O-Rings
O-rings are circular, ring-shaped mechanical seals designed to prevent the leakage of media both within and from mechanical components. These flexible sealing mechanisms effectively contain substances such as gas, air, liquids, and chemicals, ensuring reliable performance in various applications.
O-Ring FAQ
What is the main purpose of an O-ring?
An O-ring is a circular mechanical seal designed to prevent leaks of gases, liquids, or chemicals between joined components. It creates an airtight or vacuum-tight seal by deforming under pressure to fill the gap between surfaces.
How did O-rings become widely used in manufacturing?
O-rings gained prominence during World War II when the U.S. government authorized mass production for aircraft hydraulic systems. Afterward, they became standard in automotive, industrial, and agricultural machinery due to their reliability and affordability.
What materials are commonly used to make O-rings?
O-rings are made from elastomers like Viton, silicone, neoprene, nitrile rubber, Teflon, and EPDM. Metal and alloy O-rings are also used for extreme temperatures or chemically harsh environments.
What caused the Challenger disaster’s O-ring failure?
During the 1986 Challenger launch, freezing temperatures caused the rocket booster O-rings to lose flexibility, preventing proper sealing. This failure allowed hot gases to escape, leading to the explosion shortly after liftoff.
What are the advantages of using O-rings over other seals?
O-rings provide flexibility, pressure resistance, and temperature tolerance while remaining inexpensive and easy to produce. They form reliable seals without causing excessive torque or damage to surrounding components.
What industries commonly use O-rings?
O-rings are used in aerospace, automotive, food processing, healthcare, oil refining, chemical processing, and manufacturing. They perform in both static seals and dynamic systems like pumps, pistons, and turbines.
How should O-rings be installed to prevent leaks?
To install an O-ring, apply a compatible lubricant, protect it from sharp edges, and ensure even stretching below 50%. Proper alignment within the groove prevents twisting or uneven compression, ensuring a long-lasting seal.
What maintenance helps extend the life of O-rings?
Encapsulating O-rings in Teflon protects against wear and chemicals. Avoid lubricants made from the same material as the gasket, and keep replacement O-rings available for quick swaps during equipment maintenance.
The History of O-Rings
The first O-ring patent was granted in Sweden to J.O. Lundberg on May 12, 1896. However, it wasn’t until 1936 that the first American patent for an O-ring gasket was awarded to Niels Christensen. During World War II, after large corporations had infringed upon his patent, the U.S. government purchased the O-ring patent as a critical war-related asset. They then authorized multiple organizations to manufacture rubber seals for military airplane hydraulic systems. As compensation for his patent, Christensen later received a lump sum payment of $75,000.
Following the war, O-ring usage expanded beyond military applications into industrial manufacturing. These rubber seal gaskets became essential in automotive production, industrial hydraulics, and farm equipment manufacturing. Between the 1950s and 1970s, scientists and engineers made significant advancements in synthetic rubber and polymer technology, leading to the development of high-performance elastomers that manufacturers continue to rely on today.
The 1986 Challenger disaster highlighted the critical importance of O-ring performance in extreme conditions. On the morning of the launch, below-freezing temperatures caused the solid rocket booster O-rings to become permanently deformed, preventing them from properly sealing. This failure led to the Challenger’s explosion shortly after liftoff, tragically killing all seven crew members. Engineers had not accounted for extreme temperature endurance in the O-ring’s design, exposing a serious flaw in material selection and performance testing.
Since that tragedy, the O-ring and gasketing industries have conducted extensive research into material properties and endurance under extreme conditions. Regulations now govern O-ring packaging, labeling, expiration dating, and quality control. In critical applications such as aerospace and aviation, O-rings undergo rigorous inspection under UV light before distribution to detect any stress fractures or defects that could compromise sealing integrity. These safety measures underscore the precision and attention to detail required by O-ring manufacturers and suppliers, ensuring the highest quality products for demanding applications.
Advantages of O-Rings
There are numerous advantages to choosing O-rings over other types of seals, making them a preferred solution across various industries.
Flexibility Advantage
O-rings are highly flexible, allowing them to conform precisely to the surfaces they join, even if those surfaces are imperfect or uneven. This adaptability ensures a secure and reliable seal.
Airtight Seal
When an O-ring gasket deforms, it molds itself to the cavity, creating a vacuum-tight and airtight seal that effectively prevents leaks.
