Stepper Motors
A stepper motor is commonly known as a step motor. It comprises a brushless DC electric motor that divides one full rotation into equal steps. The biggest pro of a stepper motor is that it requires less maintenance and is durable. It provides accurate position control as compared to a DC motor.
Stepper motor uses digital readings, so it is a preferred mode in an environment where analog meters won’t do.
Stepper motors have wide applications, especially in the industry of mechanics. For example, in robotics, wire bonding machines, etc.
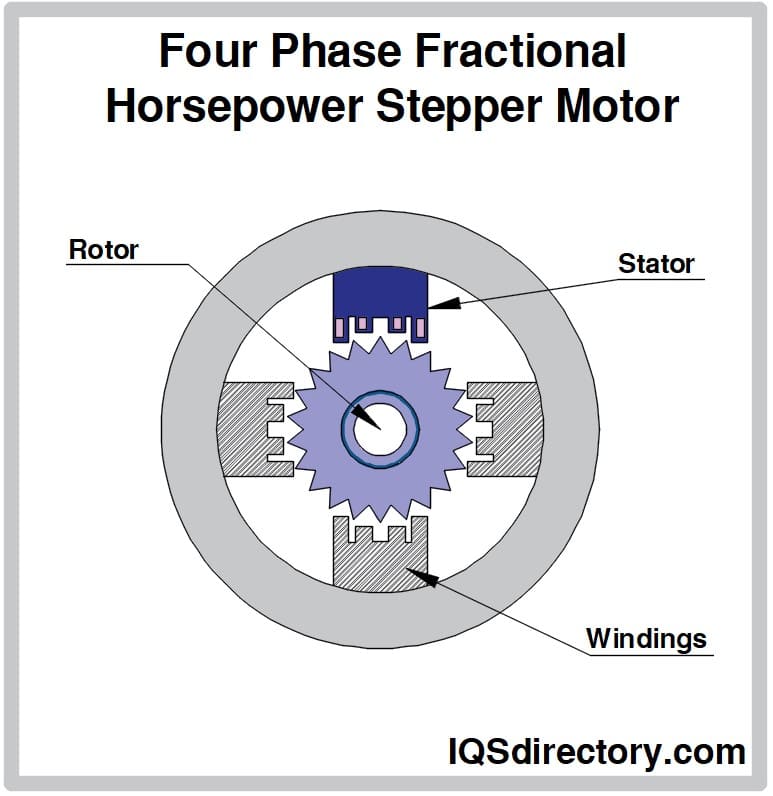 Figure 1
Figure 1
Quick links to Stepper Motors Information
How a Stepper Motor is Made
A stepper motor is based almost on the same working principle as of a DC motor. Stepper motors follow the principle of electromagnetism. It consists of two main components: a rotor and a stator. A rotor is usually magnetic in nature and is situated in the middle of the motor. The rotor is enclosed by a stator. Stator teeth are wrapped by a coil which generates a magnetic field upon the flow of current. The magnetic field acts upon rotors and makes them rotate.
The stators are controlled to act like electro-magnetic poles for rotors. Stators are activated one by one. And the alternating magnetic field generated as a result allows the rotor to move and turn.
Types of Stepper Motors
Three main types of stepper motors available in the market are:
- Permanent Magnet Stepper
- The most commonly used stepper motor nowadays. It is very inexpensive to buy because of the low production cost. It has a permanent magnet installed as its rotor. It is also called a tin-can/can-stack motor.
- Hybrid Synchronous Stepper
- The amalgamation of permanent magnet steppers and variable reluctance steppers. It is a high performance stepper motor that comes in a very manageable size. But it is more expensive than permanent stepper motors.
- Variable Reluctance Stepper
- Has been used for ages now. It is the simplest of all. It used iron instead of a permanent magnet as a rotor.
Advantages of Using Stepper Motors
Following are some of the advantages of stepper motors:
- Hardiness and ability to withstand wear and tear.
- Straightforward design.
- Works well in an open-loop control system.
- Very low maintenance is required to keep it going.
- Highly reliable and authentic.
- The motor has full torque even while not running.
- Can perform the same function repeatedly with the exact same precision.
- It is very responsive to abrupt reactions like starting, halting, and reversing.
- The reaction of the motor to input signals provides open-loop power, making the motor easier and less expensive to handle.
- Because the speed depends on the input signal’s frequency, a vast spectrum of rotational speeds can be realized.
Applications of Stepper Motors
Stepper motors are very efficient wherever motion control technology is required. Other types of motors are also available in the market, like servo motors. But stepper motors can be used in any application that requires highly precise positioning and orientation, motion control, and low speed torques. Following are some of the industrial applications of stepper motors:
- Industrial Machines
- Stepper motors are used in vehicle dials, machine tooling, and industrial automation equipment.
- Security
- These are also used in futuristic monitoring devices.
- Medical
- In medicine, medical scanners, samplers, digital dental photography, fluid pumps, etc use stepper motors.
- Consumer Electronics
- Like digital cameras etc.
Choosing the Right Stepper Motor
There are more than two types of stepper motors available. Choosing the right kind is a very critical decision. It can be made easily and accurately by considering a couple of factors. These are the questions one must have answers to before buying one:
- How is the motor going to be connected to the load?
- How quickly does the load have to move or accelerate?
- What is the amount of torque required to move the load?
- What level of precision is needed when positioning the load?

