Optical Comparators
Optical comparators use light and magnifying lenses to produce an enlarged image of a part or component. They are commonly used in manufacturing, quality control, and research to measure and inspect parts’ dimensional accuracy and surface features. The use of optical comparators in machine vision has been an important development in modern industry, allowing for accurate and efficient inspection of various components.
Quick links to Optical Comparator Information
Types of Optical Comparators
There are several types of optical comparators, each with its advantages. The most common types are:
- Vertical Optical Comparators
- Vertical optical comparators are typically used for larger parts and are designed to easily access the measuring stage. They use a large-screen projection system that allows for simultaneous viewing of the part and the projected image.
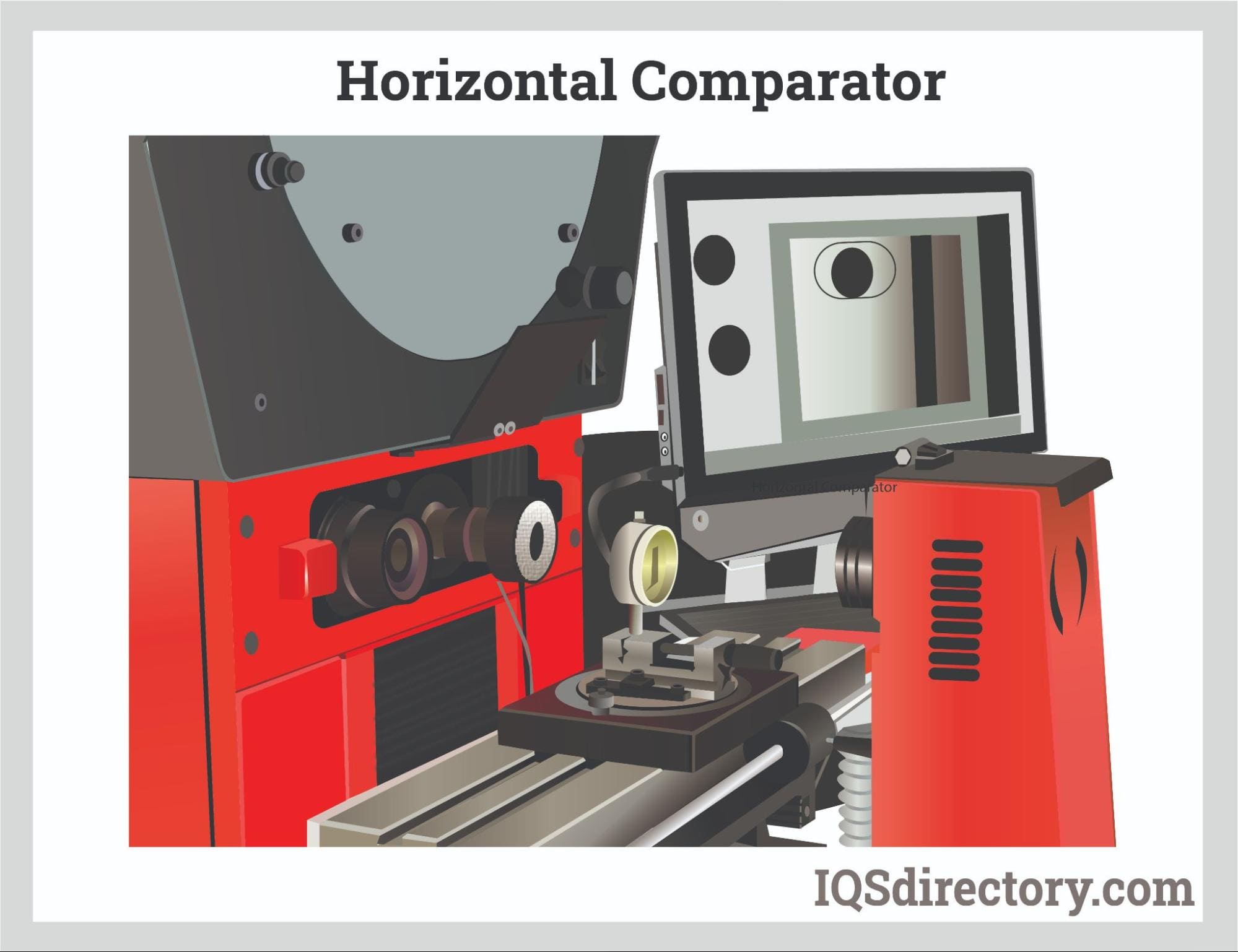
- Horizontal Optical Comparators
- Horizontal optical comparators use a table with a horizontal projection system, ideal for small parts and high-precision applications. The horizontal orientation allows easy access to the part and ensures that the measuring stage remains stable during the inspection process.