Low Manufacturing Costs
The production process for O-rings is relatively cost-effective, making them an affordable yet reliable sealing solution for machinery and equipment manufacturers who need durable seals in areas prone to leaks.
Range of Sizes
O-rings are available in a vast selection of standard and custom sizes. Manufacturers provide detailed O-ring size charts to help customers select the right fit for their specific applications.
Temperature Range
Engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, O-rings can perform reliably in both very high and very low temperature environments without compromising their sealing integrity.
Pressure Tolerance
Compared to other gaskets, O-rings demonstrate superior pressure resistance. Some are designed to endure extreme conditions, handling pressures exceeding 100 bar without failure.
Structural Protection
Because O-rings do not generate excessive torque under high pressure, they minimize the risk of structural damage, preserving the integrity of both the seal and the surrounding components.
Reusability Advantages
Certain types of O-rings—such as those made from metal, rubber, and polymer—are reusable in industrial applications. This not only reduces costs but also supports environmental sustainability by minimizing waste.
O-Ring Design
-
Manufacturing Process
O-rings are produced using one of two primary methods: compression molding and injection molding.
Compression molding involves pressing the material between two sections of a mold to form the O-ring shape. While effective, this method is less popular due to its time-consuming nature and its limitation to small production runs.
Injection molding, by contrast, is widely favored for its efficiency and high-volume production capabilities. In this process, manufacturers inject heated and pressurized material into a mold filled with O-ring-shaped cavities. The material fully conforms to the cavity dimensions, cools, and is then ejected, producing consistent and precise O-rings in large quantities.
O-Ring Material Design
O-rings are crafted from a diverse range of synthetic and natural elastomeric compounds, each offering distinct properties tailored to specific applications. These materials exhibit characteristics of both rubber and plastic, with rubber being the most commonly used elastomer in O-ring manufacturing. Some of the most widely used rubber O-ring materials include Viton, Teflon, neoprene, silicone, and nitrile rubber. Additionally, elastomer materials such as fluorocarbon elastomers are frequently employed for specialized applications.
Because standard rubber O-rings cannot withstand high temperatures without additives, manufacturers sometimes opt for metal or alloy O-rings for extreme conditions. For applications demanding exceptional temperature resistance, materials like silicone, EPDM, perfluoro elastomers, and fluorosilicone provide enhanced performance.
Design Considerations
When designing O-rings, manufacturers determine key specifications, including inner diameter, cross-sectional diameter, material hardness, durability, shape, and size. These elements are carefully selected and customized based on the O-ring’s intended application.
Material selection, for example, depends on factors such as chemical compatibility, sealing pressure, temperature tolerance, and lubrication requirements to ensure optimal performance. O-rings can be manufactured in both metric and nonmetric measurements to accommodate different industry standards.
While traditional O-rings feature a round, donut-like, and thin profile, manufacturers can also produce custom O-rings with square, rectangular, or uniquely shaped profiles to meet specialized sealing needs. Additionally, some flat or square O-ring gaskets offer the same functionality as standard O-rings, and in certain cases, manufacturers may recommend these alternatives for improved performance.
O-Ring Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts
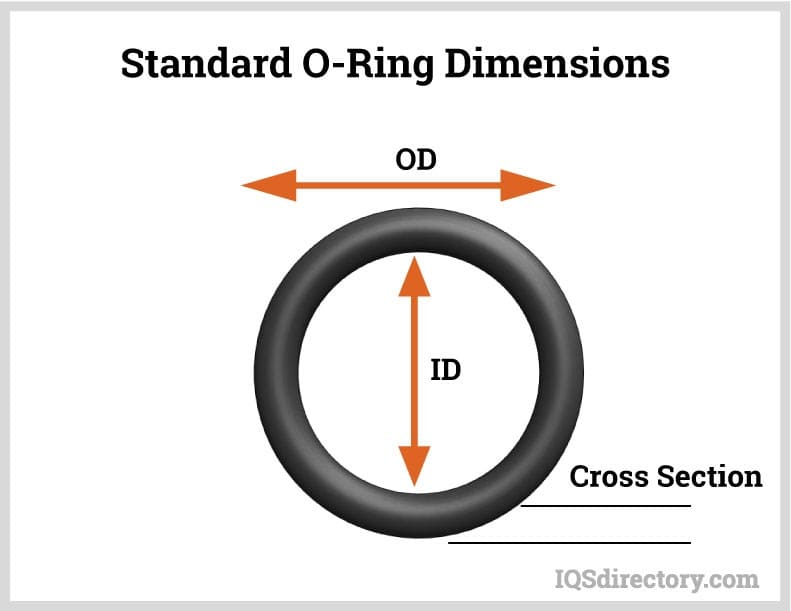 The standard dimensions of an o-ring includes inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and cross sectional (CS) diameter.
