Industrial Boilers
Industrial boilers are typically used to generate steam by applying thermal energy to transform water into steam on a large scale. Often, the steam will be used for heating or to power equipment. High-pressure boilers yield large amounts of steam within the durable chamber. Once enough steam has been created, the steam is released through valves and pressure channels to the destined machinery. Leftover cooled water is sent back to the boiler to be recycled and reheated. To avoid corrosion, fresh water should be added to counterbalance any loss of water during the process.
Quick links to Industrial Boilers Information
Applications of Industrial Boilers
Industrial boilers are built to withstand more stress than commercial boilers or hot water boilers. Industrial boilers are often larger than commercial boilers and are manufactured with steel up to 35 mm thick, allowing for pressures up to 30 bar and above. These features make industrial boilers suitable for industries that require a large heating capacity. Industries such as agriculture, ceramic, electrical, refineries, food and beverages, paper and pulp, manufacturing, and many more employ steam production from industrial boilers for a myriad of applications. These applications range from power generation, heating kilns, driving turbines, agricultural soil steaming, cement production,and large scale heating. Some industries, such as paper and pulp, utilize industrial boilers that are fueled by the waste of their operations.
Industrial Boiler Safety Considerations
The safety and efficiency of industrial boilers has come a long way since their invention. Organizations, such as ASME, helped to create the standards for both design and operation that modern manufacturers adhere to still today. Industrial boilers are now furnished with pressure sensitive gauges and relief valves and fabricated with durable materials to prevent damage. These safety measures reduce risks as well as increase efficiency by reducing heat loss levels and cutting fuel cost. It is important to evaluate your application and choose an industrial boiler constructed by a trusted manufacturer in order to minimize the risk of accidents and increase output.
