Safety Guards
A physical barrier known as a safety guard is used to shield humans from the risks associated with machinery. When, for instance, time-critical procedures must not be stopped by advancing people, they also shield the machine from humans. For example, a safety guard is a container created to contain the broken pieces of a grinding wheel and to provide the maximum amount of protection if the wheel breaks while it is being used.
Serious occupational injuries from moving machine parts might include crushed fingers or hands, amputations, burns, or blindness. Safeguards are crucial to protect workers from avoidable injuries. Any component, feature, or machine operation that could lead to harm must be protected. Hazards must be eliminated or controlled when machine operation or unintentional contact injures the operator or persons nearby.
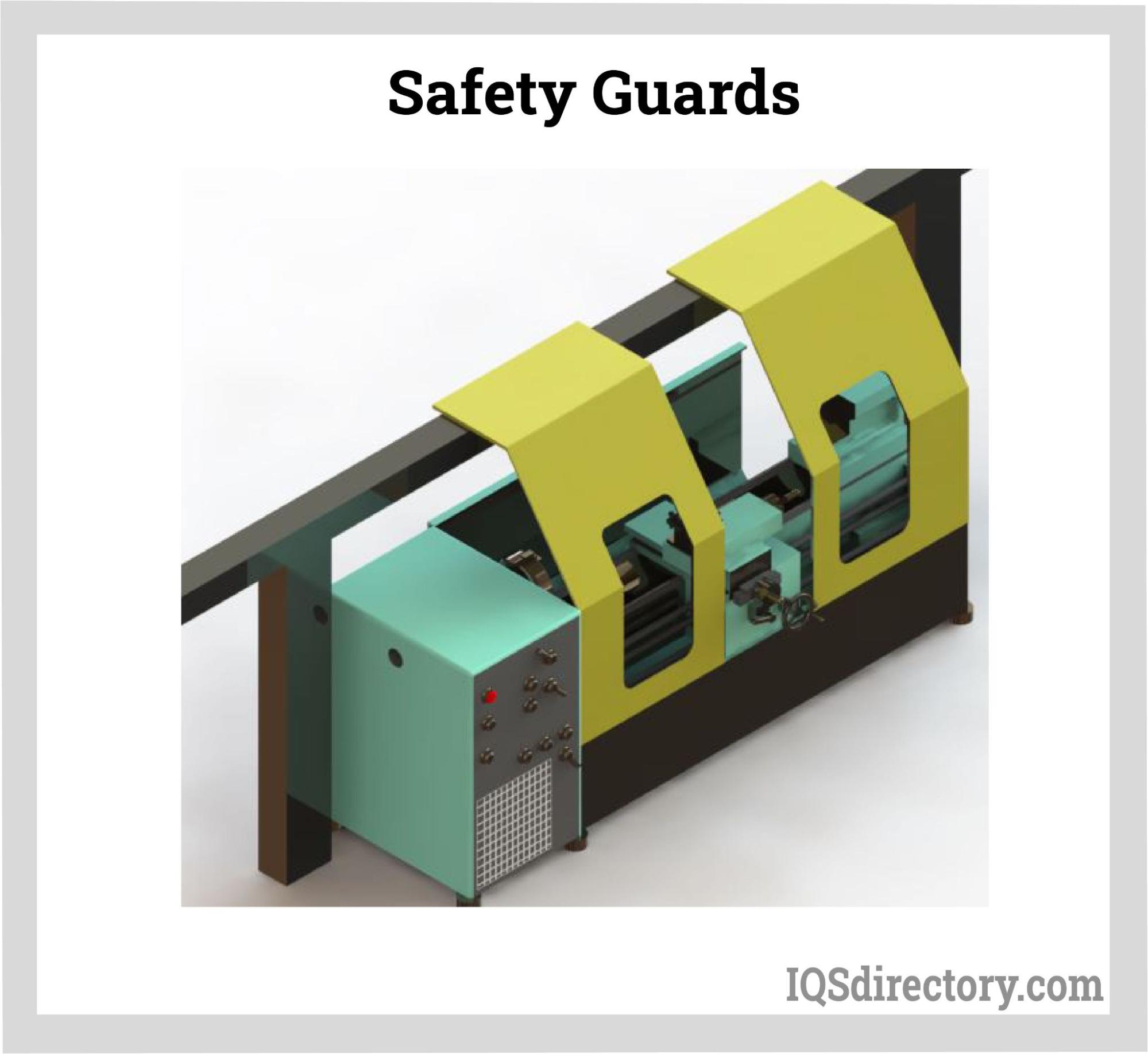
Any machine component, feature, or procedure that has the potential to hurt someone must be protected by employing management strategies that limit employee access to dangerous regions using efficient machine-guarding systems. Safety guards are also utilized to barrier the working area with scaffolds and falling debris when a risky operation is being done, such as construction.Figure 1: Safety Guards
Types of Safety Guards
Depending on the application, various types of safety guards are utilized in various industries. Protecting the worker and the equipment is the primary objective of safety guards.