The standard dimensions of an o-ring includes inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and cross sectional (CS) diameter.
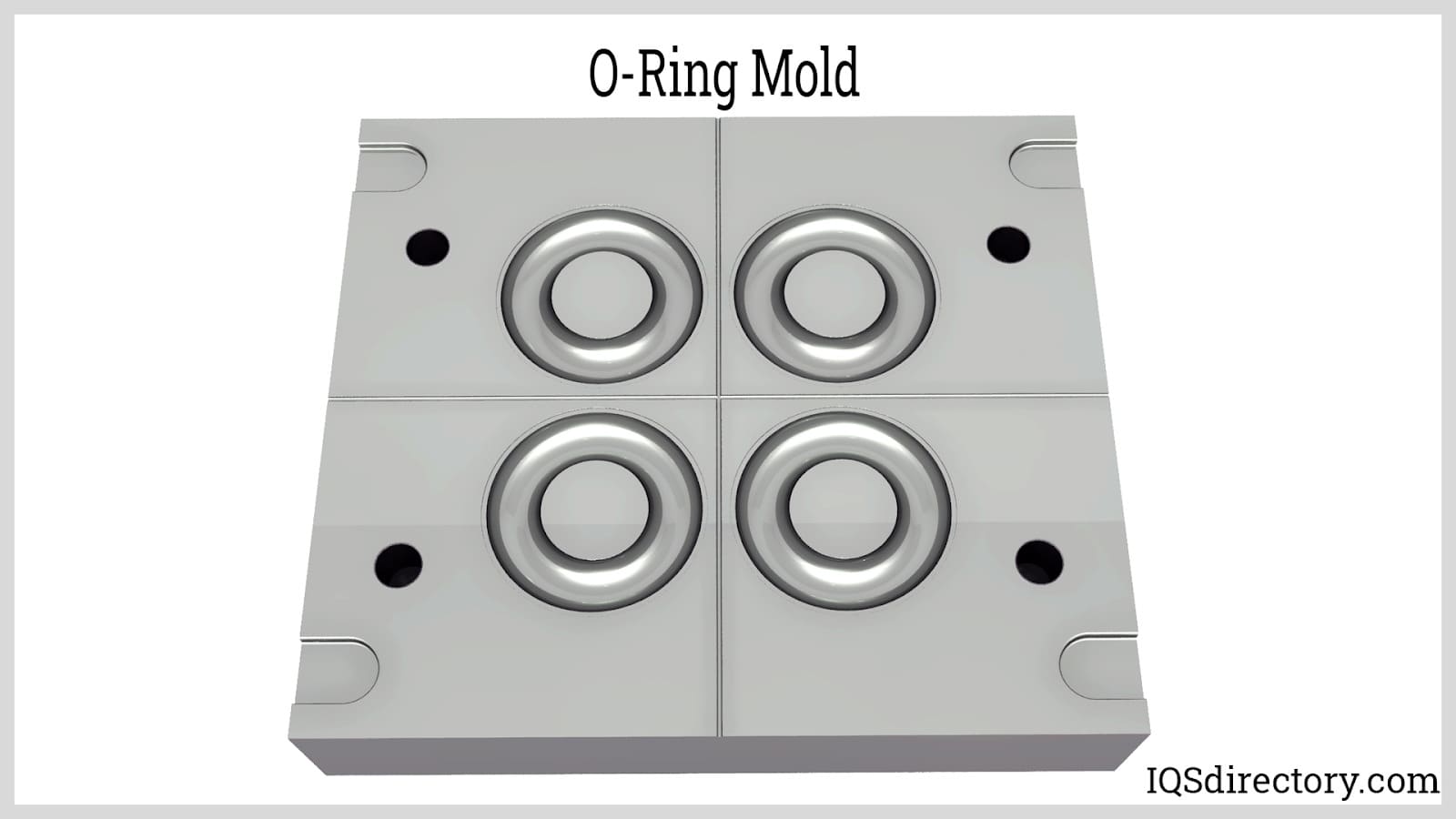 The material use for the o-rings are made from two halves and then compressed.
