Industrial Ovens
Industrial ovens are essential thermal processing machines that utilize heat to alter the properties of materials in a variety of ways. The specific heat treatment process is named according to the changes it induces—drying, baking, and dehydrating remove moisture, curing strengthens materials, and firing hardens ceramics. These ovens also play a crucial role in activating adhesives, gelling and fusing materials, heat setting, heat shrinking, preheating, sintering, melting, laminating, and thermally bonding different components.
These ovens serve a broad spectrum of applications, including powder coating, drying, baking, and curing. They are capable of reaching a wide range of temperatures to suit different industrial needs. High-temperature industrial ovens are often used for drying materials and, while sometimes referred to as kilns, they typically do not reach the extreme temperatures of traditional ceramic kilns. Lower-temperature ovens are commonly used for baking and curing and are found in settings such as factories and bakeries. Industrial ovens are available in various shapes and sizes, from compact models resembling household ovens to massive walk-in units. Some are equipped with conveyor systems that enable the efficient heating of large quantities of products in a short period.
The diversity of industrial oven designs allows for a wide range of applications. Large ovens with multiple shelves can bake numerous loaves of bread at once, while mobile ovens installed in trucks or carts provide portability. Despite these differences, all industrial ovens share one key feature: precise temperature control tailored to their specific function. drying ovens are designed to remove moisture, while curing ovens facilitate chemical reactions between coatings and substrates. Food production ovens, though similar in function to domestic ovens, are typically much larger and capable of reaching significantly higher temperatures.
Heat is an indispensable element in virtually all manufacturing industries, with nearly every production process requiring thermal energy at some stage. Industrial ovens provide this essential heat, serving as insulated, high-temperature chambers for drying, baking, or treating components before, during, or after their fabrication. Their role in modern industry is fundamental, ensuring efficient material processing, enhancing product durability, and streamlining production workflows.
Industrial Ovens FAQ
What are industrial ovens used for?
Industrial ovens are used to apply heat for processes like drying, curing, baking, and preheating. They alter material properties, strengthen coatings, and ensure consistent product quality in manufacturing environments across industries such as food, metal, and electronics.
How do industrial ovens differ from furnaces?
Industrial ovens distribute heat through ductwork for uniform, moderate-temperature processing. Furnaces, by contrast, introduce heat directly into the chamber and operate at higher temperatures, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications like metal melting and forging.
What industries rely on industrial ovens?
Industrial ovens are vital in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, pharmaceuticals, food processing, plastics, and electronics. They support processes including sterilization, curing, aging, sintering, and heat treatment to enhance product strength, safety, and durability.
What types of industrial ovens are available?
Common industrial oven types include batch, conveyor, curing, drying, infrared, and tunnel ovens. Each type serves specific purposes, from high-volume production to precision thermal treatment in laboratories or manufacturing facilities.
How do electric and gas-fired industrial ovens compare?
Electric ovens offer precise temperature control, minimal emissions, and easy maintenance. Gas-fired ovens cost more upfront but have lower operating costs and are ideal for large-scale applications requiring rapid, high-temperature performance.
What factors are important when installing an industrial oven?
Proper ventilation, level placement, and adherence to local safety codes are essential. Ovens should be installed in stable, ventilated areas by trained professionals to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with industrial standards.
Why is airflow important in industrial ovens?
Efficient airflow ensures uniform temperature distribution, prevents hot spots, and maintains consistent processing quality. Proper circulation is crucial for drying, curing, and baking materials evenly throughout the chamber.
What safety measures are required for operating industrial ovens?
Operators should wear protective gear, maintain clean surfaces, and ensure exhaust systems function properly. Regular inspections, lubrication, and adherence to operation manuals help prevent overheating and ensure long-term safety.
Benefits of Using Industrial Ovens
Industries rely on industrial ovens for a multitude of reasons, making them an essential component in manufacturing and processing. These ovens are designed with airflow efficiency in mind, ensuring uniform temperature distribution across all areas of the chamber. Proper airflow is critical to the functionality of the machine, preventing inconsistencies and enhancing overall performance.
One of the primary advantages of using industrial ovens is their precise temperature management. These devices allow for accurate heat control, reducing the likelihood of uneven temperature distribution, which can compromise the quality of the process. Consistent heat application ensures that materials are processed efficiently and to the required specifications.