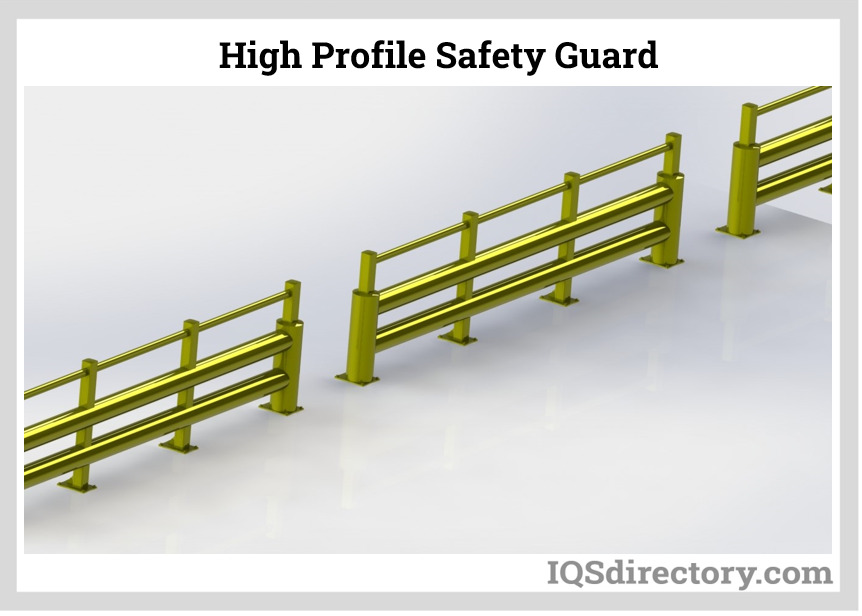
High Profile Safety Guards
These prevent damage to valuable machinery from forklifts and pallet trucks, and they are also used in areas prone to explosion, for example, at fuel stations, to protect pumps from being hit by cars. These safety guards often come in yellow with black lines for increased visible safety. In addition, the high-quality steel used in the steel impact protection solutions allows for efficient interior and outdoor protection of buildings, machinery, and goods.