The material use for the o-rings are made from two halves and then compressed.
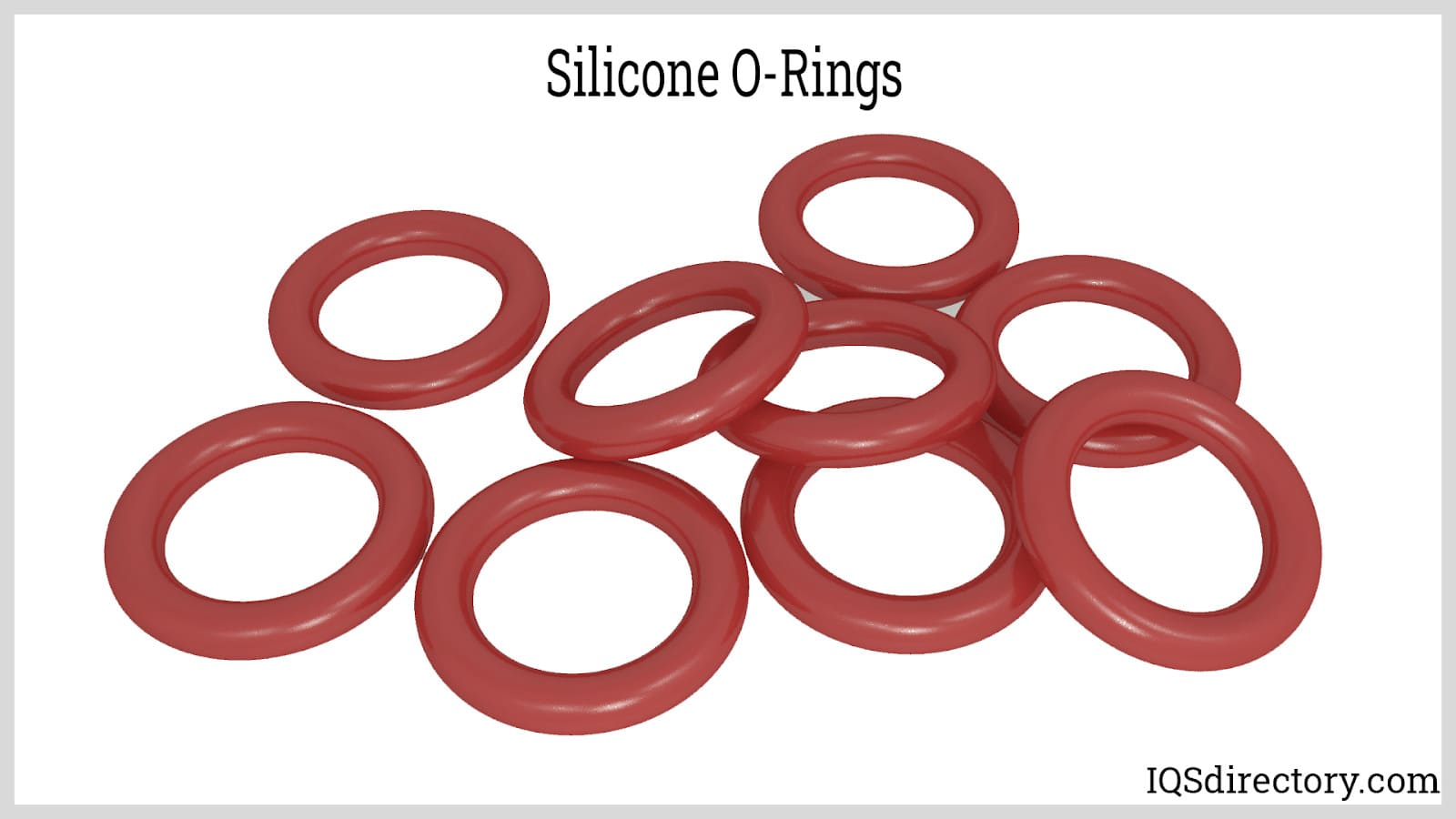 Silicone is resistant to chemicals, heat, ozone, corona, and solvents which makes in useful for different applications.
Silicone is resistant to chemicals, heat, ozone, corona, and solvents which makes in useful for different applications.
 A synthetic fluoropolymer elastomer rubber used for stressful, harsh, and rigorous conditions, which maintains performance in extreme temperature.
A synthetic fluoropolymer elastomer rubber used for stressful, harsh, and rigorous conditions, which maintains performance in extreme temperature.