Industrial Boiler Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts
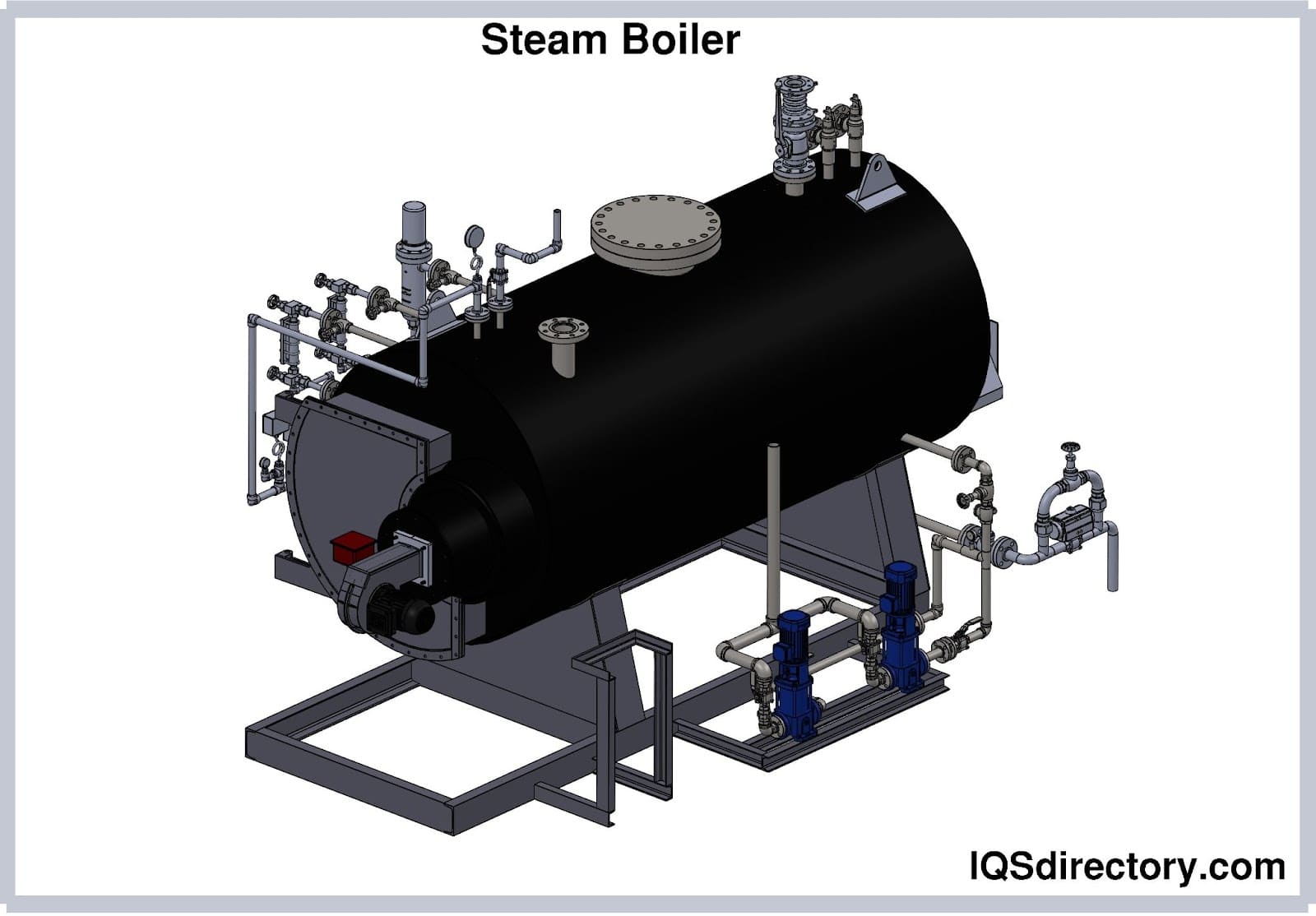 Steam boiler creates energy from boiling water and turning it into steam.
Steam boiler creates energy from boiling water and turning it into steam.
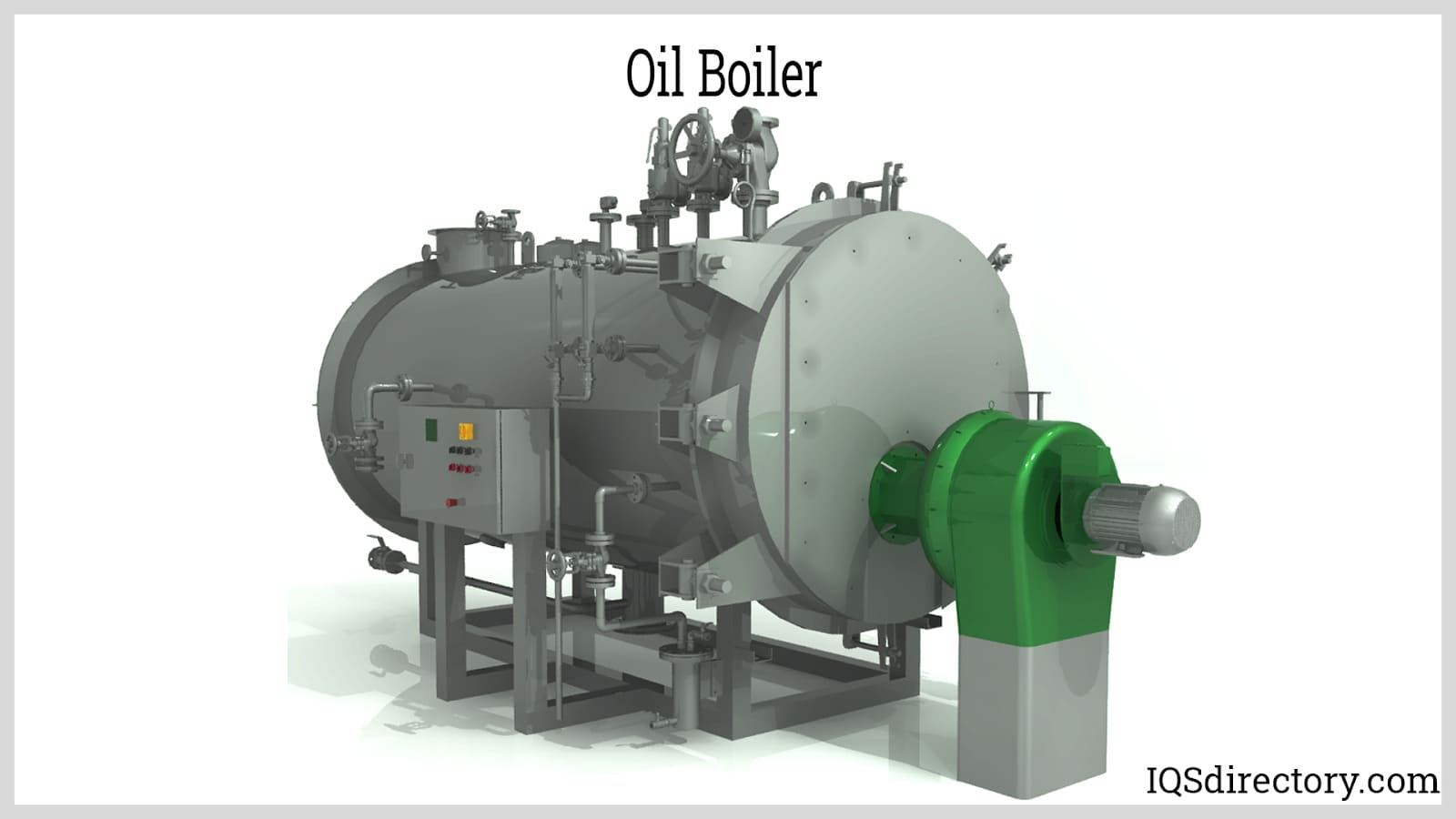 Oil boilers ignite oil in a combustion chamber and heats the heat exchanger that heats the water.
Oil boilers ignite oil in a combustion chamber and heats the heat exchanger that heats the water.
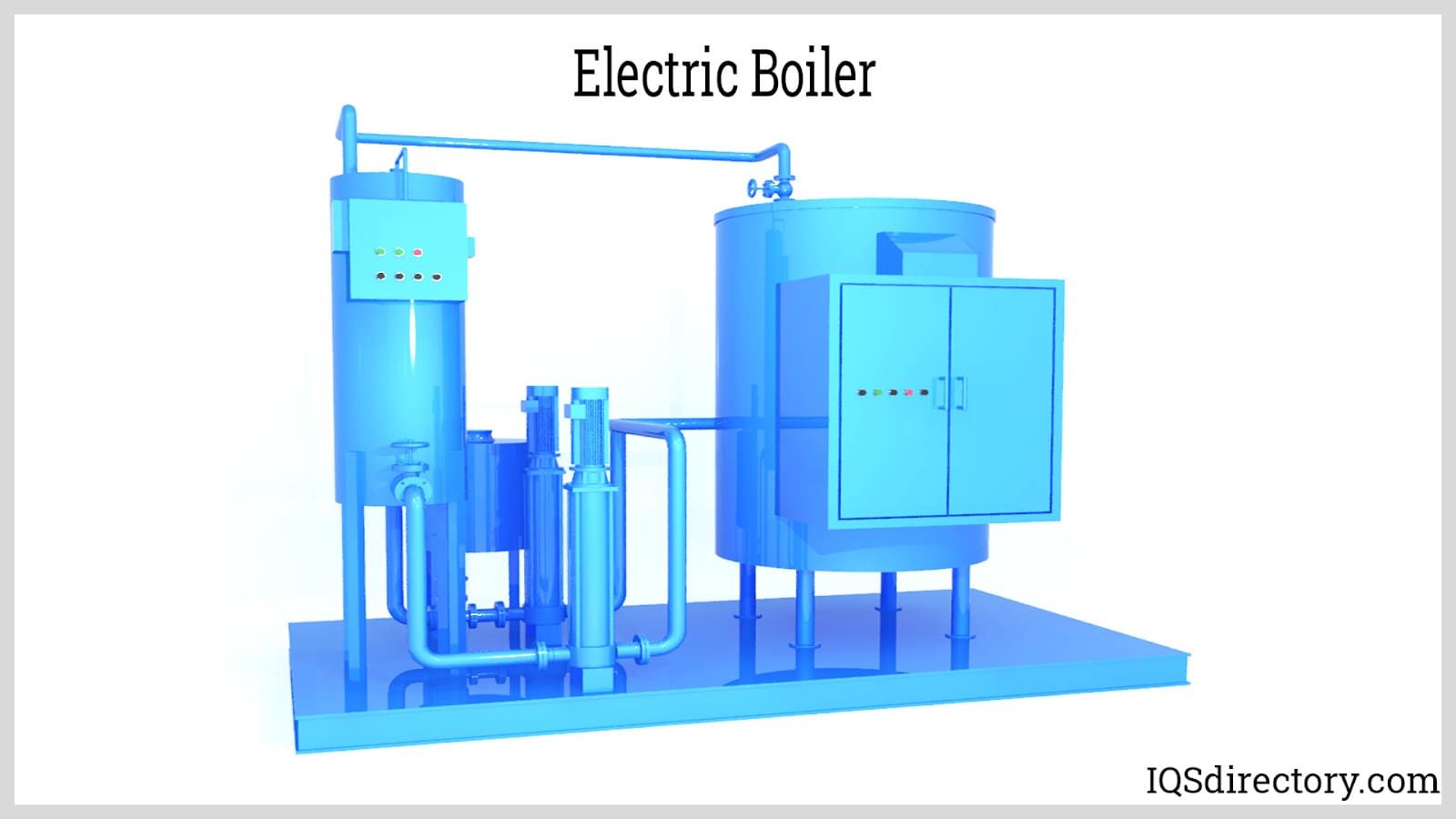 Electric boilers use electrical heating elements which heats water creating energy.
Electric boilers use electrical heating elements which heats water creating energy.
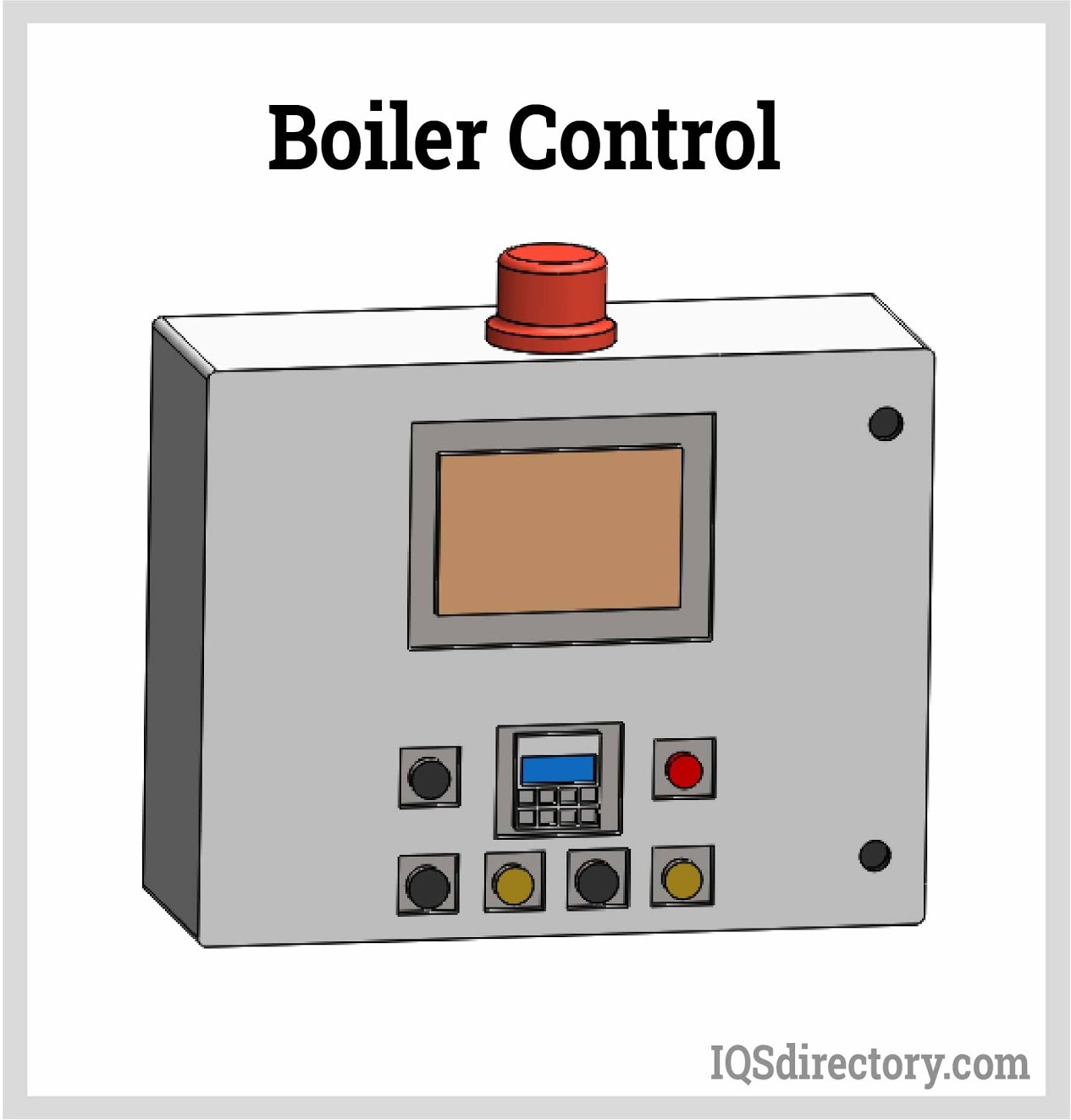 Boiler controllers monitor the operations of a boiler and check for abnormalities.
Boiler controllers monitor the operations of a boiler and check for abnormalities.
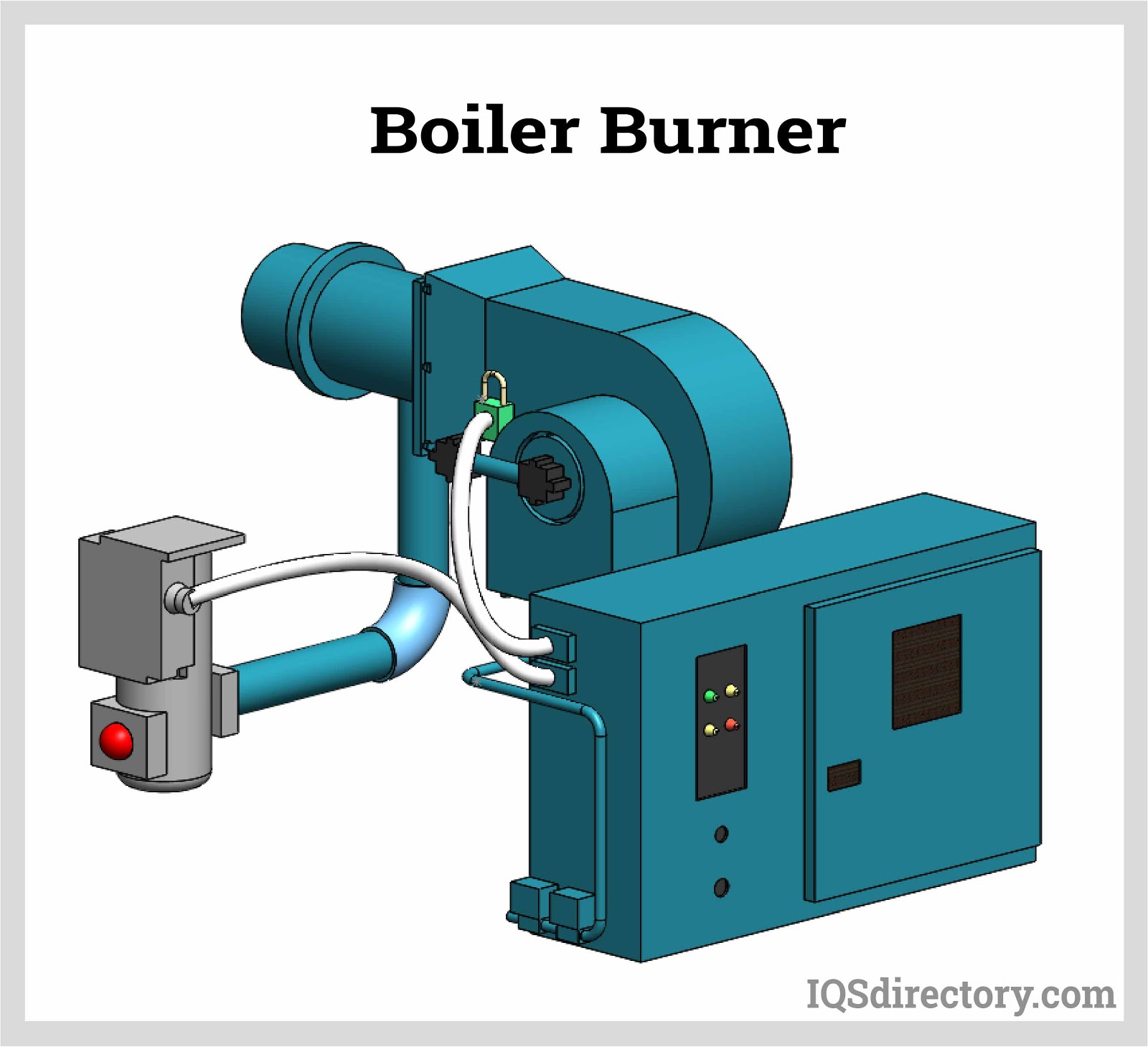 The burner, the heat source for the boiler that requires fuel to burn and is activated by the thermostat.
