PVC Coating
Plastisol is primarily replaced by polyvinyl chloride, a thermoplastic polymer often known as PVC, for use in plastic or polymer coating. PVC offers a lot of advantageous characteristics, including strong chemical and water resistance.

What is PVC Coating?
PVC is most prized for its flexibility; its resin, typically stiff and rigid, can soften or become more flexible when combined with plasticizer chemicals, such as phthalates. PVC is the preferred material for dip molding and coating services because of its versatility.
PVC Coating Process
Plastisol is the most typical polymer used in dip molding and dip coating procedures. Fine polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resins are used to make it and are suspended in a liquid plasticizer. When heated, it solidifies into a soft, flexible, rubber-like substance and returns to its liquid state upon cooling.
The toughness, superior corrosion resistance, and impact resistance of plastisol coating are well known. It is ideal for electrical applications because of its high dielectric strength. Colorants are added to alter the final product's finish.
PVC Coating Methods
The different PVC coating methods include:
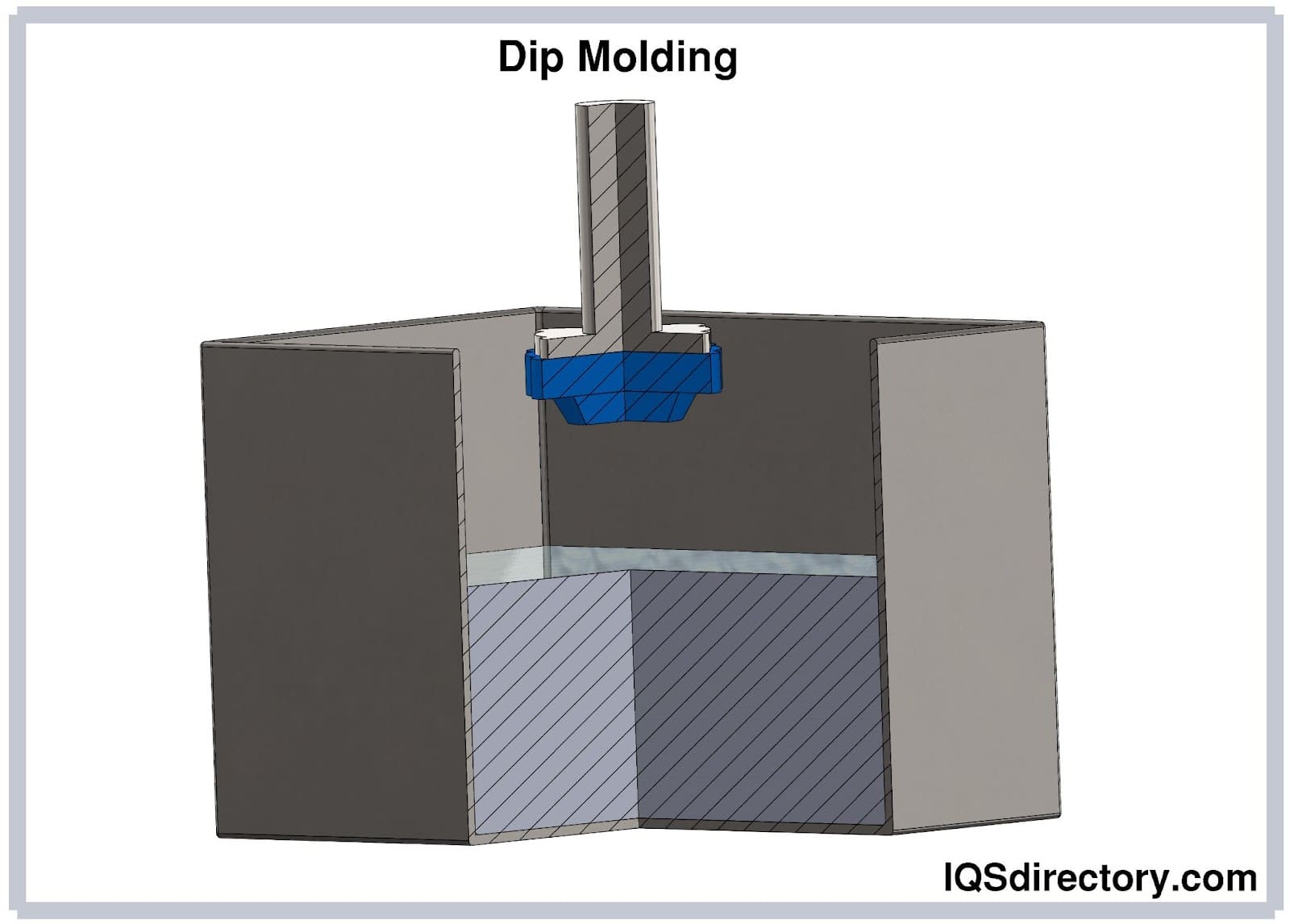
Dip Molding
Mandrels or molds can be coated in a reasonably simple and cost-effective manner using dip molding, also known as immersion molding. Dip coating, commonly called plastic coating, is a nearly identical method used to cover items or objects. Both dipping procedures involve three steps of the dip molders: immersion, residence, and withdrawal.
An object or manufactured component, such as a mandrel, is first immersed in a vat of molten PVC plastic. Then, manufacturers can choose whether or not to add a primer, such as chromate or phosphate, to the product's surface (referred to as a substrate) to strengthen the PVC's adhesion to its surface before this immersion.
The substrate is removed from the vat of molten PVC after having been submerged for a predetermined amount of time, then left to cool. The intended thickness of a substrate determines how soon it should be removed from the vat.
The "dwell time" is longer for thicker coatings and shorter for thinner coatings. A producer risks imperfections on the substrate's surface or an incorrect or uneven coating thickness if the substrate is removed too quickly.