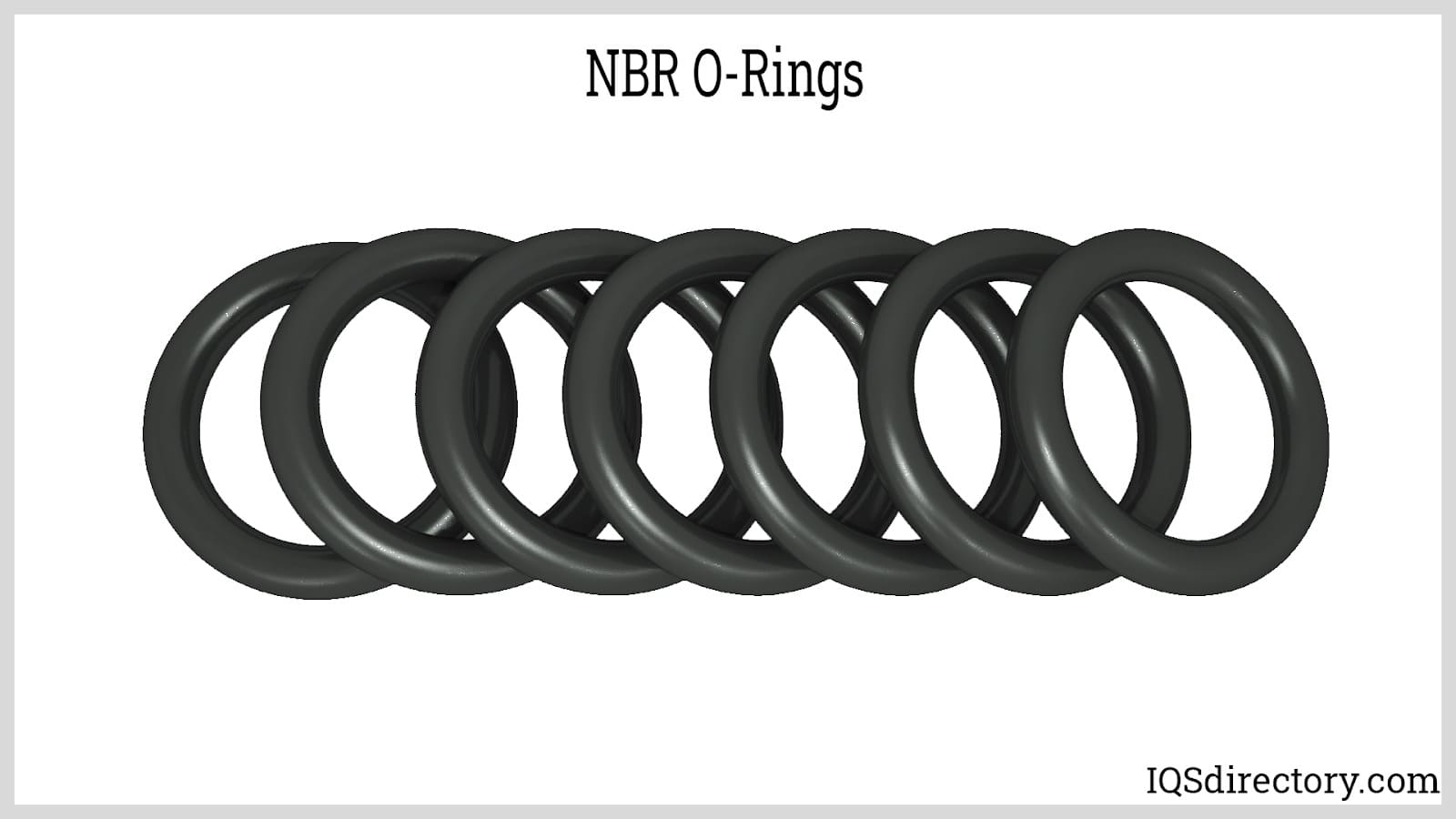 A synthetic rubber which is wear resistance and the effects of oil.
A synthetic rubber which is wear resistance and the effects of oil.