Manufacturing ovens also offer cost-effective solutions for industrial applications. Electric models, in particular, require lower capital investment and minimal maintenance, making them an economical choice for businesses looking to optimize operations. These ovens efficiently deliver rapid heat transfer to raw materials while consuming minimal power, enabling industries to complete multiple tasks within short timeframes.
Durability and reliability are key characteristics of industrial ovens. Many models are constructed with stainless steel cabinets, which not only enhance their longevity but also ensure high performance under demanding conditions. Their robust design allows them to withstand extended operational hours while maintaining efficiency and consistency.
Industrial Oven Applications
The range of applications for industrial ovens is vast, spanning across multiple industries. In the electronics sector, these ovens play a crucial role in degassing epoxy resins, facilitating chemical reactions, and performing other essential functions. The food and beverage industry utilizes industrial ovens for sterilizing items before packaging, ensuring hygiene and safety standards are met.
Beyond these industries, industrial ovens are widely used in pharmaceutical and medical fields for sterilization, chemical reactions, and incubation of samples. Research and development facilities rely on these ovens for temperature grading and precision testing. In the plastics industry, industrial ovens are used for melting, shaping, and aging products, contributing to the material's durability and consistency. In the aerospace and automotive sectors, thermal energy is essential for multiple manufacturing stages, including the creation and treatment of components and parts. The steel industry benefits from industrial ovens for iron melting and other heat-intensive processes.
For applications requiring extreme temperatures above 2000°F, an industrial furnace is the preferred solution. Unlike industrial ovens, which distribute heat through a system of ductwork, furnaces introduce heat directly into the chamber, making them more suitable for large-scale, high-temperature operations that demand intense thermal processing.
History of Ovens
The evolution of oven technology stretches back thousands of years, adapting to the needs of civilizations as they advanced. The earliest known ovens date to 2900 BC in Central Europe, where they were little more than boiling and roasting pits inside yurts, used for cooking mammoth meat. These primitive pits evolved into structures utilizing hot coal covered in ashes for heat retention. By 3200 BC, nearly every settlement had hearths, which played a crucial role not only in cooking food but also in brick-making. Over time, the Greeks refined oven technology by introducing kilns for pottery and bread baking, marking a significant leap in controlled heating applications.
As centuries passed, ceramic and earth ovens gave way to fireplaces with cauldrons. Technological transitions saw ovens fueled by wood, coal, iron gas, and eventually electricity. The early 1700s introduced the Stewart Oberlin iron oven, a compact design with its own chimney, which represented a step toward efficiency and safety. By the 19th century, coal ovens became widespread, followed by the invention of gas ovens. James Sharp revolutionized oven technology in 1826 when he patented the first gas stove, paving the way for more efficient cooking methods. Further innovations came in 1922 with the AGA cooker, developed by Gustaf Dalen, refining gas stove functionality for greater reliability and control.
The late 19th century saw the emergence of electric ovens, but due to the limited spread of electricity, their adoption was gradual. True high-tech advancements in oven technology began with Percy Spencer’s invention of the microwave in 1946, a milestone that reshaped heating and cooking methods. Once patented, the microwave sparked large-scale production, adaptations, and the development of more sophisticated ovens, leading to the advanced industrial ovens we use today.
How Industrial Ovens Work
Industrial ovens are engineered to provide a consistent heating environment, offering separate chambers for cooling and warming while utilizing various thermal energy sources. The three primary heat sources used in these ovens are hot water, electricity, and gas, all of which distribute heat through forced convection to ensure uniform temperature control.
Electrically fired ovens are the most commonly used due to their rapid heating capabilities and durability. They are cost-effective, require minimal maintenance, and produce significantly lower emissions compared to other heating methods. Gas-fired ovens, available in direct and indirect configurations, utilize either natural gas or propane. While they tend to be more expensive to purchase, their operating costs are substantially lower than those of electric ovens. Hot water ovens, on the other hand, rely on radiator coils to emit energy, making them ideal for applications requiring lower temperatures where rapid heating is not a necessity.
Among the most widely used designs, convection ovens operate by forcing jets of hot steam through coils or heated panels, ensuring rapid and even warming of materials. This enhances efficiency and improves overall operational performance. When raw materials are placed inside the oven, temperature settings are adjusted according to the specific requirements of each process. Different applications demand precise temperature control, and industrial ovens provide the flexibility needed for optimal results.
In certain models, airflow is further optimized by integrating fans that draw air through heated coils before redistributing it through plenums installed in the side walls. This design guarantees consistent and uniform temperatures throughout the oven chamber, ensuring that materials are treated evenly without fluctuations that could impact the final product.