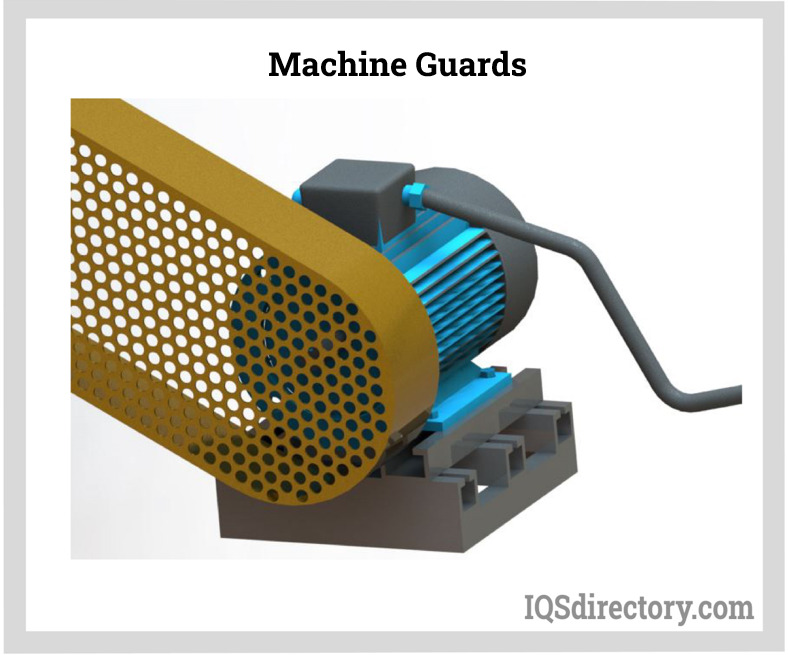
Machine Guards
Machine guards shield the operator from any threats from the machine's routine use and other workers in the area. Machine guards can protect against hazards such as flying chips and sparks, rotating parts, reciprocating motions, and nip points. It is necessary to protect any part, process, or machine function that has the potential to cause damage. Additionally, risks that could result from using a machine improperly or accidentally running into one must be minimized or eliminated.

- fixed guards
- interlocking guards
- adjustable guards
- self-adjusting guards
Fixed Guards
Fixed guards are safety measures that are affixed to engineering machines permanently. They are mostly employed to shield machine operators from dangers at work locations or places where operators seldom ever come into contact. Generally speaking, fixed guards must be impact- and vibration-resistant and surround all potential points of contact with the hazard. Additionally, they must have firmly fastened attachments that would make them rigid without impairing the machine's functionality. Gates, fences, barriers, and blade coverings are common examples of fixed guards.
Adjustable Guards
Similar to fixed guards, adjustable guards are permanent but may be moved to allow the machine to handle various material sizes. All staff operating adjustable guards must receive training on how to utilize them because they must be physically adjusted and locked into place. Adjustable guards can fail to prevent contact with moving parts if poorly set or secured, leading to serious or even fatal harm.
Self-Adjusting Guards
Self-adjusting guards serve the same objective, but they do so by automatically adjusting to the size of the material. These guards fully recline when the machine is at rest. When the operator feeds the material into the machine, the guard is opened enough to allow the material to enter. On table saws and other woodworking equipment, these guards are frequently seen.
Interlocking Guards
The power source is automatically turned off or disengaged when an interlocking or barrier guard is opened or removed. These are especially helpful when operators need to open the guard or gain access to the machine's guarded areas, such as when unclogging clogs. These guards enable safe access to the machine's interior components without requiring complete disassembly. However, they can be simple to open and need careful adjusting and upkeep accidentally.
Applications of Safety Guards
Safety guards have many applications in different industries to avoid accidents caused by human interactions or errors. Applications include the following:
- barricade the fuel pumps
- cover the rotating pulley system
- cover the drill bit when drilling
- to cover the grinding or cut disk during grinding or cutting, respectively
- They are used to barricade the working area, for example, a construction area.
- They are used on milling machines.
- They are used on the balcony's edge to prevent people from falling.
Benefits of Safety Guards
Below are the benefits of using safety guards.
- They ensure maximum protection of the user from the machine.
- increases the visibility of equipment on site
- They require minimal maintenance.
- can be designed based on the specific task
Disadvantages of Safety Guards
- Safety guards can be limited to a specific task.
- can interfere with the visibility of the operation at hand, such as grinding, cutting, or drilling
Choosing the Proper Safety Guards Manufacturer
To make sure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing Safety Guards from a Safety Guards Manufacturer, it is important to compare at least 6 Companies using our list of Safety Guards manufacturers. Each Safety Guards Manufacturer has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Safety Guards business website using our proprietary website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Safety Guards businesses with the same message.