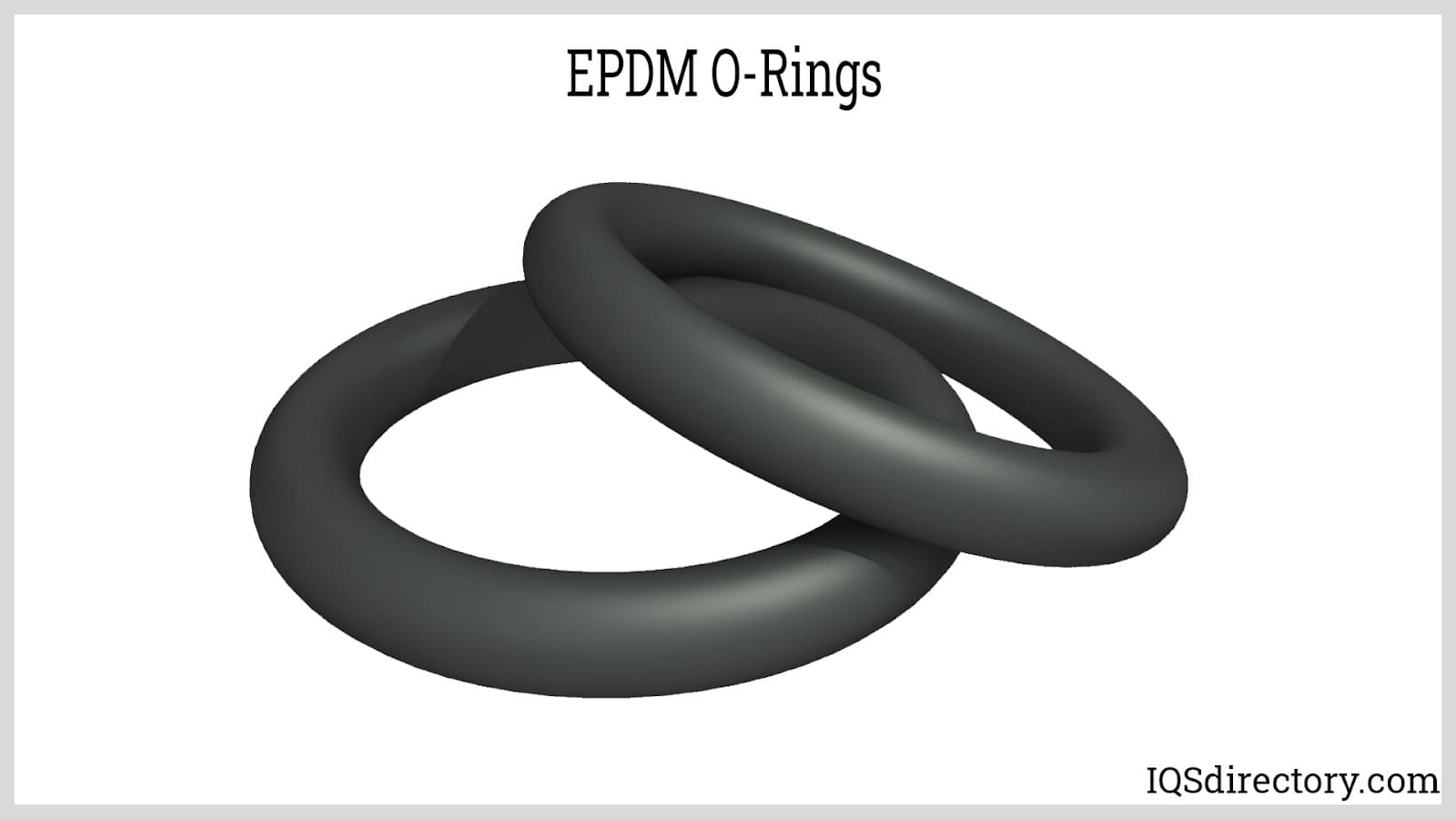 A terpolymer made from ethylene and propylene with a monomer, which makes it resistance to the elements and has good flexibility when exposed to low temperatures.
A terpolymer made from ethylene and propylene with a monomer, which makes it resistance to the elements and has good flexibility when exposed to low temperatures.
O-Ring Types
-
Clear O-Ring
Made from materials such as silicone, Teflon, or polyurethane, clear O-rings can be produced in a semi-transparent state without additives. When enhanced with additives, some can achieve ultra-clear transparency. These O-rings are particularly valued in the food and medical industries, where visibility of the sealed substance is essential.
Silicone O-Ring
Highly resistant to UV exposure, dry heat, and extreme temperature fluctuations, silicone O-rings are widely used in medical and heating applications, where durability under harsh conditions is crucial.