Components of the Industrial Oven
Industrial ovens are composed of several essential components, each playing a critical role in ensuring efficient performance and uniform heat distribution.
The motor serves as the powerhouse of the system, driving essential functions such as air circulation and burner operation. To facilitate proper airflow, exhaust and recirculation fans work in tandem to maintain consistent temperature levels within the oven chamber. These fans are crucial for preventing hot spots and ensuring even thermal treatment of materials.
The duct distribution network is responsible for venting, directing airflow, and managing exhaust gases. Proper venting ensures that excess heat and fumes are safely expelled, preventing heat buildup and potential hazards. To regulate combustion and safety processes, flame controllers and purge timers are installed to control burner ignition and ensure safe operation.
Burners serve as the primary heat source within industrial ovens. Direct-fired burners, commonly powered by electric motors, generate heat directly within the chamber, offering efficient and high-temperature operation. Some models utilize radiant tube burners, which transfer heat from gas combustion through a tube system, providing precise thermal management while minimizing direct flame exposure.
Use and Installation of Industrial Ovens
Several critical factors must be considered when installing an industrial oven to ensure safe and efficient operation. Location is a key consideration, as ovens should be positioned in areas protected from excessive heat, vibrations, and mechanical damage. Adequate space must be allocated to allow for expansion, as stainless steel cabinets tend to expand when exposed to high temperatures. To maintain stability, leveling the oven with shims is recommended.
Proper ventilation is essential to prevent the accumulation of vapors and gases, which can pose safety risks. Industrial ovens should be installed in well-ventilated areas to ensure a continuous flow of fresh air, reducing the chances of hazardous buildup.
The method of heating also plays a crucial role in installation. Whether powered by electricity, hot water, or gas, the oven must be installed according to manufacturer specifications and local safety codes. Adhering to these guidelines ensures optimal performance and longevity while maintaining compliance with safety regulations.
Above all, industrial oven installation should be performed by trained professionals who possess the necessary expertise and technical knowledge. Attempting to install or operate the oven without proper training can lead to inefficiencies, safety hazards, or equipment damage. Familiarizing yourself with all operational aspects and safety protocols is essential for maximizing the oven’s performance and ensuring a safe working environment.
Design and Customization of Industrial Ovens
The design of an industrial oven involves multiple factors, allowing manufacturers to either purchase a standard model or customize a unit to meet specific operational requirements. While pre-designed ovens can efficiently perform various industrial tasks, a custom-built oven ensures precise alignment with unique applications. Whether modifying an existing machine or designing one from the ground up, customization enhances functionality, efficiency, and performance.
The first step in designing a custom industrial oven is determining its intended purpose. Will it be used for food processing, material curing, or equipment manufacturing? Understanding the primary function—or a combination of functions—directly influences the necessary design optimizations. The next critical decision involves the power source—whether the oven will operate using electricity or gas. The required temperature range must also be considered, as different processes demand specific heat intensities to achieve optimal results.
Other Necessary Components for Industrial Ovens
Although industrial ovens are designed as standalone units, additional components are essential for proper installation and operation. Beyond fundamental power sources such as electricity, gas, or water, appropriate piping and venting systems must be in place to facilitate efficient airflow and heat management. Shims are necessary to ensure stability, preventing movement or misalignment due to thermal expansion.
To support safe operation, incinerators and exhaust systems play a crucial role in waste disposal, reducing the accumulation of byproducts and emissions. Additionally, industrial oven setups must incorporate safety features, including fire alarms and extinguishers, to mitigate potential hazards. Properly integrating these components not only enhances efficiency but also ensures compliance with industry safety standards, promoting a secure and reliable operating environment.
Safety and Compliance Standards for Industrial Ovens
Industrial ovens operate for extended periods with doors closed and compartments exposed to raw material residues, making regular cleaning and maintenance essential for optimal performance. Compliance with safety regulations is critical to ensuring longevity and preventing hazardous conditions.
Proper protective gear must be worn at all times during operation to minimize exposure to heat and potentially harmful gases. Direct inhalation of fumes should be avoided, and operators must keep a safe distance from heated components. In case of wet spills or boil-overs, industrial-grade cleaning solutions should be used to prevent contamination or equipment damage. Before turning on the machine, it is vital to confirm that all compartments are securely sealed to maintain consistent heat distribution and prevent energy loss.
