Industrial Lubricants
Industrial lubricants are oils, liquids, greases, and other mixtures that lessen wear, moisture, binding, and friction. The main use of these lubricants is to ease the way for the movement of solid surfaces; in addition, they may alter surface characteristics, control temperature, or clear debris. An optimal industrial lubricant minimizes solid-to-solid contact to reduce wear and friction.

Mineral, synthetic, and grease lubricants are the most popular industrial lubricants. Each has a unique function and set of qualities that make it suitable for its intended purpose. Due to its low cost and simplicity of handling, mineral oil is the most widely used industrial lubricant in numerous industries. However, synthetic oil has taken the place of mineral oil as the industry standard due to its increased performance. Synthetic oils are also capable of withstanding high temperatures in applications without degrading, which makes them perfect for engine components, bearings, and gears.
Grease lubricant is sourced from animal fats like lard or tallow, which are converted into a thick paste and then applied to machinery or equipment. The building, mining, and oil industries employ industrial lubricants to lessen wear and friction. For industrial lubricants to function properly, they must be free of contaminants and dangerous compounds. These goods lessen friction and the temperature of metal surfaces, which lessens machine wear. Industrial lubricants also lower machine use, which results in energy savings.
Manual and Automatic Lubrication
There are two ways to apply lubricants: manually or automatically.
With manual lubrication, a technician must manually lubricate the machinery using a grease gun. Manual lubrication frequently results in inconsistent lubrication and prolonged machine downtime, though some prefer this method.

With automatic lubrication, the precise quantity of lubricant needed is applied to the desired parts using automated lubricating machinery. However, manual lubrication is more reliable, effective, safe, and environmentally friendly, which results in lower maintenance costs.
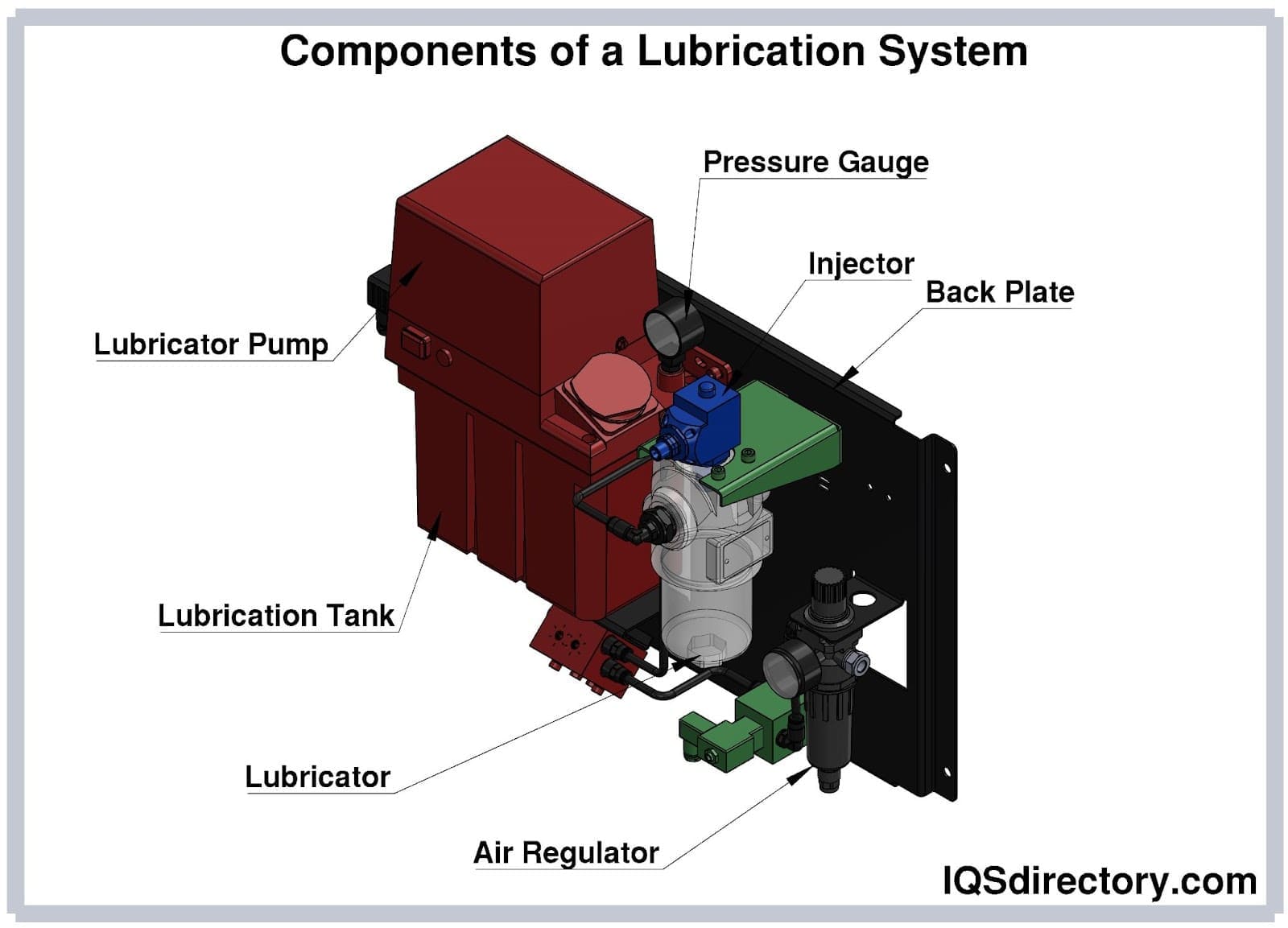
Applications of Industrial Lubricant
Industrial lubricants can be applied to any application that involves mechanical machinery with moving components, regardless of the industry. These things include:
- Automotive industry – for under-hood applications, NVH, and engine optimization
- Aerospace industry – landing gear, actuators, and flight controls
- Marine industry – gear systems, compressors, and turbines
- Textiles industry – steamers, motors, and dyeing equipment
- Medical industry – ventilators and gas cylinders
- Energy sector – for hydraulics, generator bearings, and turbine blades
Main Types of Industrial Lubricants
The most common kinds of industrial lubricants include:
- Gear oil in the transportation sector
- Bearing oil
- Motor oil
- Heatproof and oxidation- and corrosion-resistant grease
- Chain and cable oil in agricultural equipment
- Compressor oils to safeguard compressors
- Hydraulic oils for brakes, pumps, excavators, and other hydraulic systems