Neoprene O-Ring
Commonly used to seal refrigerants such as Freon in liquid chiller systems and heat exchangers, neoprene O-rings provide excellent chemical resistance and durability in refrigeration applications.
Nitrile O-Ring
Recognized as the most widely used standard O-ring, nitrile O-rings are prized for their exceptional resistance to oils and fuels, making them a top choice for automotive, industrial, and petroleum-based applications.
Static O-Ring
Designed to seal two rigid, non-moving components, static O-rings can be made from various rubber or metal materials. Since they remain stationary, they do not require lubrication, making them ideal for applications where movement is minimal.
Metric O-Ring
O-rings with measurements specified in metric units, commonly used in global applications and industries outside of the United States, where metric sizing is the standard.
EPDM O-Ring
Highly resistant to polar solvents such as MEK, acetone, and alcohol, EPDM O-rings are commonly used in solvent-based applications. However, they offer poor resistance to greases and petroleum oils, limiting their use in oil-heavy environments.
Viton O-Ring
Known for their high-temperature resistance and strong chemical compatibility, Viton O-rings perform exceptionally well in harsh environments requiring thermal stability and chemical durability.
Metal O-Ring
Valued for their superior resistance to extreme temperatures, corrosion, and harsh processing conditions, metal O-rings are used in high-performance applications where elastomeric materials may not be suitable.
O-Ring Cord
A specialized O-ring product sold by the foot, allowing users to splice and customize lengths for large-diameter, static sealing applications. This makes it a convenient option for quick repairs or custom sealing needs.
Oil Seal
An O-ring designed to:
- Prevent lubricant leaks in static or dynamic equipment.
- Block contaminants, such as dirt and debris, from entering machinery.
- Prevent fluid mixing, ensuring that substances like oil and water remain separated within a system.
Large O-Rings
The largest-sized O-rings available, produced either as mass-manufactured standard sizes or custom-fabricated to meet unique dimensions. Made from elastomeric rubber or thermoplastic materials such as silicone, Teflon, or Viton, these O-rings maintain the same sealing and durability properties as their smaller counterparts.
Backup Ring
Constructed from hard, extrusion-resistant materials such as high-durometer nitrile, nylon, or PTFE, backup rings are placed between the O-ring and the extrusion gap to prevent O-ring failure due to extrusion, ensuring long-lasting performance in high-pressure environments.
Applications of O-Rings
O-rings are designed not only to prevent leaks but also to create a durable, reliable seal between two joining components in an application.
Recognized as the smallest gaskets, these compact elastomer loops are among the most widely used seals in machine design due to their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and dependability. Available in a wide range of sizes and materials, O-rings serve essential roles across numerous industries, including food processing, healthcare, manufacturing, hydraulics, pneumatics, vacuum flow, aerospace, aviation, petrochemical and oil refining, chemical processing, and water treatment.
They function in both dynamic applications, such as hydraulic cylinder pistons and rotating pump shafts, and static applications, like water bottle lids and gas caps. In aerospace and aviation, O-rings are critical for high-stakes applications, ensuring the integrity of engine turbines, brake systems, and other essential components
Features of an O-Ring
Viewed in cross-section, O-rings have a disc-shaped profile. When placed within a groove between two joints and subjected to pressure, the cross-section deforms, creating a tight seal. As additional pressure is applied from within or outside the seal, the O-ring compresses further, reinforcing its sealing effectiveness.
Beyond forming a strong and airtight seal, O-rings also produce an insulating effect through their elastic deformation properties. This deformation hardens the seal, ensuring stability and safety within the application. As the circular cross-section distorts under pressure, it takes on an elliptical shape. This subtle twisting effect fills or closes the gap between the two surfaces, enhancing both the seal’s integrity and its insulating properties.
O-Ring Installation
O-rings are designed for easy installation and replacement. To begin, lightly coat the O-ring with a compatible lubricant unless you are working with a type that does not require lubrication. If necessary, cover any sharp edges that could cut or damage the O-ring during installation.
If you are using a backup ring, ensure it is positioned on the low-pressure side of the system. This placement allows the high-pressure side to push the O-ring securely against the backup ring, enhancing its performance. Once these steps are complete, your O-ring is installed—it’s that simple!
After installation, check that the O-ring is evenly stretched rather than being stretched only on one side. Keep the installation stretch below 50% to maintain its integrity. Lastly, confirm that the O-ring is not twisted within the groove or gland. Proper alignment is essential for maximizing seal longevity and preventing application failure. Any misalignment can compromise the seal, leading to system inefficiencies or potential damage.