Several key safety measures must be followed to ensure industrial oven operation remains both safe and efficient:
- Thoroughly reviewing the installation and operation manual to understand proper procedures.
- Installing ducts in areas made of noncombustible materials to reduce fire hazards.
- Never leaving an oven unattended while in operation to prevent overheating or malfunction.
- Ensuring all safety equipment is in place, including fire extinguishers and alarms.
- Performing routine inspections to identify flaws and make necessary adjustments.
- Lubricating moving parts regularly to maintain smooth operation and reduce wear over time.
Choosing an Industrial Oven Supplier
With numerous manufacturers offering industrial ovens for various production processes, selecting the right supplier is critical to ensuring a machine that fits your specific operational needs. The best choice is not only one that provides a high-quality oven but also one that delivers a unit optimized for available space, ensures peak performance, and guarantees long-term durability.
Not all ovens on the market meet industry standards for operation and maintenance, so it is essential to verify compliance before making a purchase. A reputable supplier will offer a cost-effective solution with minimal operational expenses, easy maintenance, and an accessible cleaning process. Additionally, verifying that the manufacturer meets required certifications ensures compliance with safety and performance regulations.
Beyond certification, it is crucial to assess the vendor’s after-sales support. Delays in troubleshooting or a lack of technical support can lead to downtime, impacting production efficiency. The right supplier will conduct factory acceptance testing (FAT), running the oven to confirm full functionality before shipping. Post-purchase installation services are also a significant factor—does the supplier provide a professional team for setup and ongoing maintenance? A manufacturer offering both installation and long-term servicing ensures that your industrial oven continues to operate at peak efficiency while reducing potential downtime.
Industrial Oven Images and Illustrations
 An electrical industrial oven is powered by incoloy sheathed heating elements which allows for the oven to be less expensive and not produce pollutants or emissions.