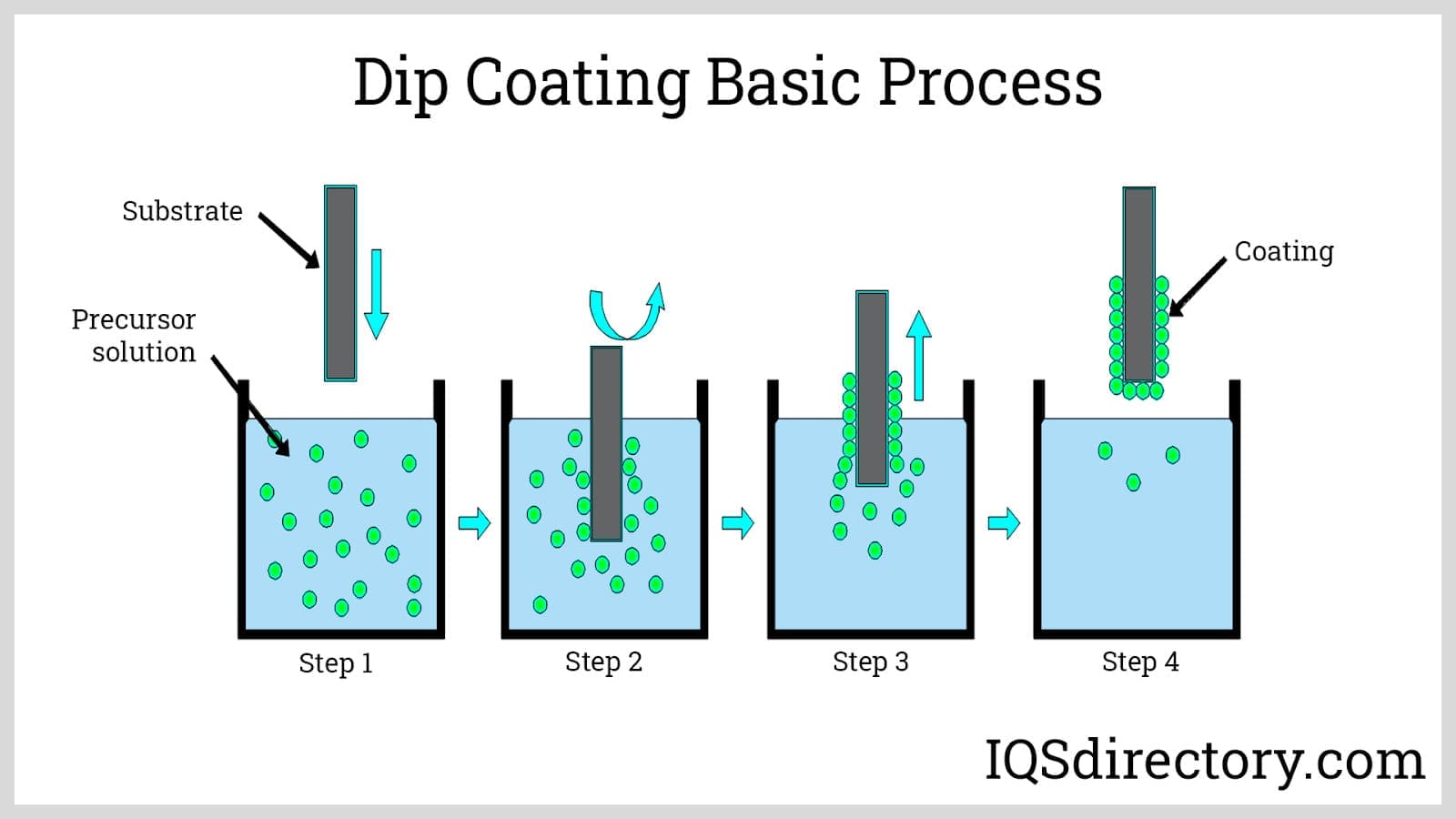
Dip Coating
Any substrate that can fit into a vat can be coated with dip. Given that vats come in various sizes, practically any object can be coated or dipped into molten PVC as long as it can withstand the heat. In some instances, a substrate is subjected to additional heat treatment to finish the fusing of PVC to its surface. This only happens if the substrate was coated using cold dip rather than hot dip.
The less popular of the two procedures, cold dip coating, involves dipping a substrate into liquid PVC without heating it first. The fusion is then completed by placing the substrate in a heated chamber. On the other hand, hot dip coating entails heating and perhaps priming a substrate before it is submerged in a liquid polymer. There is no post-coating heat treatment used in this method.
Advantages of PVC Coating
- Dip molding machines are mostly automatic, allowing rapid molding, hardening, and cooling. As a result, dip molding and coating have significant turnaround times.
- Dip coating creates very little material waste because the molten PVC sticks only to the surface of the coated object. Instead, any remaining molten PVC can be reused in the vat. This lowers the cost of materials, energy, time spent manufacturing items, and manufacturers' use of fossil fuels.
Applications of PVC Coating
- Manufacturers may use PVC coatings for ornamental or protective purposes. However, PVC's protective capabilities frequently outweigh its attractive features.
- PVC coatings can coat many objects due to its high degree of flexibility, water resistance, and chemical resistance. These items consist of storage for frozen foods, cords, wires, wire mesh, and dishwasher baskets.
- PVC coatings' insulative properties make them suitable for electrical and thermal insulators on electrical parts frequently used outdoors or subjected to heavy use, such as extension cords and jumper cables.
Choosing the Right PVC Coating Company
For the most constructive outcome when selecting a PVC coating business, it is important to compare several businesses using our directory of PVC coating companies. Each PVC coating company has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the company for more information or request a quote. Review each PVC coating company using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in. Then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple businesses with the same form.