Standards and Specifications for O-Rings
Due to the potential consequences of an O-ring malfunction, both governments and industries enforce strict O-ring standard requirements to ensure safety and reliability. Organizations such as ISO and SAE International (including the Aerospace Standard) have established widely recognized guidelines for O-ring performance and compliance. To determine the specific standards that apply to your O-rings, consult with your supplier to ensure they meet the necessary regulations for your application.
Things to Consider When Purchasing O-Rings
To obtain O-rings that meet the precise specifications of your application, it is essential to source them from a reliable manufacturer or supplier. While a quick Google search may generate an extensive list of potential suppliers, it can be challenging to determine which businesses are truly trustworthy and reputable. Instead of relying on random search results, we recommend using a trusted directory, like this one.
Here at IQS, we have already vetted and identified reliable manufacturers and suppliers. By scrolling up to the top of this page, you will find a curated list of top picks, complete with company profiles, website links, contact details, service coverage, and product offerings. To efficiently compare their services and pricing, visit their websites. For a more informed decision, consider these key steps when selecting the right supplier:
- Confirm whether they deliver to your location.
- Provide detailed specifications, including pressure and temperature tolerance, O-ring size and shape, and the quantity required. Request a quote based on these details.
- Specify your required delivery timeline to ensure they can meet your deadlines.
- Inquire about customization options to see if they can tailor O-rings to your unique requirements.
By following these guidelines, you can confidently select an O-ring manufacturer that best fits your needs.
Proper Care for O-Rings
To extend the lifespan of your O-ring, consider encapsulating it in Teflon. This added layer protects more vulnerable O-ring materials from natural wear and exposure to harmful chemicals, ensuring greater durability. Additionally, avoid using an O-ring lubricant made from the same material as your gasket, as this can lead to erosion and premature failure of the O-ring.
For added preparedness, keep a set of replacement O-rings on hand so you can quickly swap them out when necessary. These can be conveniently found in an O-ring kit, allowing for easy access and maintenance when needed.
O-Ring Terms
-
Adhere
When materials stick or cling to one another, forming a bond that holds them together.
Aging
The process in which a material undergoes physical changes over time due to environmental exposure, stress, or chemical interactions.
Back-Up Ring
A rigid ring placed in the gland between the O-ring and the groove walls to prevent extrusion and enhance sealing performance.
Batch
The final product resulting from a mixing operation, ensuring consistency in material composition.
Cell
A small cavity within a material, either fully or partially enclosed by surrounding walls.
Elastomer
A flexible, rubber-like material with elastic properties, often used in place of springs as an energizer in sealing applications.
Energizer
A component within some O-rings that helps retain the ring’s natural shape. Springs or elastomers are commonly used as the core energizers to maintain sealing effectiveness.
Friction
The resistance encountered when two or more surfaces move against each other, impacting wear and performance.
Gland
The cavity where an O-ring is installed, including the groove and the mating surface of the second part, ensuring a secure and effective seal.
Inside Diameter
The measurement taken from one inner point of an O-ring straight across to the opposite inner point, determining the internal width.
Lubricity
The degree of slipperiness in an O-ring material, affecting how easily it moves and resists friction during operation.
Memory
The ability of a material to return to its original shape after deformation, ensuring long-term performance and durability.
Mil-Spec
O-rings that meet or exceed the stringent standards set by the United States military for quality and reliability.
Off-Register
A defect that occurs when a mold is misaligned, resulting in an out-of-round cross-section in an O-ring.
Outside Diameter
The measurement taken from one outer point of an O-ring straight across to the opposite outer point, determining the external width.
Overflow Groove
A groove surrounding the mold cavity of an O-ring, designed to capture excess material and ensure a precise fit during molding.
Parting Line
A visible line left on the exterior of an O-ring where the two mold plates met during manufacturing.
Polyurethane
A versatile resin that varies in flexibility and is commonly used in chemical-resistant coatings, foams, and adhesives.
Squeeze
The degree of cross-sectional compression in an O-ring gland assembly, measured between the groove bottom and the mating metal surface to ensure a proper seal.
Vulcanized
A process that enhances the strength, flexibility, and resilience of rubber by combining it with sulfur and other additives under heat and pressure.
Water Swell
The increase in size or bulging of an O-ring due to water absorption, which can impact sealing performance and longevity.