An electrical industrial oven is powered by incoloy sheathed heating elements which allows for the oven to be less expensive and not produce pollutants or emissions.
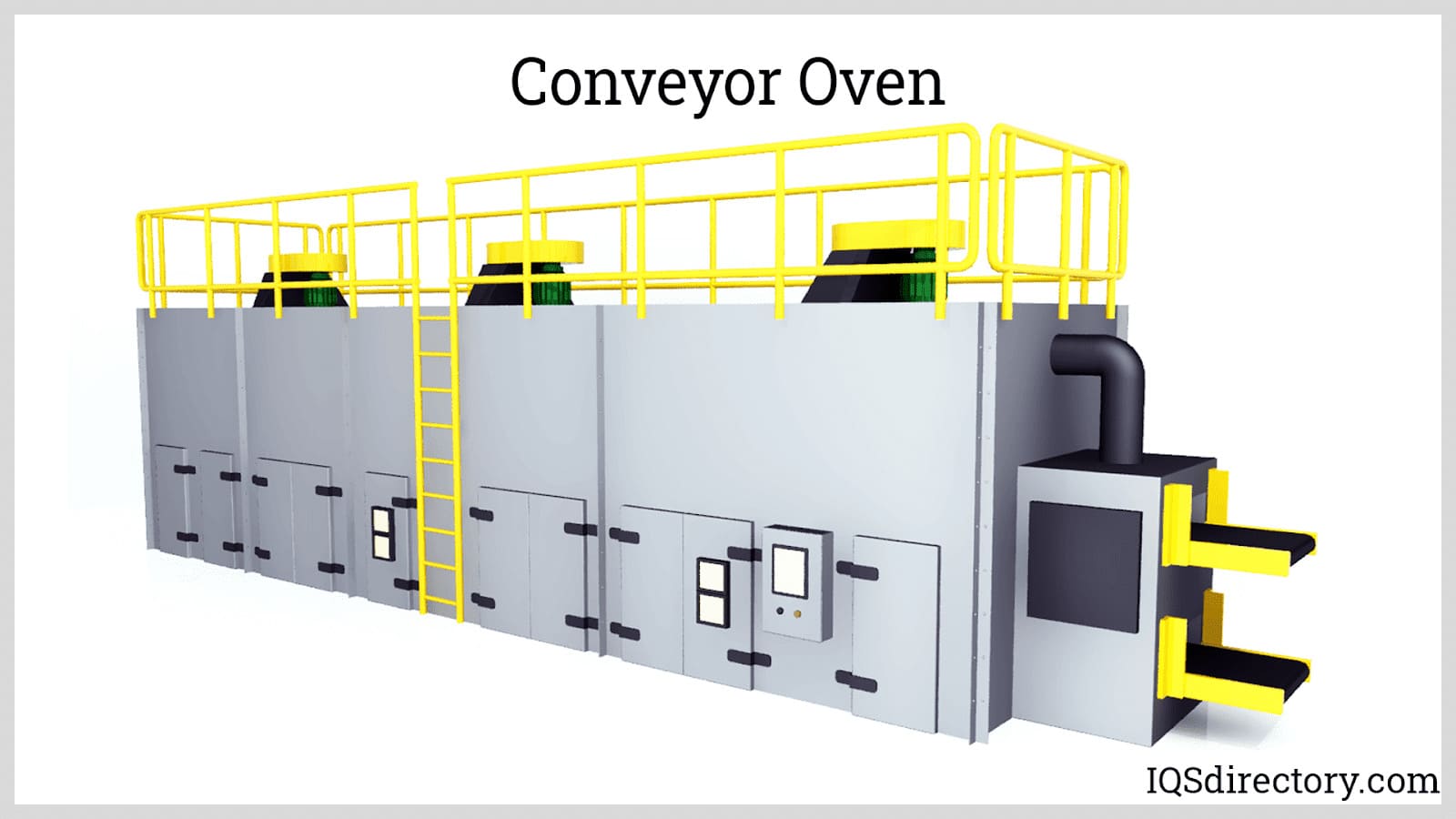 Continuous ovens are primarily used for mass production, while having the abilities to dry, cure, anneal, relieve stress, bonding, tempering, preheating, and forming.
Continuous ovens are primarily used for mass production, while having the abilities to dry, cure, anneal, relieve stress, bonding, tempering, preheating, and forming.
 Releases moisture, volatile compounds, or trapped gases from coatings on the finished product.
Releases moisture, volatile compounds, or trapped gases from coatings on the finished product.
 Uses high intensity lighting to maximize production while minimizing the energy usage.
Uses high intensity lighting to maximize production while minimizing the energy usage.
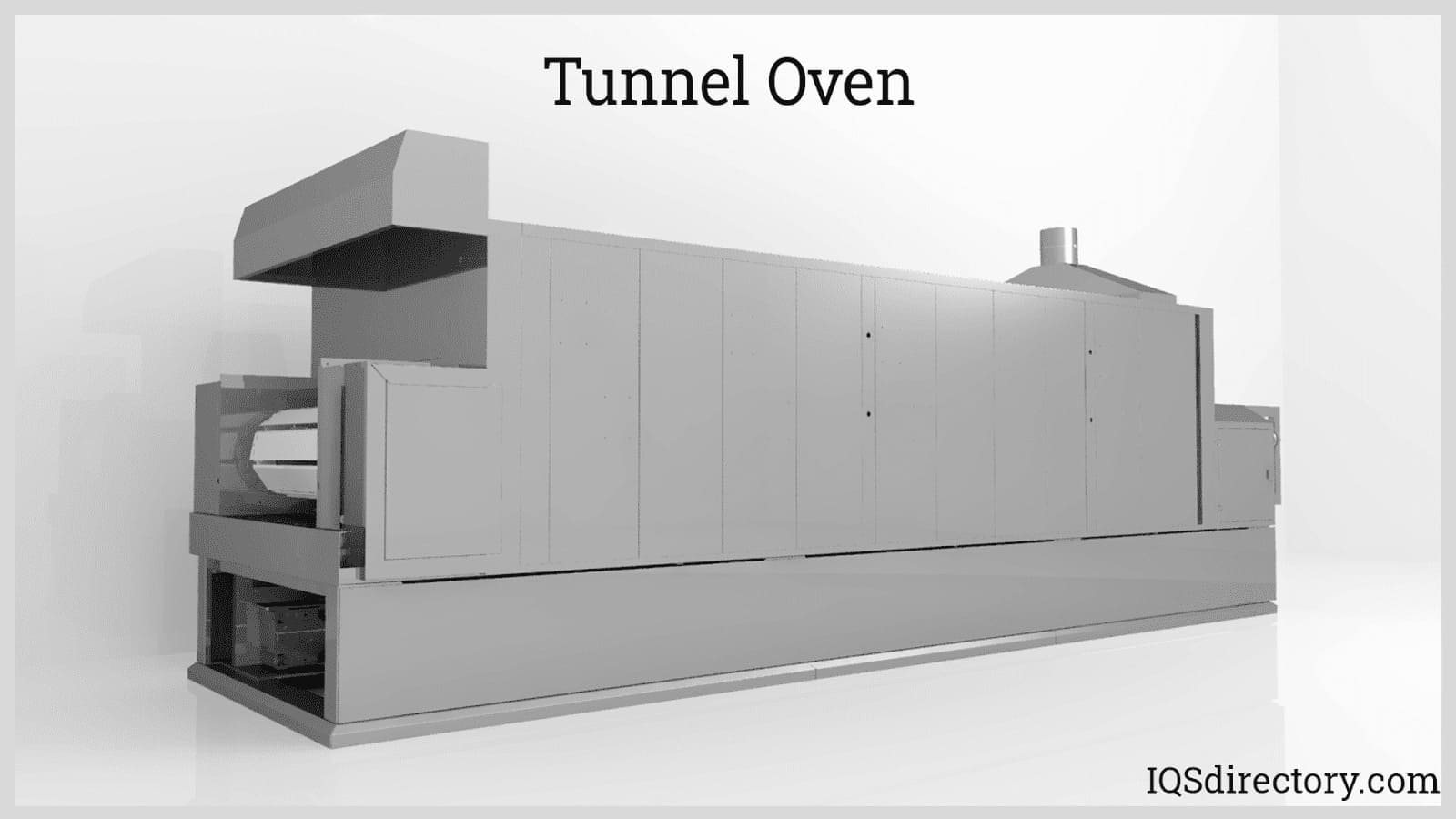 Tunnel ovens are open-ended chambers with a metal belt and a baking platform.
Tunnel ovens are open-ended chambers with a metal belt and a baking platform.
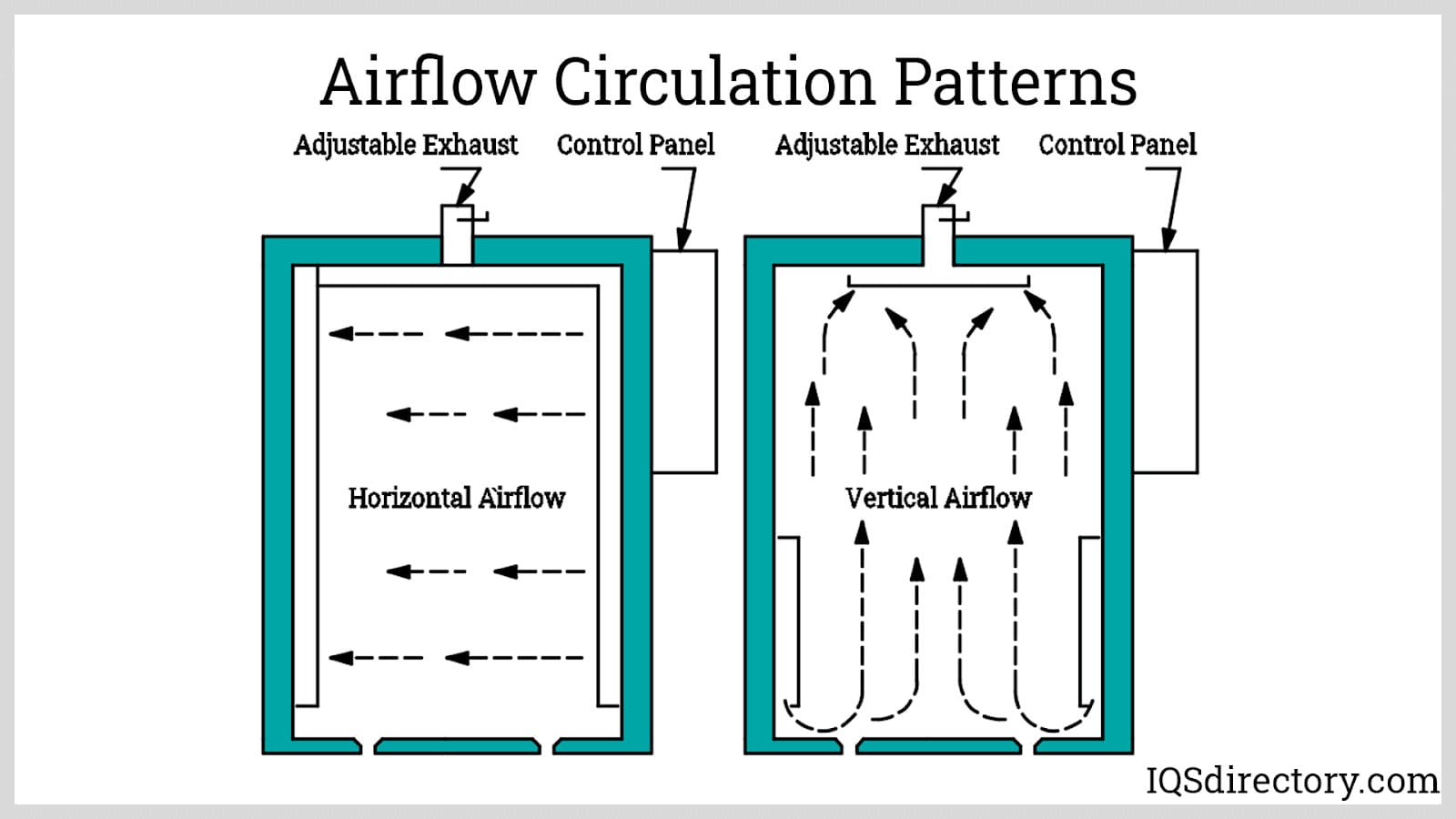 The air circulation patterns which can affect uniformity, pattern, and impingement.