Benefits of Industrial Lubricants
- Less abrasion on the machine's components
- Reduced pollutants and increased engine economy
- Decreased heat generation and fuel consumption due to less friction between moving parts
- Higher productivity
- Decreased mechanical and equipment failures
- Decreased downtime expenses with preventative maintenance on idle machinery and equipment
- Lowered labor costs
Choosing an Effective Industrial Lubricant
Choosing the right industrial lubricant is essential to ensure that the machine performs at its best. Here are some considerations to remember when choosing a lubricant:
- Incorrect oil viscosity
- Chemical composition
- Equipment usage
- The lubrication system in use (which may need special lubricants)
- Impurities like dirt flakes and heavy metals like lead in the lubricant
- Corrosion resistance
In regards to oil viscosity, consider that applications with pumping and moving fluids require low-viscosity lubricants with high shear thinning that allow them to pass through small pipes. Other applications need high-viscosity lubricants to run smoothly. In addition, some heavy-duty machines require industrial lubricants that can withstand high temperatures because of their high-temperature resistance. For example, fluids with a high boiling point can withstand temperatures up to 392 °F (200 °C).
Finally, in environments containing corrosive environments or fumes, a lubricant may require an extremely high flash point. However, a gear or bearing, a sliding component, can also prematurely wear out.
Common Mistakes in Choosing Lubricants
Since choosing the wrong lubricant for an application is simple, many individuals opt to have a technical expert on hand to support all lubrication applications and questions. Avoid the following mistakes when selecting an industrial lubricant:
- Missing crucial details on industry norms and specifications. Always compare the technical data sheet for the lubricant with the industrial requirements of the application.
- Choosing lubricant vendors who are unqualified or unreliable.
- Deciding on lubricants based only on cost rather than necessity – long-term benefits of quality lubricants include decreased downtime and enhanced component and machinery performance.
- Using the same lubricant more than once in various applications. Each application is unique; thus, a lubricant in one application might not be effective in another.
Conclusion
Friction and wear between two surfaces can be decreased by placing a lubricant between them. In any case, the proper lubricant should be used in the proper quantity and at the proper time.
Choosing the Right Industrial Lubricant Supplier
To make sure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing industrial lubricants from an industrial lubricant supplier, it is important to compare at least five different suppliers using our list of industrial lubricant companies. Each industrial lubricant supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each industrial lubricant company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple industrial lubricant companies with the same message.

