowing agents.
- Cold Molding
- A production technique for high-resiliency foam where the pouring process occurs at or near room temperature, without additional heat application.
- Combustion Modifying Additive
- An additive that will decrease the ability of flexible polyurethane foam to ignite or make it burn more slowly.
- Compression Force Deflection (CFD)
- Also known as compression load deflection (CLD), this measures the foam’s load-bearing capacity.
- Compression Molding Foam
- A forming and fabricating process used for thermoplastics and rubber. Compression molding is a preferred technique for creating regular and contoured 3D foam parts with or without intricate details.
- Convoluting
- A specialized cutting process that creates a foam sheet with a dimpled texture.
- Clickability
- The ability of flexible polyurethane foam to return to its original shape after being compressed during die cutting.
- Closed Pour
- A molding process where the mold lid is locked in place, and the foaming mixture is injected through ports in the lid.
- Contour Cutting
- The cutting of foam blocks into specific patterns using specialized saws, producing custom foam parts.
- Core
- The inner portion of a foam piece, distinct from the outer skin.
- Crushing
- A mechanical or vacuum-assisted process used to open the closed cells in high-resilience slab stock or molded foam.
- Dead Foam
- A type of foam with low resiliency that does not quickly return to its original shape after being compressed.
- Deformation
- A process in which foam is permanently or temporarily reshaped through compression or heat exposure.
- Die Cutting
- A method similar to stamping, where foam parts are cut to precise shapes. This is ideal for large production runs requiring consistent sizing.
- Drilling
- The process of boring holes into foam to improve air circulation, facilitate tufted designs, or enhance softness.
- Elastomers
- Polymers that exhibit rubber-like elasticity, resisting deformation and returning to their original shape.
- Flame Lamination
- Also called "flame bonding," this technique bonds foam to fabric, film, or other materials by briefly melting the foam’s surface with a flame before pressing it onto the material.
- High Resilience (HR) Foam
- A polyurethane foam made with polymer or graft polyols. Its non-uniform cell structure improves comfort, support, resilience, and bounce compared to conventional foams.
- Hot Wire Cutting
- A cutting method using heated wires instead of saw blades, often used for shaping intricate foam components.
- Isocyanate
- A shorthand term for diisocyanates, one of the two main chemical ingredients in polyurethane foam production.
- Laminating
- The process of bonding multiple foam layers to form a composite. This can be achieved through adhesives or heat-based techniques like flame lamination.
- Peeling
- A method used to cut thin sheets from a foam cylinder.
- Skin
- The denser outer surface of foam, typically formed due to faster cooling compared to the core.
- Slab Stock
- A type of flexible polyurethane foam created through continuous pouring of liquid mixtures onto a conveyor system, forming a long, continuous loaf.
- Slitting
- A cutting process used to create foam sheets from a rectangular foam block.
- Voids
- Unintentional hollow spaces within foam structures, often resulting from improper mold filling or inadequate material flow.
- Thermoforming Foam
- A process used to shape thermoplastic foam, which has a sponge-like consistency and can be formed in solid or liquid states through frothing and cooling of a molten polymer.