The air circulation patterns which can affect uniformity, pattern, and impingement.
Industrial Oven Types
- Baking Ovens
- Designed for baking food and materials, these ovens are built with inflammable materials and smooth interior surfaces for easy cleaning. They provide consistent heat to ensure uniform baking results.
- Batch Ovens
- Also known as walk-in ovens or cabinet ovens, batch ovens are large enough to accommodate a wide range of thermal processes, including aging, drying, annealing, and curing. They are ideal for applications requiring repeated heat treatment at different times, allowing flexibility in processing various materials. Raw materials can be loaded manually or automatically onto trucks, carts, or racks before being placed inside the oven for treatment.
- Bench Ovens
- Compact and sometimes portable, bench ovens are typically placed on tables or stands for convenience. They are commonly used for low-volume process heating applications that require precise temperature control.
- Commercial Ovens
- Used for drying, baking, heating, and curing a variety of materials, commercial ovens are versatile units suitable for various industrial and commercial applications.
- Continuous Ovens
- Engineered for mass production, continuous ovens perform multiple applications simultaneously, ensuring efficient and consistent thermal treatment. Equipped with separate warming and cooling compartments, they eliminate the need to wait for chambers to cool down before introducing new materials, significantly reducing process time.
- Convection Ovens
- These ovens utilize fluid circulation to maintain uniform heating. Heated gases circulate through the chamber, ensuring consistent internal temperatures for efficient process heating.
- Conveyor Ovens
- Designed for high-volume continuous processing, conveyor ovens incorporate accessories such as belt conveyors to transport materials through the heating chamber, ensuring streamlined production and uniform thermal treatment.
- Curing Ovens
- Curing ovens, including composite curing ovens, paint curing ovens, and UV curing ovens, chemically or physically alter materials during processing. They play a crucial role in hardening rubber and paint, powder coating applications, and food preservation.
- Drying Ovens
- Specially designed to remove moisture from raw materials, drying ovens operate in three stages. The heat-up phase raises the material’s temperature to optimize moisture evaporation, followed by the soak phase, where the material remains at a consistent temperature for a set duration. The cool-down phase then exhausts hot air and introduces cooler air. These ovens are widely used for sterilization, temperature testing, and incubating temperature-sensitive experiments.
- Electric Ovens
- Electric ovens rely on electricity as their primary heat source, providing precise temperature control and uniform heating for various industrial applications.
- Heat Treating Ovens
- These ovens alter the physical and chemical properties of metals and glass through a three-step heat treatment process involving heating, cooling, and reheating. This process improves properties such as hardness, tensile strength, and toughness.
- Infrared Ovens
- Infrared ovens utilize electromagnetic radiation to transfer heat directly to a product, eliminating the need to heat the surrounding air. This method allows for rapid and efficient thermal processing.
- Laboratory Ovens
- Designed for research, testing, and experimentation, laboratory ovens provide controlled heating environments for a variety of scientific and industrial applications.
- Ovens
- As general thermal processing machines, ovens apply heat to change the properties of materials, whether for industrial, research, or food processing purposes.
- Portable Ovens
- Compact and transportable, portable ovens are designed for applications requiring mobility and flexibility, making them ideal for on-site heating processes.