- Profile Projectors
- Profile projectors are used for measuring the profiles of a part, including angles, radii, and other geometric features. They use a collimated light source and a projection lens to magnify the image of the part onto a screen, where it can be measured with a micrometer or other measuring instrument.
- Optical Comparators With Digital Readouts
- Optical comparators with digital readouts use an electronic display to show the measurement results, which makes the inspection process faster and more accurate. They are often used in quality control applications where repeatability and precision are critical.
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Optical Comparators
- CNC optical comparators use a computerized system to control the movement of the measuring stage, allowing for fast and accurate inspection of complex parts. They are ideal for high-volume production environments where speed and accuracy are critical.
- Video-Based Optical Comparators
- Video-based optical comparators use a camera and software to capture and analyze the image of a part. They can measure features such as angles, radii, and surface roughness and are often used in research and development applications.
- Benchtop Optical Comparators
- These compact and portable optical comparators are designed for small-scale applications such as measuring small parts, tools, and components. They are commonly used in workshops, laboratories, and inspection rooms.
- Floor-Standing Optical Comparators
- These are large-sized optical comparators designed for heavy-duty applications such as measuring large parts and components. They are commonly used in manufacturing plants, tool rooms, and industrial settings.
- Projection Microscopes
- These are advanced optical comparators that offer high magnification and resolution capabilities. They are used in scientific research, material science, and advanced manufacturing applications.
- Scanning Optical Comparators
- These use a laser or a mechanical probe to scan the surface of the object being measured. They offer high accuracy and precision and are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and other high-tech industries.
- Automated Optical Comparators
- These optical comparators are used with robotics, machine vision, and other automation technologies to automate the measurement process. They are commonly used in high-volume production environments to improve efficiency and reduce errors.
Comparison of Types
Each type of optical comparator has its strengths and weaknesses, which should be considered when selecting a device. The main factors to consider include the size and complexity of the parts being inspected, the precision required, and the volume of parts being inspected. For example, vertical comparators are better suited for larger parts, while horizontal comparators are better suited for smaller parts with high precision requirements.
Applications of Optical Comparators
Optical comparators are widely used in manufacturing, quality control, and research. In manufacturing, they ensure that parts are made to the correct specifications and are free of defects. In quality control, they measure and inspect the dimensional accuracy and surface features of parts, ensuring that they meet any required standards. Finally, in research, they are used to study the properties of materials and components, and to develop new products and processes.
Optical comparators are complex devices that use a combination of lenses, mirrors, and light sources to produce an enlarged image of a part. These devices are typically produced and sold by manufacturers, suppliers, and companies specializing in metrology and precision measurement tools.
The accuracy and repeatability of optical comparators depend on several factors, including the components' quality, the device’s calibration, and the maintenance schedule. Therefore, choosing a device from a reputable manufacturer or supplier is important to ensure that it meets your specific needs and requirements.
Calibration of the device is critical to ensure that it provides accurate and reliable measurements. This process involves checking the accuracy of the magnification, the measurement stage, and the illumination system. Calibration should be performed regularly to ensure that the device remains accurate over time.
Maintenance of the device is also critical to ensure that it operates at peak performance. This maintenance includes cleaning the lenses, checking the alignment of the optics, and replacing worn or damaged components as needed. Manufacturers and suppliers typically provide maintenance and repair services for their devices, and it's important to follow their recommended maintenance schedules to ensure the longevity and accuracy of the device.
In addition to calibration and maintenance, it's important to understand the device’s technical specifications, including the magnification range, the field of view, and the illumination system. Manufacturers and suppliers typically provide detailed technical specifications for their devices, and it's important to review these specifications to ensure that the device meets your specific needs and requirements.
Overall, the technical information on optical comparators is complex and requires a thorough understanding of the principles of metrology and precision measurement. By working with a reputable manufacturer, supplier, or company that specializes in these tools, you can ensure that you select a device that provides accurate and reliable measurements and meets your specific needs and requirements.
Considerations When Purchasing an Optical Comparator
When selecting an optical comparator, there are several factors to consider, including the size and complexity of the parts being inspected, the level of precision required, and the volume of parts being inspected. Other factors to consider include your budget, the availability of technical support, and the manufacturer’s reputation.
Choosing a device that meets your specific needs and requirements is critical. Some key criteria to consider include the following:
- Magnification range: The magnification range of the device should be suitable for the parts being inspected.
- Accuracy and repeatability: The device should be accurate and repeatable, with low measurement uncertainty.
- Field of view: The field of view should be large enough to accommodate the parts being inspected.
- Illumination: The illumination system should be adjustable to suit the surface features of the part.
- Software and data management: The device should have software and data management capabilities for easy data analysis and reporting.