The burner, the heat source for the boiler that requires fuel to burn and is activated by the thermostat.
Notable Types of Industrial Boilers
Industrial boilers can be categorized based on design, fuel used to generate heat, and combustion technology. In regards to design, there are two main concepts. Fire tube boilers and water tube boilers. Fire tube boilers are easy to operate and have a simple design. They transport hot gases, generated by the heating source, through tubes that pass through a water-filled chamber, transferring heat from the gas filled tubes to the water. While fire tube boilers are often less expensive, they have a bulky design, small steam capacities, and low to medium degrees of pressure. Fire tube boilers produce steam rates up to 26,000 pounds per hour. Water tubes, also known as high pressure boilers, have an inverse structure compared to fire tube boilers. Water flows through tubes that are surrounded by a cavity of hot gases. Water tube boilers are capable of producing 10,000 to 1,000,000 pounds of steam per hour. This design is more efficient but more complex and expensive to manufacture. The other downfall to water tube boilers is that the water that goes into the systems needs to be treated to keep the tubes clear from contaminants. To ensure optimal performance, a supporting water treatment system is recommended to supply filtered water.
Industrial boilers can also be classified by fuel type, such as coal, oil, biomass (burnable plant materials such as wood chips or rice husks), natural gas, and steam. Boilers that use steam as fuel (hydronic industrial boilers) need to be coupled with another boiler type. Each fuel type offers varying cost, safety, and environmental benefits. Finally, industrial boilers can be distinguished by the combustion technology used. There are three types. Fluidized Bed systems “bubble” fuel and sand together to create a fuel-air mixture that helps keep uniform temperatures in the fuel bed and reduce emissions. Stoker systems burn coal and spread the heat by either continuous and even coal distribution or by feeding fuel into one area and then distributing the coal with a moving grate. The third combustion technology used to classify industrial boilers is thermic fluid heaters, which use a closed system of petroleum-based fluids to deliver consistent temperature control and good thermal efficiency.
Factors to Consider When Purchasing Industrial Boilers
Other than the combustion technology, you as a buyer need to consider the type of fuel that will be used in a boiler. There are a number of options, ranging from coal to electric to gas to oil.
The standard fuel is coal; however, modern designs use a fine powder of coal called pulverized coal, as fine particles burn more efficiently than lumps. With the addition of a fluidized bed, even biomass can be used as a fuel, which means all organic materials and agricultural waste products are fuel. In homes, electric-powered boilers are used to heat the water. Other than these, gas and oil are extensively utilized in boilers. Gases like natural gas and propane are most commonly used in boilers, as they are cost effective.