- Powder Coating Ovens
- Powder coating ovens, which can be either infrared or convection-based, heat powder-coated products to melt and flow the coating evenly. The curing process involves exposing the product to ultraviolet light for a few seconds to harden the finish, ensuring durability and adherence.
- Rotary Ovens
- Typically large and used for commercial applications, rotary ovens generate high heat to bake large quantities of food products or cure industrial materials efficiently.
- Storage Ovens
- Storage ovens heat components to enhance assembly processes, making pressure-sensitive adhesives more effective at higher temperatures while improving material pliability for easier fitting.
- Tunnel Ovens
- Characterized by their tube-like shape, tunnel ovens allow raw materials to pass through on conveyor belts or via continuous loading. The belts’ speed determines the heating duration, making these ovens highly efficient for food processing applications such as baking and meat preparation.
- Vacuum Ovens
- These airtight enclosures operate at pressures lower than atmospheric levels to prevent oxidation, contamination, or undesirable thermal effects. Vacuum ovens are essential in sensitive applications that require precise environmental control.
- Walk-in or Truck-in Ovens
- Designed for processing large objects or bulk product quantities, walk-in ovens feature spacious enclosures with large doorways, shelves, cabinets, and racks for convenience. They are commonly used in industries requiring large-scale heat treatment, such as automotive and heavy equipment manufacturing.
Industrial Oven Terms
- Aging
- A heat treatment process that alters the properties of a metal or alloy by subjecting it to controlled temperature changes using an industrial oven.
- Annealing
- A process that softens an object or modifies its physical properties by cycling it through heating and cooling phases in an industrial oven.
- Atmospheric Pressure
- The force exerted by the Earth's atmosphere on a given surface, measured at 14.7 psi at sea level.
- Baking
- A thermal process that removes entrapped gases from a material by exposing it to low heat in an industrial oven.
- BTU (British Thermal Unit)
- A unit of measurement representing the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
- Conduction
- A heat transfer process in which thermal energy is applied to a solid object, spreading evenly throughout the material when processed in an industrial oven.
- Convection
- A form of heat transfer occurring between a solid and a fluid (either liquid or gas). The process relies on gravity, which causes heated molecules to rise while cooler molecules descend, facilitating consistent thermal circulation.
- Curing
- A process in which a material undergoes solidification through heating and drying in industrial ovens. The temperature is carefully maintained throughout to achieve the desired structural transformation.
- Drying
- The removal of solvents, such as moisture, from an object using controlled heat in an industrial oven.
- Emittance
- A material’s ability to release radiant energy from its surface, affecting heat retention and transfer efficiency.
- Heat Transfer
- The movement of thermal energy between different materials or within a single object, always flowing from warmer to cooler regions.
- Heat Treatment
- A controlled heating and cooling process that alters the physical and mechanical properties of solid metals or alloys, often to improve durability, strength, or machinability.
- Heatsetting
- A process that stabilizes the shape of yarn or carpet fibers by applying heat or steam in industrial ovens, ensuring a permanent twist or texture.
- Postheating
- The application of heat to an object after a primary manufacturing process such as brazing, welding, or soldering, often to enhance strength or reduce residual stress.
- Powder Coating
- A dry finishing technique where finely ground, electrostatically charged powder particles are sprayed onto a surface. When the coated part is heated in an industrial oven, the particles melt and fuse to form a durable, even coating.
- Preheating
- The controlled application of heat in an industrial oven before a manufacturing process, ensuring consistent temperature distribution and improving process efficiency.
- Process Heating
- The application of industrial oven-generated heat to an object or material for thermal processing.
- Quenching
- A rapid cooling process used after heating an object in an industrial oven, typically to harden metals and improve their mechanical properties.
- Radiation
- The transfer of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves, particles, or rays, enabling heat movement without direct contact between objects.
- Radio Frequency
- A process in which energy transfer generates heat, often used in industrial applications requiring precise and efficient thermal treatment.
- Sintering
- A heat treatment that bonds fine particles together into a larger, solid mass while keeping the temperature below the material’s melting point. This process enhances strength and structural integrity.
- Stress Relieving
- A controlled heating process in which a metal object is gradually heated and held at a specified temperature within an industrial oven, reducing internal stresses caused by previous manufacturing steps.
- Tempering
- A heat treatment applied to hardened steel by reheating it in an industrial oven to a precise temperature before controlled cooling, reducing brittleness while maintaining strength.
- Thermal Bonding
- The process of applying heat in an industrial oven to create an interlocking effect between fibers and fabrics, improving material cohesion and durability.